DNA Packaging and the Nucleus
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Prokaryotic Genome
single, circular DNA molecule
Average size: 20 kilobases
Nucleoid
The 'bacterial chromosome'; negatively supercoiled, extensively folded, and complexed to a few proteins
Human genome
3.2 * 10^9 base pairs
Located inside 23 molecules with two pairs each = 46 chromosomes
3.5 meters long (cell is 30-50 micrometers, a nucleus is 10)
Histone composition
5 proteins: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4
2 copies of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 form a histone octamer
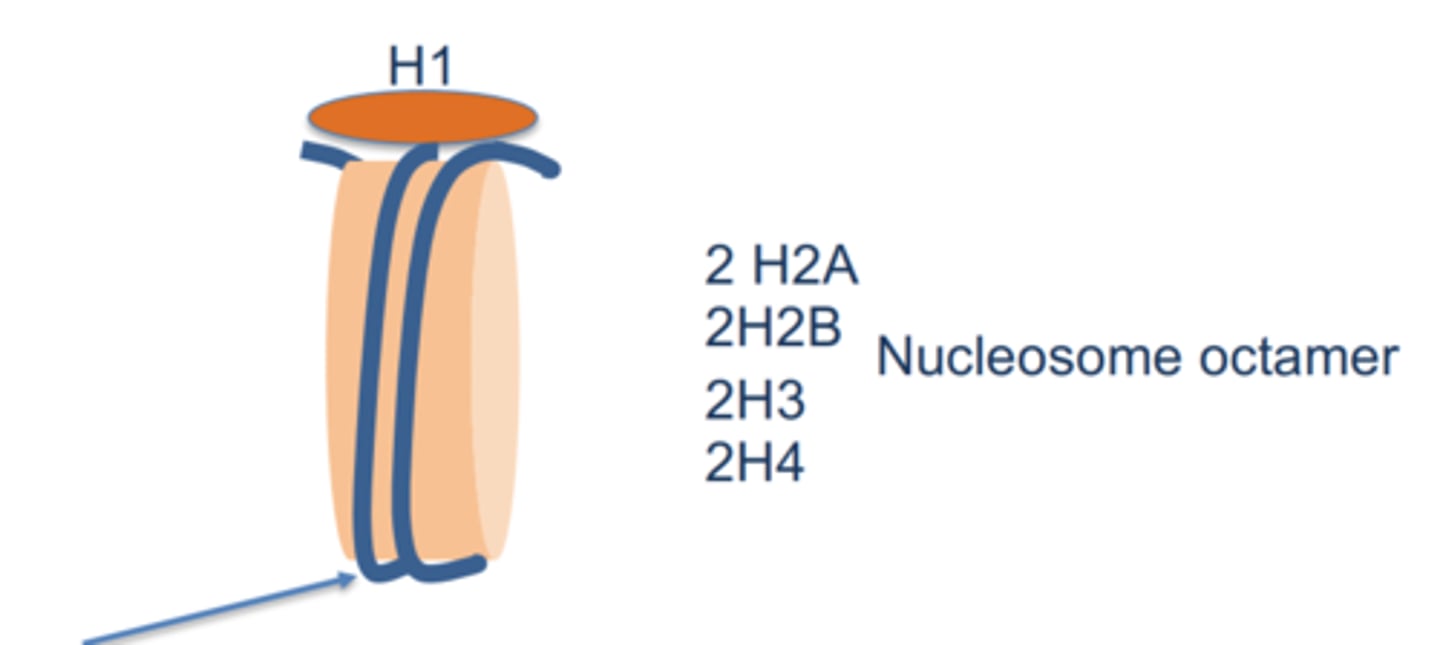
Nucleosome core
DNA wrapped around histone octomer
Total BP: 200
Linker BP: 50
Nucleosome bead: 150 bp + 8 histone proteins
Appear as 'beads on a string'
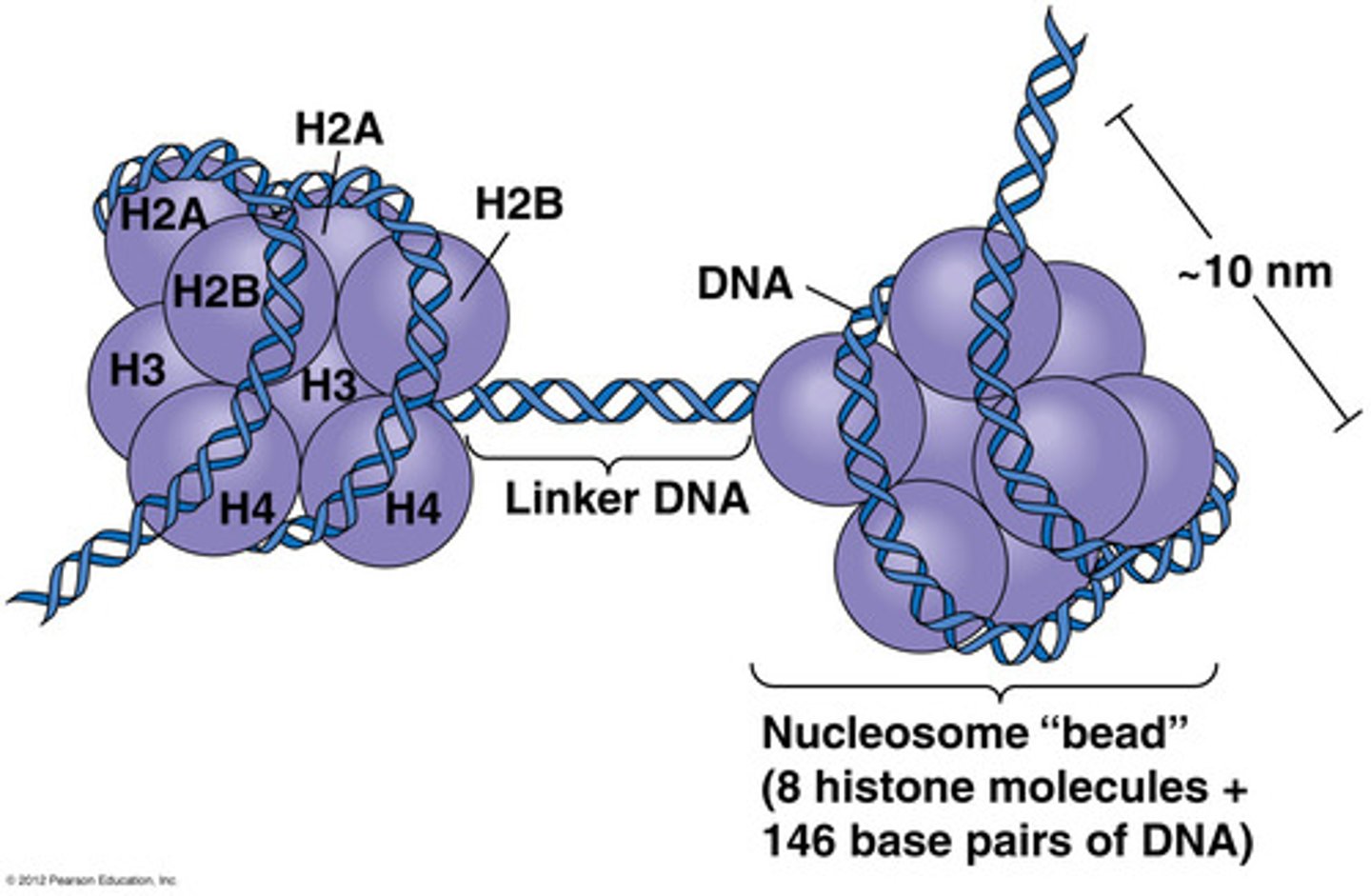
Linker DNA
DNA between two nucleosomes. 50bp long.
Nucleosome fragment experiment
Nuclease breaks down some of the linker regions. When the fragments are analyzed via gel electrophoresis, the fragments are multiples of 200 base pairs in length.
Show that DNA around histones is 200 bp long.
Nuclease
Breaks down nucleotides/ DNA
Chromatin organization (smallest to largest)
nucleosome, 30 nm chromatin fiber, euchromatin (loops), heterochromatin (highly compacted), chromosomes (highly condensed)
Euchromatin
Decondensed, available for transcription (along with the units before it)
Heterochromatin
Condensed, not available for transcription (along with the units after it)
Levels of euchromatin and heterochromatin
At any given time, some DNA is euchromatin and some is heterochromatin. This is not fixed, as what is being transcribed changes
DNA and histone bonding
DNa is attracted to histones because of the lysine residues on the histones (DNA's negative phosphate backbone is attracted to the positive lysines, forming an ionic bond)
3 methods of regulating chromatin packing
2 methods modify specific lysine residues: methylation and acetylation
3rd method: chromatin remodeling proteins
Methylation (what is it and what enzyme)
Methylation leads to tighter packing. Histone methyltransferase adds a methyl group to the lysine residues inducing a stronger charge.
Demethylation (what is it and what enzyme)
Histone demethylase removes the methyl group, returning it to looser packing
Acetylation (what is it and what enzyme)
Histone acetyltransferase adds an acetyl group to lysine residue, masking the positive charge, causing looser packing
Deacetylation (what is it and what enzyme)
Histone deacetylase removes the acetyl group, returning it to tighter packing
Chromatin remodeling proteins
Reposition nucleosomes to make DNA more accessible (longer linker regions)
Nucleus structure
2 membrane organelle. It's membrane is connected to the ER, and contains nuclear pores. Has a nuclear lamina.
Nuclear lamina
Network of intermediate filament proteins ("nuclear lamins") that provide shape and integrity to the nucleus; lines the inner face
Nuclear lamins
Intermediate filament proteins that make up the nuclear lamina
Nuclear pore function
Allows for movements in and out of the nucleus
- around 3k-4k per nucleus
- RNA is transferred out; proteins are transferred in
Nuclear transport types
Molecules < 40 kD (kiloDaltons) diffuse freely
-mRNA diffuses into cytosol
Most molecules are larger than 40kD and are actively transported
-rRNA and iRNA (and more) must be exported out to cytosol
Nuclear pore structure
-Nucleoporins line the pore
- FG repeats extend into pore
Nucleoporins
Proteins that line the nuclear pore
FG repeats
phenylalanine-glycine repeats; stretches of amino acids that extend into the pore
Importin
Protein that navigates through the FG repeats and transports cargo through the nuclear pore into the nucleus
Binds to the NLS
Nuclear localization signal (NLS)
Comprised for serine and arginine residues; located on proteins to allow importin to bind
Nuclear import (5 steps)
1. Importin binds cargo (with a NLS) and they move into the nucleus
2. Importin binds Ran-GTP and releases the cargo protein
3. Importin bound to Ran-GTP moves into cytosol. *
4. Ran-GTP encounters it's GAP, becomes Ran-GDP, and releases importin
5. Ran-GDP diffuses back into the nucleus, encounters it's GEF, releases its GDP and binds GTP again*
* Ran GTP gradient provides energy to cotransport importin from nucleus to cytosol, establishing importin gradient. Importin gradient provides energy to cotransport cargo proteins out of the cytosol into the nucleus
GAP
GTPase activating protein; causes protein to hydrolyze it's GTP into GDP
GEF
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors, that causes a protein to lose a GDP and replace it with a GTP
Nuclear export (4 steps)
1. Exportin binds proteins with a NES and binds Ran-GTP, and they move out of the nucleus.
2. Ran-GTP encounters its GAP, becomes Ran-GDP, releases cargo and exportin.
3. Exportin and Ran-GDP diffuse back into nucleus. *
4. Ran-GDP encounters its GEF, releases GDP, and binds GTP
*Ran GDP gradient provides energy to cotransport exportin and cargo from nucleus to cytosol against their gradient
Nuclear export signal
sorting signal on proteins that allows them to be bound by exportin
Exportin
nuclear receptor protein that binds to the nuclear export signal (NES) of proteins in the nucleus and then transports the bound protein out through the nuclear pore complex and into the cytosol
Concentration gradients in/ out of nucleus
Nucleus: Low concentrations of importin and Ran-GDP
Cytosol: Low concentration of Ran-GTP, high concentration of importin
Secondary active transport in the nucleus
-Ran GDP diffuses into nucleus
-Ran GTP diffuses into cytosol
- Ran GDP gradient provides energy to cotransport exportin and cargo from nucleus to cytosol against their gradient
- Ran GTP gradient provides energy to cotransport importin from nucleus to cytosol, establishing importin gradient
- Importin gradient provides energy to cotransport cargo proteins out of the cytosol into the nucleus