Membrane Structure and Function: Fluid Mosaic Model, Proteins, and Lipids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
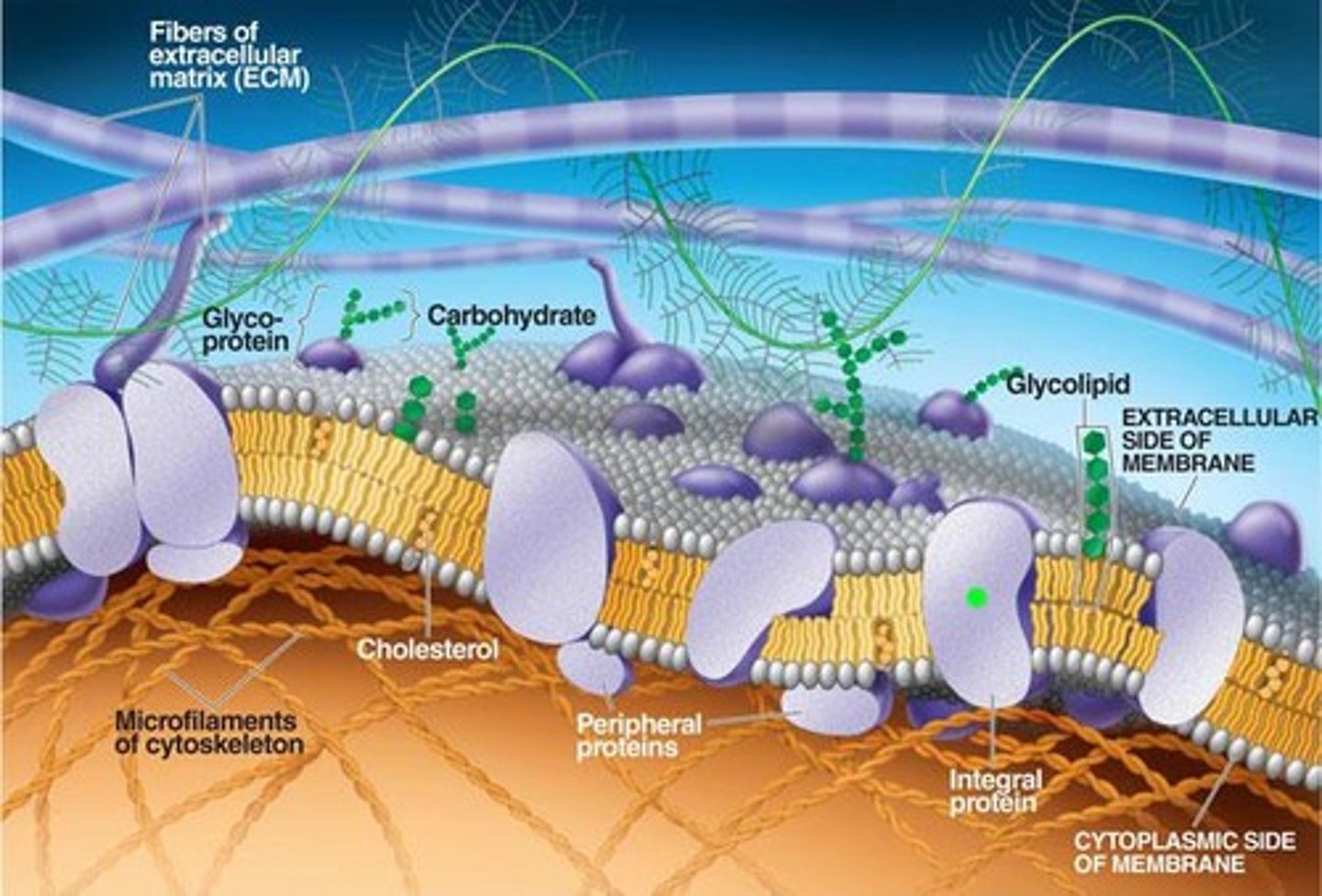
Fluid Mosaic Model
States that membrane proteins float freely throughout the phospholipid bilayer.
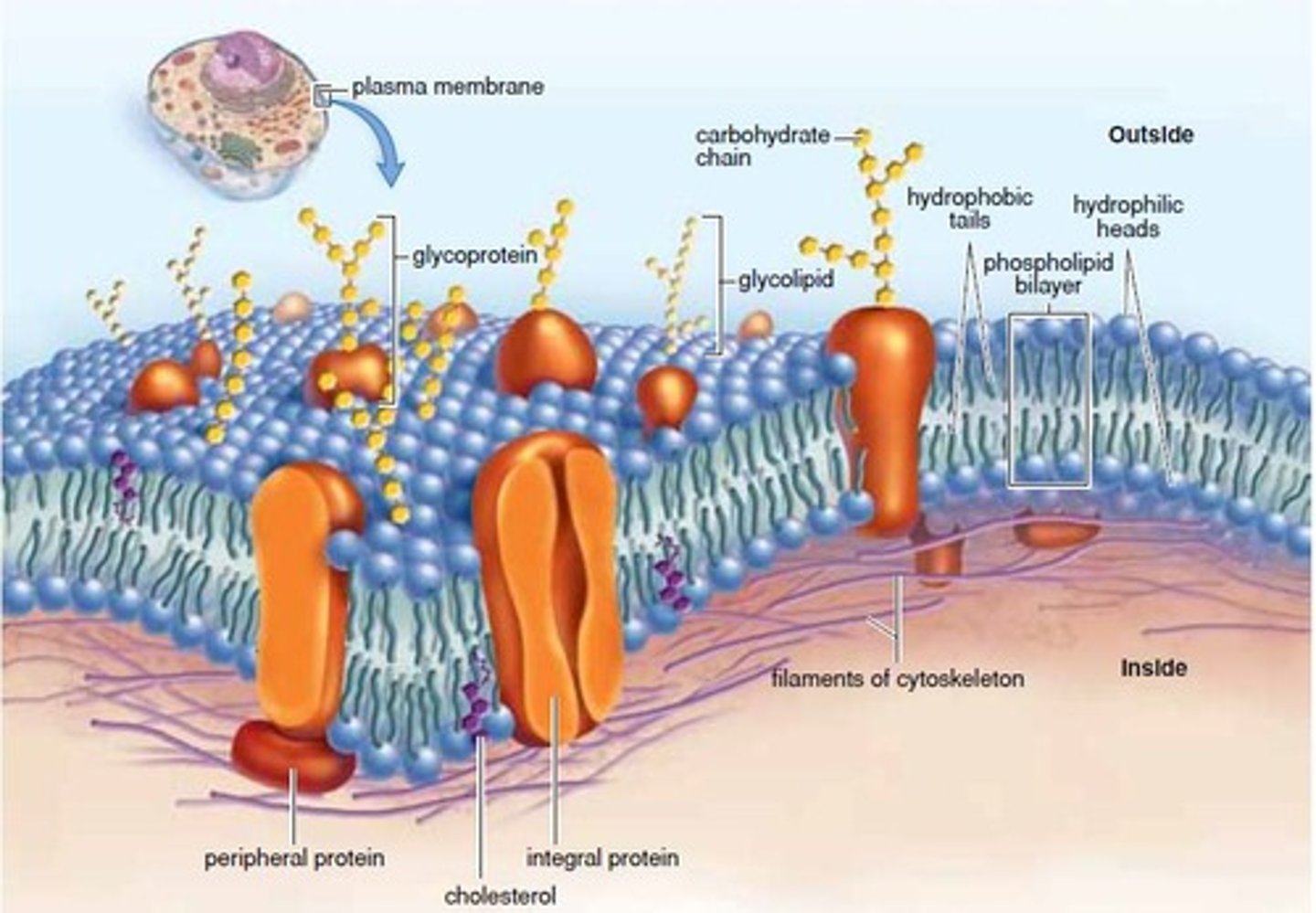
Glycolipid
A membrane lipid attached to a carbohydrate group.
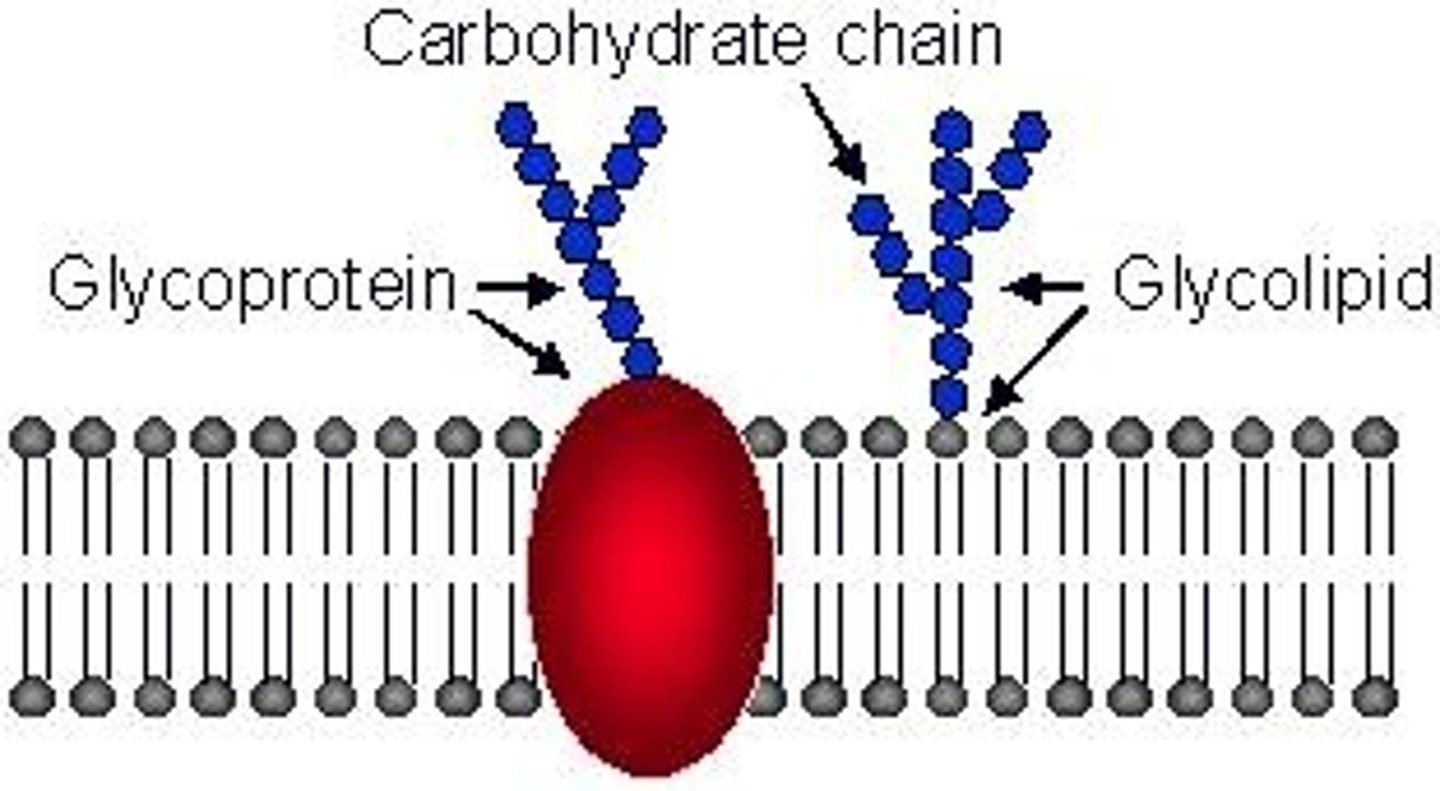
Glycoprotein
A membrane protein attached to a carbohydrate group.
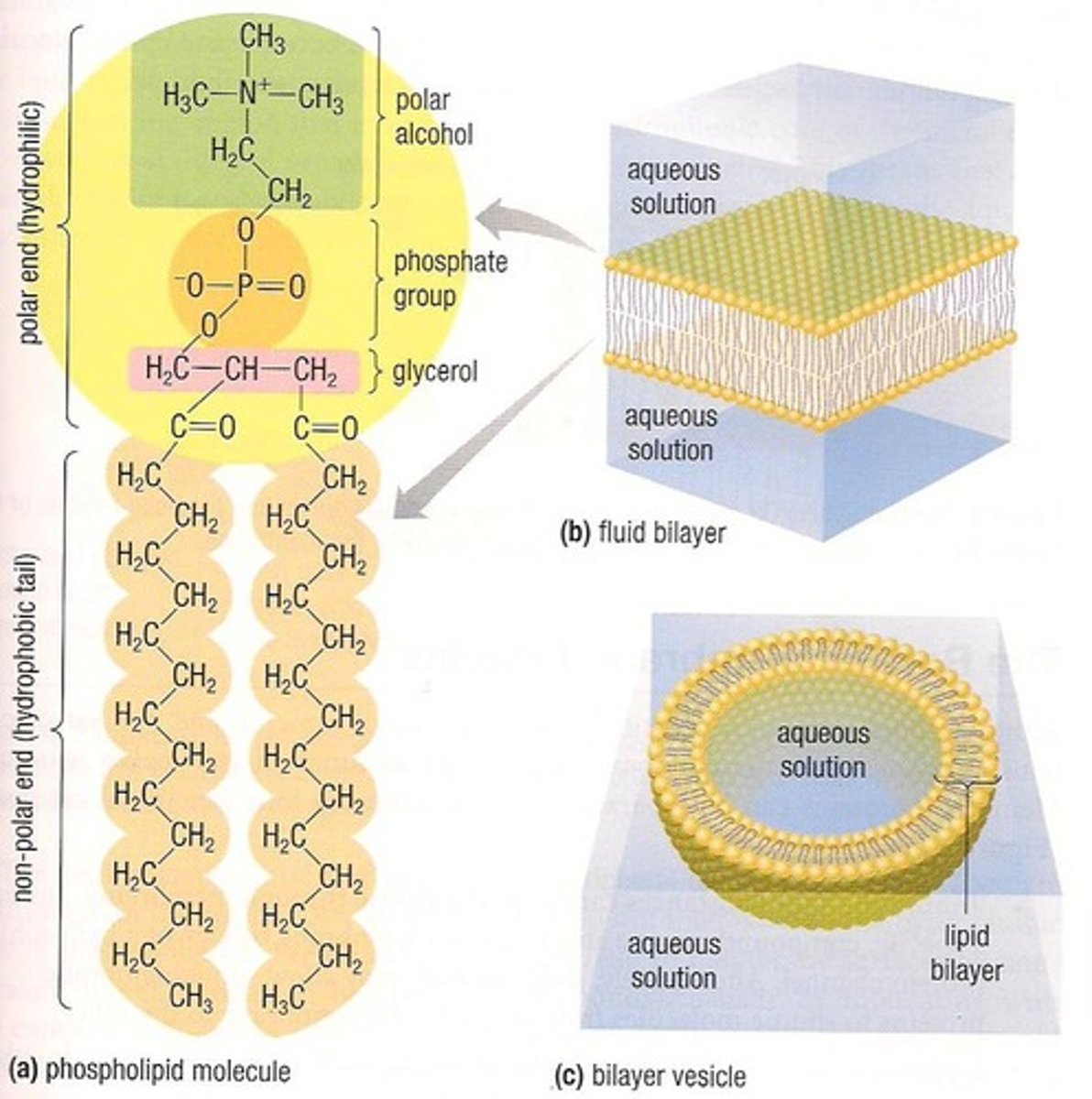
Phospholipid Bilayer
Formed by hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads in water, making up the majority of the cell membrane.
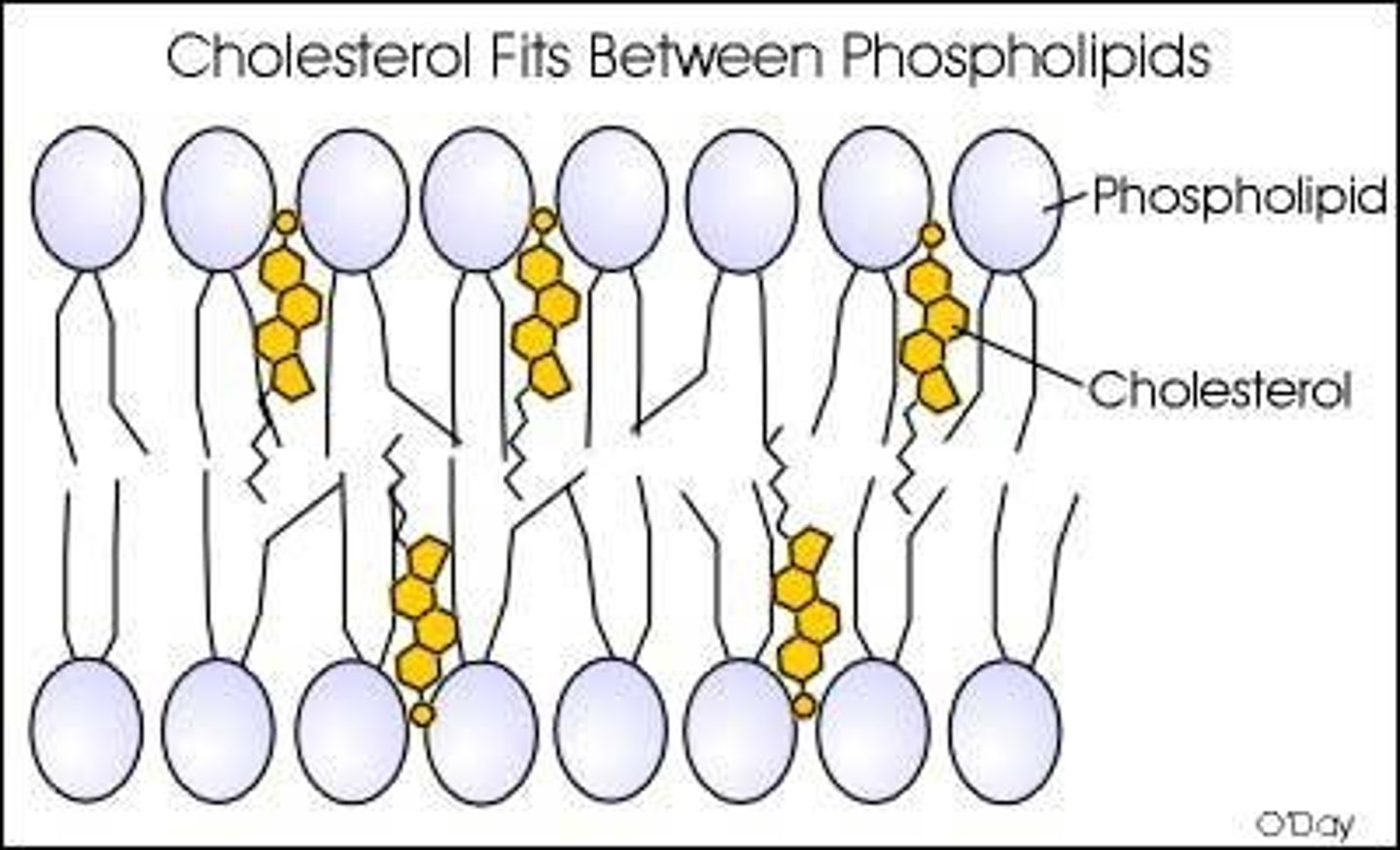
Sterols
Commonly Cholesterol, helps to stop membranes from becoming too rigid in cold temperatures and holds membranes together at higher temperatures.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Embedded in the lipid bilayer and has areas that interact with water/lipids.
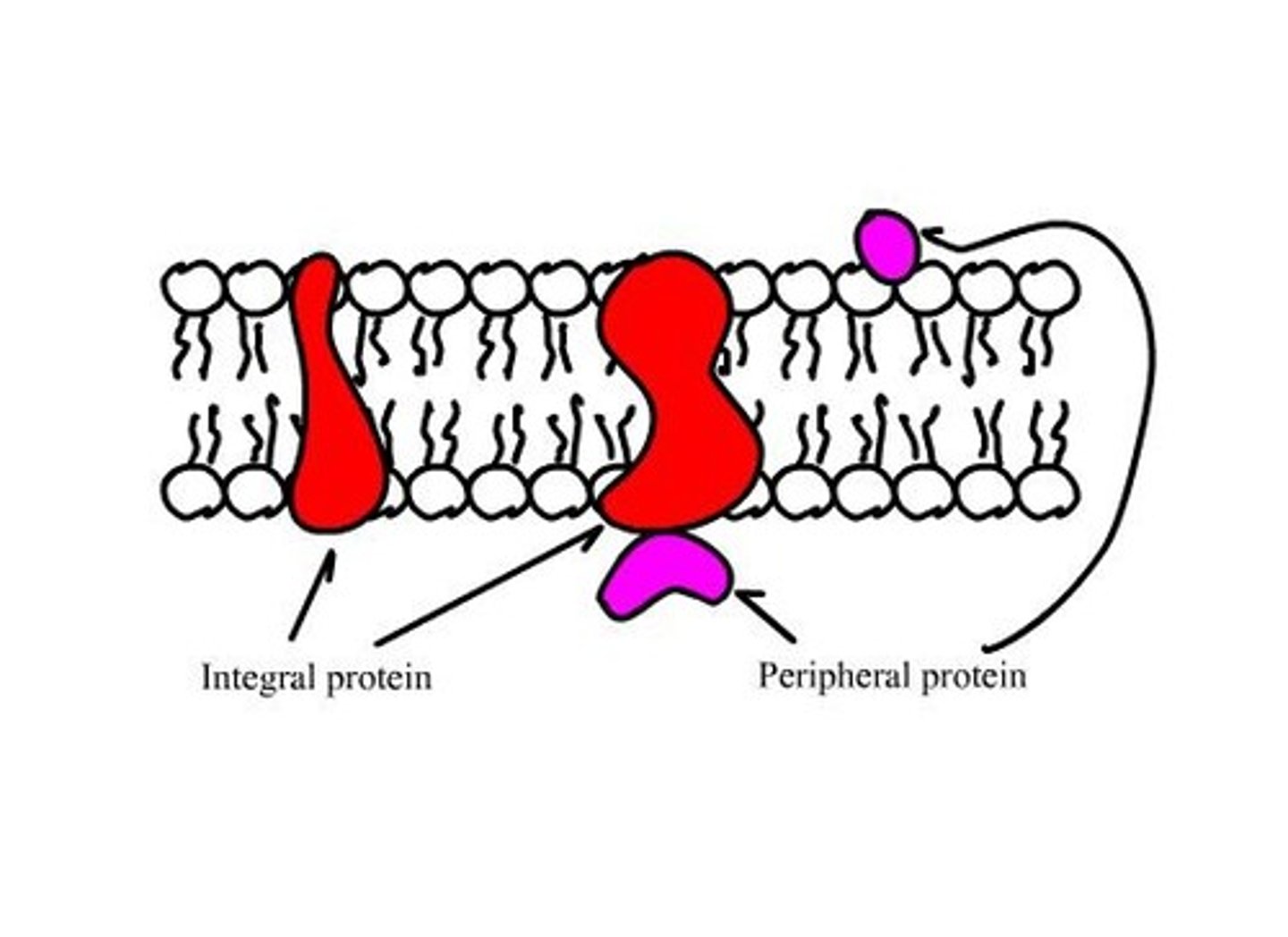
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
Located on the surface of the membrane and don't interact with the hydrophobic core of the bilayer.
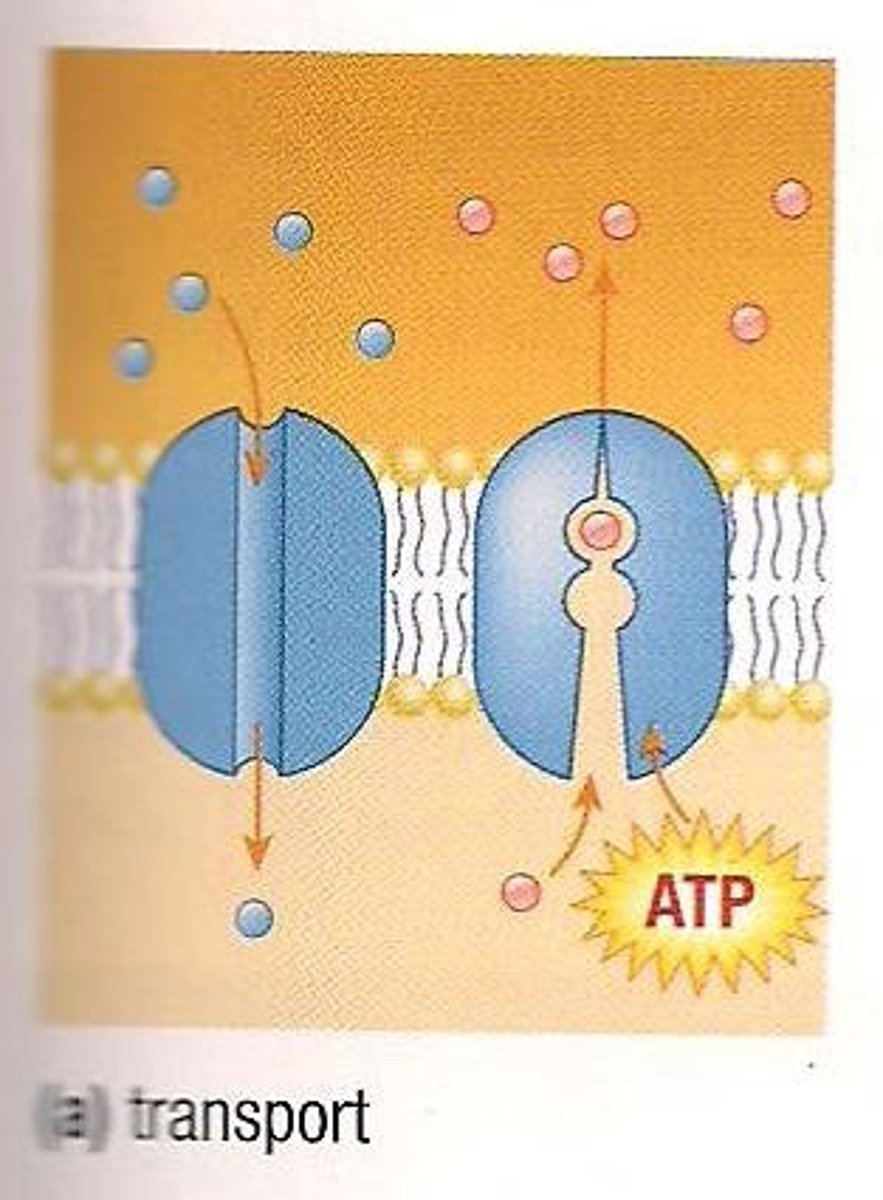
Transport
The function of membrane proteins that transport substances across the membrane that cannot simply diffuse.
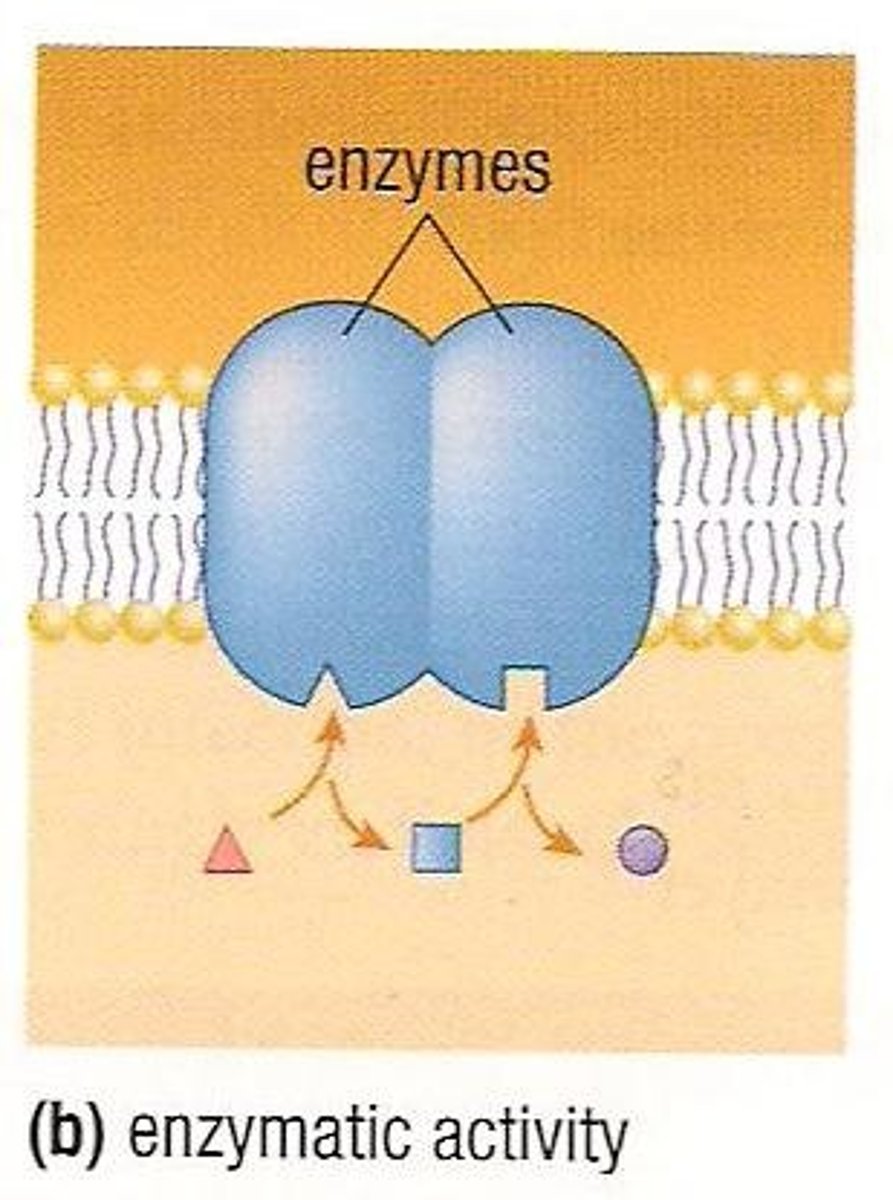
Enzymatic Activity
The function of membrane proteins that help with cellular respiration/photosynthesis, such as ATP Synthase used to create ATP.
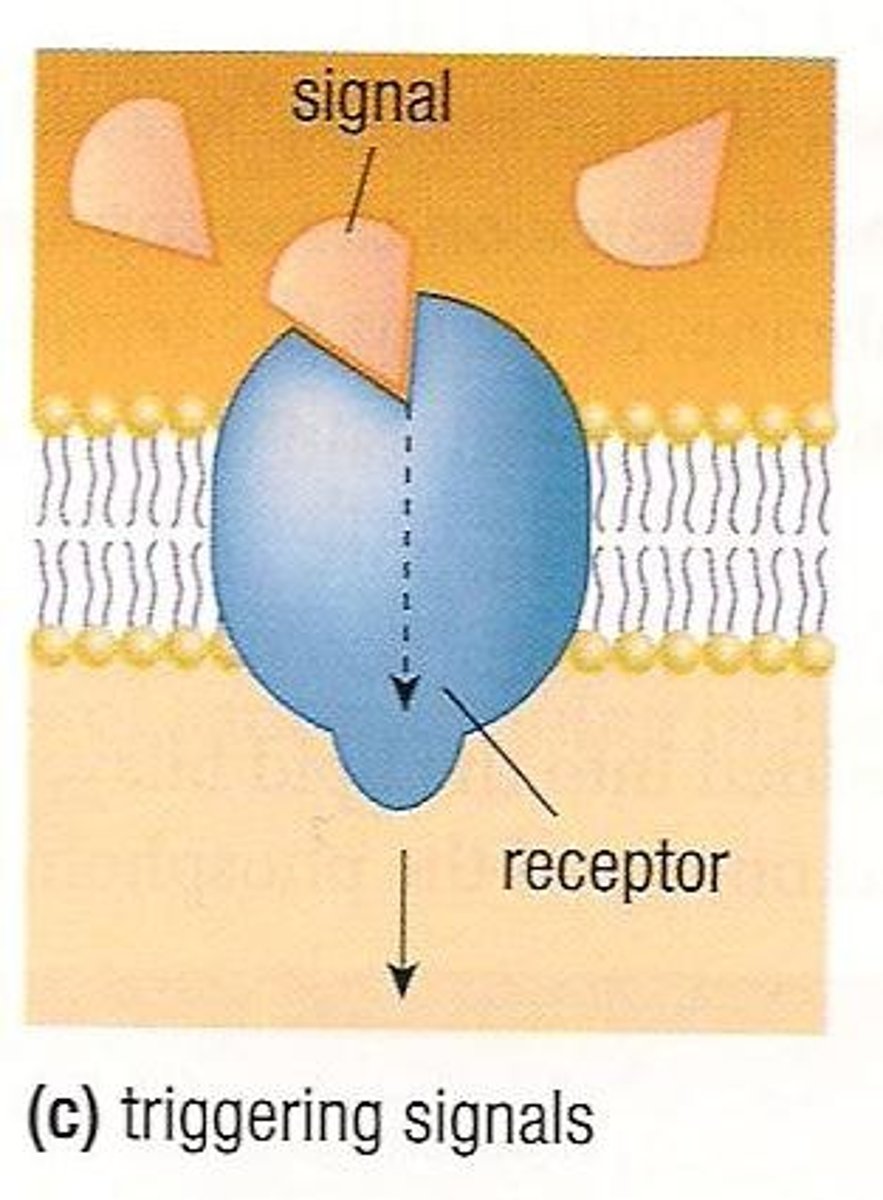
Triggering Signals
The function of membrane proteins that bind to chemicals and cause changes within the cell.
Attachment
The function of membrane proteins that help anchor parts of the cytoskeleton.
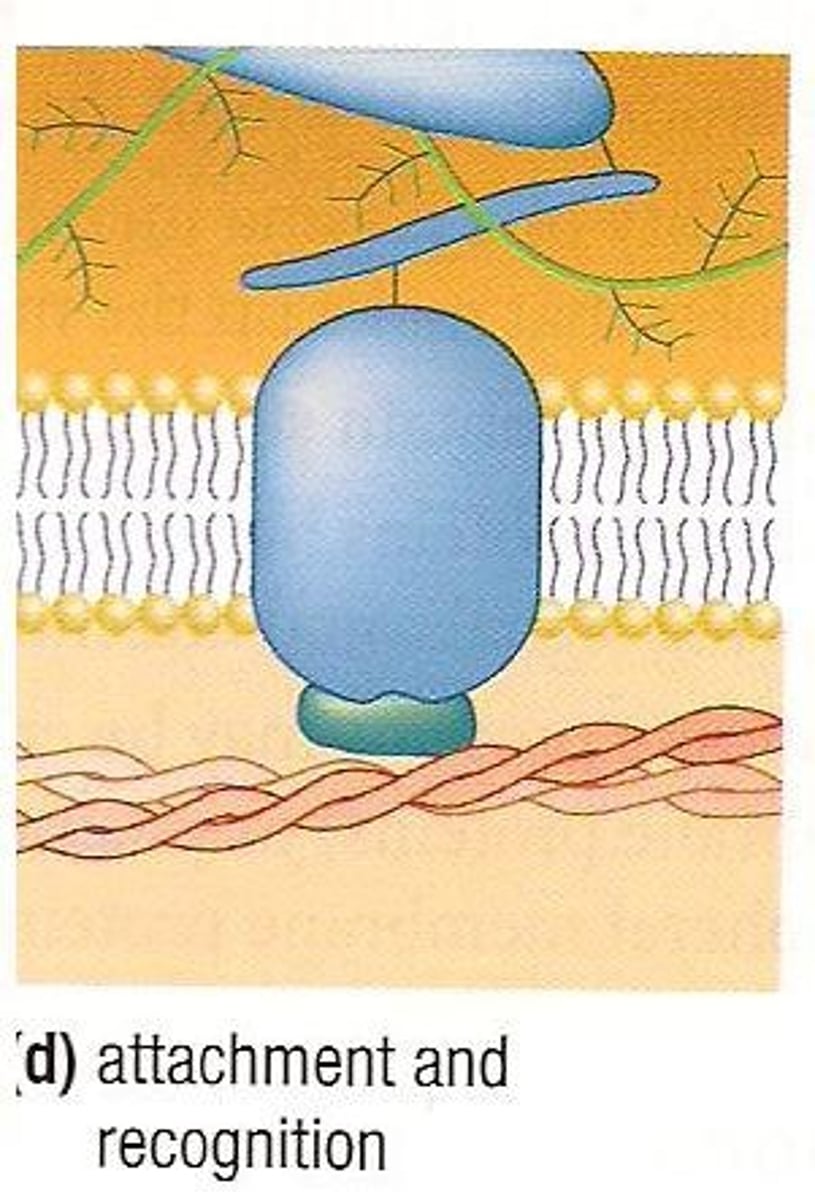
Recognition
The function of membrane proteins that allows cells to recognize one another and invading pathogens.
Chemical Changes
Changes that occur inside the cell when hormones bind to membrane proteins.
Cell Recognition
The process by which neighboring cells recognize one another based on specific proteins.
Hydrophobic Tails
The part of phospholipids that repels water, forming the inner layer of the bilayer.
Hydrophilic Heads
The part of phospholipids that attracts water, forming the outer layer of the bilayer.
Cell Membrane
A biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment.
Amino Acids Transport
An example of substances that may be moved across the membrane by transport proteins.
Microtubules
Structures to which proteins can attach to help anchor parts of the cytoskeleton.
Blood Types Differentiation
Glycoproteins are used to differentiate blood types, such as Type A made of Type A Glycoproteins.