lec 9 - capillaries and veins
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
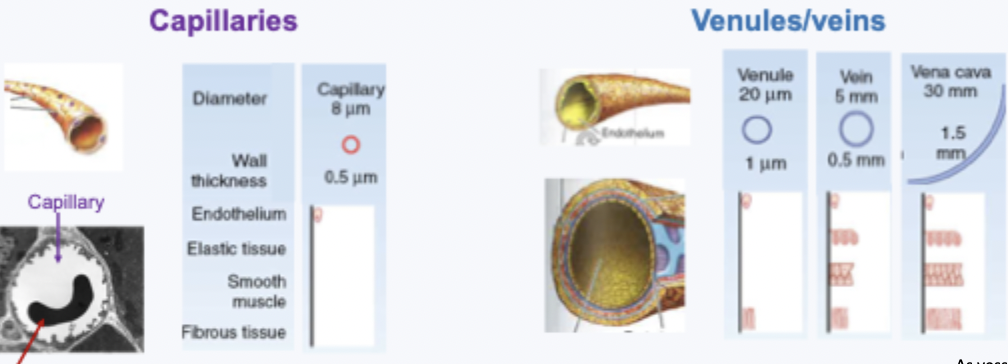
capillary vs vein structure
capillaries: very thin wall and small lumen - can be so small only a RBC can fit through - good for exchange
venules/veins: as vessels get bigger the wall structure get more complex
primary function of capillaries
exchange of nutrients and metabolic end products
thin walled - endothelial cells with no smooth muscle
hgihly branched network (high CSA)
blood velocity in capillaries
velocity = flow/total CSA
so when you increase area have decreased velocity (this is what we see in the capillaries)
large CSA and low velocity help enable fluid exchange
capillary circulation
link between arterial and venous circulation
several routes between arterioles and venules - controlled by precapillary sphincters and metarterioles (help redirect blood to the capillary bed which is needed the most)
pathway blood takes is variable dependant on metabolic demand
starlings forces
hydrostatic pressure: capillary and interstitial
osmotic pressure (colloid): capillary and interstitial
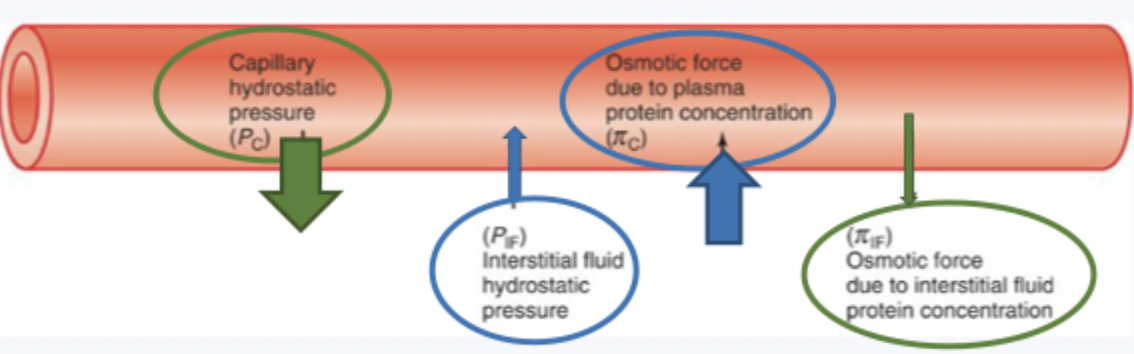
starlings forces equation
balance = Pc + πIF - PIF - πC
PC+πIF is out
Pif - πC is in
balance of fluid exchange depends on
location
in the arterioles get net filtration, in the venules get net reabsorption
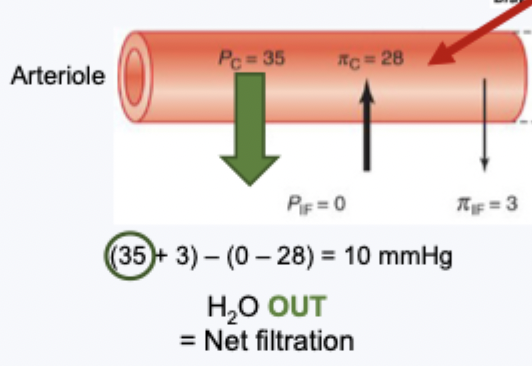
fluid exchange at arteriole end of capillary
high Pc (because higher blood pressure at arterioles end than in venule end of capillary), everything else low
get a positive number e.g. ~10mmHg
so water moves out - net filtration
fluid exchange at venule end of capillary
lower pressure at this end (Pc)
get a negative number e.g. -10mmHg
water moves in - net reabsorption
role of arteriole resistance in capillary hydrostatic pressure
small changes in the Pc alter the balance of fluid exchange in/out of capillaries
drop in BP occurs over the arterioles
vasodilation: decreased resistance, small drop in BP, increase Pc = fluid out
vasoconstriction: increased resistance, large drop in BP, decrease in Pc = fluid in in
what is a major determinant pf Pc
the resistance of the small arterioles upstream
net filtration
collection of fluid in the interstitial spaces
e.g. in the kidneys
net (re)absorption
movement of fluid into the blood
e.g. in lungs
fluid exchange - lymphaticsystem
drain excess interstitial fluid into the systemic circulation
damaged lymphatics - poor draining of excess fluid from ISF = lymphedema
functions of venules and veins
collect blood from capillaries and take it back to the heart
veins have thinner walls than arteries and are low pressure and low resistance
~60% of blood volume within venous system and ~40% is in veins
veins capacitance
high capacitance vessels - blood volume reservoir
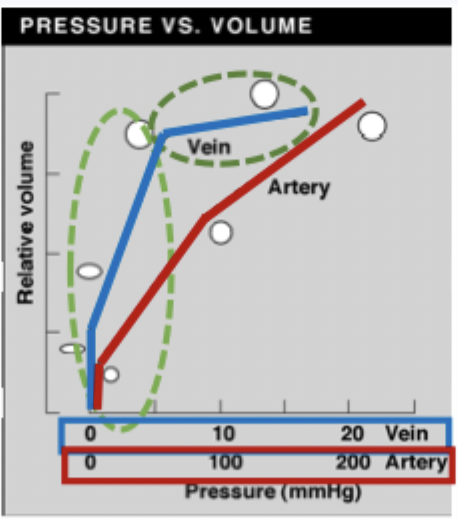
veins pressure vs volume
high compliance
initially small increase in pressure = large increase in volume
plataeu - large increase in pressure = small increase in volume (near max volume)
arteries are compliant but less so than veins
determinants of venous pressure
total blood volume (~60% in venous circuit) - increasing total blood volume increases venous blood pressure
hormonal and paracrine venodilators and venoconstrictors can decrease/increase venous pressure
venoconstriction and flow
venoconstriction increases flow
unlike vasoconstriction which reduces flow
venous pressure and sumpathetic nervous system
noradrenaline binds to a1-adrenergic receptors → causes venoconstriction → increased flow
venous pressure and blood pressure
venous pressure determines venous return
venoconstriction = increased VR = increased EDV = increased SV = increased CO
venous pressure - role of posture - vertical (standing) -
different heights from ground = different gravitational forces = blood pools in lower limbs
venous pressure increases with distance below the heart
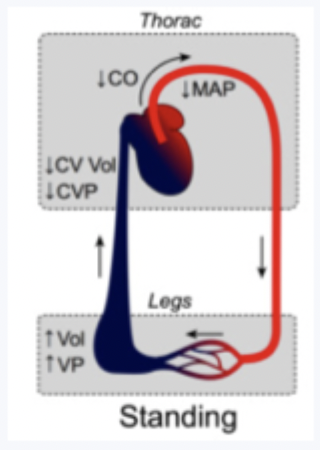
have low venous pressure (eg-35) above the heart and high venous pressure at the feet (eg105) when standing with the heart being 1
venous pressure - role of posture - horizontal (laying down)
same height from ground = same gravitational forces
venous pressure similar throughout the body
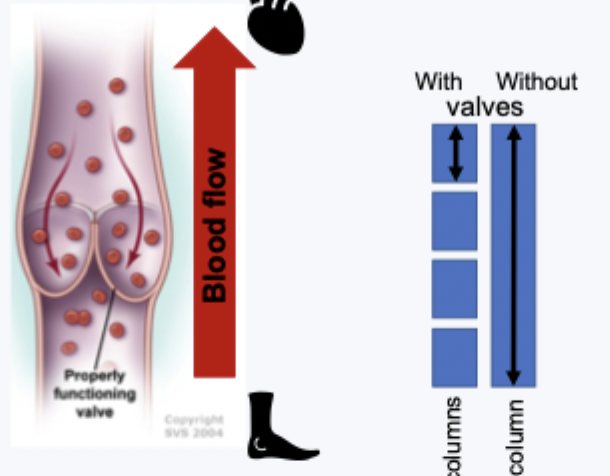
vein valves
preventing venous pooling
unidirectional blood flow towards the heart counteracts gravity
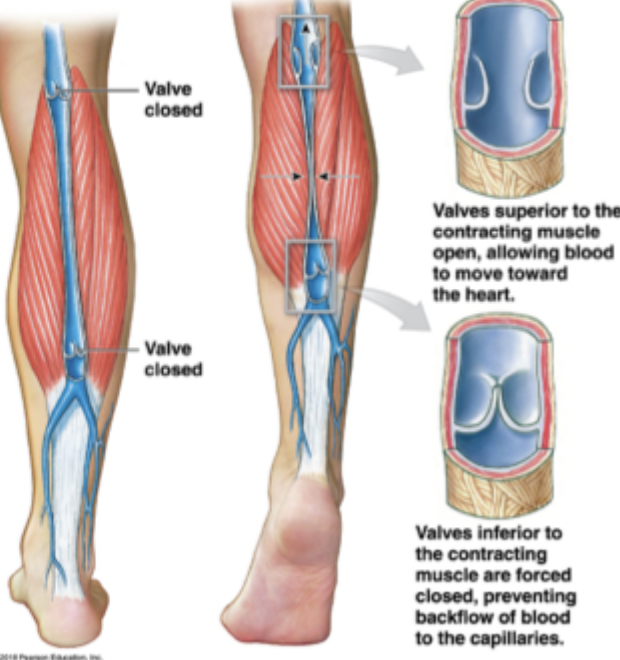
skeletal muscle pump
venous pooling counteracted by muscle pump
thermoregulation changes blood distribution - cutaneous veinsin extremities dilate to heat, also makes it harder for blood to get back to heart so can be dangerous for long time
important factors in venous return
valves
skeletal muscle pump
respiratory pump
respiratory pump - venous return inhalation
diaphragm decreased intrathoracic pressure, increased intrabdominal pressure
pulls blood in thoracic vena cava, compresses abdominal vena cava
facilitates venous return
respiratory pump - venous return exhalation
diagram relaxes → increased intrathoracic pressure, decrease intra-abdominal pressure → valves prevent backflow of blood
negative pressure created by deep inhalation aids blood flow in vena cava → important during exercise