DENT Fun. I - Neurotransmitters
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
What are the 2 subdivisions of the PNS?
- Somatic
- Autonomic
Somatic Nervous System
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles via motor units
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The part of the PNS that regulate the basic visceral processes of the body such as the glands and muscles of the internal organs
What are the 3 divisions of the ANS?
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
- Enteric
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
The component of the ANS that responds to stressful situations by initiating the fight-or-flight response via Epinephrine (E) and Norepinephrine (NE)
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)
Division of the ANS that slows down body functions ("Rest & Digest") via ACh
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
Division of the ANS located in the digestive system; Regulates secretions and intake
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
What are the 3 types of Neurons?
- Sensory
- Interneuron
- Motor
What are the 4 functional regions of Neurons?
- Input: Dendrites
- Integrative: Through Soma/Cell Body
- Conductive: Down Axon
- Output: NTs at Axon terminus
Reflex
- A simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
- Typically just involves a sensory neuron and motor neuron
Electrical Synapses
- Synapses that transmit information via the direct flow of electrical current at gap junctions
- Very fast and bidirectional
Electrical Synapses are typically found in ____ and ____ muscle.
cardiac/smooth
Chemical Synapses
- Synapses that transmit information via the secretion of NTs
- Unidirectional
Action of a NT is dependent on the properties of the ____.
postsynaptic receptor
What are the 2 means of removing NTs from the synaptic cleft?
- Reuptake
- Enzymatic Degradation
What are the 2 features of Receptors?
- They are membrane spanning proteins
- They carry out an effector function
Ionotropic Receptors
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
Metabotropic Receptors
- Receptors that are associated with signal proteins and G proteins
- Initiate a secondary messenger system
Excitatory Receptors
Cause depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron
Inhibitory Receptors
Cause postsynaptic cell to hyperpolarize
G-Protein Coupled Receptors are ____ than Ionotropic Receptors.
slower
Few extra steps
Neurotransmitter Release Process
(1) Synthesis and Storage of NTs
(2) Action Potential travels to Presynaptic Terminal
(3) Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels open
(4) Ca2+ allows vesicle docking via SNAREs and NT release
(5) NTs bind postsynaptic receptors
(6) Removal of NTs via enzymes or reuptake
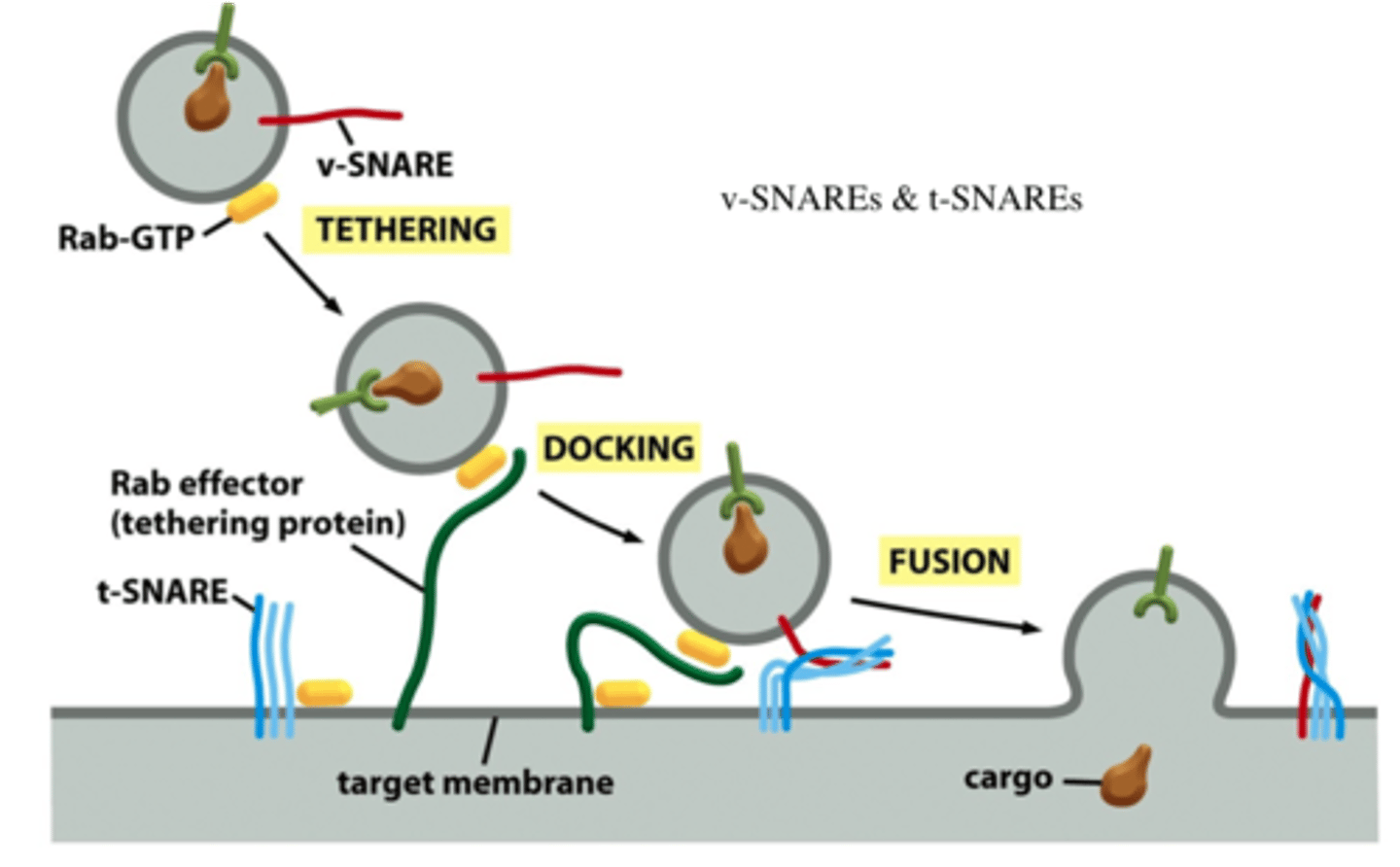
SNAREs
Ca2+ dependent complexes that fuse NT vesicles to the presynaptic membrane to release NTs
EPSPs
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials
- Depolarize via Na+ Channels
- Typically mediated by Glutamate
IPSPs
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials
- Hyperpolarize via Cl- Channels
- Typically mediated by GABA or Glycine
What are the 2 main classes of NTs?
- Small
- Large
Small Molecule NTs
- Amino Acids (Glutamate, GABA, Glycine)
- Monoamines (NE, E, Serotonin, Dopamine)
- ACh
Large Molecule NTs (Neuropeptides)
Small polypeptides that range from 3-36 amino acids
Dopamine, NE, and E all derive from ____.
Tyrosine
ACh derives from ____.
Choline
Aminobutryic Acid (GABA) derives from ____.
Glutamine
The PNS consists of ____ neurons.
cholinergic
Motor Unit
All muscle fibers that are controlled by a single motor neuron
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
Synapse between the axon terminal of a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
AChE
Acetylcholinesterase
- Degrades ACh
Botulinum Toxin
Inhibits ACh release
Myasthenia gravis
Chronic autoimmune disease that creates antibodies that attack the cholinergic receptors of the NMJ and produces serious weakness of voluntary muscles
Glutamine
Excitatory NT
GABA
Inhibitory NT that hyperpolarizes the cell via Cl- Channels
Glycine
Inhibitory NT that hyperpolarizes the cell via Cl- Channels