Agile Development
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Agile Development
A methodology emphasizing flexibility and customer collaboration.
Manifesto for Agile Software Development
A guiding document prioritizing individuals over processes.
4 BREAKING POINTS:
1. Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
2. Working software over comprehensive documentation
3. Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
4. Responding to change over following a plan
Agility
Rapid and adaptive response to changing requirements.
Software Increments
Multiple versions of software delivered throughout development.
Agile Process
is driven by customer descriptions of what is required (scenarios), recognizes that plans are short-lived, develops software iteratively with a heavy emphasis on construction activities, delivers multiple 'software increments', and adapts as changer occur
Agility Principles - I
highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software, welcome changing requirements, frequent software delivery, business and developers collaborate daily, build projects around motivated individuals, and Face-to-face communication is most effective
Agility Principles - II
- Working software is the primary measure of progress
- sustainable development
- continuous attention to technical excellence and good design
- simplicity
- self organizing teams
- regular reflection and adaption
Simplicity
the art of maximizing the amount of work not done - is essential.
Human Factors
the process molds to the needs of the people and team, not the other way around
Key traits must exist among the people on an agile team and the team itself:
Competence.
Common focus.
Collaboration.
Decision-making ability.
Fuzzy problem-solving ability.
Mutual trust and respect.
Self-organization.
Competence
innate talent/skills
common focus
same goals
collaboration
team members collaborate with stakeholders
decision making
team given autonomy to decide project issues (tech/nontech)
fuzzy
ambiguity and will continually be buffeted by change
self-organization
In the context of agile development, ______________ implies three things: (1) the agile team organizes itself for the work to be done, (2) the team organizes the process to best accommodate its local environment, (3) the team organizes the work schedule to best achieve delivery of the software increment
Extreme Programming (XP)
The most widely used agile process, originally proposed by Kent Beck
XP Planning
Begins with the creation of "user stories"
Agile team assesses each story and assigns a cost
Stories are grouped to for a deliverable increment
A commitment is made on delivery date
After the first increment "project velocity" is used to help define subsequent delivery dates for other increments
Project velocity
- is the number of customer stories implemented during the first release.
- help define subsequent delivery dates for other increments
- can then be used to (1) help estimate delivery dates and schedule for subsequent releases and (2) determine whether an overcommitment has been made for all stories across the entire development project.
TRUE (about XP planning)
(TRUE or FALSE)
XP Planning starts by creating "user stories," which describe features or tasks from the user's perspective.
FALSE (about commitment - first increment*)
(TRUE or FALSE)
A commitment is made to deliver the last increment by a set date.
TRUE (about project velocity)
After the first increment, the "project velocity" (the rate at which the team delivers user stories) is used to estimate and set dates for future increments.
Stories
____________ are grouped together to form a deliverable increment of software.
User stories
Short descriptions of features from the user's perspective.
XP Design
- Follows the KIS principle
- Encourage the use of CRC (Class Responsibility Collaborator) cards
- For difficult design problems, suggests the creation of "spike solutions"
- Encourages "refactoring"
Class Responsibility Collaborator (CRC)
identify and organize the object-oriented classes that are relevant to the current software increment.
KIS principle
Keep It Simple; focus on simplicity in design.
Spike solutions
a design prototypes created to explore difficult design problems.
Refactoring
- an iterative refinement of the internal program design
- is the process of changing a software system in such a way that it does not alter the external behavior of the code yet improves the internal structure.
XP coding
- Recommends the construction of a unit test for a store before coding commences
- Encourages "pair programming"
Pair programming
where two developers work together on the same code to improve quality and share knowledge.
XP Testing
- All unit tests are executed daily
- "Acceptance tests" are defined by the customer and executed to assess customer visible functionality
FOUR XP process
- XP Planning
- XP Design
- XP Coding
- XP Testing
Unit tests
Tests for individual components before coding starts.
Acceptance tests
Tests defined by customers to validate functionality.
Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
- Agile methodology focusing on mission-driven planning (CENTERED)
- a technique for building complex software and systems
- Originally proposed by Jim Highsmith
ASD — distinguishing features
- Mission-driven planning
- Component-based focus
- Uses "time-boxing"
- Explicit consideration of risks
- Emphasizes collaboration for requirements gathering
- Emphasizes "learning" throughout the process
Time-boxing
Fixed time periods for completing tasks or activities.
THREE ASD Process
- Speculation
- collaboration
- learning
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- is an iterative software process in which each iteration follows the 80 percent rule. That is, only enough work is required for each increment to facilitate movement to the next increment. The remaining detail can be completed later when more business requirements are known or changes have been requested and accommodated.
- Promoted by the DSDM Consortium
80 percent rule
- which means that each iteration of the software should focus on delivering enough functionality to move to the next stage.
- 80% of the work is done initially, with the remaining 20% being refined and completed later as more information becomes available or as new business needs and changes arise.
DSDM Consortium
Organization promoting the Dynamic Systems Development Method.
DSDM—distinguishing features
Nine guiding principles
- Active user involvement is imperative.
- Empowered to make decisions.
- Frequent delivery of products.
- Fitness for business purpose
- Iterative and incremental development
- Reversible changes
- High level requirements baselining
- Integrated testing
Scrum
- Agile framework partitioning work into sprints.
- is a specific Agile methodology that is used to facilitate a project.
- Originally proposed by Schwaber and Beedle
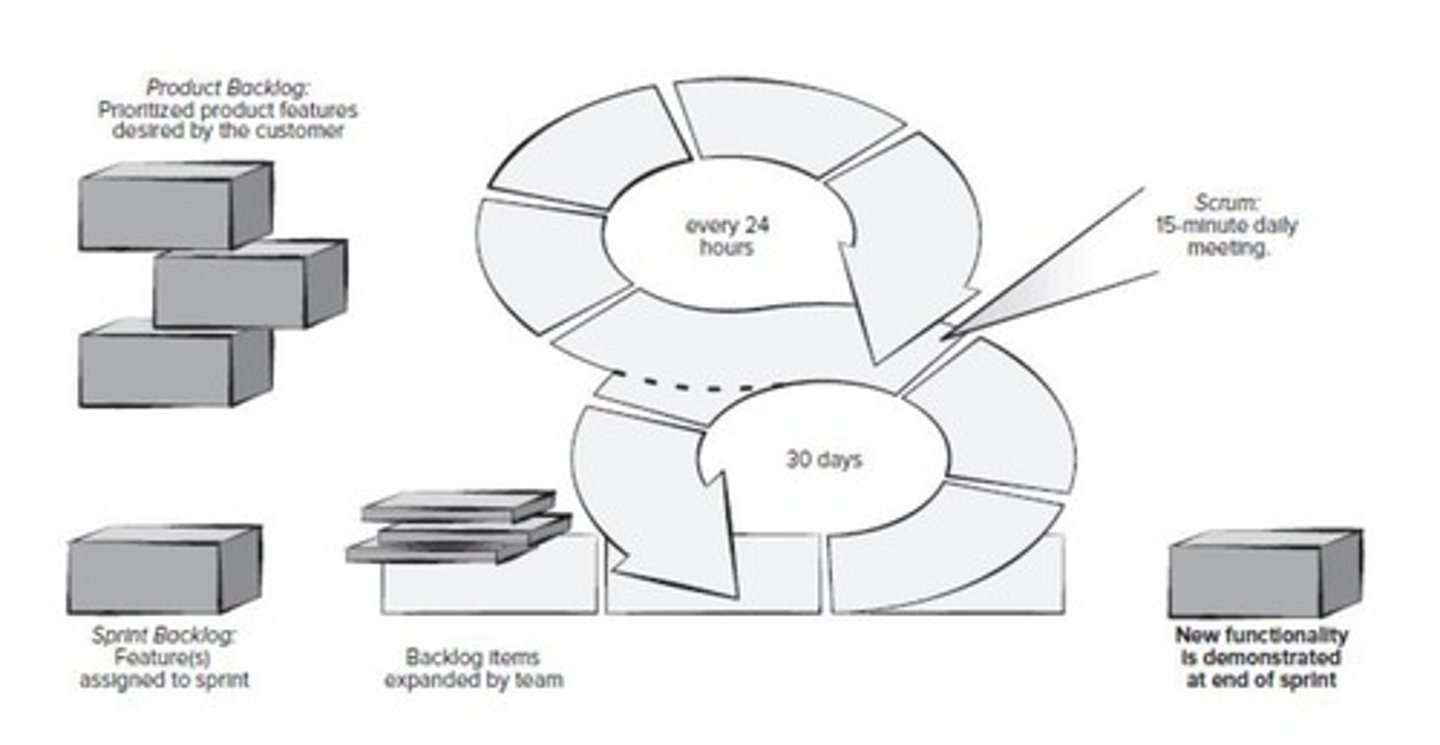
Scrum—distinguishing features
- Work partitioned into "packets"
- ongoing testing and documentation
- work in "sprints"
- short meetings
- Time-Boxed Demos
Demo
- is presented to the customer or stakeholders
- time-boxed - it has fixed duration to showcase the completed work
Sprints
Time-boxed periods for development, typically 2-4 weeks (typically 30days)
Backlog
Prioritized list of customer-valued product features.
Crystal
- is an agile methodology proposed by Alistair Cockburn and Jim Highsmith. It is a family of process models, which means it offers different approaches to development based on the unique characteristics of a project or problem
Crystal—distinguishing features
- family of process models
- face-to-face communication
- reflection workshops
maneuverability
meaning the process can be tailored to suit the specific needs of the project.
Feature Driven Development (FDD)
Originally proposed by Peter Coad et al
FDD—distinguishing features
- emphasis on Features
- Feature template
- feature list and "plan by feature"
- Designed and construction merged
FDD process
- Develop an overall model
- build a features list
- plan by feature
- design feature
- build by feature
Agile Modeling
is a practice proposed by Scott Ambler that emphasizes flexible and efficient modeling techniques in software development. It promotes the idea of using models to help guide development while being adaptable to the needs of the team and project. Closely aligned with agile principles, encouraging light, purpose-driven modeling rather than heavy documentation.
Agile modeling - distinguishing features
- Model with a purpose
- Use multiple models
- Travel light
- Content is more important than representation
- Know the models and the tools you use to create them
- Adapt locally
Travel Light
Keep models simple and straightforward.
Agile-Scrum
is a combination of two concepts: Agile as a project management philosophy and Scrum as a specific methodology used to implement Agile principles.
Agile
is a project management philosophy that utilizes a core set of values or principles
TRUE (about the term "scrum")
was first used in a 1986 paper titled "The New New Product Development Game" by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka.