1.5 gas laws, ideals and gas equations
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
ideal gas properties/assumptions in kinetic theory of gases
kinetic theory of gases states that molecules in gases are constantly moving, makes the following assumptions:
The gas molecules are moving very fast and randomly
The molecules hardly have any volume
The gas molecules do not attract or repel each other (no intermolecular forces)
No kinetic energy is lost when the gas molecules collide with each other (elastic collisions)
The temperature of the gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
ideal gases
Gases that follow the kinetic theory of gases are called ideal gases However, in reality gases do not fit this description exactly but may come very close and are called real gases. The volume that a gas occupies depends on: Its pressure and its temperature
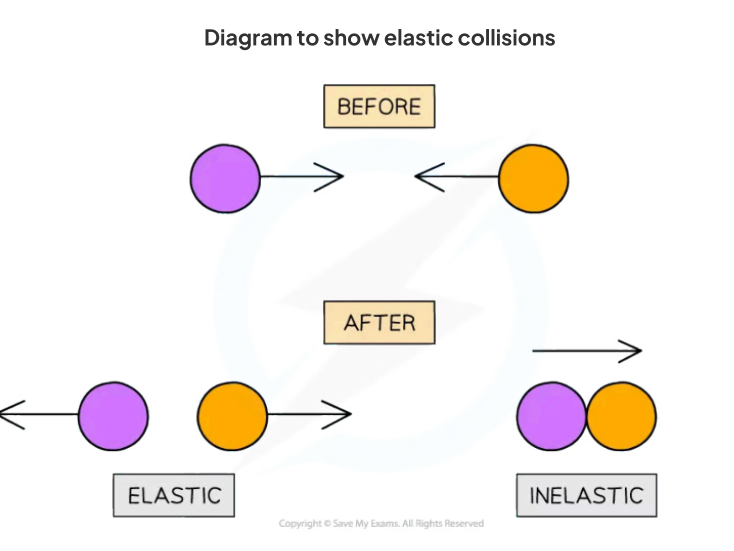
elastic collisions
In an elastic collision, energy is conserved and the particles colliding strike each other then move away in opposite directions whereas in an inelastic collision kinetic energy is not conserved and the particles usually strike and stick together
Molar Gas volume
Gases in a container exert a pressure as the gas molecules are constantly colliding with the walls of the container
Decreasing the volume (at constant temperature) of the container causes the molecules to be squashed together which results in more frequent collisions with the container wall
Thus, pressure of the gas increases