sex differences lecture 4 - sex differences in the brain
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
is there sex differentiation in the brain?
structural differences
functional differences
what causes these sex differentiation in the brain?
source -of these differences – hormones
These can be due to:
– Hormones (activational and organizational)
– Genetics (genes on sex chromosomes XX , XY, XXY)
– Environment (e.g. peers, culture,... – potentially prominent influence e..g having long hair – dominantly women(behaivour difference)
Brain e.g. practicing a certain behaviour – certain behaivorus change the brain e.g. professional musicians brains are different than non musicians
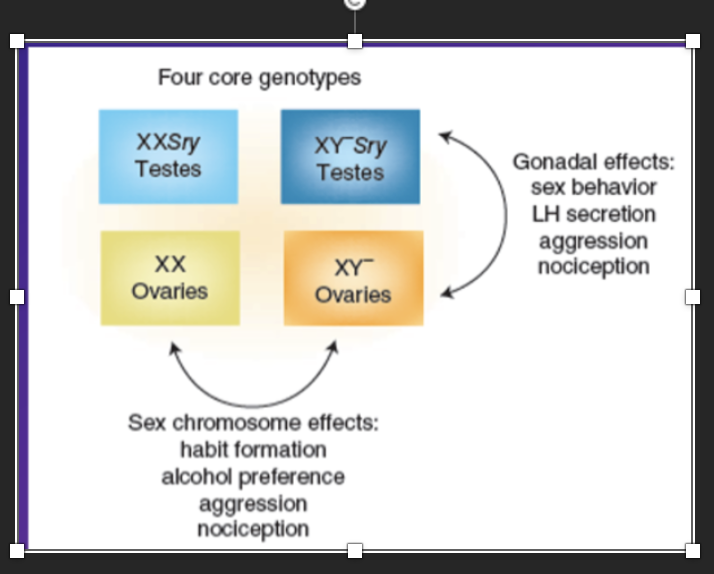
evidence of sex differences causes in the brain - mice study
To examine If hormones or genetics influences sex differences in the brain and studies the mices development:
Created 4 core genotypes – i.e. separated the SRY gene from the Y chromosome , removed sry chromosome from Y gene in second mouse)
XX, added SRY gene mouse – genetically female mouse produces testes and subsequent testosterone ,
XY with SRY testes – typical male genetics = mouse developes testes and then testosterone ,
Typical XX mouse - no SRY present = develop ovaries and have low levels of testoerone and all “female” genes ,
XY, SRY gene removed and left rest of chromosome in tact = ovaries develop in mouse, and so don’t develop early testosterone, but have all “male genes” minus SRY
Evidence sex differences occur which are purely hormonal - due to the presence/ absence of early testoerone – influenced by hormomes
Evinece sex differences occur which are purely genetic - occur due to presence/ absence of SRY gene – influenced by genetics
No need to memorise lists – just illustrates how to separate genetic from hormonal effects
Male external genitalia start growing at puberty in 46,XY individuals with 5a-reductase deficiency because
A) the enzyme is fixed by puberty
B) the adrenal gland makes more testosterone
C) high testosterone levels interact with DHT receptors
D) there is no peak in oestradiol
answer - C
Can source of Sex Differentiation in the Brain be studied and evidenced in Humans
No experimental manipulations possible – but are conditions were we hae XY chromosoms and no testosterone sensitivity – intersex individuals with
• Information can be gathered from:
– Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in 46,XX – have high T during development -enables usto see horomone and gene developement
– Complete Androgen Insensitivity in 46,XY
– Hormone treatment in transgender individuals – tells us activations roels of hormones in humans
causes of Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Behavioural Differences - toy preferences
Boys and girls tend to have different toy preferences
although many Parents try to be gender neutral but on average gender specific toyprefernce still ococur
Showed infant vervet monkeys range of toy choices
Found – monkeys showed sec typical toy preferences
- female monkeys preferred to play with a doll
- male prefers to play with a toy car
in humans with CAH – enables us to study what is due to early testosterone
found
• CAH 46,XX individuals have more masculine toy preferences
• CAIS 46,XY individuals typically have feminine toy preferences
• Correlation between play style and prenatal testosterone – evidence potential sex differences in toy preferences due to hormones
Males generally had higher – Testosterone levels on average than females, but in both there is a sig correlation between how much testosterone they experience and their plat style – suggesting that there is slightly more than socialisation
Although have had female social environment thougout childhood
causes of Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Behavioural Differences -mental rotation
Men tend to be faster in spatial mental rotation tasks
CAH 46,XX individuals are more masculine in some measures than other 46,XX individuals
• CAH 46,XX individuals perform better than non-CAH 46,XX individuals – on average are more male like in this trait if CAH
• CAIS 46,XY individuals scores are indistinguishable from non-CAIS 46,XX
individuals
• Suggests a role of testosterone in spatial mental rotation
however, criticised
as men may perform better due to socialisation – more familiar with physical toys such as blocks/ lego
causes of Sex Differentiation in the Brain:Structural differences
Male brains are ~ 10% larger
• Female cortex is thicker (more grey matter)
• Males have larger white matter volume & subcortical
structures, tend to have larger corpus colosum - axons which run between two hemispheres (Thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain)
These differences already existed in MRI scanning in younger children, evidencing that they aren’t environmentally influenced differences
criticised - Differently organised but not differently structured
CAIS (androgen insensitivity syndrome) 46,XY individuals have some features that are masculine (genetics), and some that are feminine (hormones or environment)
• Sex differences in the brain are complex and specific, and due to many different causes
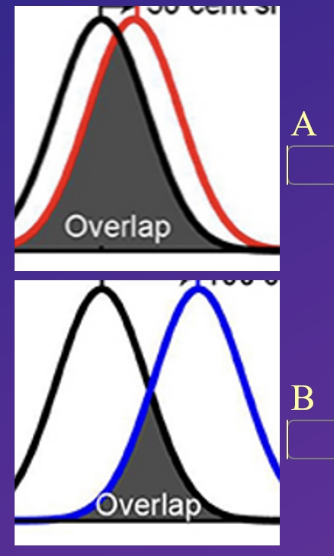
does a typical sex difference in brain or behaviour look like a or b
A - because its always statistical/ always population level
as traits are indvidial specific
Sex Differences: Sexual orientation
• One of the most extreme sex differences (that occurs during devleopement sometimes)
• 90-95% of human males are attracted to human females exclusively (“gynophile” – interested in romantic/ sexual relationship with a female thing gy = guy likes girl)
• 85-90% of human females are attracted to human males exclusively (“androphile” interested in romantic/ sexual relationship with a male
genophyle
male exclusively attracted to women
androphile
woman exclusively attracted to men
reference evidence that Sex differences in the brain that co-vary/ correlate with sexual orientation in humans
evidence that sexual orientation is a physiological difference in the brain
◦ • SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus – nucuelus that sets your internal biological clock) larger in androphile individuals (Swaab & Hofman 1988) - larger in heterosexual women and androphile males)
• Anterior commissure (bundle of axons between two hemispheres is) larger in both male and female androphile individuals (Allen & Gorski 1992)
◦ • nucleus called INAH-3 : smaller in androphile individuals (Levay 1991) – (both androphile women (women attracted to men AND men attracted to men ) - but could be due to AIDS pandemic that it is smaller
(think INAH-3 = I know three things)
Arguably shows them its not purely cultural – monkey study suggest something beyong human experience, and other one evidnces it may be hormonal
however it is still heavily debated in society
what causes brain differences in sexual orientation ? list three things
• Could be causal to sexual orientation
• Could also be purely correlation, as indicators of other
mechanisms (hormonal, genetic)
• Could be consequence of sexual orientation!
Origins of Sex Differences in Brain and
Behaviour
• Experiential/Cultural Effects
• Activational Hormonal Effects
• Organizational Hormonal Effects
• Genetic Effects
The 4 potential causal roots for any sex difference – can be a combination of these things feeding into it
Environmental Effects on Sex Differences
Influences on brain development (e.g. what you’re exposed to in childhood), bandura bobo doll experience evidence this
• Effects of practice (e.g. you are better at what you spend more time doing) – mental orientation task
• Social effects (expectations, stereotypes,...)
• HOWEVER – little to NO evidence that this affects sexual orientation
Experience and Sexual Orientation summary
Most people feel their sexual orientation has always been this way
• No good evidence to support effects of parenting, learning, etc.
• Evidence from other species that it is not a cultural construct
• 8% of male sheep are exclusively interested in other males
• Sexually Dimorphic Nucleus (SDN- because its bigger in males than females) of preoptic area is smaller in these males
• Size of SDN is influenced by developmental T levels
Evidence early Testoerone might be linked to sexual orientation – but in this cause it is purely correlational not causation