types of tissues
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Tissue
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Histology
Study of tissues.
Four Basic Tissues
Connective Tissue; Epithelial Tissue; Muscle Tissue; Nervous Tissue.
Epithelial Tissue
Covers the body, lines the cavities, tubes, ducts and blood vessels inside the body. Covers the organs inside of the body cavity. Protection from physical & chemical injury. Protection against microbial invasion;responds to stimuli; Filers, secretes and reabsorbs materials.
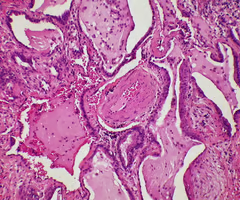
Connective Tissue
Most abundant and widely distributed tissue; Connects, binds, and supports structured : Tendons & ligaments; Protects and cushions organs & tissues; Transports substances (blood).
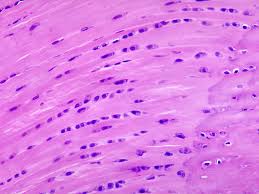
Muscle Tissue
Associated with the bones of the skeleton, the heart and in the walls of the hollow organs in the body; Movement; maintains posture; produces heat; pumps blood; peristalsis (digestion).
Nervous Tissue
Main component of the nervous system i.e., brain, spinal chord & nerves; Regulates and controls body functions; Generates and transports nerve impulses; Supports, insulates and protects impulse generating neurons.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple: One cell thick; Forms solid layer of cells which line blood vessels, body cavities, and line organs in body cavities.
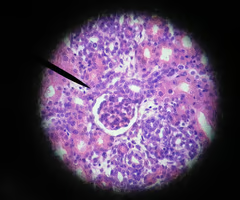
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified: Multiple layers; Forms Epidermis.
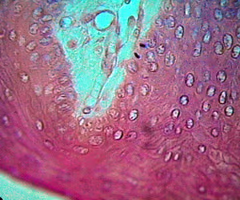
Columnar Epithelium
Simple; Column shaped: long and narrow; Line digestive tract where reabsorption and secretion take place.
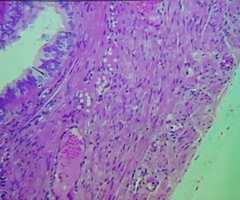
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudo: Fake or False; Gives the appearance of more than one layer of columnar epithelium cells.
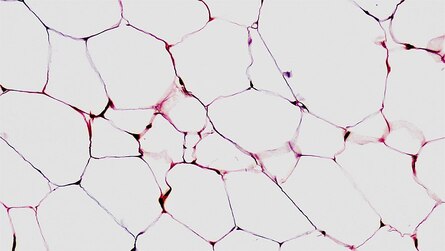
Connective-Adipose
Honeycomb appearance; Stores energy (fat); Insulates; Supports and protects organs.
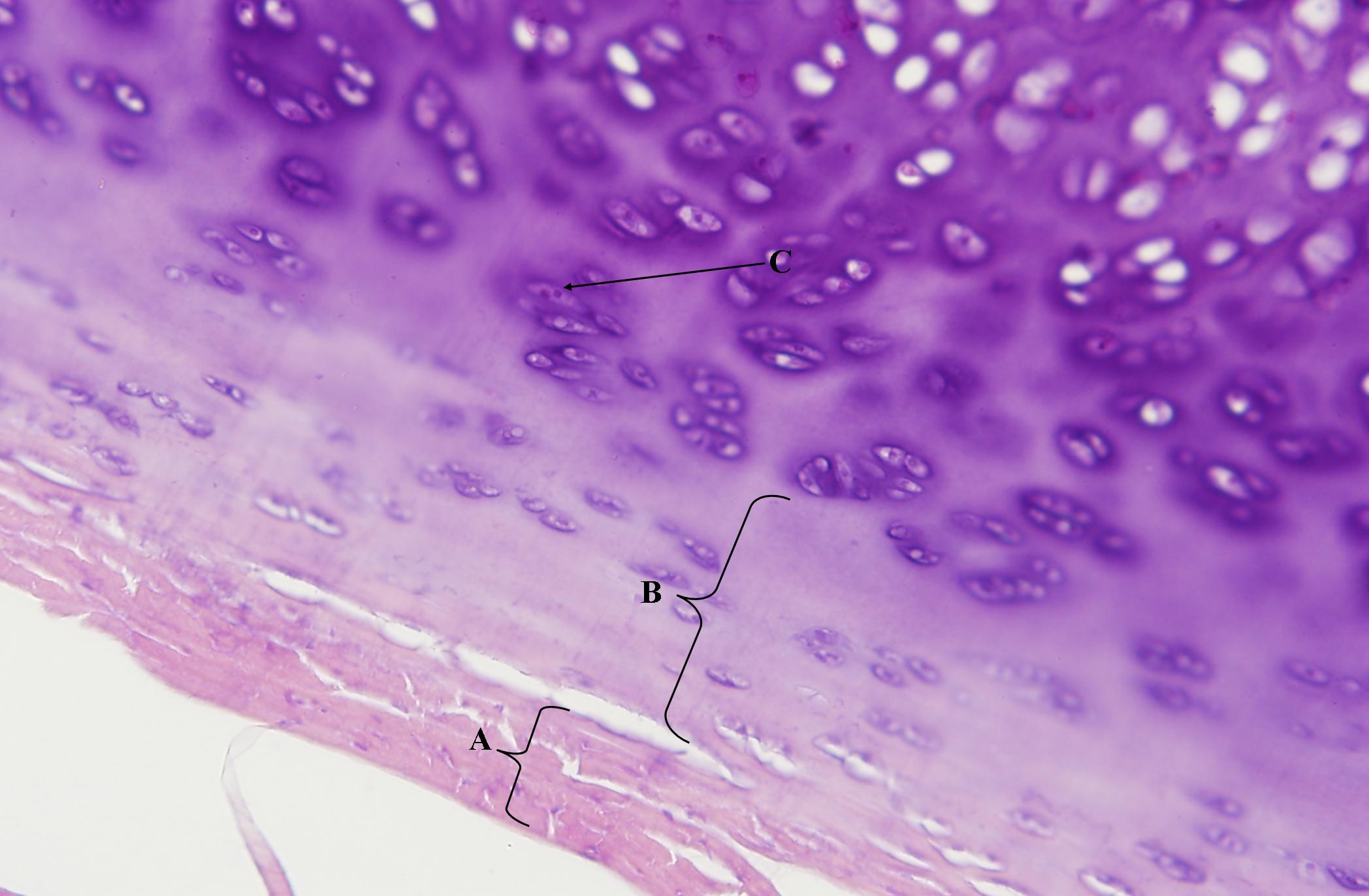
Connective-Bone
Tree ring-like appearance; Supports & Protects; Mineral storage; Fat storage; Blood cell production.
Connective-Hyaline Cartilage
Supports while providing flexibility; Absorbs compression between bones and joints (articular cartilage); Holds open respiratory passages; Most abundant type of cartilage in the body.
Muscle-Skeletal
Muscle fibers(cells), long, parallel & cylindrical; Multinucleate; Striations (cross stripes that run perpendicular; Produce voluntary movement; Locomotion; Heat.
Muscle-Cardial
Heart; Striated; Intercalated discs: double membrane separating each adjacent cells in cardiac muscle fibers.
Muscle-Smooth
Lining of tubes (blood vessels, digestive tract etc.); Non-striated; Involuntary.
Nervous-Neuron
Branching cells with many long processes; Large central nucleus; Transmit impulses from one area of the body to other areas; Regulate activities through neuron impulses.
loose proper
holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues
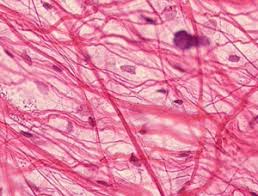
connective tissue reticular
a type of connective tissue with a network of reticular fibers, made of type III collagen
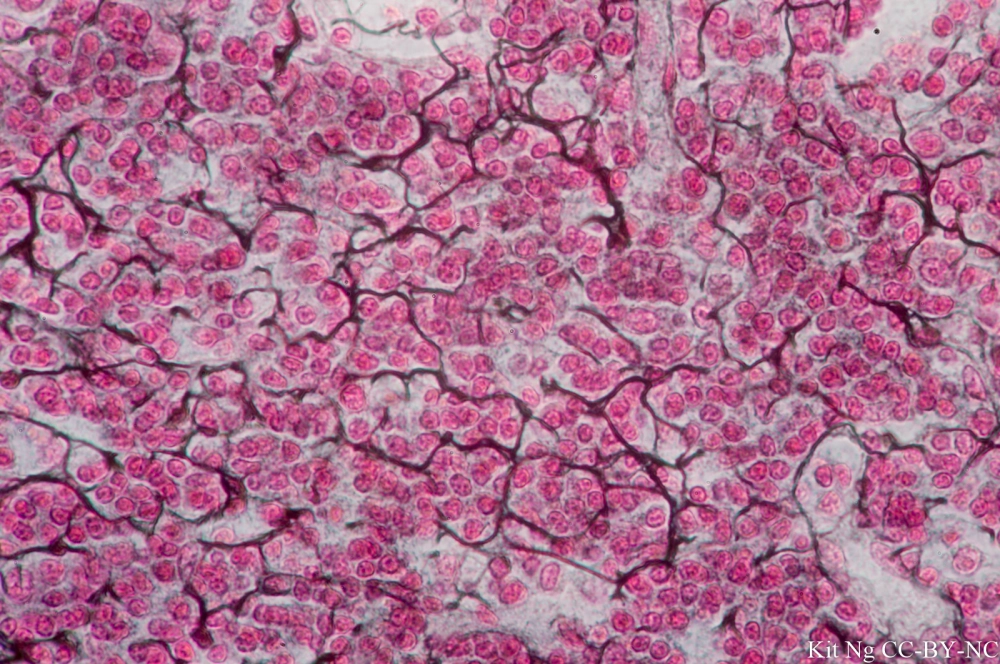
dense proper regular
a type of connective tissue where collagen fibers are tightly packed and arranged in parallel bundles, providing strong tensile strength in one direction
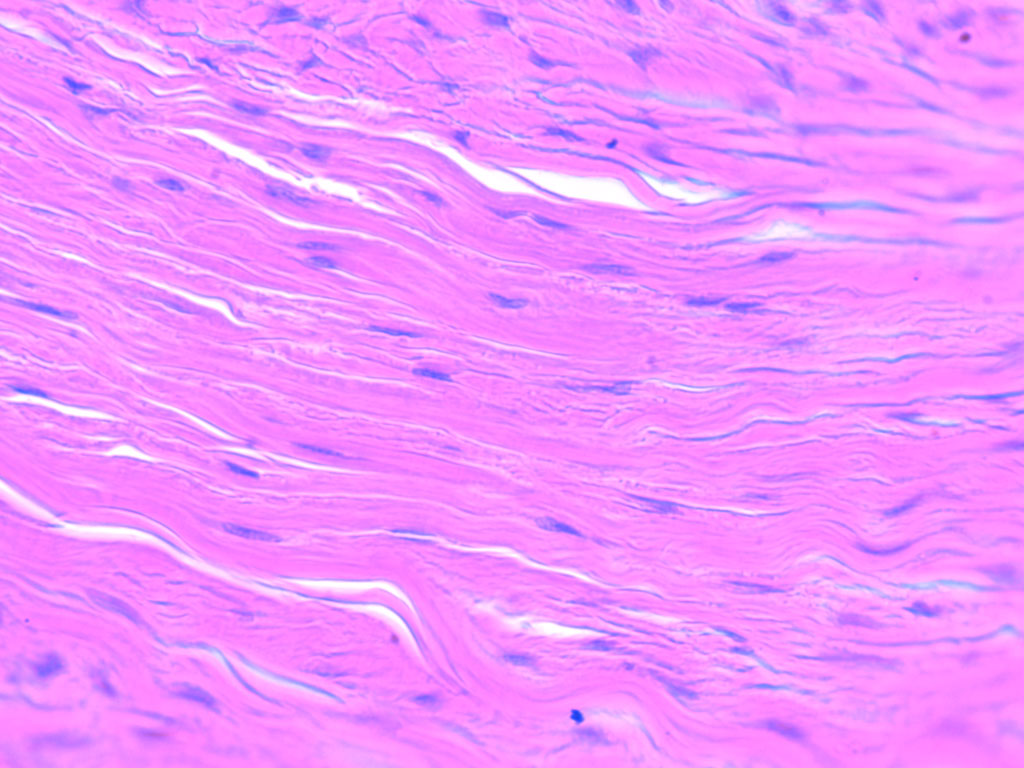
dense proper irregular
a type of connective tissue that contains many collagen fibers that are arranged in bundles that point in different directions.
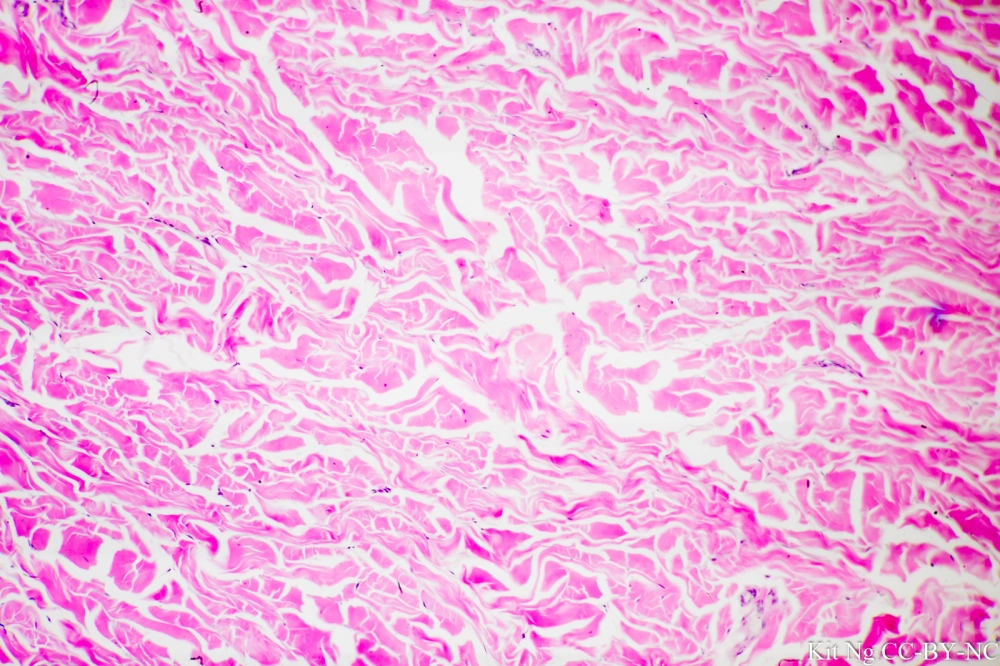
connective tissue elastic
contains elastic and collagen fibers
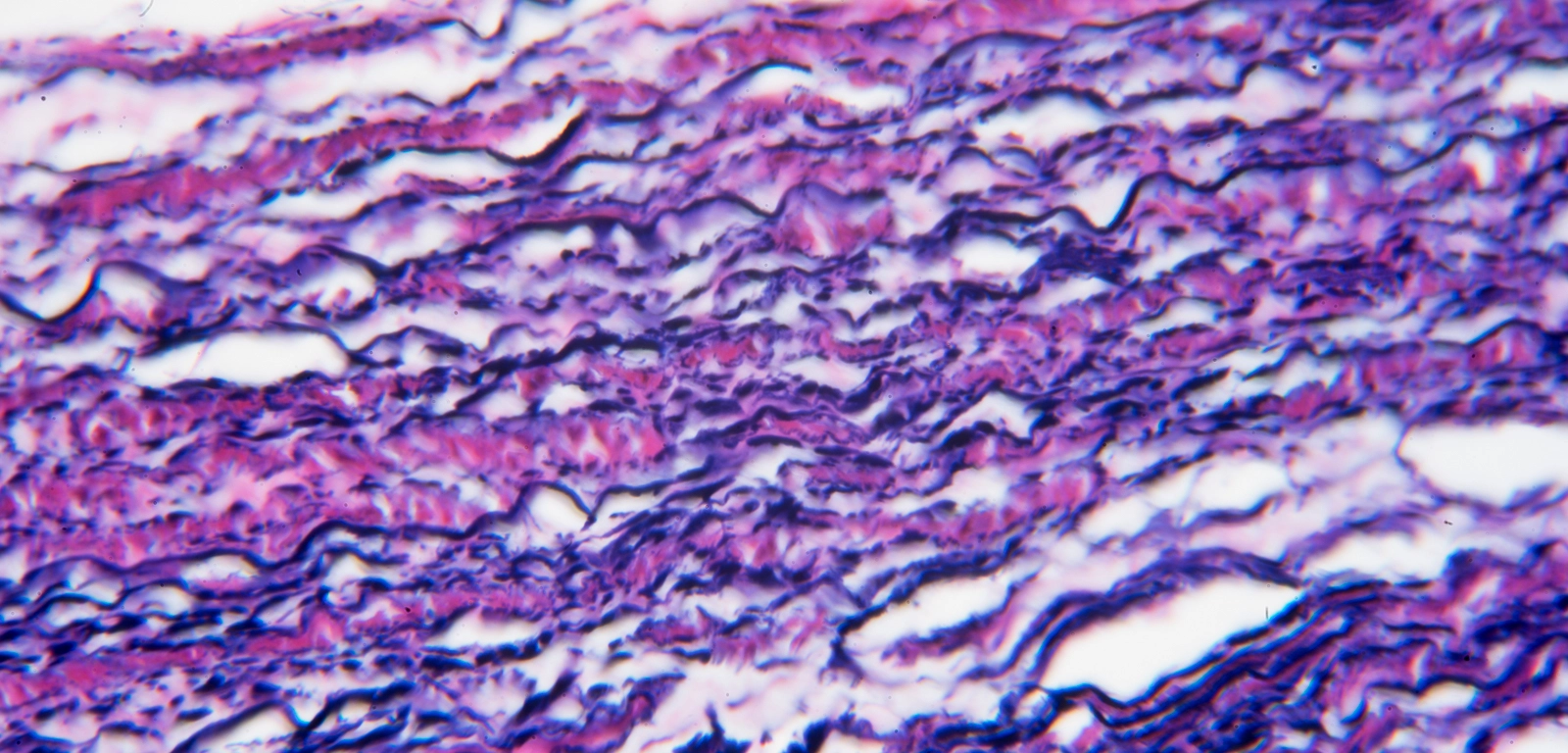
connective tissue fibrocartilage
provides structural support for the musculoskeletal system