AP Chemistry - Chapter 9
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Hybridization
the combining of two or more orbitals nearly equal energy within the same atom forming orbitals of equal energy
sp3 hyrbrid orbitals
an s orbital is combined with three p orbitals to create four equal hybrid orbitals
has an electron-pair geometry of tetrahedral
How do you think the energies of these new hybrid sp3 orbitals compare to the original s and p orbital energies they are made from?
The energy of the sp3 orbital is the average energy of the s orbital and p orbitals.
The sp3 orbital have MORE energy than the 2s orbital and LESS energy than the 2p orbital.
sp2 hyrbrid orbitals
combines two orbitals from a p sublevel with one orbital from an s sublevel to make three identical hybrid orbitals
What happens to the remaining unhybridized p orbital?
The remaining p orbital (pair of electrons) keeps its “normal shape“ and remains perpendicular to the sp2 orbital.
sp hyrbrid orbitals
one s orbital combines with a single p orbital to create two sp hybridized orbital — leaving two normal p orbitals
sigma bonds
exist in the region directly between two bonded atoms
pi bonds
exist in the region above and below a sigma bond between two atoms
How many sigma and pi bonds are in a…
single bond
double bond
triple bond
1 sigma bond
1 sigma bond, 1 pi bond
1 sigma bond, 2 pi bond

The De-Localized Electron Model
The sharing of unhybridzed p-orbitals that allows for resonance.
isomers
same molecular formula, different chemical structure
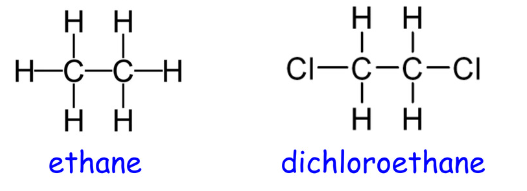
Are these isomers?
Note: Single bonds allow rotation about a bond. Double and triple bonds do not allow rotation.
No, they have different molecular formulas.
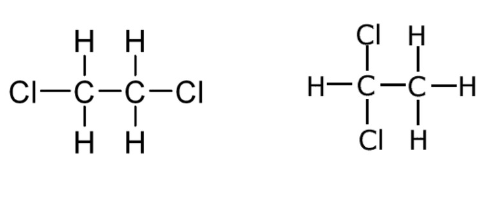
Are these isomers?
Note: Single bonds allow rotation about a bond. Double and triple bonds do not allow rotation.
Yes, they have the same molecular formula, but different chemical structures.
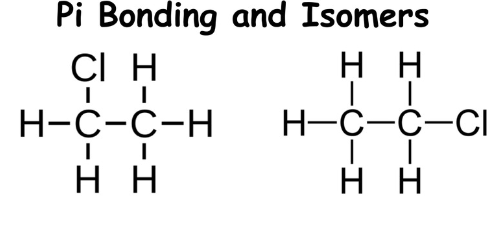
Are these isomers?
Note: Single bonds allow rotation about a bond. Double and triple bonds do not allow rotation.
No, they have the same structure if you rotate it.

Are there pi bonds present in each of these models?
Can the central bond rotate?
Are any molecules identical?
Which, if any, are isomers?
Yes, they can be located in the double bonds.
No, this is due to the double bonds between the two Carbon atoms.
No, even if you can rotate them they won’t look identical to each other.
#2 and #3 are isomers