Overview of Plasma Proteins: Structure, Function, and Testing
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
Human Proteome
~20,000 protein-coding genes in humans.
Proteins
Macromolecules made of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Plasma Proteins
Most produced in liver; exceptions include immunoglobulins.
Immunoglobulins
Antibodies secreted by plasma cells, not liver.
Hormones
Regulate synthesis and breakdown of plasma proteins.
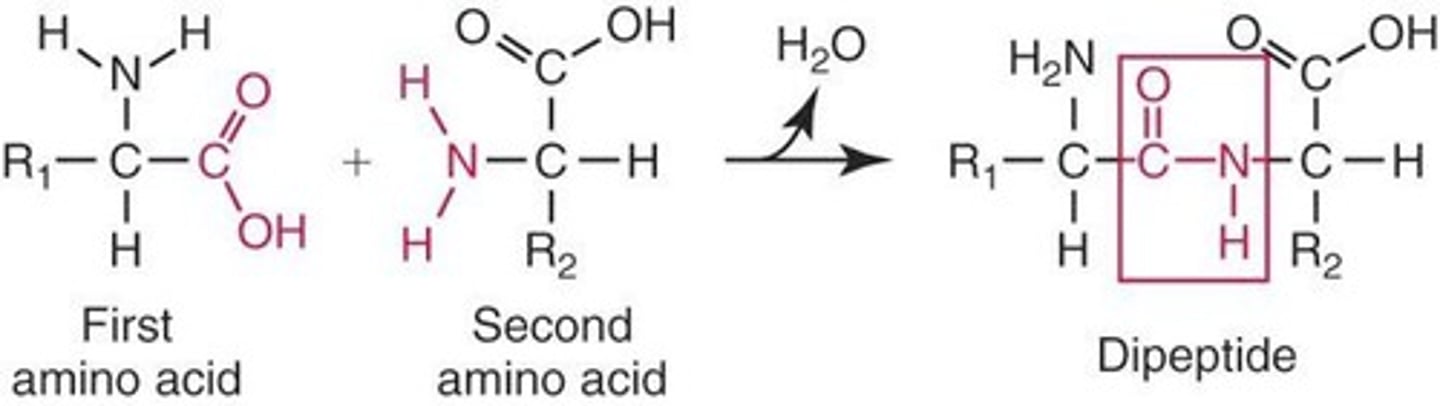
Peptide Bonds
Covalent bonds linking amino acids, releasing water.
Protein Structure
Levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary.
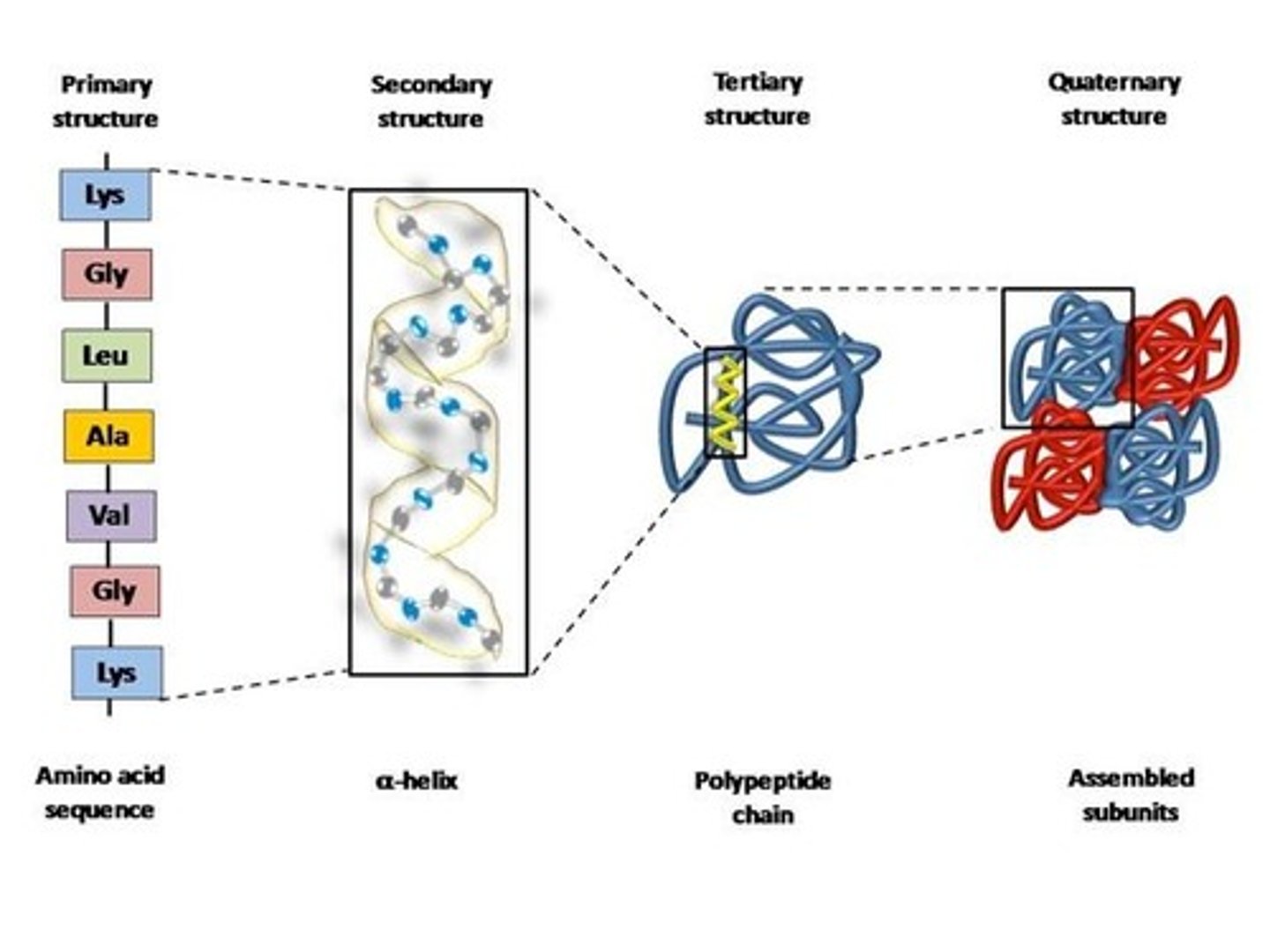
Primary Structure
Linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Secondary Structure
Polypeptide chains form coils, helices, or sheets.
Tertiary Structure
3D folding of polypeptide chains.
Quaternary Structure
Interaction of multiple peptide chains in a protein.
Simple Proteins
Composed solely of amino acids.
Conjugated Proteins
Contain non-protein groups attached to protein.
Apoproteins
Proteins without their non-protein groups.
Apolipoprotein
Protein remaining after lipid removal from lipoprotein.
Chromoprotein
Protein with a pigment, e.g., hemoglobin.
Metalloprotein
Contains metal ions, e.g., ceruloplasmin.
Glycoprotein
Protein with carbohydrate groups, e.g., mucin.
Lipoproteins
Complexes of lipids and proteins.
Nucleoproteins
Proteins combined with nucleic acids (DNA/RNA).
Serum Total Protein (TP)
Measured nitrogen balance; normal range 6.2-8.3 g/dL.
Plasma vs Serum
Plasma contains fibrinogen; serum does not.
Heparin Anticoagulant
Used to prevent blood clotting in plasma.
Hyperproteinemia
Elevated total protein levels in serum.
Dehydration
Loss of body water affecting protein concentration.
Multiple Myeloma
Cancer causing increased gamma-globulins in serum.
Hypoproteinemia
Decreased total protein levels in serum.
Kwashiorkor
Protein deficiency causing malnutrition in children.
Nephrosis
Kidney disorder leading to protein loss in urine.
BUN
Blood urea nitrogen; elevated in kidney dysfunction.
Prealbumin
Transport protein for thyroid hormones; short half-life.
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
IV nutrition for patients unable to eat.
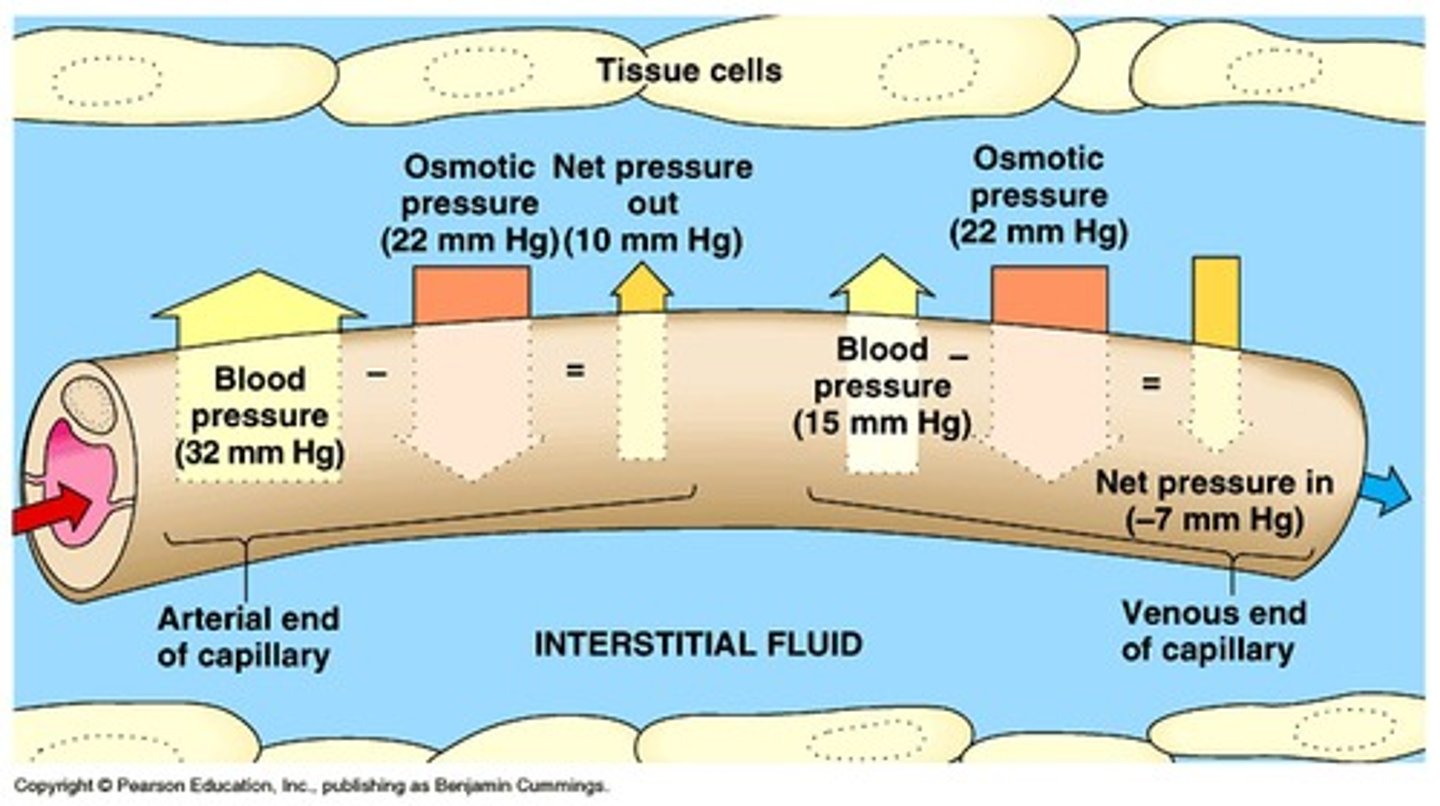
Colloidal Osmotic Pressure
Pressure exerted by proteins in blood plasma.
Osmotic Pressure
Pressure that drives fluid movement across membranes.
Edema
Excess fluid accumulation in interstitial spaces.
Hypoalbuminemia
Low albumin levels indicating various health issues.
Hyperalbuminemia
Elevated albumin levels, often due to dehydration.
Albumin
Most abundant serum protein; maintains osmotic pressure.
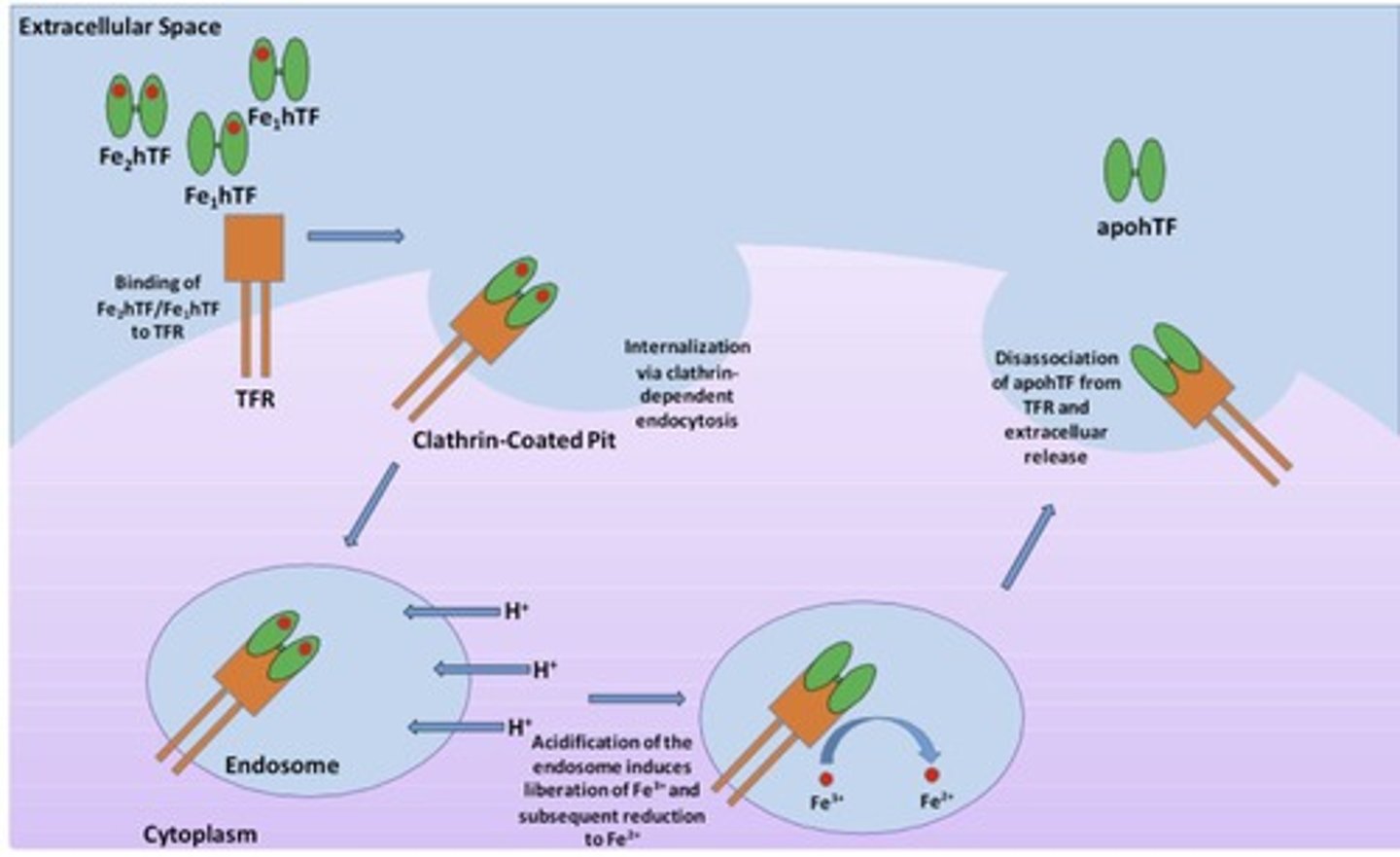
Transferrin
Iron transport protein in blood plasma.
C-Reactive Protein
Marker for inflammation in the body.
Ceruloplasmin
Copper-carrying protein; involved in iron metabolism.
Fibrinogen
Protein essential for blood clotting.
Alpha-Fetoprotein
Protein produced by the liver; tumor marker.
Clinical Correlation
Linking lab results to patient health status.
Protein
Total protein concentration in blood, measured in g/dL.
Albumin
Main protein in blood plasma, maintains oncotic pressure.
Prealbumin
Indicator of nutritional status, measured in mg/L.
A/G Ratio
Albumin to globulin ratio, indicates protein balance.
Globulins
Group of proteins in blood, includes four fractions.
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (A1AT)
Inhibits enzymes causing tissue damage, acute phase reactant.
Congenital A1AT Deficiency
Genetic condition linked to early-onset emphysema.
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Technique to separate proteins based on size and charge.
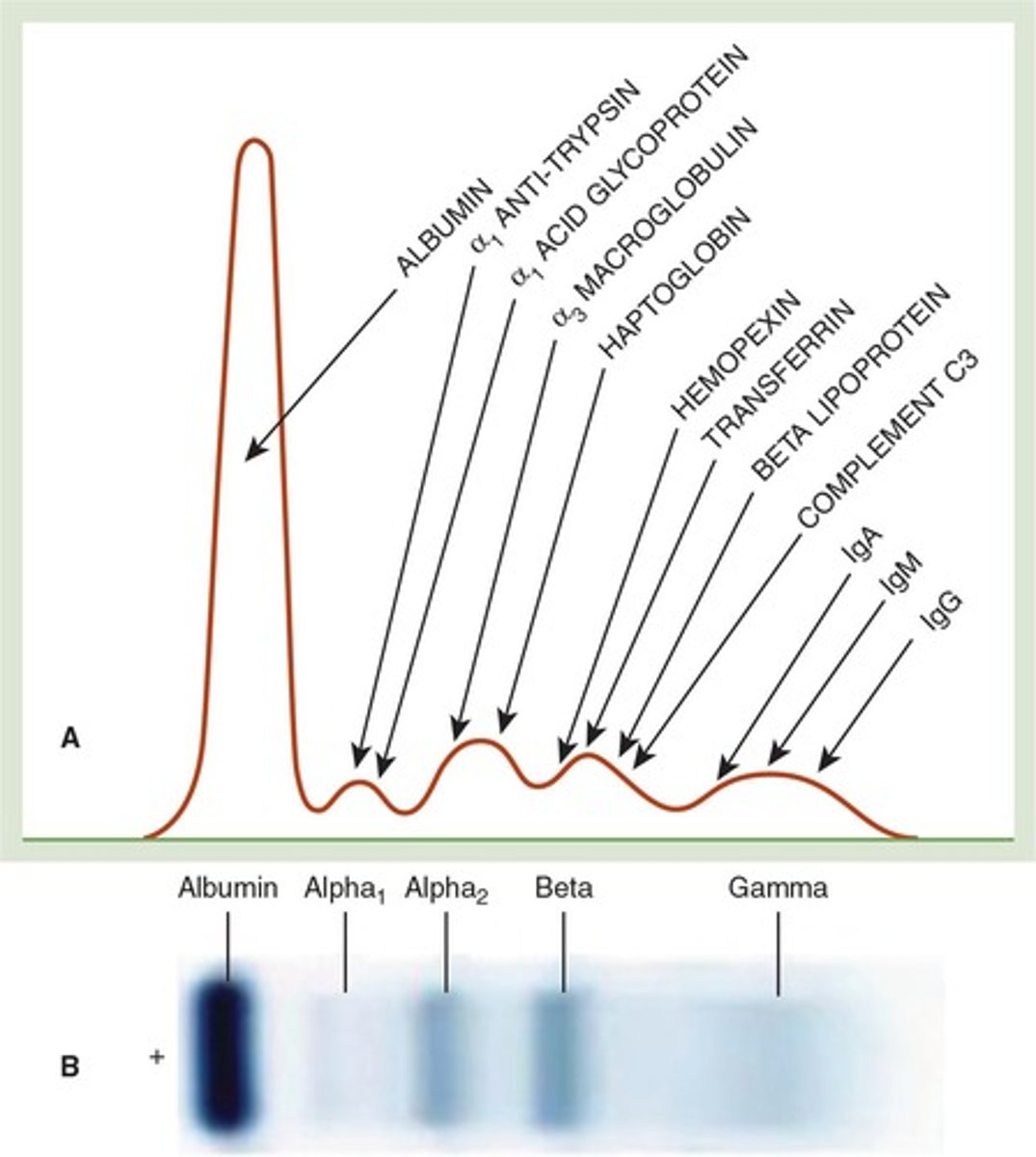
Haptoglobin
Binds free hemoglobin, evaluates hemolytic anemia.
Ceruloplasmin (CER)
Copper transport protein, positive acute-phase reactant.
Wilson's Disease
Autosomal recessive disorder causing copper accumulation.
Kayser-Fleischer Ring
Copper deposits in cornea, indicative of Wilson's Disease.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Fetal protein, tumor marker for liver and germ cell cancers.
Neural Tube Defects
Congenital malformations detectable by elevated AFP.
Emphysema
Lung condition characterized by damaged alveoli.
Acute Phase Reactants
Proteins that increase during inflammation or injury.
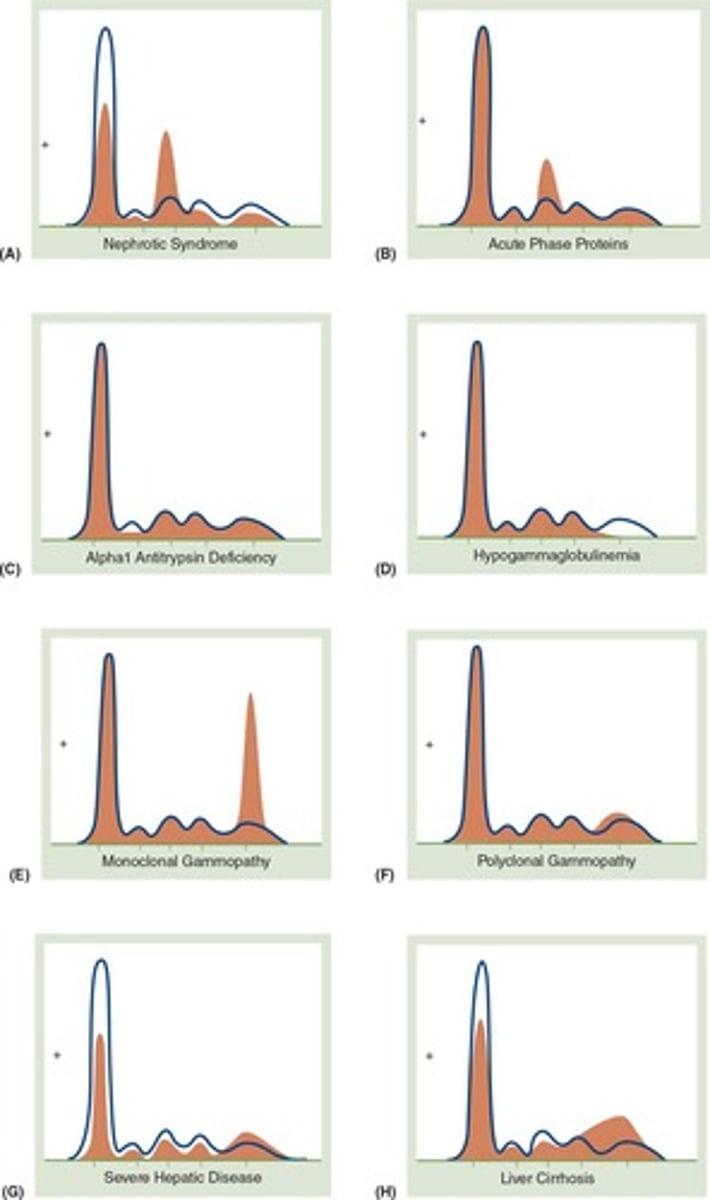
Proteinuria
Presence of excess protein in urine, indicates kidney issues.
Generalized Edema
Swelling due to fluid accumulation in tissues.
Ascites
Fluid buildup in abdominal cavity, often due to liver disease.
Increased Urine Copper
Sign of Wilson's Disease, indicates copper metabolism disorder.
Liver Biopsy
Procedure to diagnose liver conditions, including Wilson's Disease.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
Imaging technique to visualize internal structures, like lungs.
Chronic Inorganic Dust Exposure
Long-term inhalation of dust, risk factor for lung disease.
Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Elevated bilirubin due to liver dysfunction.
Severe coagulopathy
Increased bleeding risk from clotting factor deficiencies.
Tremors
Involuntary muscle contractions at rest or during action.
Kayser-Fleischer rings
Copper deposits in the cornea, indicative of Wilson's disease.
Sunflower cataracts
Copper accumulation causing characteristic eye lens changes.
Ceruloplasmin
Copper-carrying protein; low levels indicate copper metabolism issues.
Serum protein
Total protein concentration in blood; normal range 6.4-8.3 g/dL.
Serum albumin
Main protein in blood; low levels indicate liver dysfunction.
Alanine transaminase (ALT)
Liver enzyme; elevated levels indicate liver damage.
Aspartate transaminase (AST)
Enzyme indicating liver or muscle injury; elevated levels.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Enzyme associated with liver and bone disorders; elevated levels.
Bilirubin
Breakdown product of hemoglobin; elevated levels indicate liver issues.
α2-Macroglobulin
Inhibits proteases; increased in nephrosis.
Transferrin (TF)
Iron transport protein; levels increase with iron deficiency.
β-Globulins
Group of proteins including transferrin and β-microglobulin.
β2-Microglobulin (BMG)
Protein indicating tumor burden in malignancies.
Complement C-3
Part of immune system; increased in inflammation.
Fibrinogen
Clotting factor; increased during inflammation and liver disease.
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Inflammation marker; rises with infections and inflammation.
hs-CRP
High-sensitivity CRP; assesses cardiac risk.
Immunoglobulins
Antibodies produced by plasma cells in immune response.
Acute phase reactants
Proteins that change in response to inflammation.
Reticuloendothelial system (RES)
Part of immune system involved in iron storage.
Immunoglobulins (Igs)
Antibodies classified into five distinct classes.
Polyclonal increase
Normal immune response to inflammation or infection.
Monoclonal increase
Single clone produces one specific immunoglobulin.
IgG
Most abundant immunoglobulin in serum, four subclasses.
IgM
5-10% of circulating immunoglobulins.
IgA
10-15% of circulating immunoglobulins.
IgE
Trace levels, associated with allergic reactions.
IgD
Trace levels, function remains unknown.
Cryoglobulins
Proteins that precipitate in cold temperatures.
Total Nitrogen
Measures all chemically bound nitrogen in a sample.