BUS 387 Quiz 3 - Cal Poly - Daubert S22
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is the functional purpose of MBTI?
It helps us understand our strengths/weaknesses and reactions
Personality definition
how people affect others and how they understand and view themselves, as well as their pattern of inner and outer measurable traits and the person-situation interaction.
Main finding from twin studies
identical twins raised apart have similarities in personality, leading researchers to believe that both nature and nurture contribute to personality
Personality is a ______.
trait theory
self-concept definition
-one's overall view of oneself
-consists of emotion, intelligence, and a sense of efficacy
-comes from within
self-esteem definition
-how you feel about yourself
-sense of self-worth, value
-derived from other people, a personality trait
social evolution definition
humanity is evolving along the lines of social phenomena such as trust, collaboration, and competition.
organization-based self-esteem (OBSE) definition
-the self-perceived value that individuals have of themselves as organization members acting within an organization context
-global concept of personal self-esteem applied to orgs
purpose of fostering OBSE
making employees feel valued will yield intangible and tangible benefits
socialization process definition
the continuous impact from the social environment on us
T/F: Socialization begins at birth, goes through childhood, and expands into your adult life.
True
6 specific steps that can lead to successful organizational socialization:
1. provide a challenging first job
2. provide relevant training
3. provide timely and consistent feedback
4. select a good first supervisor to be in charge of socialization
5. design a relaxed orientation program
6. place new recruits in work groups with high morale
T/F: new employees attending a socialization training program are more socialized than those who do not.
True
T/F: socialization tactics influence perceived organizational support, which has an impact on voluntary turnover and organizational commitment.
True
The Big Five Personality Traits
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, emotional stability
conscientiousness definition
being careful, reliable, hard-working
-2nd most associated with leadership effectiveness, most associated with job performance
openness definition
being creative, less abstract, providing new ideas
extroversion definition
sociable, fun-loving, most strongly associated with leadership, more influenced by heredity than environment
agreeableness definition
generous, kind, nurturing, weak association with leadership, good at getting along with others
emotional stability definition
anxious, temperamental, emotional, worrying, more influenced by heredity than environment, people who score low are positive and keep things in perspective
T/F: MBTI is a strong enough predictor of personality to for it to be used in job selection decisions.
False
motivation definition (psychological)
the internal state of a person that leads to behavior
motivation definition (managerial)
activities managers do to induce results that are desirable
extrinsic motivation
-tangible
-results from the potential or actual receipt of extrinsic rewards
-salary, gifts
intrinsic motivation
-intangible
-occurs when an individual is turned onto one's work because of the positive internal feelings that are generated by doing well
-recognition, praise, happiness
5 reasons why managers care about motivation
1. join the organization
2. stay with the organization
3. be engaged at work
4. perform organizational citizenship behaviors
5. help others
content theories of motivation definition
revolve around the notion that an employee's needs influence motivation
needs definition
physiological or psychological deficiencies that arouse behavior
5 content theories:
1. McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
2. Maslow's need hierarchy theory
3. acquired needs theory
4. self-determination theory
5. Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
-Theory X is a pessimistic view of employees (they dislike work, must be monitored, and can only be motivated with rewards or punishment)
-Theory Y is an optimistic view of employees, more modern (they are self-engaged, committed, responsible, and creative
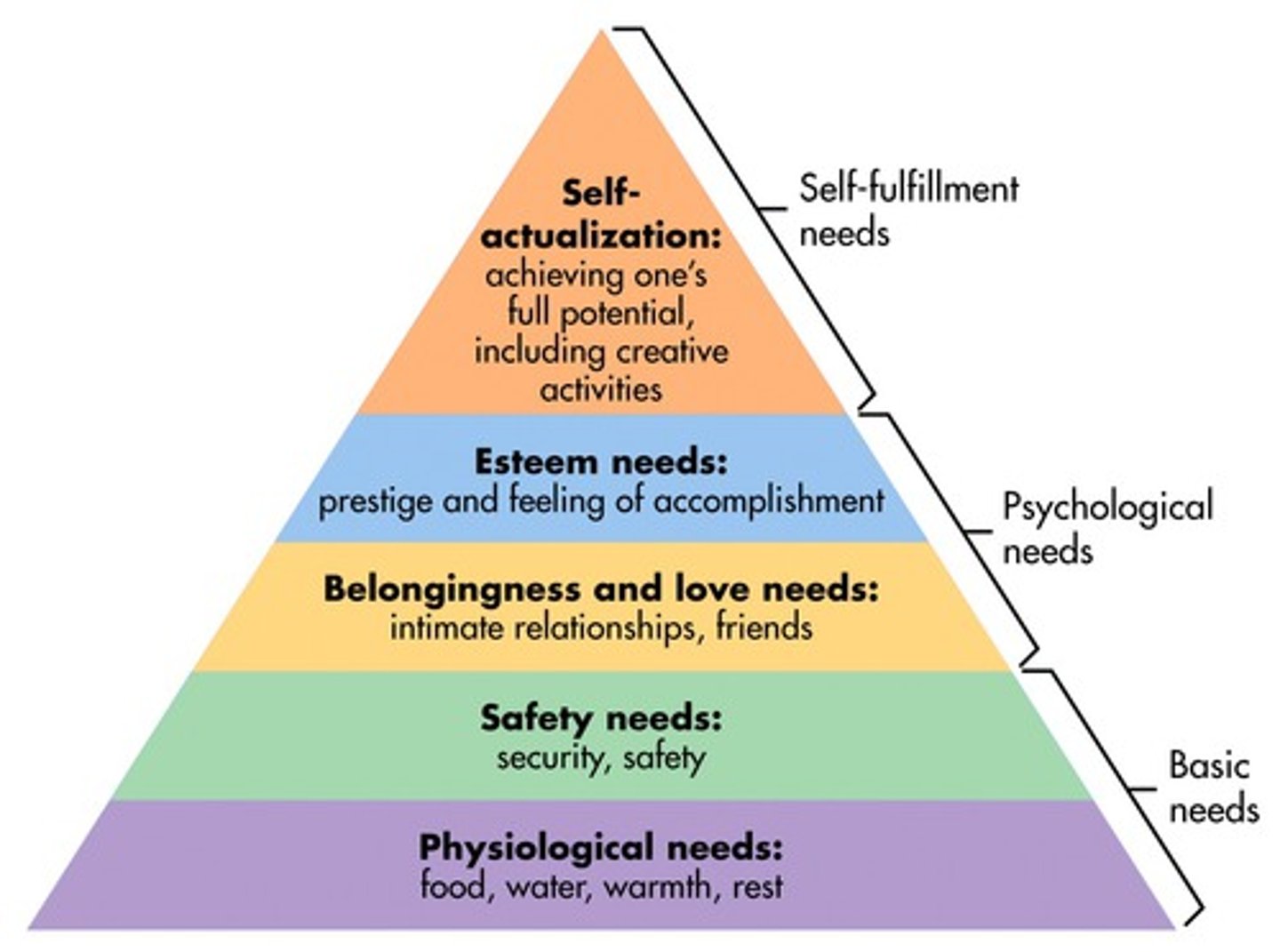
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
applied to a work environment:
-self-actualization: realizing one's full potential, creativity, and self-development
-esteem/ego: self-esteem, confidence, autonomy, reputation, status, self-direction, recognition
-love/social: acceptance from others, belonging to a group, communication with others
-safety: protection from harsh supervision or unsafe environment, job security, predictable environment and coworkers
-physiological: good working conditions, good pay
T/F: Managers tend to overemphasize the importance of extrinsic rewards compared to intrinsic rewards.
True
Acquired needs theory
states that three needs - achievement, affiliation, and power - are the key drivers of employee behavior
need for achievement definition
the desire to excel, overcome obstacles, solve problems, and rival and surpass others
need for affiliation definition
the desire to maintain social relationships, to be liked, and to join groups
need for power definition
the desire to influence, coach, teach, or encourage others to achieve
self-determination theory definition
-assumes that three innate needs influence our behavior and well-being - competence, autonomy, and relatedness
-focuses on intrinsic motivation
What could a manager do to fulfill a competency need?
they can try to create work environments that support and encourage the opportunity to experience competence, autonomy, and relatedness.
motivator-hygiene theory definition
job satisfaction/dissatisfaction arise from two different sets of factors
-satisfaction comes from motivating factors
-dissatisfaction comes from hygiene factors
hygiene factors
-company policy and administration, technical supervision, salary, interpersonal relations with one's supervisor, and working conditions
-cause a person to move from a state of no satisfaction to dissatisfaction
motivating factors
-achievement, recognition, characteristics of the work, responsibility, and advancement
-cause a person to move from a state of no satisfaction to satisfaction
T/F: motivating and hygiene factors interact.
False
T/F: Herzberg advocates eliminating hygiene factors first, then adding motivating factors, then using verbal recognition.
True
process theories of motivation definition
attempt to describe how various person factors and environmental factors in the Integrative Framework affect motivation
3 process theories:
-Equity/justice theory
-Expectancy theory
-Goal-setting theory
equity theory definition
-explains how people strive for fairness and justice in social exchanges or give-and-take relationships
-inputs (skill level, hard work, enthusiasm) lead to outputs (salary, recognition, reputation)
organizational justice definition
the extent to which people feel they are being treated fairly at work
distributive justice definition
reflects the perceived fairness of how resources and rewards are distributed or allocated
procedural justice definition
the perceived fairness of the process and procedures used to make allocation decisions
interactional justice definition
the quality of the interpersonal treatment people receive when procedures are implemented
Five lessons that can be drawn from equity/justice theories:
1. employee perceptions are what count
2. employees want a voice in decisions that affect them
3. employees should be given an appeals process
4. leader behavior matters
5. a climate for justice makes a difference
expectancy theory definition
holds that people are motivated to behave in ways that produce desired combinations of expected outcomes
3 key elements of expectancy theory:
1. expectancy - can I achieve my desired level of performance?
2. instrumentality - what rewards will I receive if I reach my desired level of performance
3. valence - how much do I value the rewards I receive?
three practical lessons for applying expectancy theory:
1. enhance effort -> performance expectancies
2. determine desired levels of performance and set SMART goals
3. link rewards to desired outcomes
goal setting theory
-goals that are specific and difficult lead to higher performance than general goals
-certain conditions are necessary for goal setting to work
-performance feedback and participation in deciding how to achieve goals are necessary but not sufficient for goal setting to work
-goal achievement leads to job satisfaction, which reinforces employees to commit to even higher levels of performance
4 motivational mechanisms of goal-setting theory
1. goals direct attention
2. goals regulate effort
3. goals increase persistence
4. goals foster the development and application of task strategies and action plans
job design definition
any set of activities that involve the alteration of specific jobs with the intent of improving the quality of employee job experience and productivity
top down approach to job design
hierarchy, traditional
bottom up approach to job design
employees design their own work
i-deals approach to job design
idiosyncratic ideals blend top down and bottom up
job crafting definition
-the physical and cognitive changes individuals make in the task or relational boundaries of their work
-bottom up approach
-reserved mostly for senior level management, requires trust
idiosyncratic ideals definition
employment terms individuals negotiate for themselves, taking myriad forms from flexible schedules to career development
Positive Psychology Video Notes
-most people exist in null state, how do we rise above?
-positive psychology is concerned with strengths along with weaknesses, building the ideal life, using your talent to lead to a fulfilling life
-Three Happy Lives:
-The Pleasant Life: as much positive emotions as you can handle, being mindful, only 50% heritable, not malleable, raw feels
-Life of Engagement: finding your flow, doing what makes you tick
-The Meaningful Life: altruism, finding something not within, long-lasting
-life satisfaction = positive affectivity + engagement + meaning
the purpose of positive psychology
to use scientific methodology to discover and promote the factors that allow individuals, groups, organizations, and communities to thrive
3 levels of positive psychology
1. valued subjective experiences
2. positive individual traits
3. civic virtues and the institutions that move individuals toward better citizenship
4 positive organizational behavior constructs
1. self-efficacy
2. optimism
3. hope
4. resiliency
self-efficacy definition
an individual's conviction/confidence about their abilities to mobilize the motivation, cognitive resources, and courses of action needed to successfully execute a specific task within a given context.
major sources of self-efficacy
1. mastery experiences or performance attainments
2. vicarious experiences or modeling
3. social persuasion
4. physiological and psychological arousal
optimism definition
reacting to problems with a sense of confidence
T/F: optimism is known to lead to greater academic, athletic, political, and occupational success.
True
T/F: optimism exists on a sort of continuum.
True
T/F: optimists are people who expect good things to happen to them, and pessimists are people who expect bad things to happen to them.
True
hope definition
a positive motivational state where successful feelings of agency and pathways/goals interact
T/F: hope and self-efficacy are close in meaning.
True
Two dimensions hope depends on
pervasiveness and performance
resiliency definition
a positive way of coping with distress/adversity. Ability to recuperate from stress, conflict, failure, change, or increase in responsibility
psychological capital (PsyCap) definition
-combination of all four areas
-can be developed over one's life
-high scorers can deal well with organizational change
Situational Well-Being/happiness definition
-the area above the null state where we wish to exist
-people's affective and cognitive evaluations of their lives
3 conclusions based on SWB research
1. happiness is a process, not a place
2. there is an optimal level of happiness
3. though not linear, happiness is clearly related to health and longevity, relationships, and effectiveness at work