Health Psychology: Stress, Coping, and Treatment Approaches
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
What is Health Psychology?
The study of psychological influences on health, illness, and illness responses, including health maintenance and prevention, focusing on social, behavioral, biological, and cognitive factors.
What is the Biopsychosocial Model?
A model that integrates biological, psychological, and social factors to explain health outcomes.
What does the Theory of Reasoned Action state?
Effective change requires intentions that precede behaviors, positive attitudes that encourage behavioral intentions, and social norms that support the behavior.
What is the Theory of Planned Behavior?
An extension of the Theory of Reasoned Action that includes perceived behavioral control, which refers to perceptions of control over the behavior.
What are the stages of the Stages of Change Model?
1. Precontemplation: not thinking about change; 2. Contemplation: acknowledging the problem; 3. Preparation: planning for action; 4. Action: implementing the plan; 5. Maintenance: sticking to new behaviors; 6. Relapse: returning to unhealthy behaviors.
What is social support?
The benefits felt by knowing one can call upon a supportive social network, which reduces stress and provides tangible assistance, information, and emotional support.
How is stress defined?
The physiological, psychological, and emotional response to harm, threats, or challenges, where the perception of stressors can invoke a stress response.
What is the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)?
A model describing the body's response to stress, consisting of three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
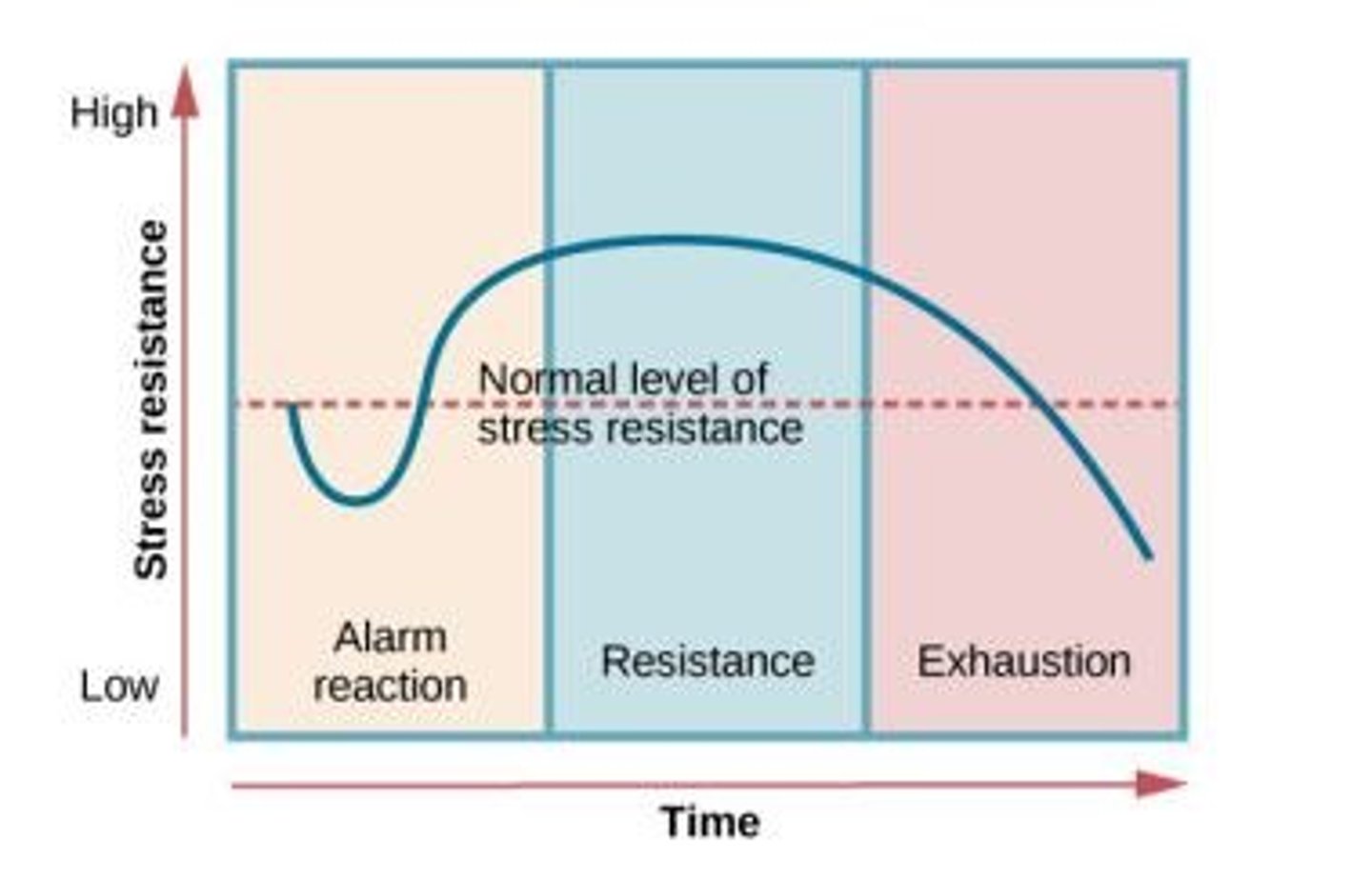
What are the impacts of stress on the immune system?
Stress suppresses immunity, inhibits immune responses to cancer cells, and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and clotting.
What are lymphocytes?
White blood cells that respond to foreign pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses.
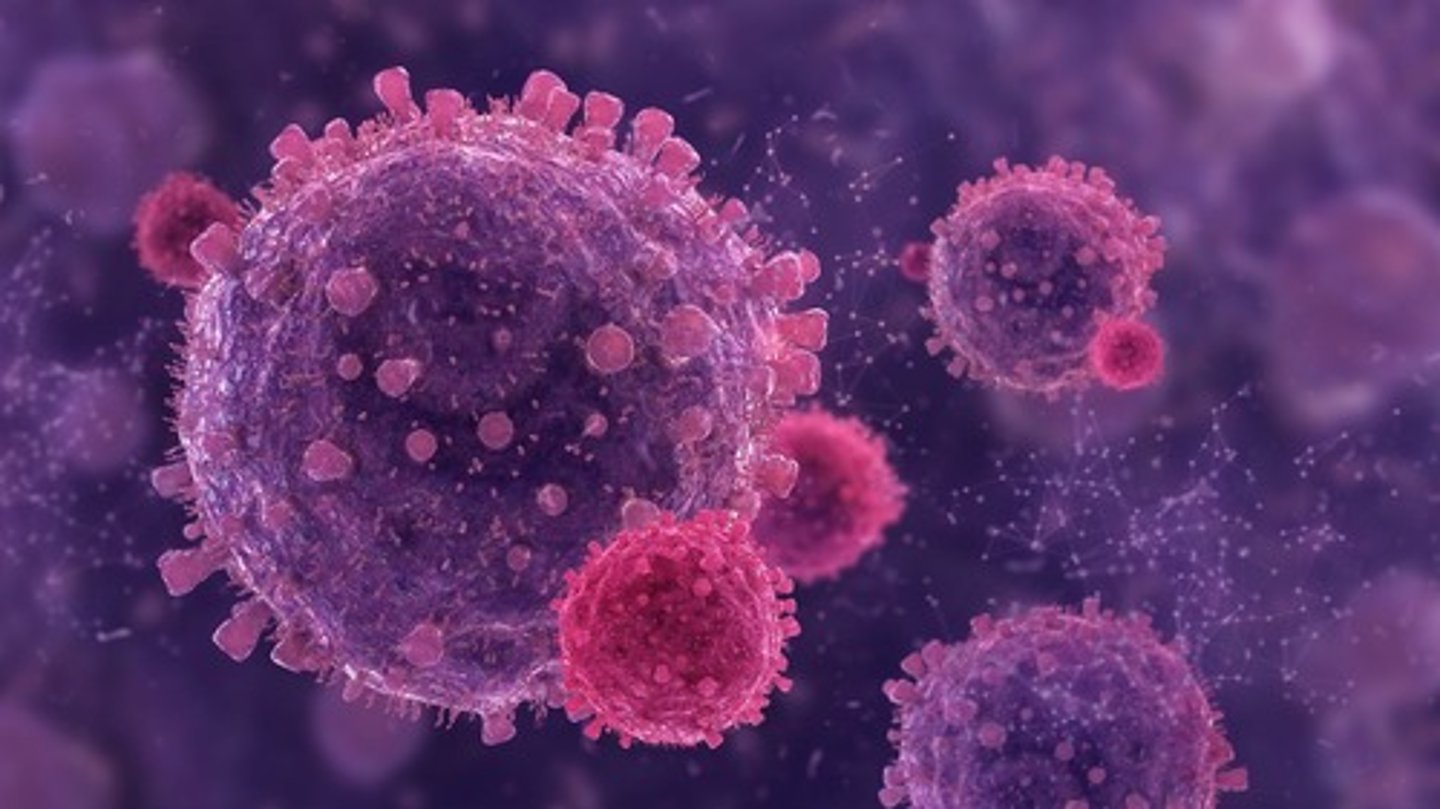
What is the difference between non-specific and specific immunity?
Non-specific immunity is a general response to any foreign invader, while specific immunity is an immune response tailored to a specific pathogen.
What is coping in the context of stress?
Coping refers to how individuals manage their stress, utilizing various resources and strategies.
What are the two types of coping strategies?
Emotion-focused coping and problem-focused coping.
What do stress management programs teach?
They teach how to appraise/reappraise stressful events, promising practices in coping, and stress relief skills such as deep breathing and mindfulness.
What are some healthy behaviors for quitting smoking?
Using nicotine substitutes, therapy, consulting a physician, and combinations of these aids.
What are the ACSM guidelines for physical activity?
150 minutes of cardio per week and training each major muscle group 2-3 times weekly.
What are the benefits of regular exercise?
Longer life, better quality of life, increased disease resistance, improved stress coping abilities, and enhanced cognitive abilities and mood.
What is the FITT principle in exercise?
Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type of exercise.
What constitutes healthy eating?
A diet high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, with more fruits, vegetables, and grains, while limiting fats and sugars.
What are some strategies for successful weight loss?
Exercising at least 30 minutes a day, planning meals, and self-monitoring.
What should you check first on nutrition labels?
The serving size.
What is the recommended proportion of fruits and vegetables on a dinner plate?
The specific proportion can be found at ChooseMyPlate.gov.
What is the Ocean Therapy program at Camp Pendleton?
A program that combines learning to surf with group discussions to help veterans recover from PTSD.
What percentage of U.S. adults experience mental illness in a given year?
Approximately 19%.
What percentage of adolescents (ages 8-15) experience mental illness in a given year?
Approximately 13%.
What treatment methods were historically used for mental illness based on the supernatural perspective?
Exorcism, trephining, execution, and imprisonment.
What was the purpose of asylums established in the 18th century?
To house people with psychological disorders, focusing on ostracization rather than treatment.
Who was Philippe Pinel and what was his contribution to mental health treatment?
A French physician who advocated for humane treatment of the mentally ill and implemented unchaining patients in asylums.
What did Dorothea Dix accomplish in the 19th century?
She advocated for the mentally ill, revealing the abuse in care systems and helped establish the first American mental asylum.
What were common conditions in American asylums during the 19th century?
Filthy environments, little treatment, and long-term institutionalization.
What treatment method was introduced in 1954 for psychosis?
Antipsychotic medications.
What are some symptoms of psychosis?
Hallucinations and delusions, indicating a loss of contact with reality.
What was the focus of treatments in asylums during the 18th century?
Ostracizing individuals from society rather than providing treatment.
What did Philippe Pinel implement in Paris in 1795?
He suggested that patients be unchained and talked to, leading to their benefit and release.
What did Dorothea Dix discover about the care for the mentally ill?
An underfunded and unregulated system that perpetuated abuse.
What was a common treatment method in American asylums before the 20th century?
Submersion into cold baths and electroshock treatment.
What is trephining?
A historical treatment method involving drilling a hole in the skull to release spirits.
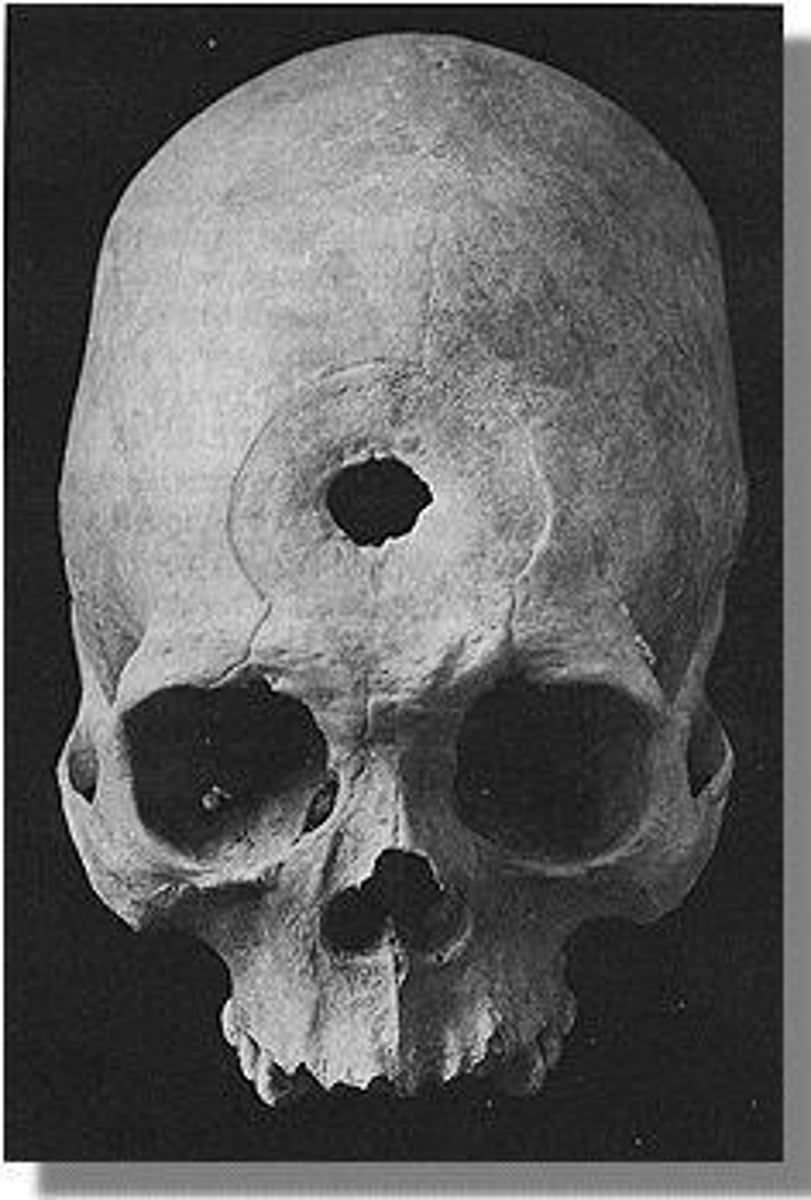
What was the general treatment approach for mental illness before the 20th century?
Cruelty and poor treatment, often based on supernatural beliefs.
What did the painting 'The Madhouse' by Francisco Goya depict?
The conditions and inhabitants of a mental asylum in the early 1800s.
What was the state of care for the mentally ill before Dorothea Dix's reforms?
It was characterized by neglect and abuse, with little regulation.
What was the impact of antipsychotic medications introduced in 1954?
They proved successful in treating symptoms of psychosis.
What did Philippe Pinel's humane treatment approach lead to?
Many patients were able to be released from the hospital.
What was the treatment for individuals in asylums during the 19th century?
They often underwent treatments like cold baths and electroconvulsive therapy.
How did the percentage of adults seeking mental health treatment change from 2004 to 2008?
It increased slightly.
What act in 1975 provided federal support for community mental health centers and initiated deinstitutionalization?
The Mental Retardation Facilities & Community Mental Health Centers Construction Act.
What is deinstitutionalization in the context of mental health?
The closing of large asylums and providing for people to stay in their communities and be treated locally.
What were some consequences of deinstitutionalization?
Patients were released into a system that was not effectively set up, leading to underfunded centers, untrained staff, and an increase in homelessness.
What percentage of homeless individuals in U.S. shelters have a severe mental illness according to HUD 2011?
About one-quarter.
What types of facilities have replaced asylums for mental health treatment?
Psychiatric hospitals and local community hospitals focused on short-term care.
What is the average length of stay in psychiatric hospitals today?
Less than two weeks.
Under what conditions are individuals usually hospitalized for mental health issues?
If they are an imminent threat to themselves or others.
What is involuntary treatment in mental health?
Therapy that is not the individual's choice, such as counseling sessions as a condition of parole.
What is voluntary treatment in mental health?
When a person chooses to attend therapy to obtain relief from symptoms.
What are some sources of psychological treatment?
Community mental health centers, private practitioners, school counselors, school psychologists, school social workers, and group therapy.
Who are some treatment providers in mental health?
Psychologists, psychiatrists, clinical social workers, marriage and family therapists.
What is psychotherapy?
Psychological treatment that employs various methods to help someone overcome personal problems or attain personal growth.
What does biomedical therapy involve?
Medication and/or medical procedures to treat psychological disorders, often used in combination with psychotherapy.
Who developed psychoanalysis and when?
Sigmund Freud in the early 20th century.
What are the main techniques used in psychoanalysis?
Free association, dream analysis, and transference.
What is free association in psychoanalysis?
A technique where the patient relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, revealing repressed feelings.
What is dream analysis in psychoanalysis?
A technique where the therapist interprets the underlying meaning of dreams.
What is transference in psychoanalysis?
When a patient transfers emotions associated with other relationships to the psychoanalyst.
How has psychoanalysis evolved in modern therapy?
It has been expanded upon by incorporating modern theories and methodology, leading to psychodynamic psychotherapy.
What is psychodynamic psychotherapy?
Talk therapy based on the belief that the unconscious and childhood conflicts impact behavior.
What was the traditional setting for psychoanalysis sessions?
Patients would lie on a couch facing away from Freud.
How has the setting for psychotherapy changed today?
Patients are more likely to sit facing the therapist.
What is play therapy?
A psychoanalytical therapy that uses interaction with toys instead of talk, primarily used in child therapy to help clients prevent or resolve psychosocial difficulties and achieve optimal growth.
What techniques are used in play therapy?
Techniques include using toys like dolls, stuffed animals, and sandbox figurines to help children express their hopes, fantasies, and traumas.
What is sandplay or sandtray therapy?
A form of play therapy where children create a three-dimensional world using various figures and objects that reflect their inner state.
How does a therapist use toys in play therapy?
The therapist observes how the child interacts with toys to understand the roots of the child's disturbed behavior and can use this for diagnosis.
What is nondirective play therapy?
A type of play therapy where children are encouraged to work through problems by playing freely while the therapist observes.
What is directive play therapy?
A type of play therapy where the therapist provides structure and guidance by suggesting topics, asking questions, and playing with the child.
What is behavior therapy?
A therapeutic approach that applies principles of learning to change undesirable behaviors, based on the belief that dysfunctional behaviors can be modified.
What is classical conditioning in behavior therapy?
A method where conditioning principles are applied to recondition clients and change their behavior.
What is counterconditioning?
A technique where a client learns a new response to a stimulus that previously elicited an undesirable behavior.
What is aversive conditioning?
A method that uses an unpleasant stimulus to stop an undesirable behavior, often used to eliminate addictive behaviors.
What is exposure therapy?
A therapeutic technique that seeks to change the response to a conditioned stimulus by repeatedly exposing the client to the object or situation that causes their problem.
Who developed the first type of exposure therapy?
Mary Cover Jones.
What was the aim of Mary Cover Jones' study with Peter?
To replace Peter's fear of rabbits with a conditioned response of relaxation by gradually exposing him to a rabbit while he was eating a snack.
What is systematic desensitization?
A type of exposure therapy developed by Joseph Wolpe, where a calm state is gradually associated with increasing levels of anxiety-inducing stimuli.
What principle underlies systematic desensitization?
Fear and relaxation are incompatible; if a client can relax around fear-inducing stimuli, the unwanted fear response will eventually be eliminated.
What is progressive relaxation?
A technique where the client is taught how to relax each muscle group to achieve a relaxed and comfortable state of mind.
How is progressive relaxation used in therapy?
It is used while the client imagines anxiety-inducing situations to help them become desensitized to those stimuli.
What is virtual reality exposure therapy?
A method that uses simulation to help clients confront fears when it is impractical, expensive, or embarrassing to recreate anxiety-inducing situations.
What condition is often treated with virtual reality exposure therapy?
Arachnophobia, or fear of spiders.
What principle is operant conditioning based on?
Behaviors become extinguished when not reinforced.
What is applied behavior analysis?
An operant conditioning technique designed to reinforce positive behaviors and punish unwanted behaviors, effective in helping children with autism.
What types of reinforcers are used in applied behavior analysis for children with autism?
Child-specific reinforcers such as stickers, praise, and candy.
What is the purpose of punishment in applied behavior analysis?
To discourage undesirable behaviors, such as using timeouts.
What is a token economy?
A system where individuals are reinforced for desired behaviors with tokens that can be exchanged for items or privileges, often used in psychiatric hospitals or prisons.
Who developed cognitive therapy and when?
Aaron Beck in the 1960s.
What does cognitive therapy focus on?
How thoughts lead to feelings of distress, emphasizing that emotional reactions result from thoughts about a situation rather than the situation itself.
What are cognitive distortions?
Thinking errors that clients are made aware of in cognitive therapy.
What is overgeneralizing in cognitive distortions?
Taking a small situation and making it seem much larger.
What is polarized thinking?
Seeing things in absolutes, such as thinking 'I am either perfect or a failure', which is common in depression.
What does jumping to conclusions refer to in cognitive distortions?
Assuming that people are thinking negatively about you or reacting negatively without evidence.
What is the goal of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)?
To change cognitive distortions and self-defeating behaviors by examining how thoughts affect behavior.
What does the ABC model in cognitive-behavioral therapy stand for?
Action (activating event), Belief (about the event), Consequences (of the belief).
What is the focus of humanistic therapy?
Helping people achieve their potential and increasing self-awareness and acceptance through conscious thoughts.
What is Rogerian/Client-centered therapy?
A form of therapy developed by Carl Rogers that emphasizes the importance of the client taking control of their own life.