1.5.2 DNA replication ❤️
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Why is semi-conservative replication important
Ensures genetic continuity between generations of cells
Describe the process of semi conservative replication
DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, unwinding the double helix
Both strands act as templates
Free DNA nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases and join by specific complementary base pairing
Hydrogen bonds form between pairs
DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides on the new strand by condensation reactions
Forming phosphodiester bonds
Define semi-conservative
Each new DNA molecule consists of one original template strand and one new strand
Why does DNA polymerase move in opposite directions along DNA strands (enzyme action)
DNA has antiparallel strands
So shapes/ arrangements of nucleotide on two ends are different
Since DNA polymerase is an enzyme with a specific active site, it can only bind to substrate with complementary shape
Which is the phosphate end of developing strand
Name 2 scientists who proposed models of the chemical structure of DNA and DNA replication
Watson and Crick
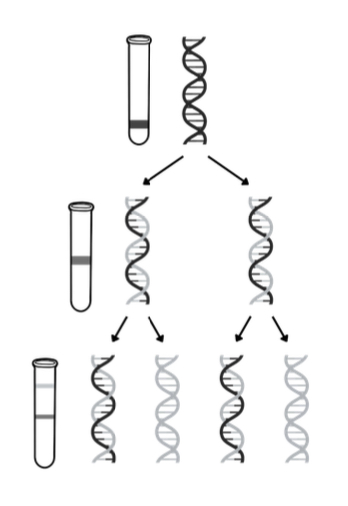
Describe the work of Meselson and Stahl (invalidated Watson and cricks model)
Grew bacteria in medium containing heavy nitrogen, so heavy nitrogen is incorporated into DNA bases. DNA extracted and centrifuged, settles near bottom as there’s 2 heavy strands
Bacteria transferred to medium containing light nitrogen, allowed to divide one. DNA extracted and centrifuged, settles near middle as contains 1 heavy and 1 light
Bacteria in light nitrogen is allowed to divide again. DNA extracted and centrifuged. Half settles in middle (1 heavy, 1 light). Half settles near top (2 light)
Draw the results of Meselson and Stahl
.