P2.6 - Metabolic/Crystal Deposition Disorders
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Gout
- Hyperuricemia with secondary sodium monourate crystal deposition:
• Cartilage
• Synovium
• Periarticular
• Subcutaneous
Inflammatory
With gout, crystals evoke a strong _____ joint disease
- M:F → 20:1
- 4th/5th decades
State the clinical features of gout
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
- Acute gouty arthritis
- Polyarticular gouty arthritis
- Chronic tophaecous gout
State the 4 stages of gout
- Elevated ESR
- Leukocytosis
- Hyperuricemia**
- Joint aspiration
State the lab findings of gout
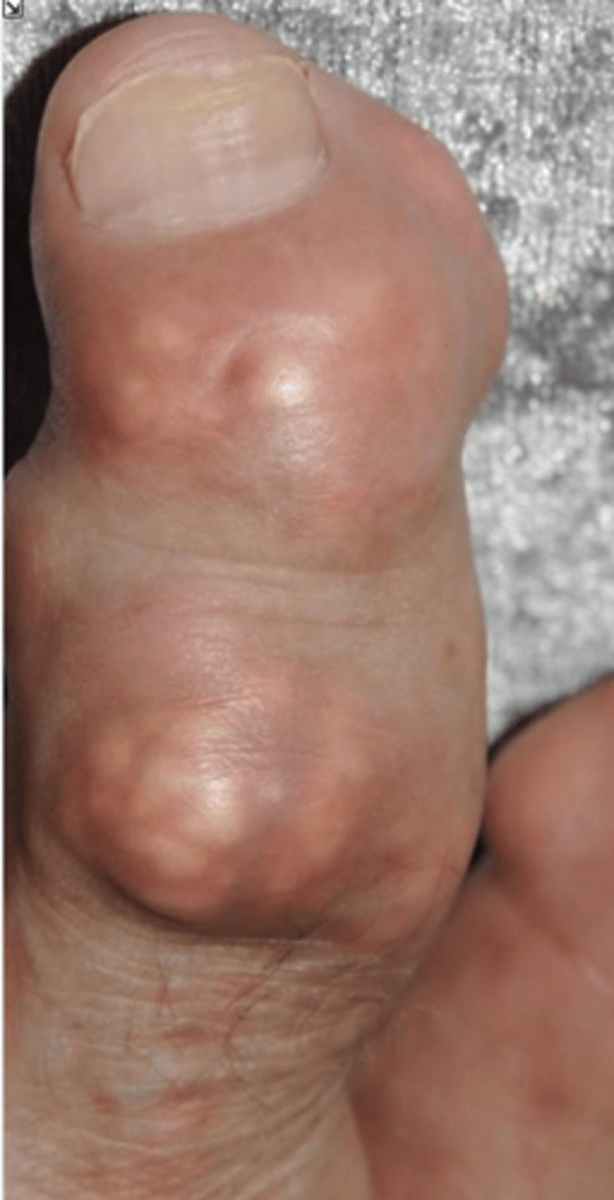
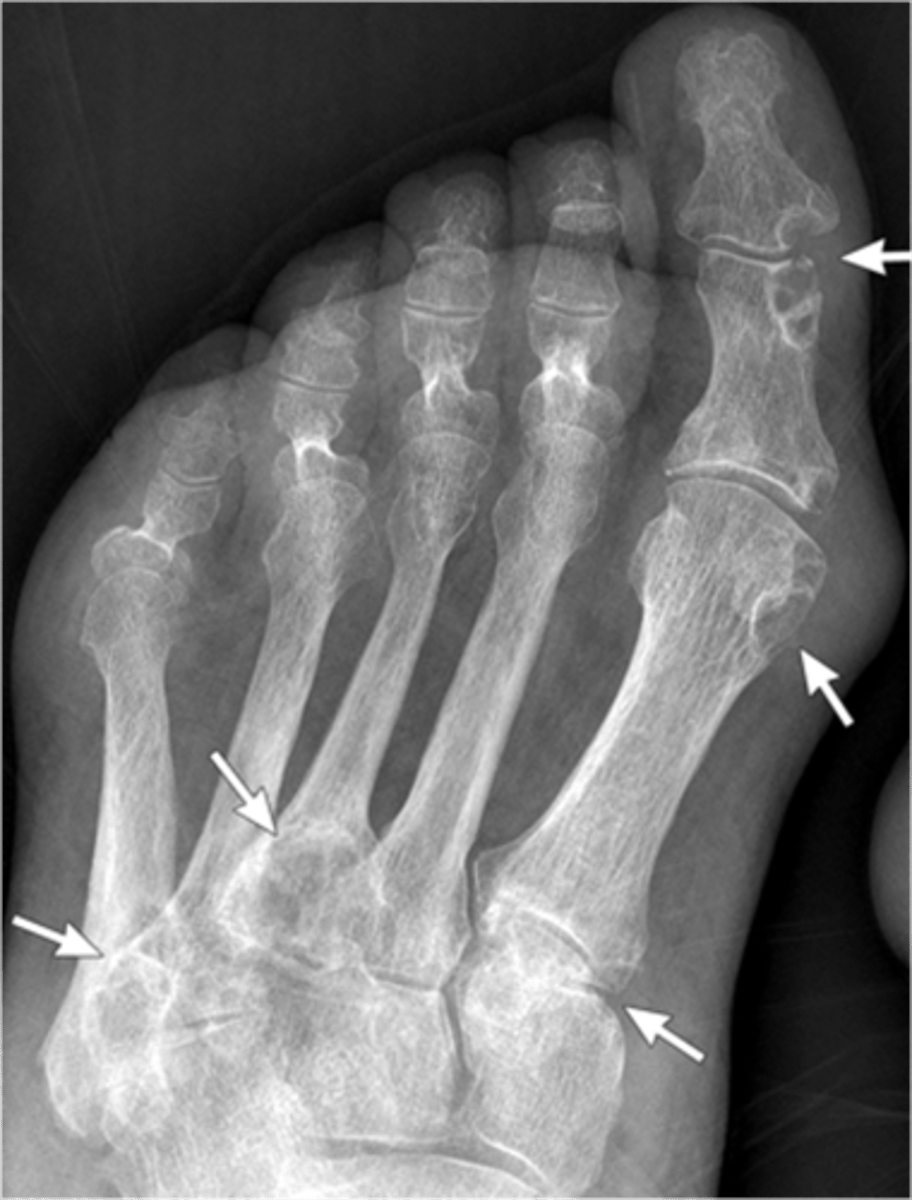
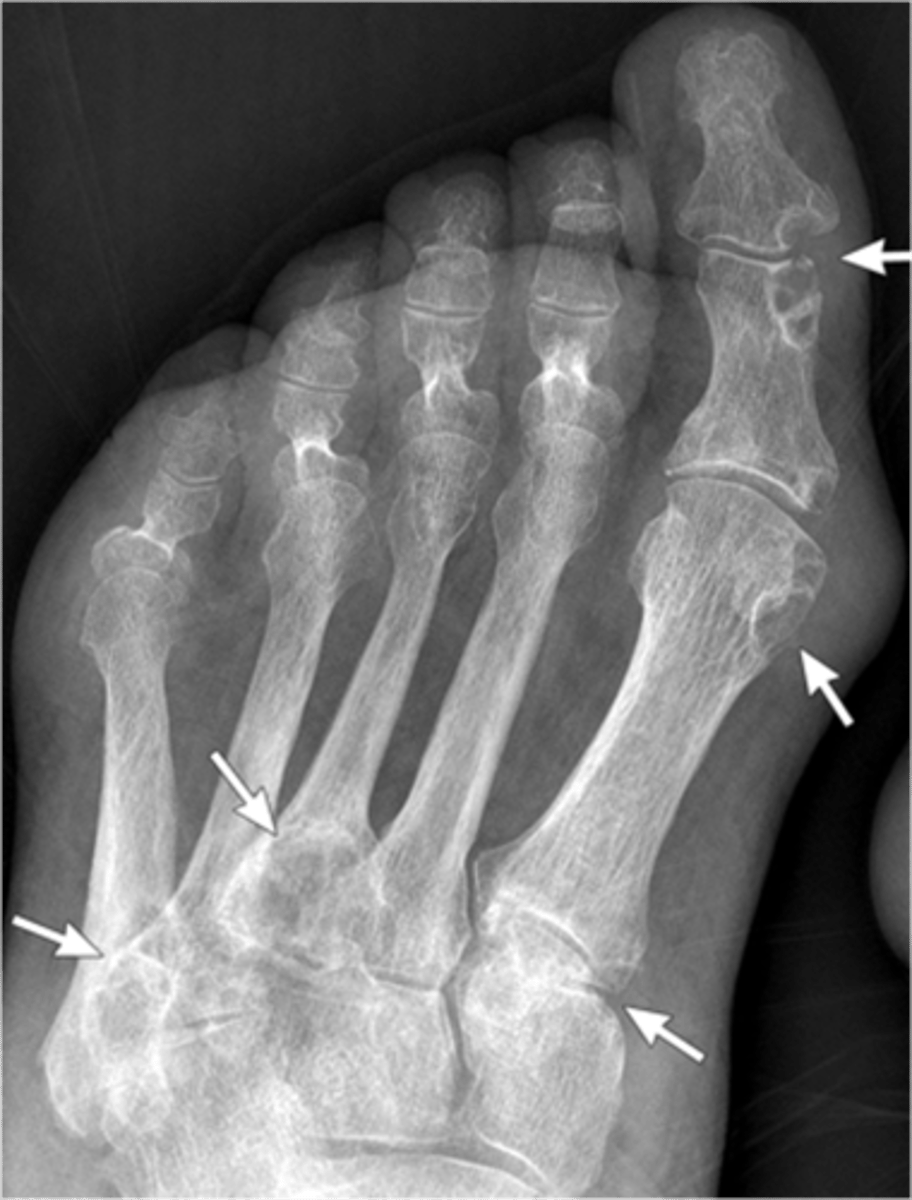
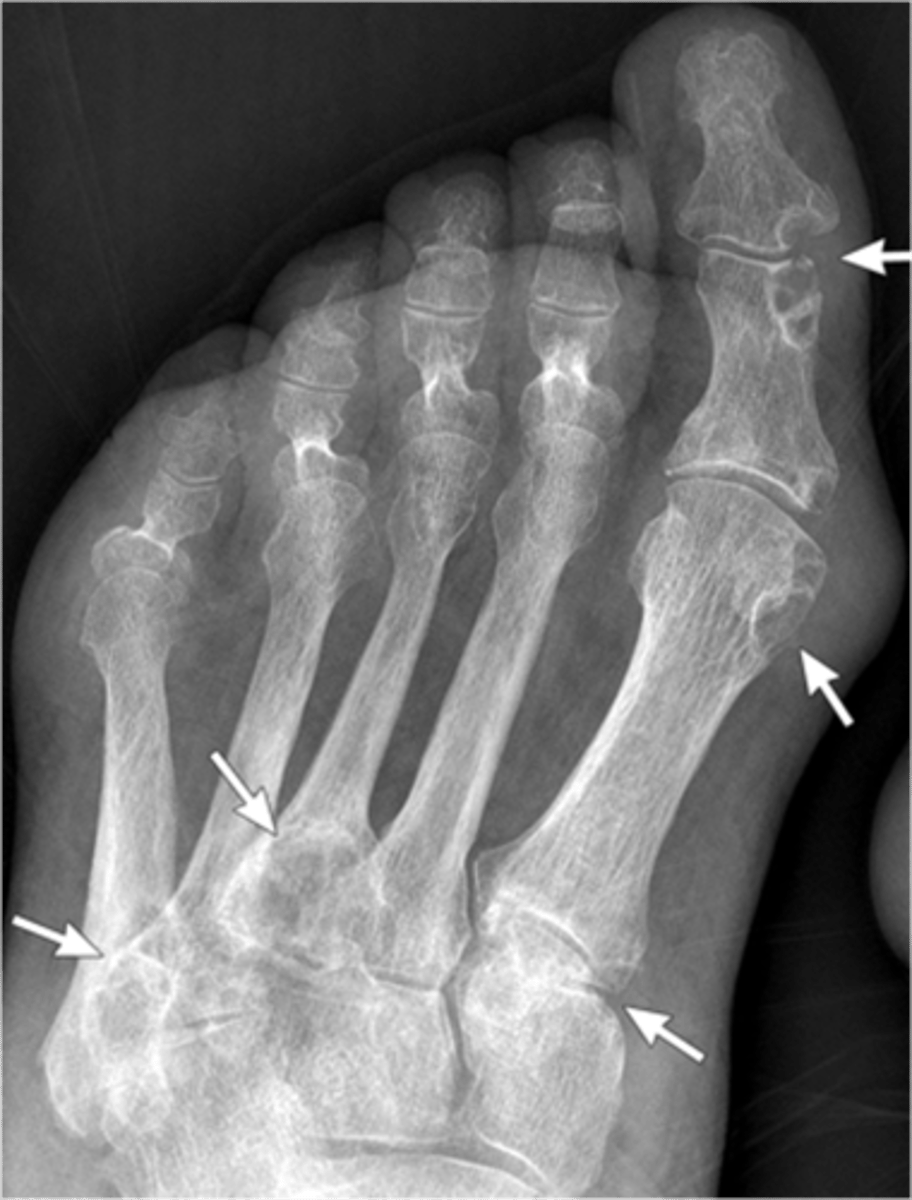
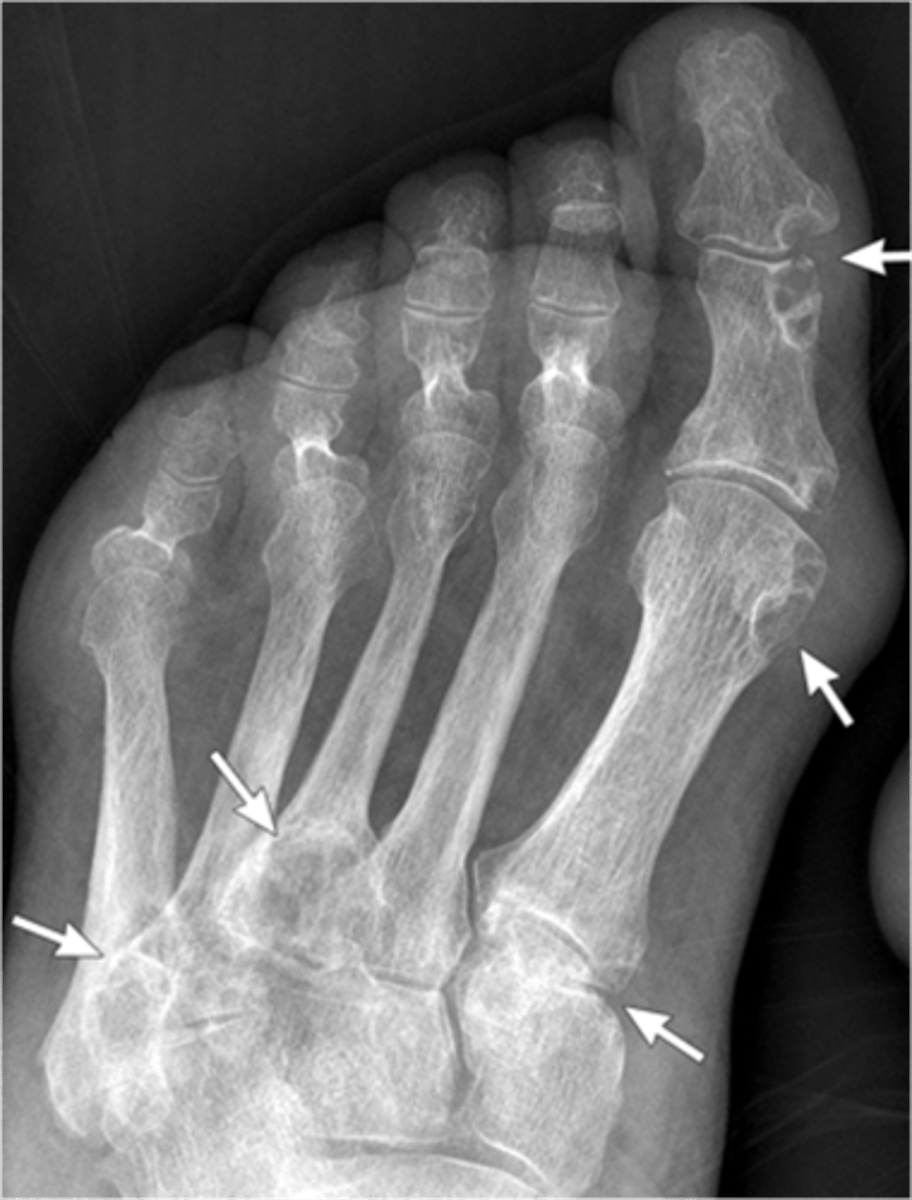
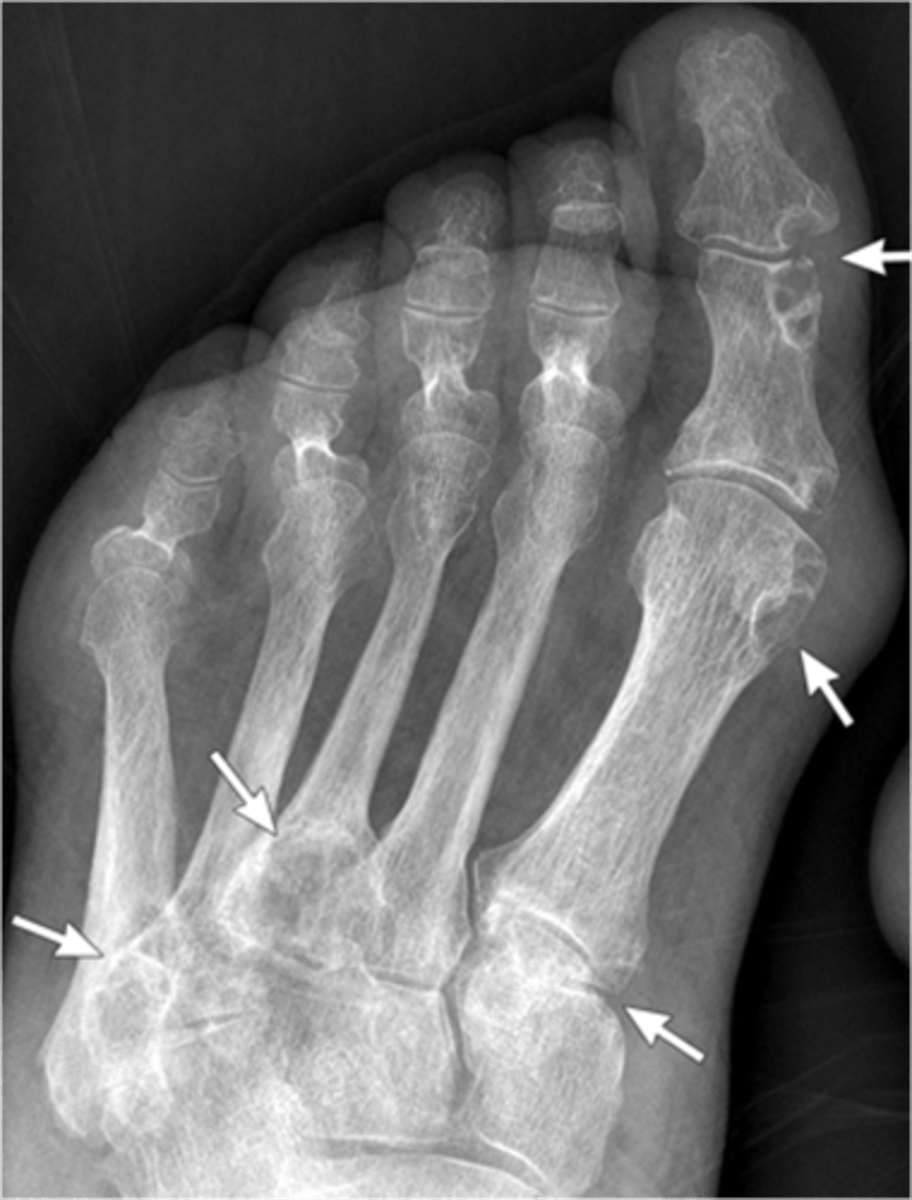
- Dense soft tissue tophi (swelling)
- Bone erosions
- Overhanging margin sign
- Secondary degeneration
- 1st MTP MC joint
State the radiographic findings of gout
- Rapid recovery within days of the attack
- Moist Heat
- Colchicine
- Allopurinol
- Black cherry juice
State the treatments for gout
- Pseudogout
- >50 y.o.
- M=F
- May be asymptomatic
- Acute inflamed joint
- Bilateral asymmetric
State the clinical features of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CCPD)
- Knee
- Symphysis pubis
- Hand/wrist
- Hip
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Spine
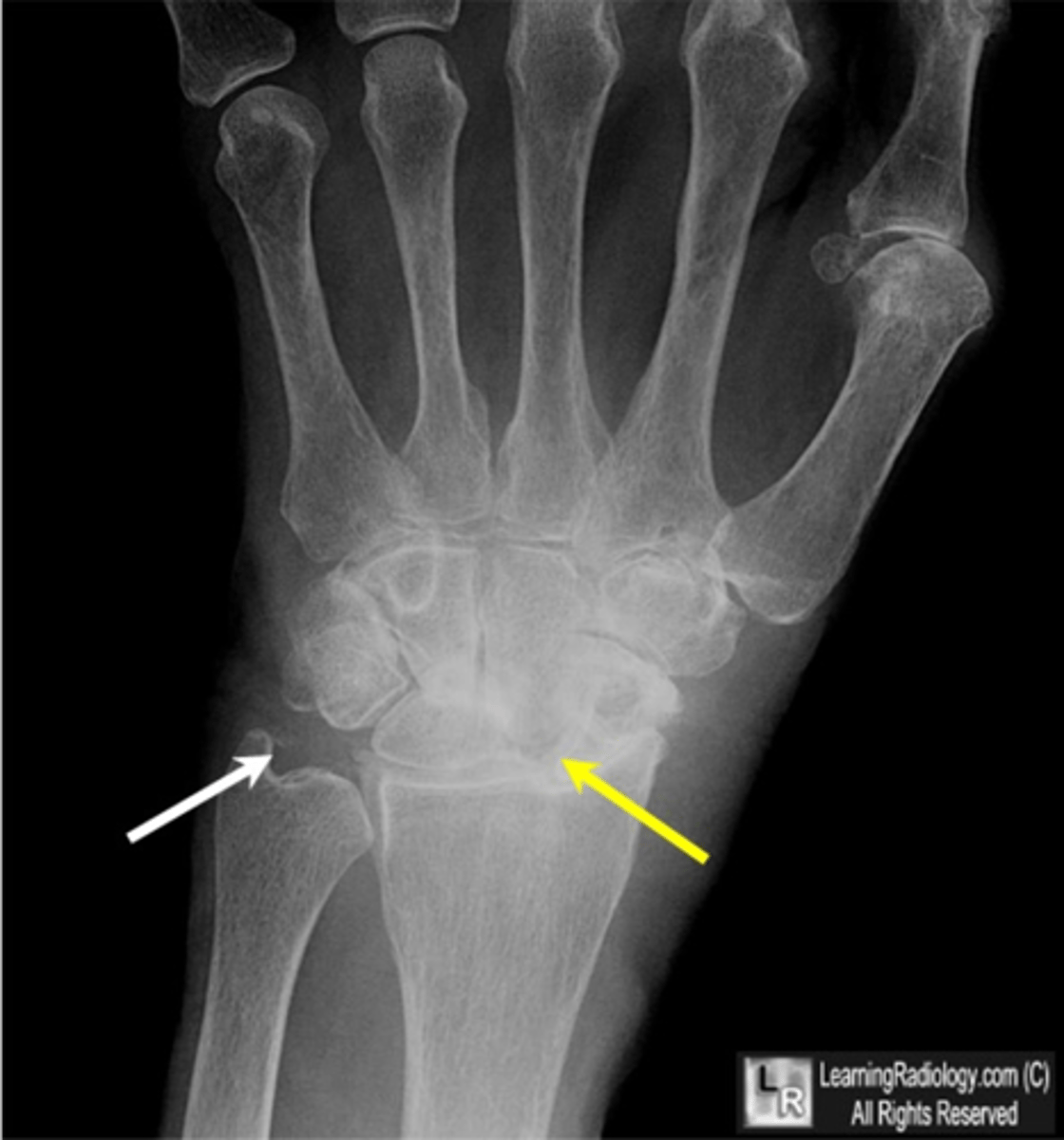
State the target sites of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CCPD)
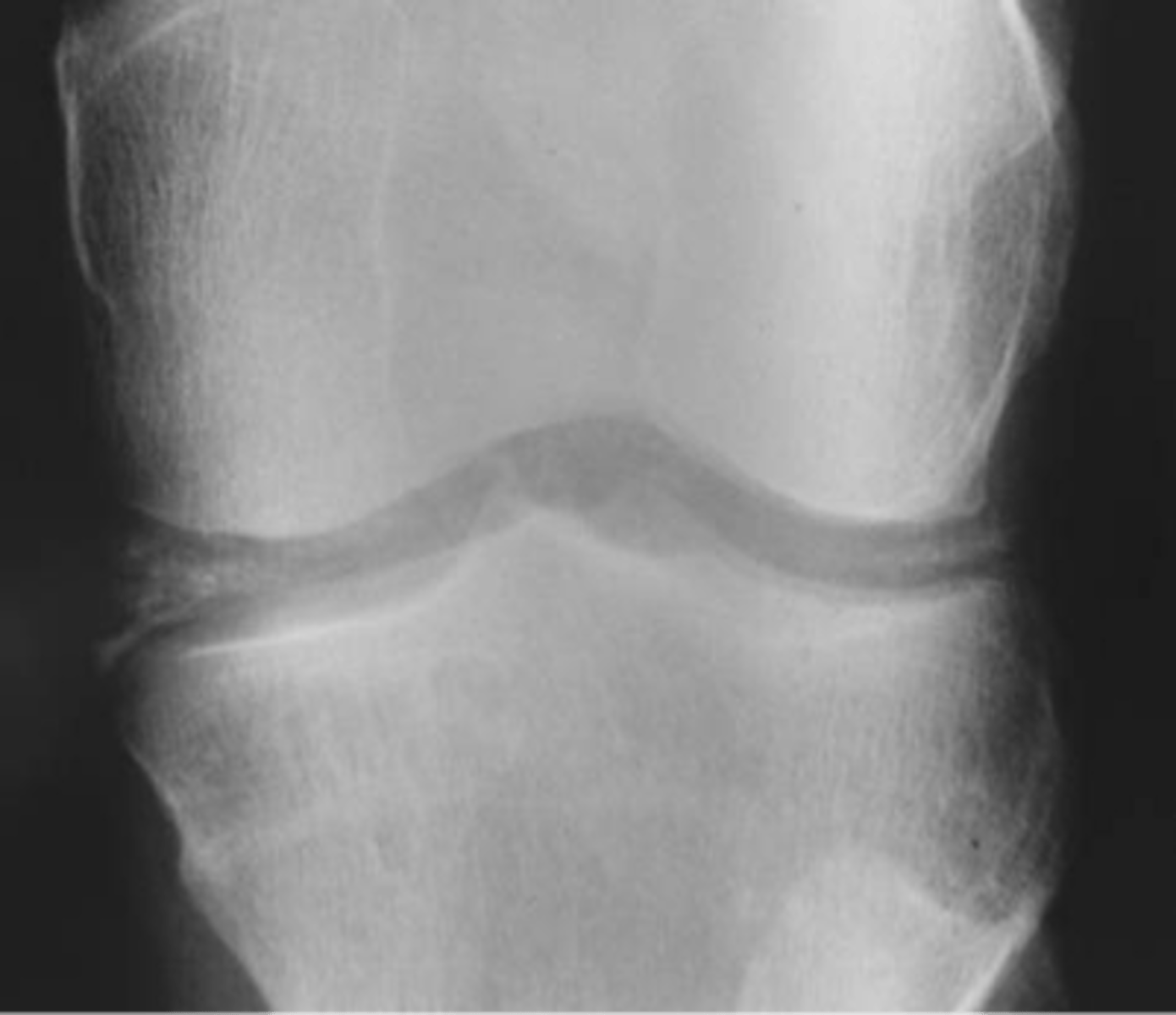
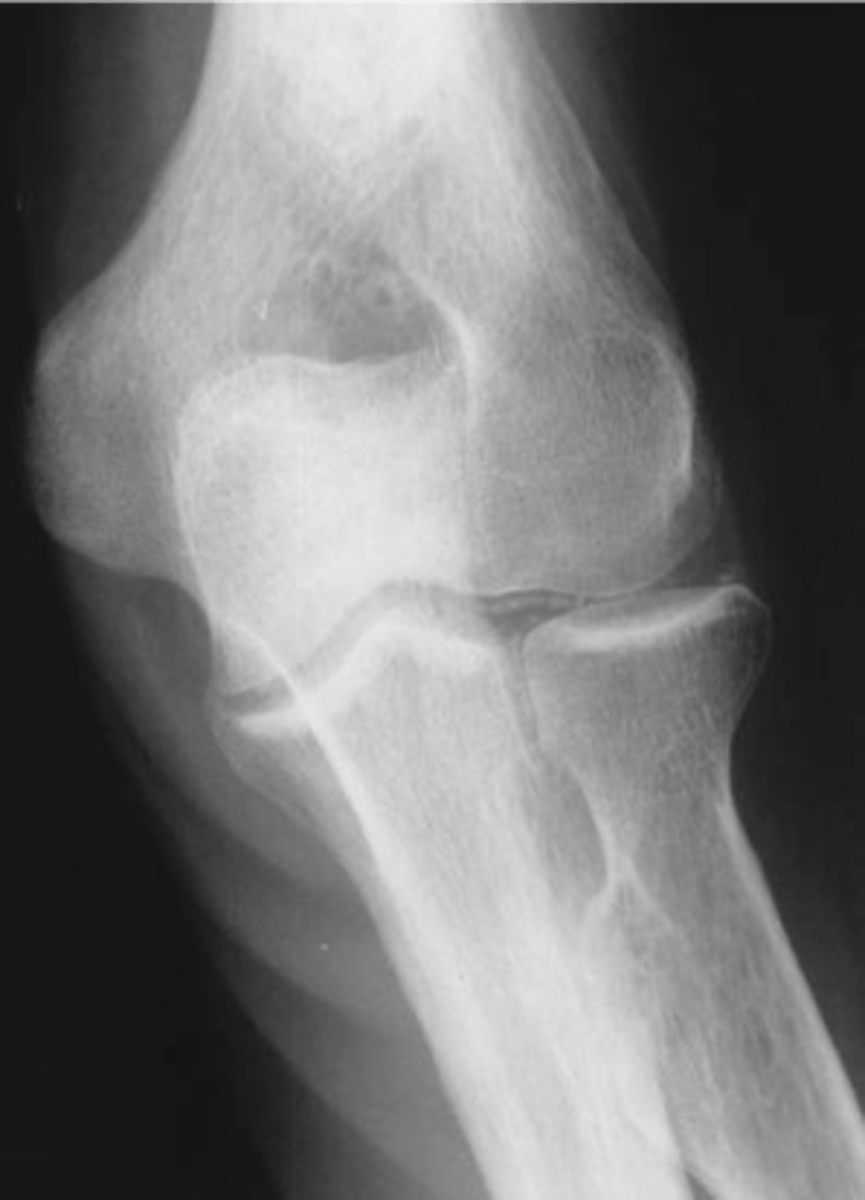
- Soft tissue swelling
- Chondrocalcinosis
- Severe degeneration
- Pyrophosphate arthropathy
- Articular destruction
- SLAC wrist (scapholunate advanced collapse)
State the radiographic findings of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CCPD)
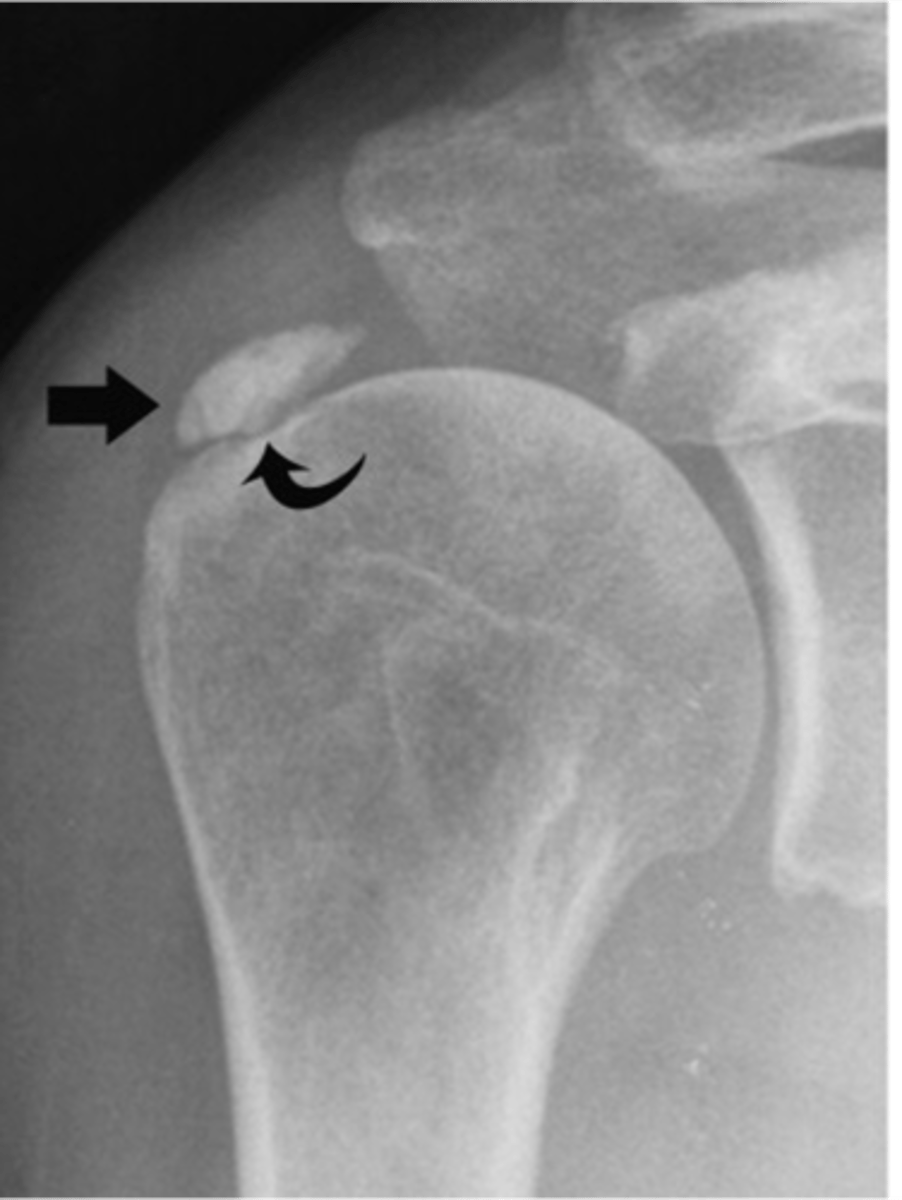
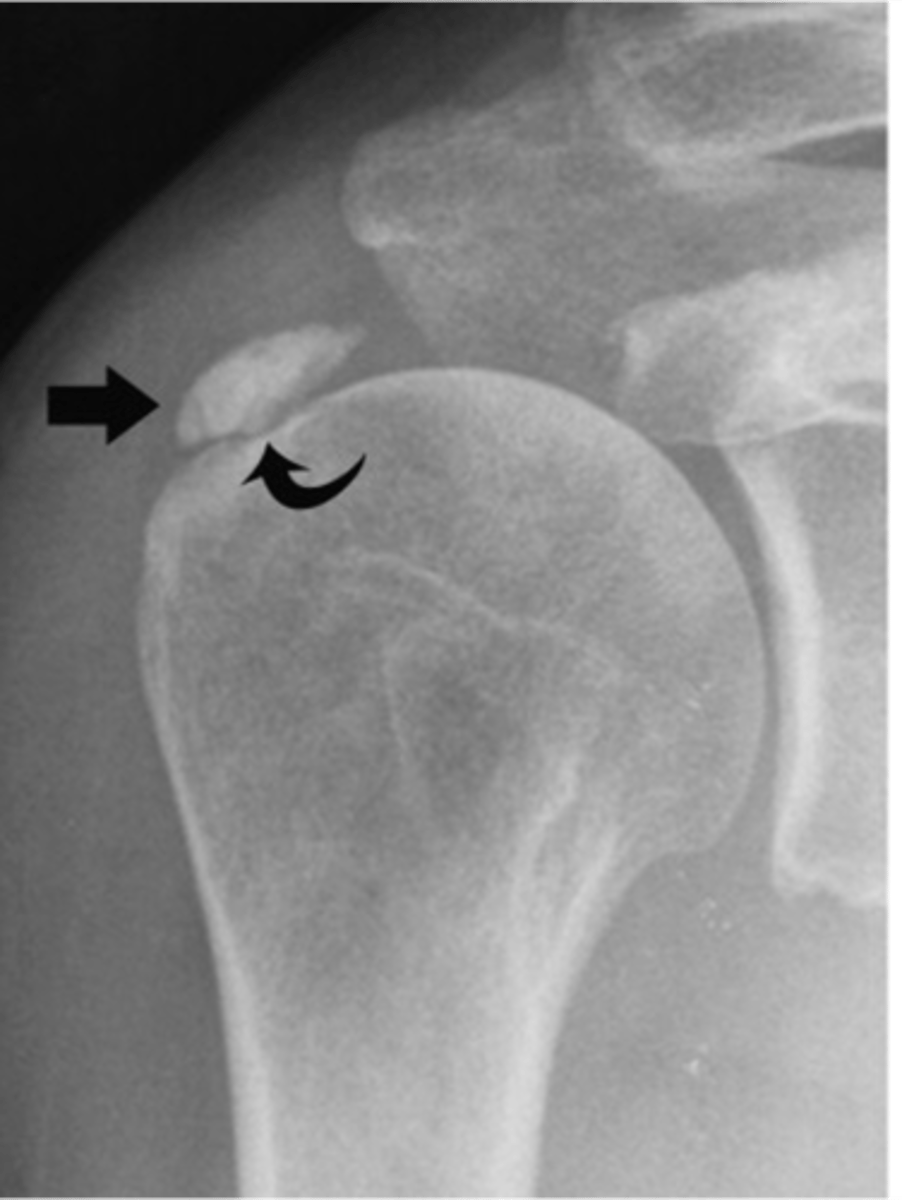
- Deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite within a tendon, bursa, or other periarticular soft tissue
- May cause tendinitis, bursitis, and joint pain
State the pathophysiology of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CCPD)
- 40-70 y.o.a
- M=F
- Pain, tenderness, localized swelling
- Decreased ROM
State the clinical features of hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD)
Calcific tendinitis
Another term for hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD)
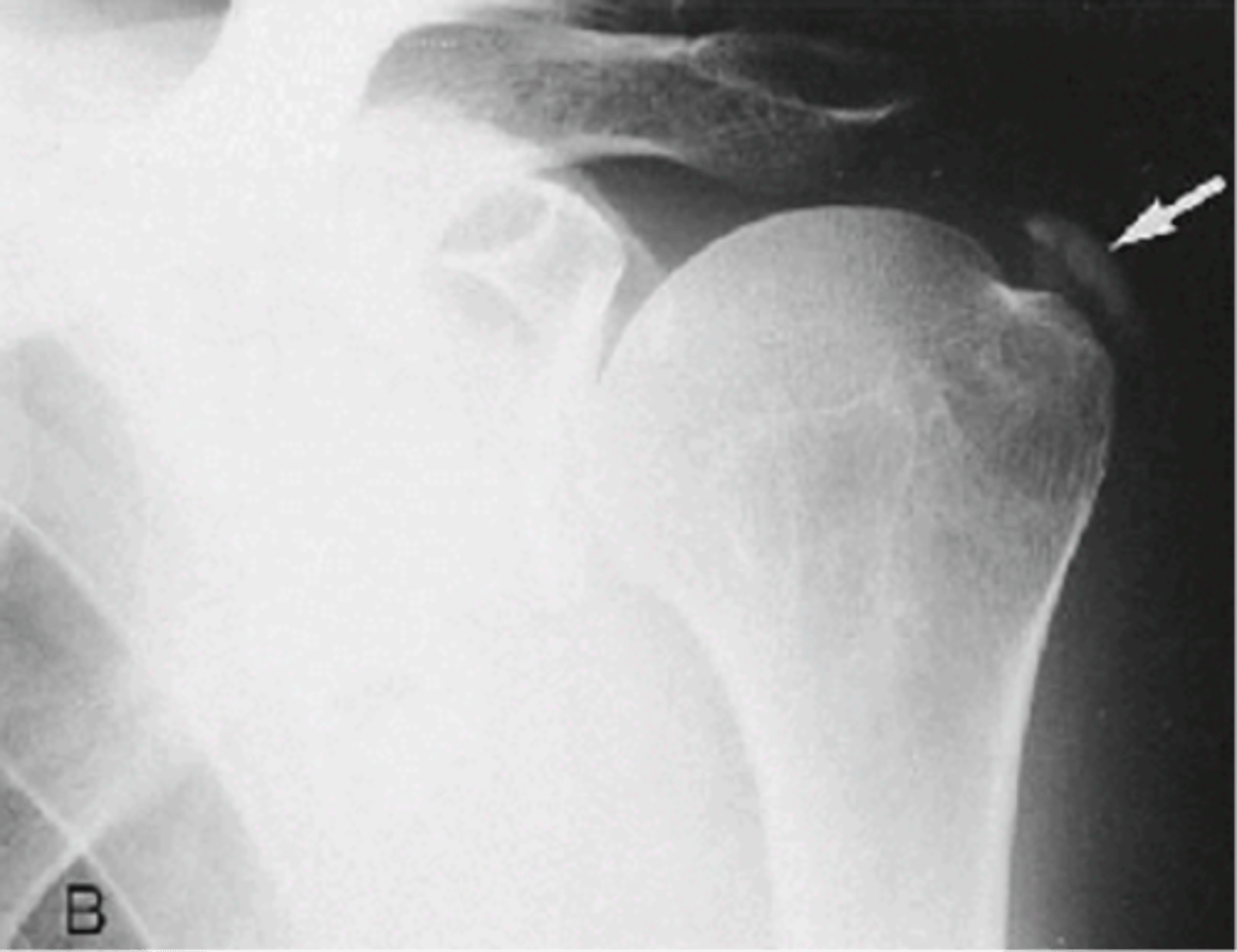
Supraspinatus
Hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) of the _____
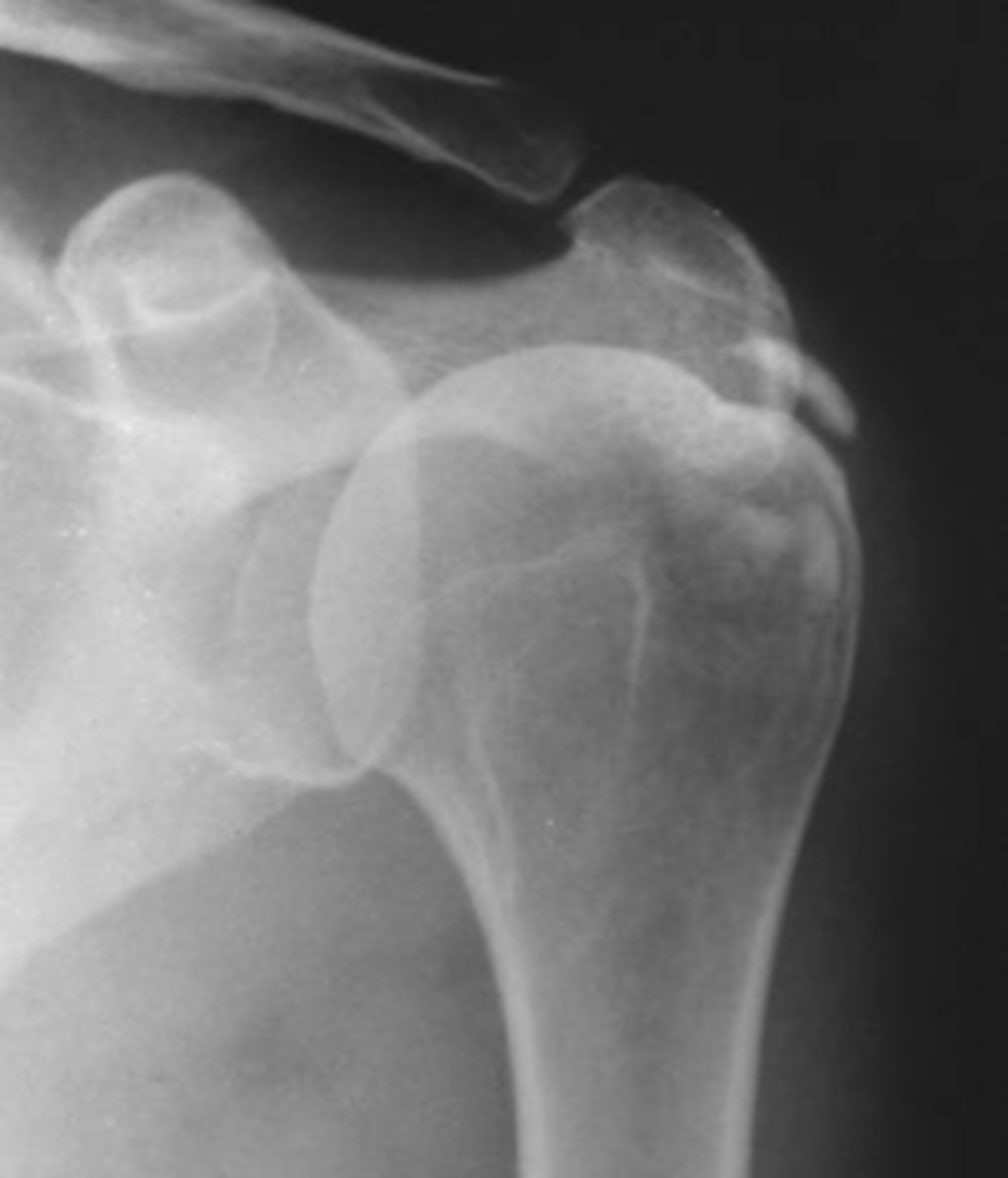
Infraspinatus
Hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) of the _____
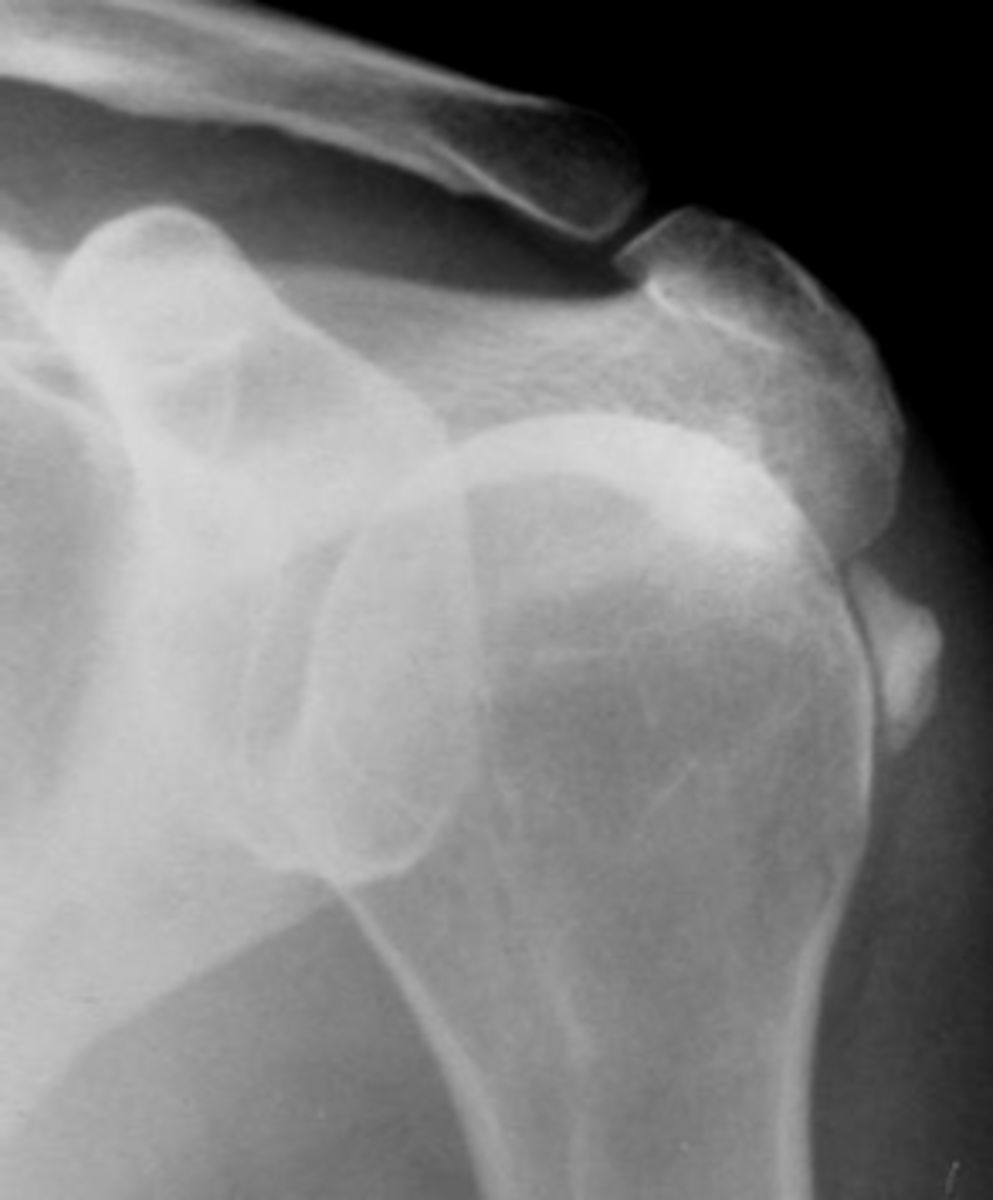
Long head of biceps brachii
Hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) of the _____
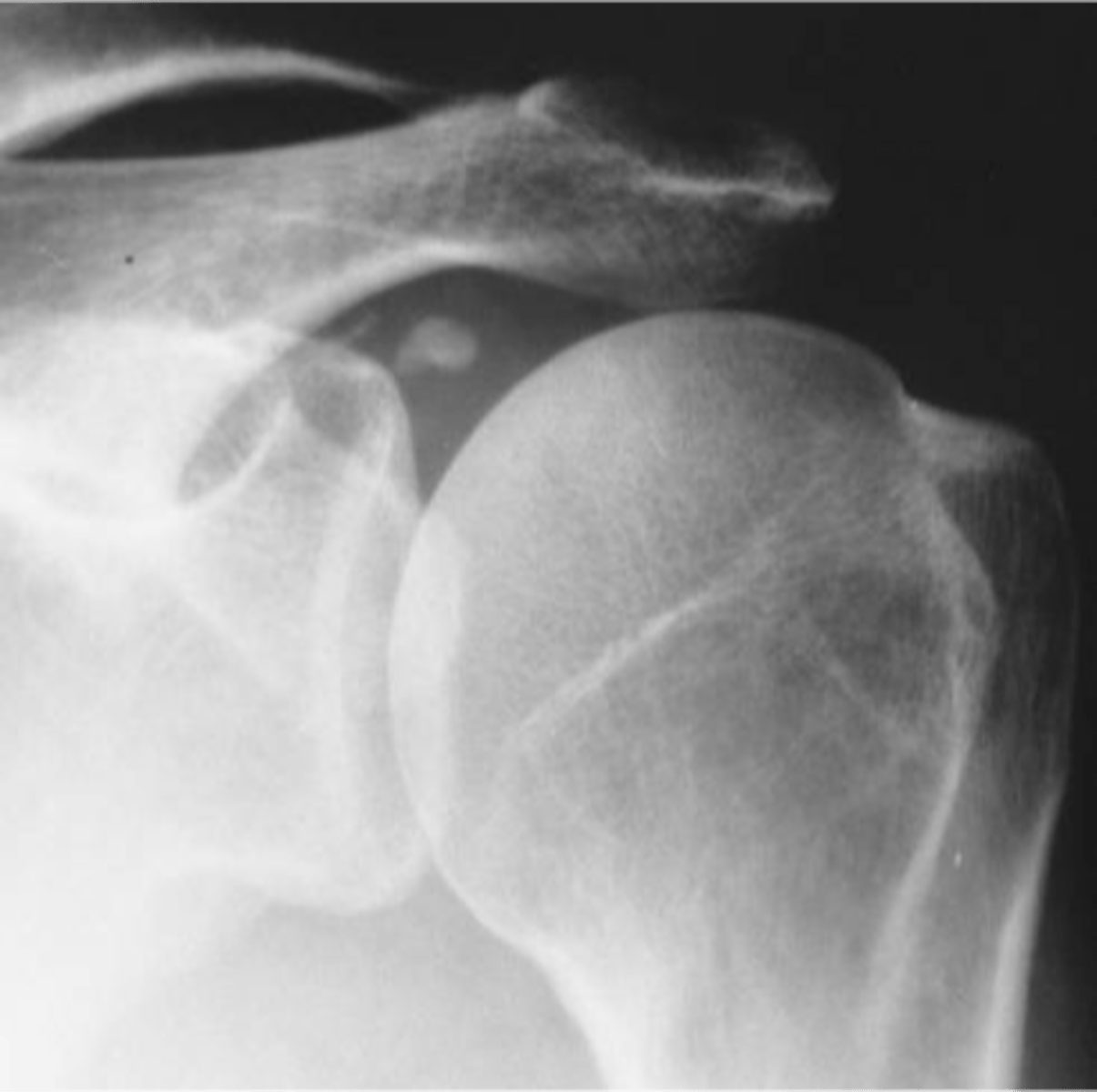
Longus coli tendon
Hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) of the _____
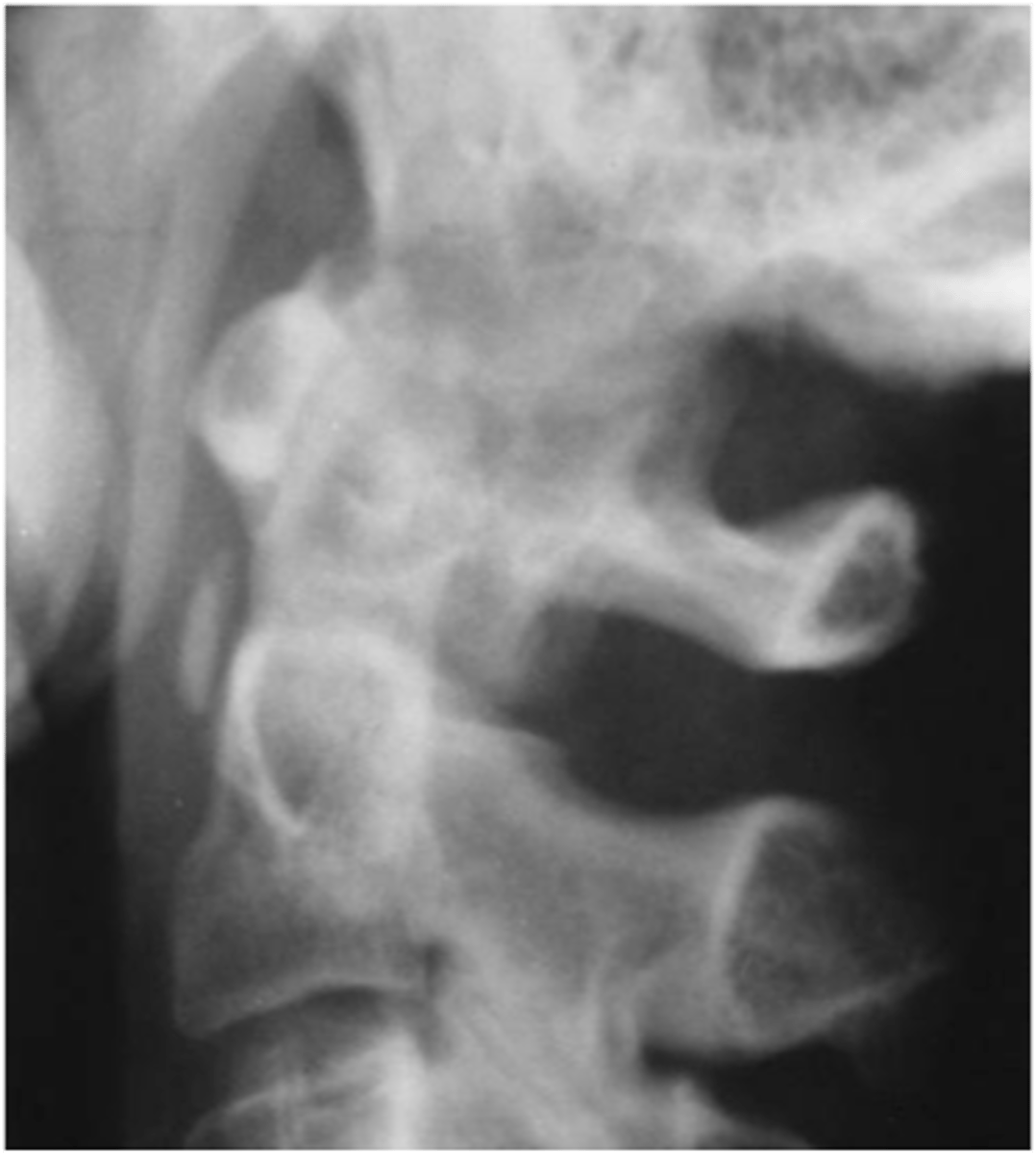
- 2-5% of the population are heterozygous carriers (Caucasian population)
- MC genetic disorders in Caucasians of Northern European ancestry
• Hyper-pigmented skin "bronze" (90%)
• Hepatomegaly (90%)
• Arthralgia (50%)
• Diabetes (30%)
• Heart failure/arrhythmia (15%)
• M=F (M express earlier)
State the clinical features of hemochromatosis
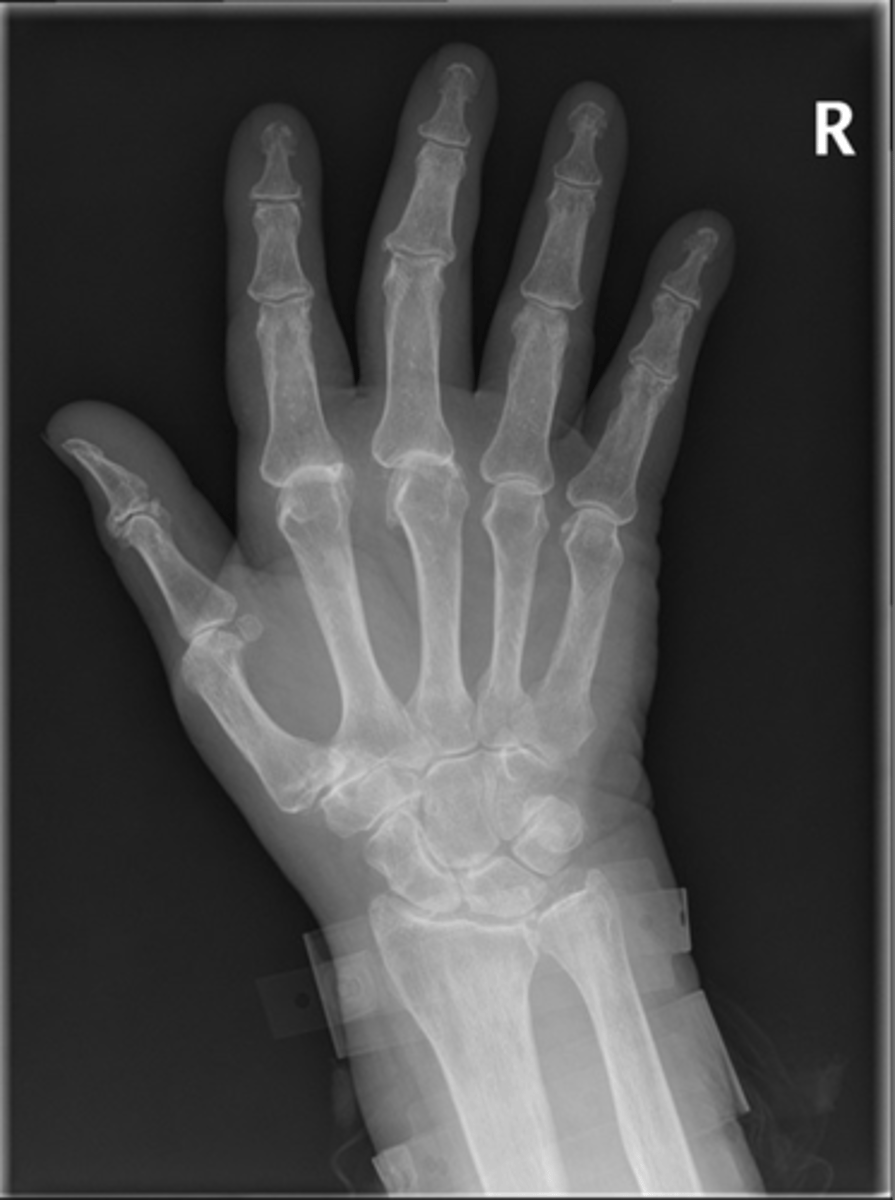
Sodium monourate
Crystal/substance deposition of gout
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate
Crystal/substance deposition of CPPD
Calcium hydroxyapatite
Crystal/substance deposition of HADD
Iron
Crystal/substance deposition of hemochromatosis