EDSP 161 Neuro/Anat Quiz 1
1/17
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
supine
on the back
prone
on the belly
What is the CNS encased in?
bone (skull and vertebrae)
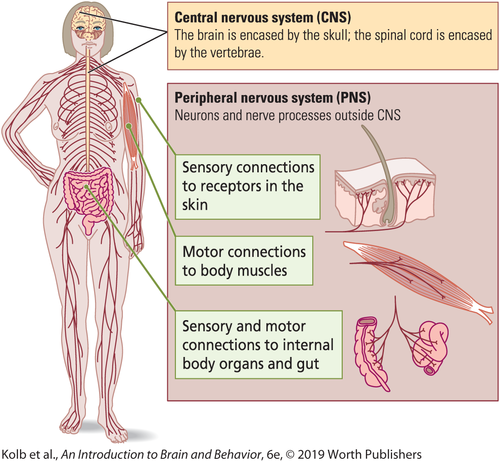
What parts does the CNS include?
cerebral cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, basal ganglion, brain stem, spinal cord
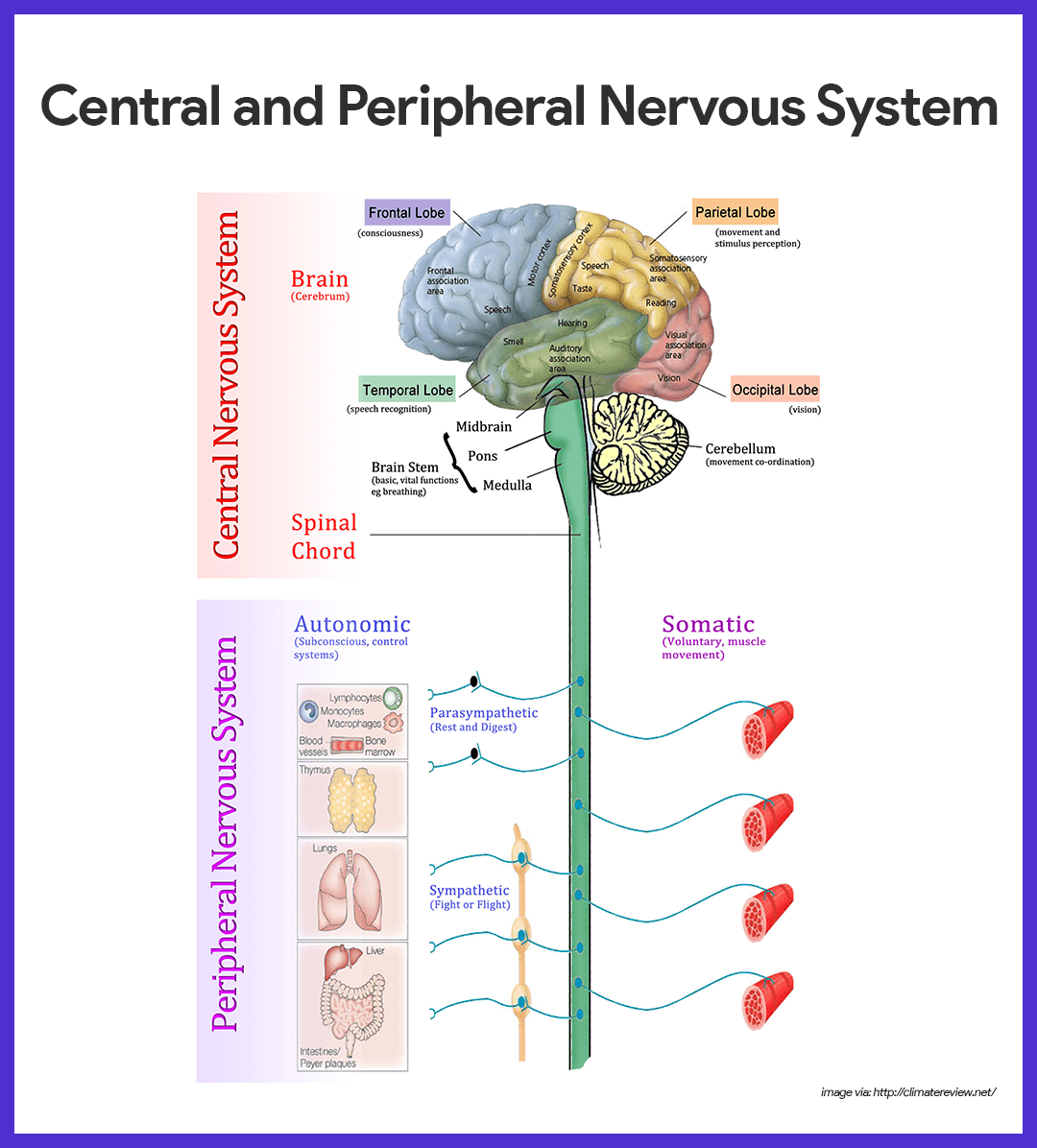
coronal
separates front and back
sagittal
separates right and left
transverse
separates top and bottom
What is the most basic unit of the nervous system?
neurons (nerve cells)
Where is the pre-central gyrus found?
aka motor strip; found in the frontal lobe
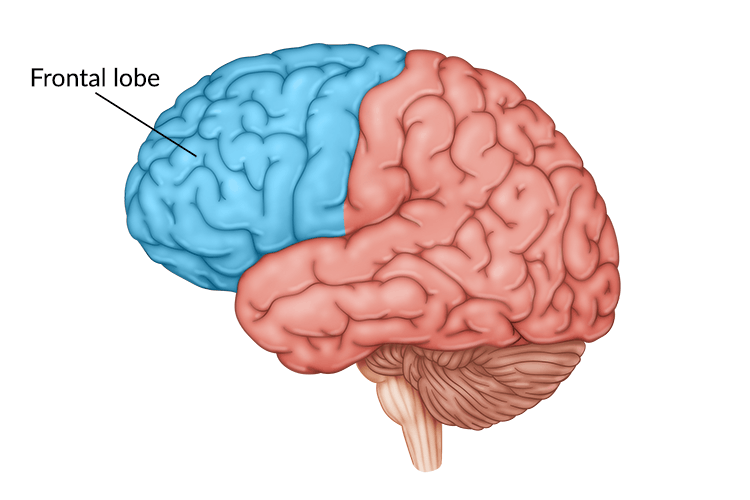
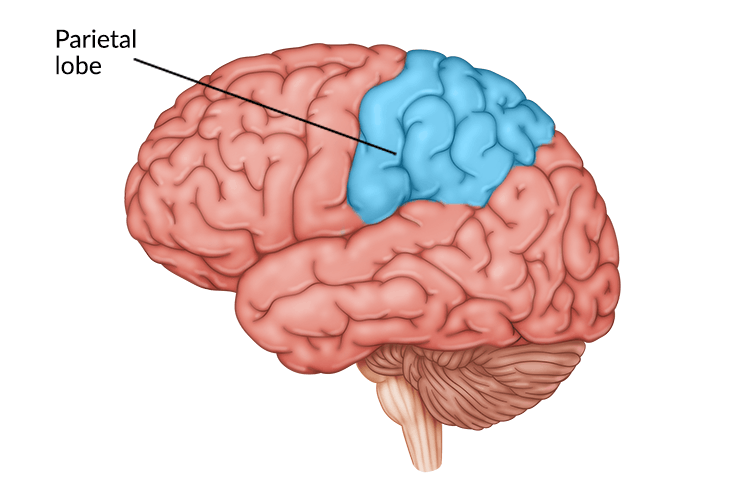
Sensory receptors are found in which lobe?
parietal lobe (post-central gyrus)
sensory aphasia
Wernicke’s aphasia
motor aphasia
Broca’s aphasia
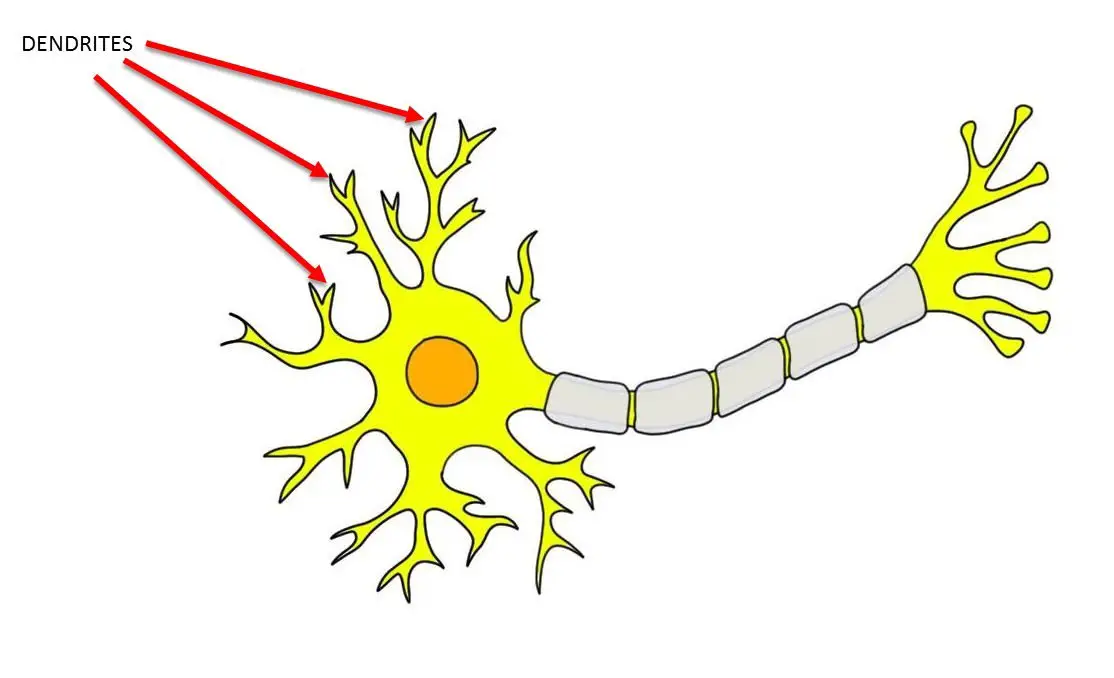
What part of the neuron receives information?
dendrites
The cerebellum has two hemispheres; is it ipsilateral, contra-lateral, or both? Does it give information of movement
the two hemispheres provide coordination of fine movements ipsilaterally; responsible for rapid and precise movements
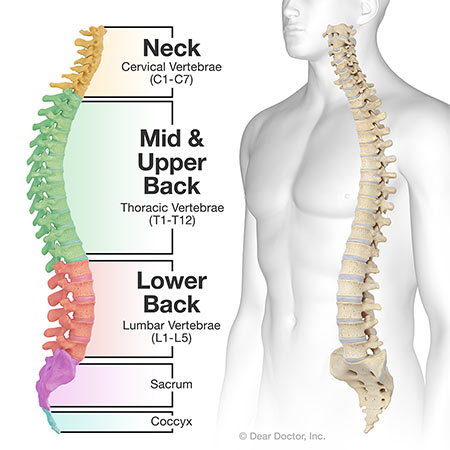
Does the spinal column go all the way, or does it stop?
Divided into 5 sections; does NOT extend the complete length of the vertebral column
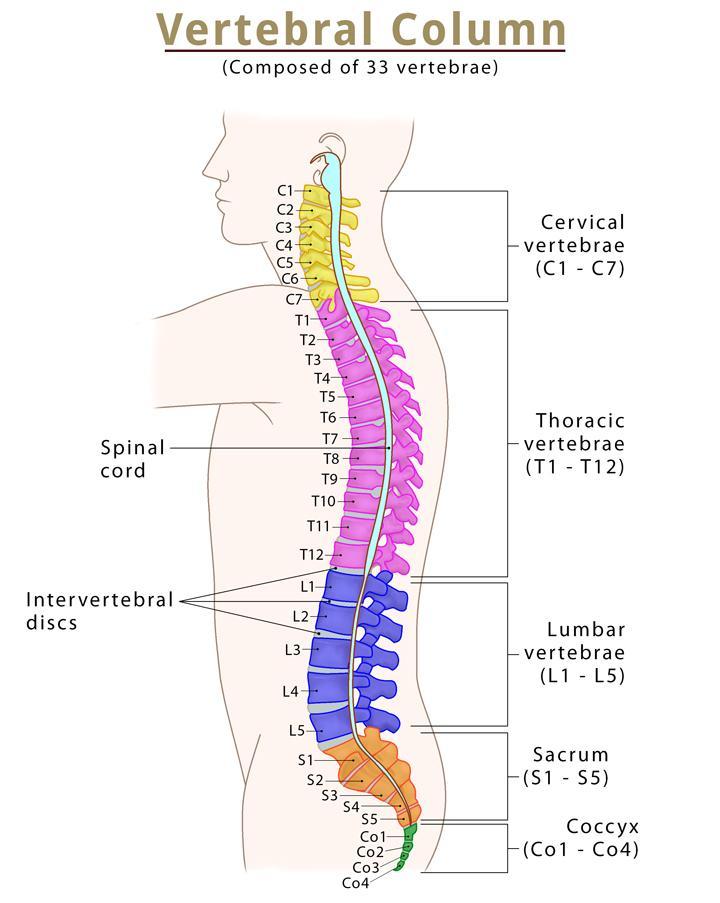
How far does the spinal column go and how big is it?
stops at lower border of the first lumbar vertebra ADults; stops at the upper border of the 3rd lumbar vertebra CHildren
Impairment in the substantia nigra (Parkinson’s) – where is it located?
impairment of the basal ganglion; impairment here results in reduction of transmission of dopamine, which eventually result in Parkinson’s
What is the fatty wrapping around the neurons called?
myelin sheath