5.2 Gonads, Pineal Gland, and Other Organs
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Testes
Secrete testosterone in response to gonadotropins FSH and LH.
Testosterone
Causes sexual differentiation of the male during gestation and also promotes the development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty.
Ovaries
Secrete estrogen and progesterone in response to gonadotropins FSH and LH.
Estrogen
Involved in development of the female reproductive system during gestation and also promotes the development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty.
Pineal Gland
Located deep in the brain where it secretes melatonin to regulate the circadian rhythm.
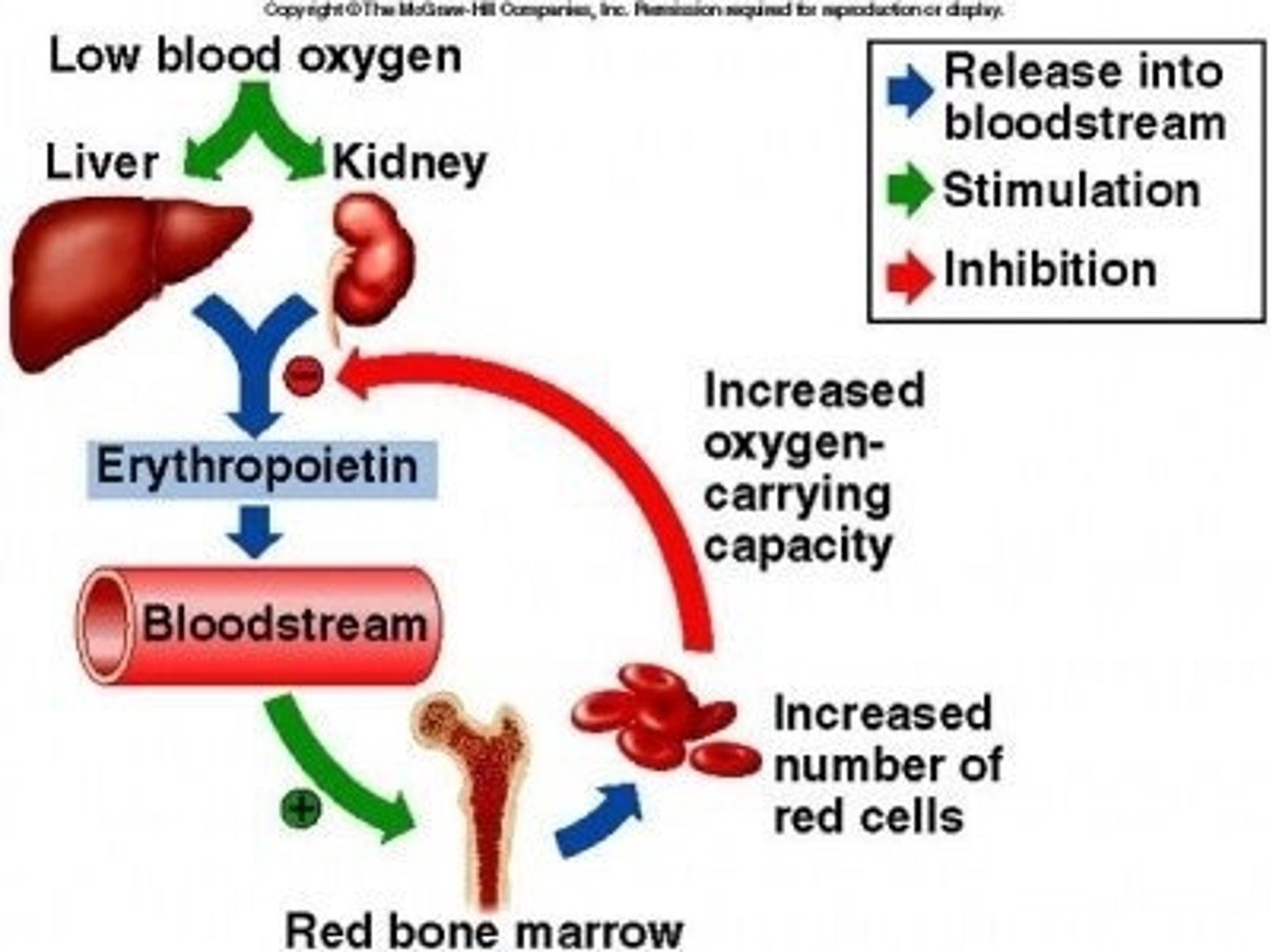
Erythropoietin
Produced by the kidneys, it stimulates the bone marrow to increase erythrocyte production. It is secreted in response to low blood oxygen levels.
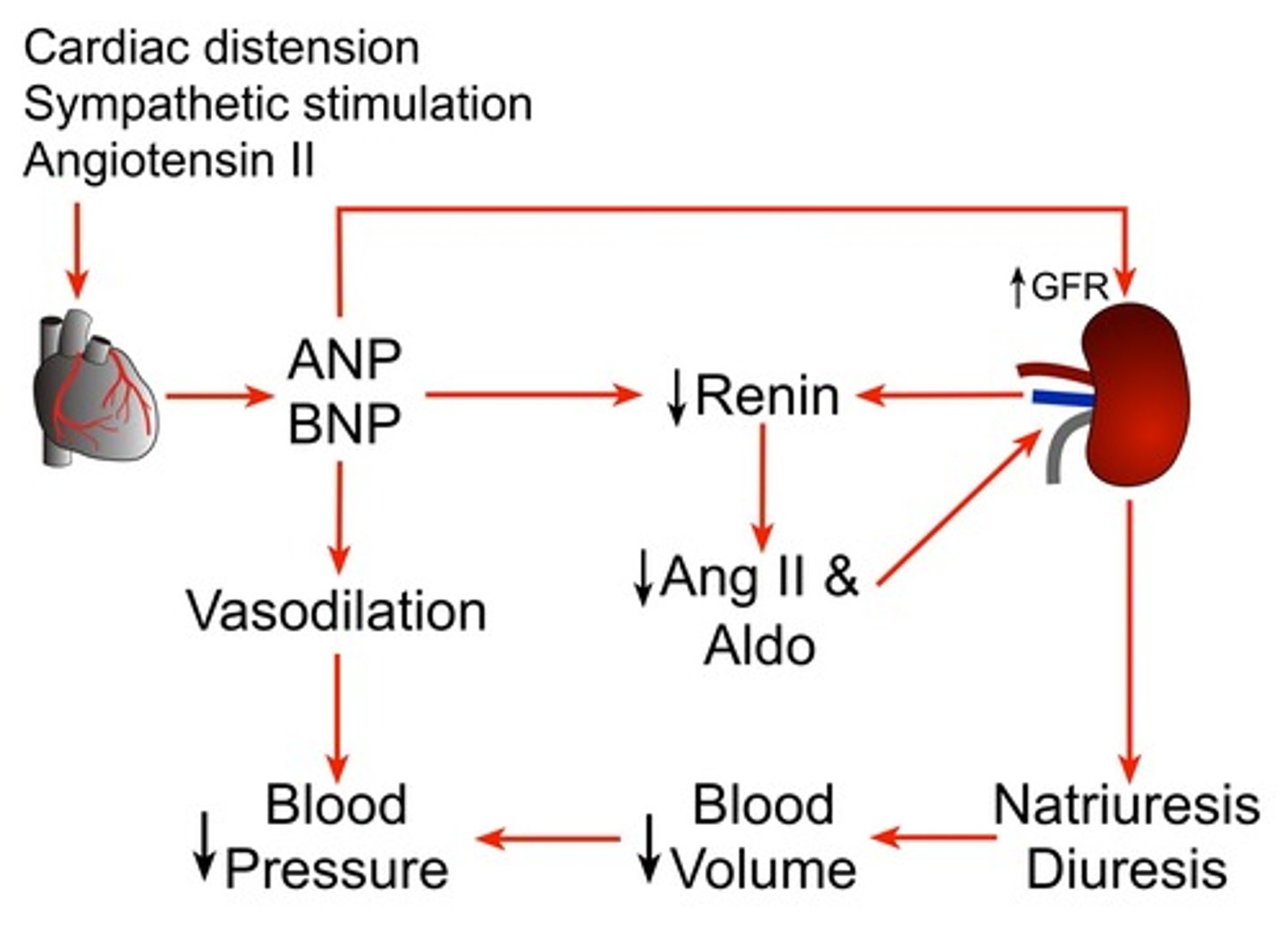
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
Hormone secreted by the heart to help regulate the salt and water balance. When the cells of the atria are stretched from excess blood volume, they release ANP. It leads to sodium excretion which increases urine volume, and decreases blood volume. It is antagonistic to ADH because it lowers blood pressure and volume, and has no effect on blood osmolarity.
Thymosin
The thymus is located behind the sternum, and it produces this to promote proper T-cell development and differentiation. The thymus atrophies by adulthood, leading to decreased production.