Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Cells
basic structural & functional units of every organism
Prokaryotes
(Pro-No): bacteria, DNa in nucleoid region, smaller than Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes
(Eu-Do): fungi, animals, plants, DNA in nucleus, have membrane-boudn organelles
Organelles
membrane bound structures in Eukaryotes
Endomembrane organelles
Energy organelles
Endomembrane organelles
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi complex
lysosomes
vesicles/vacuoles
plasma membrane
Energy organelles
mitochondria
chloroplasts
Compartmentalization
allows for diff metabolic reactions to occur in diff locations
increases surface area
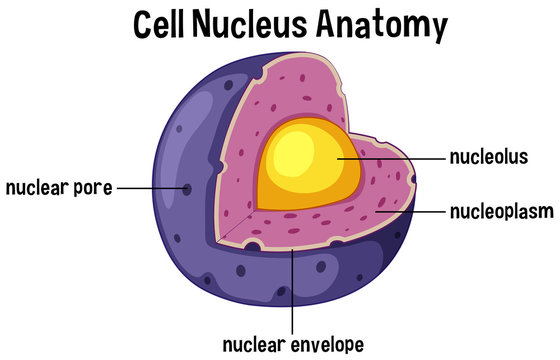
Nucleus
has genetic info
double membrane
has pores (materials in & out)
has nucleolus (rRNA is made)
subunits exit via nuclear pores → turn into ribosomes
Ribosomes
made up of rRNA & protein
function: make proteins
locations: Cytosol & ER
Endoplasmic Reticulum
network of membranous sacs & tubes
functions: creates membranes, compartmentalize cell
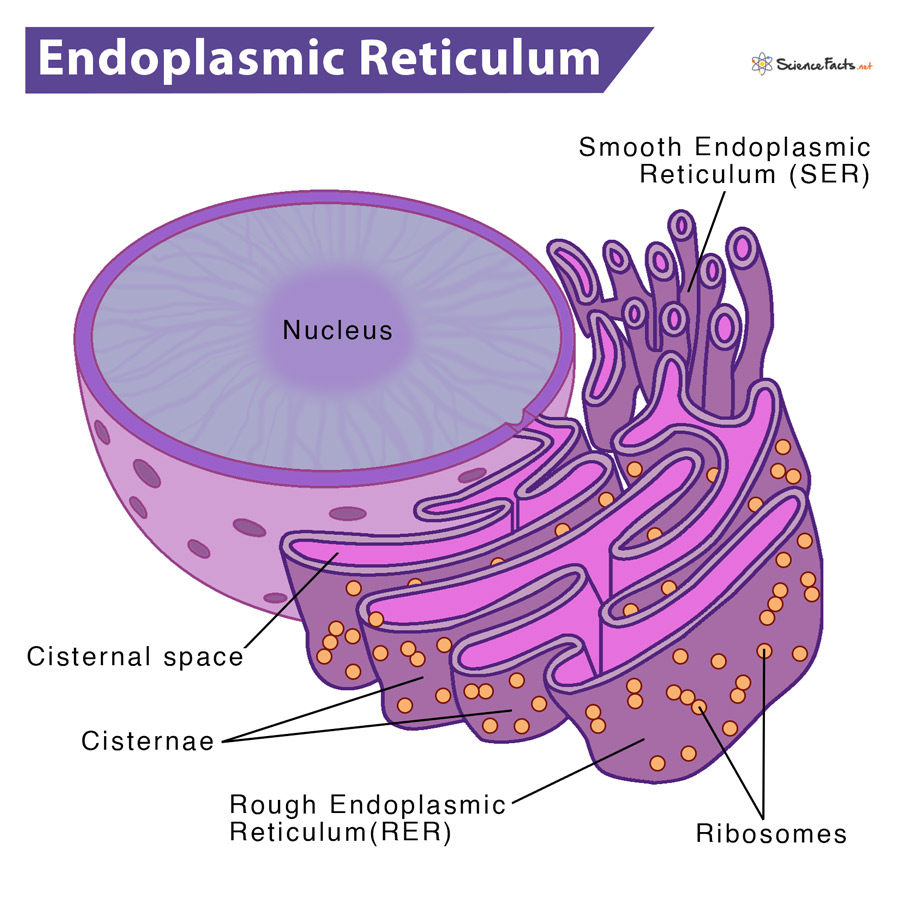
Rough ER
has ribosomes
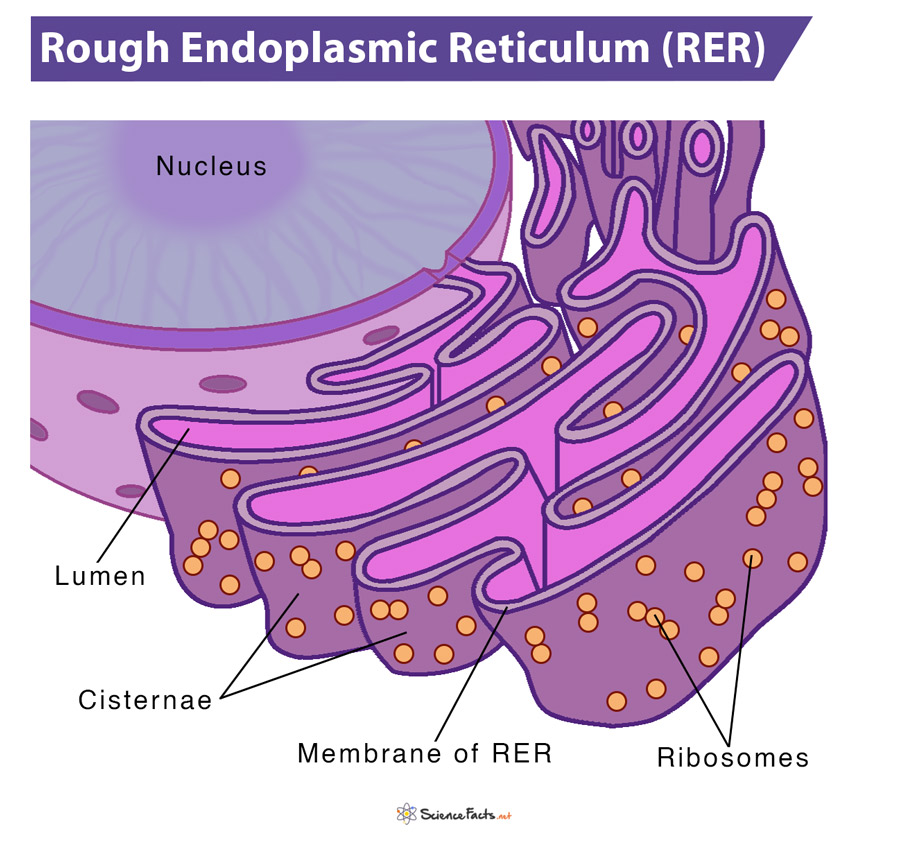
Smooth ER
no ribosomes
creates lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates, cleans cell
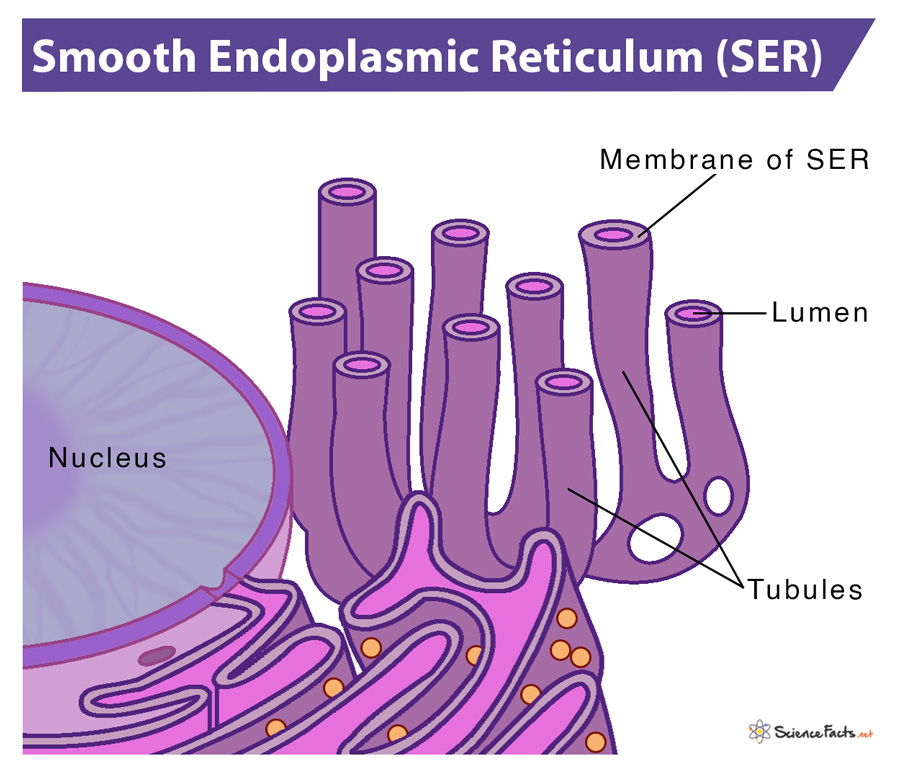
Golgi complex
contains cisternae
has directionality
Cis face: receives vesicles from ER
Trans face: sends vesicles back into cytosol for production
functions: Receives transport vesicles w/ stuff from ER → Modifies, Sorts, Adds molecular tags, Packages materials that exit membrane via exocytosis
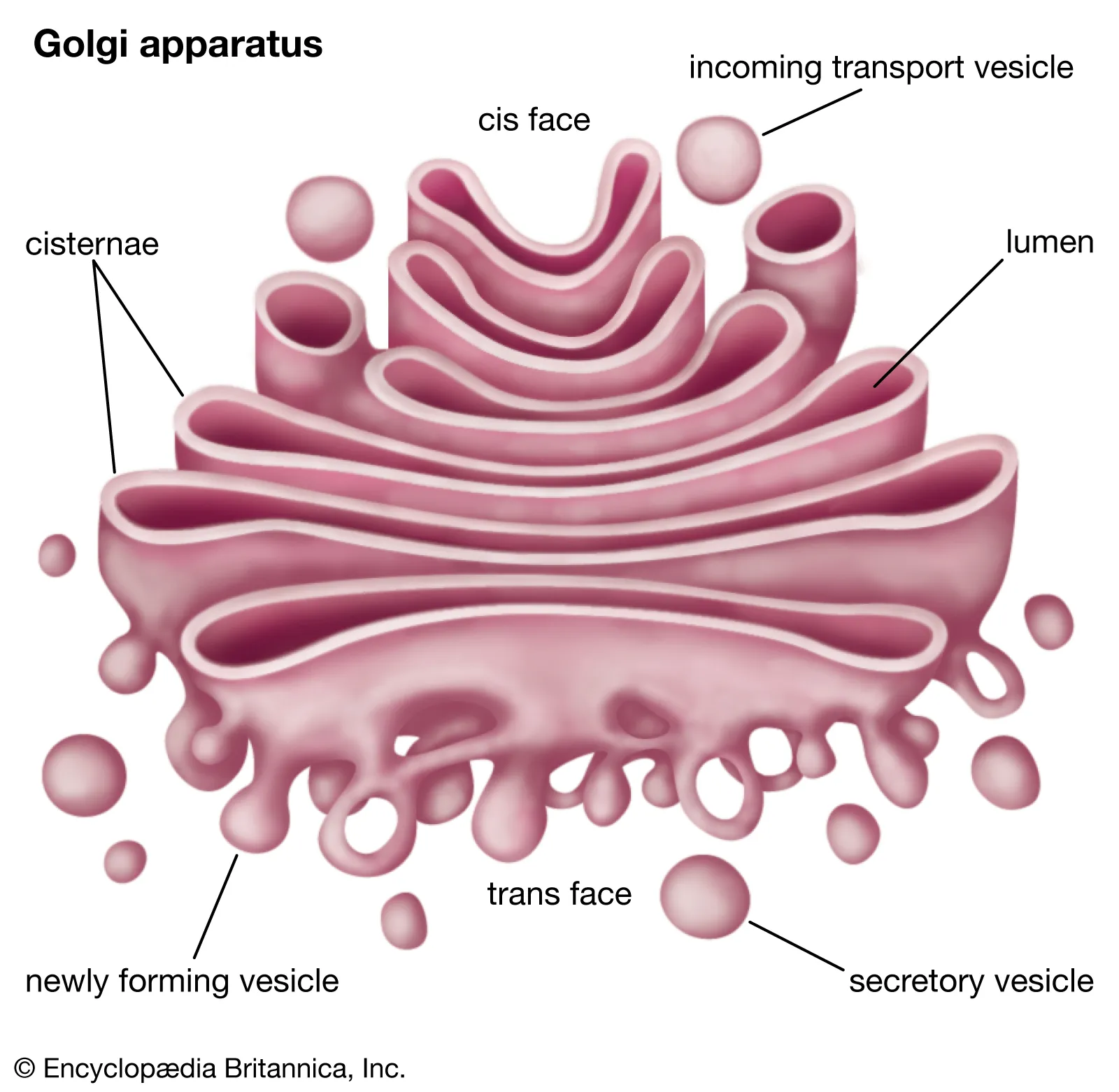
Lysosomes
hydrolyzes (breaks down) macromolecules in animal cells
Autophagy: lets cells renew itself
animal cells
Peroxisomes
to break things down
catalyze reactions that produce H2O2 → break it down to H2O
(similar to lysosomes)
plant cells
Vacuoles
storage space
large vesicles from ER & Golgi
selective in transport
Food vacuole
form via phagocytosis (cell eating) → then digested by lysosomes
Contractile vacuole
maintain water levels in cells
Central vacuole
(in plants): contain inorganic ions & water
crucial for turgor pressure
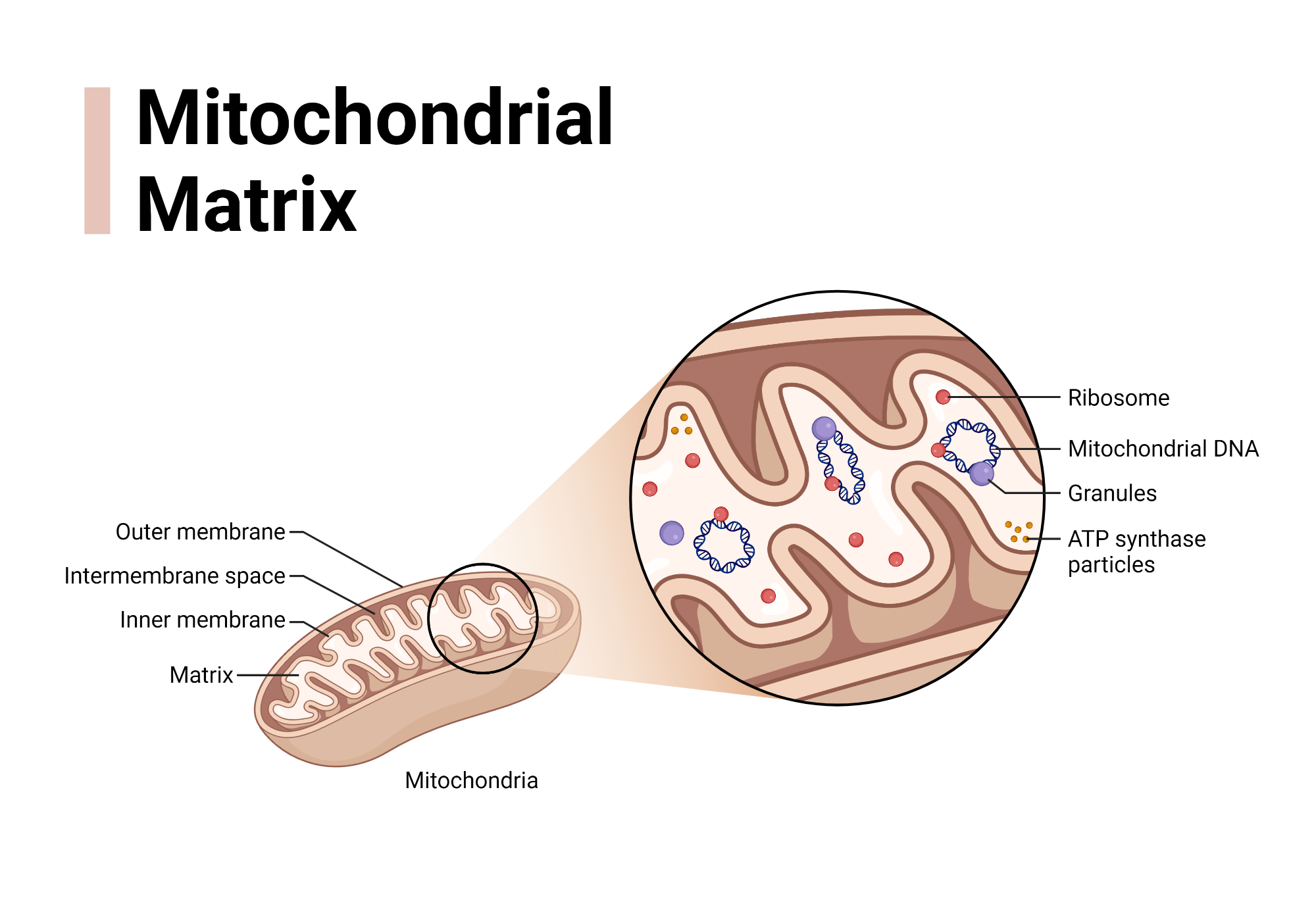
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration
double membrane
has folds → increase surface area
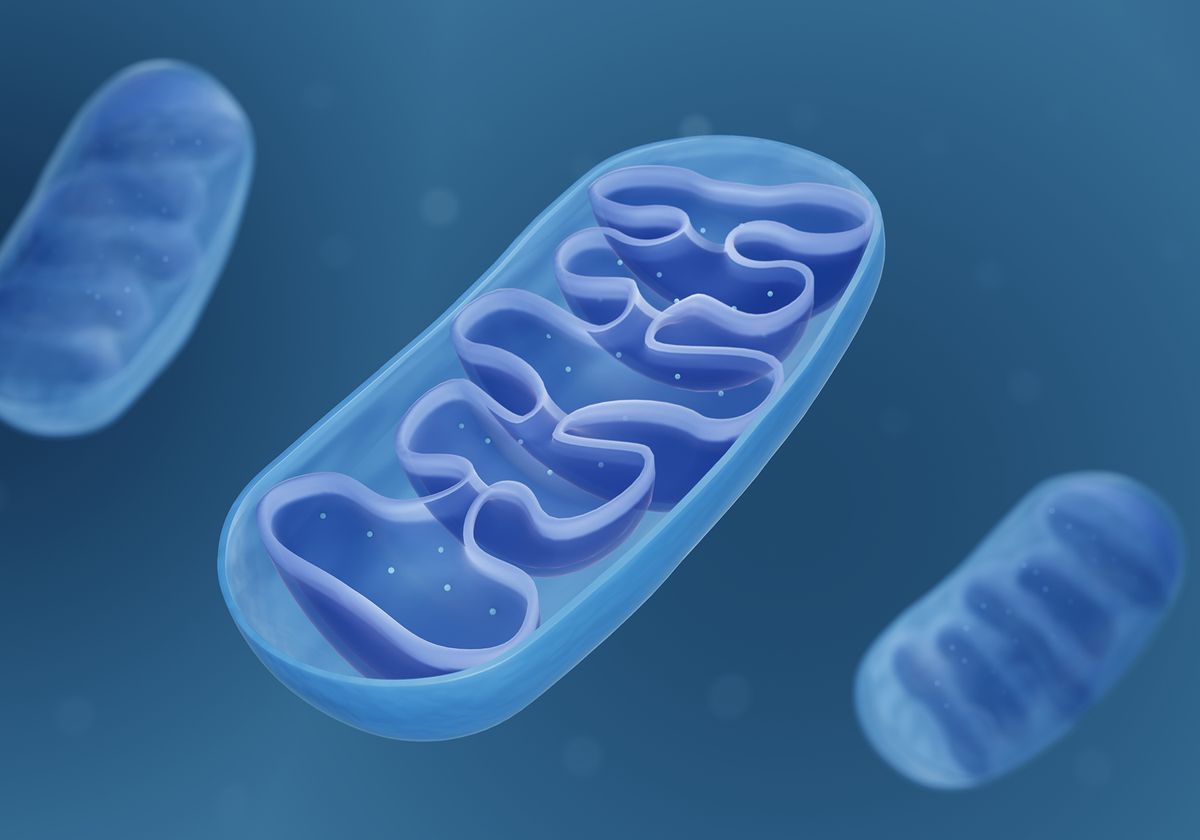
Mitochondrial matrix
contains:
enzymes that catalyze(speed up) cellular respiration & produce ATP
mitochondrial DNA
ribosomes
Chloroplast
(only plant cells)
site of photosynthesis
contains chlorophyll (green pigment)
has thylakoids & storm
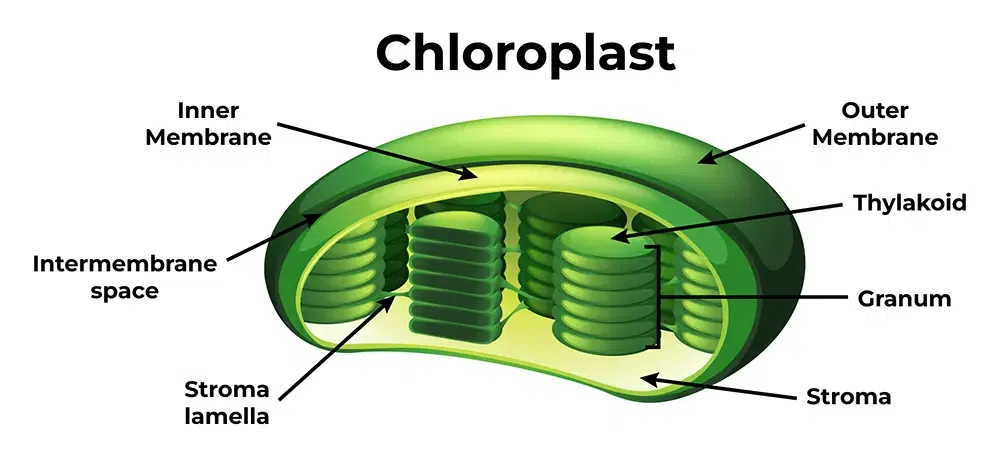
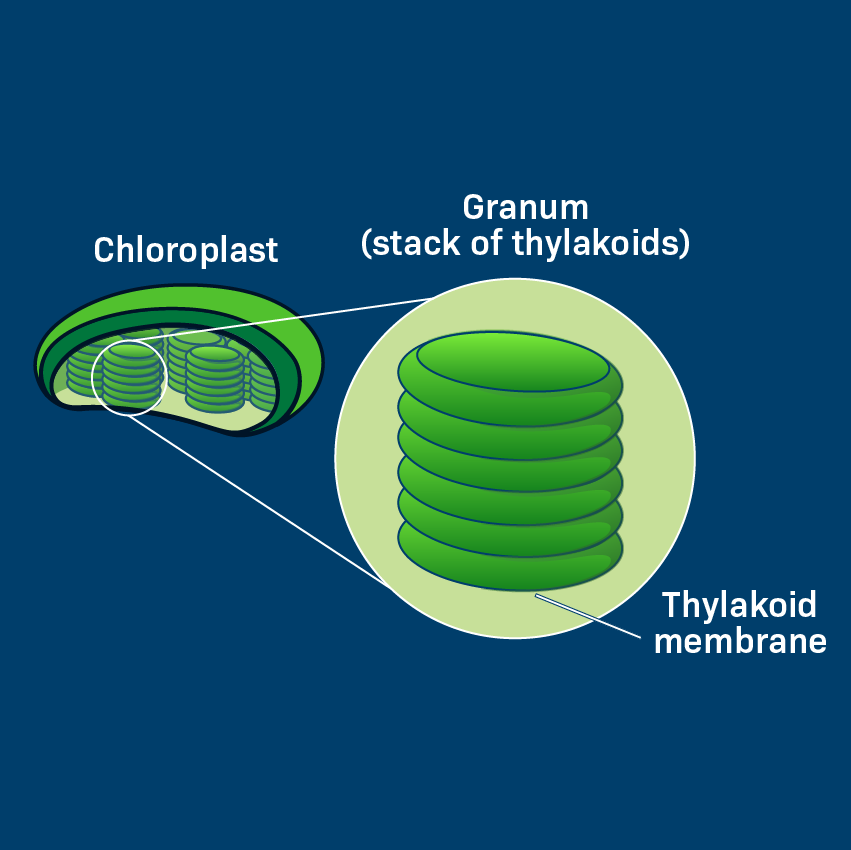
Thylakoids
membranous sacs → organize into stacks (grana)
Grana: where light dependent reactions occur
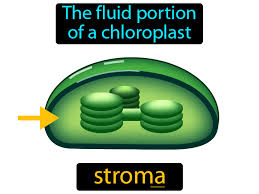
Stroma
fluid around thylakoids
location for Calvin Cycle
Contains: Chloroplast DNA, Ribosomes, Enzymes
Cytoskeleton
network of fibers throughout cytoplasm
give structural & mechanical support
anchor organelles (ensure position)
allow for movement
Microtubules
hollow, rod-like structure made of tubulin (protein)
structural support
cell motility (flagella)
Microfilaments
thin, solid rods made of actin (protein)
maintain cell shape
bear tension
cell motility
cleavage furrow
Intermediate Filaments
fibrous proteins made up of varying subunits
structural elements
maintain cell shape
anchor nucleus & organelles
form nuclear lamina (lines nuclear envelope)
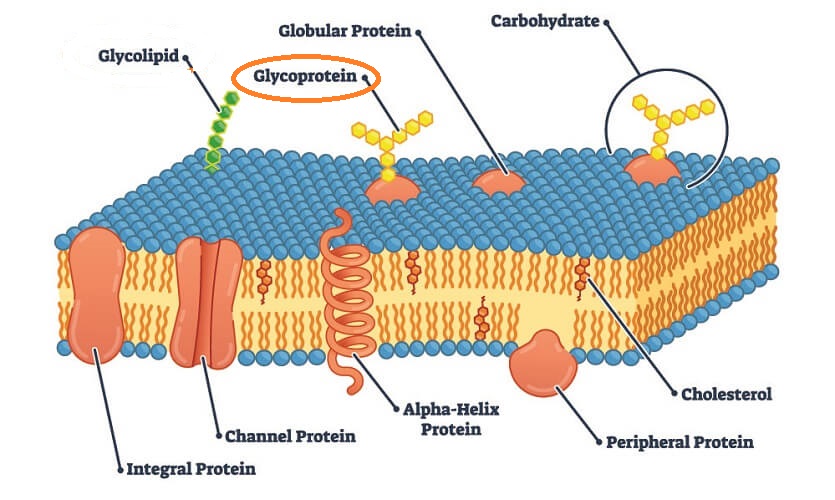
Plasma membrane
separates internal & external cell environment
consists phospholipids (amphipathic): contain head & tail
forms a bilayer
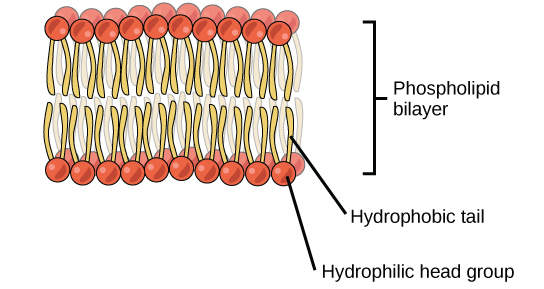
Fluid Mosaic Model
temp affects fluidity
Unsaturated hydrocarbon tails: maintain fluidity at low temps
Kinked tailed: prevent tight packing of phospholipids (low temp)
Cholesterol: maintain fluidity at high & low temps
High temp: reduce movement
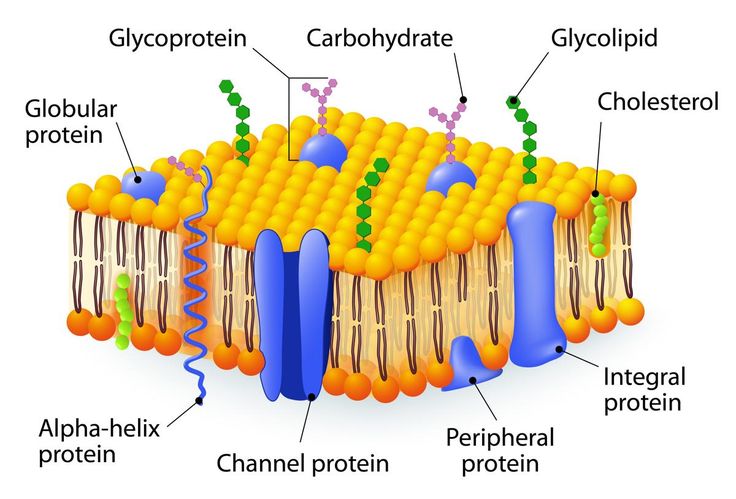
Integral proteins
embedded into lipid bilayer (very stuck=very hard to remove)
amphipathic
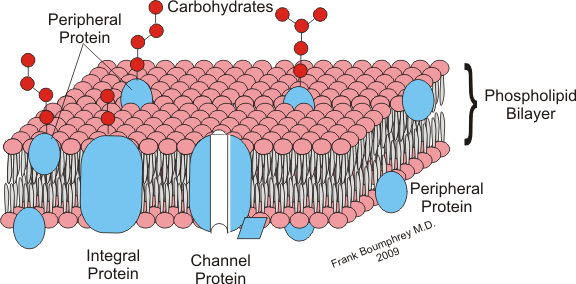
Peripheral proteins
not embedded into lipid bilayer (kinda attached→remove themselves from membrane)
attach to cell → make it do smt → then leave
Membrane carbohydrates
crucial for cell-to-cell recognition
acts as a marker for recognition (molecular tag)
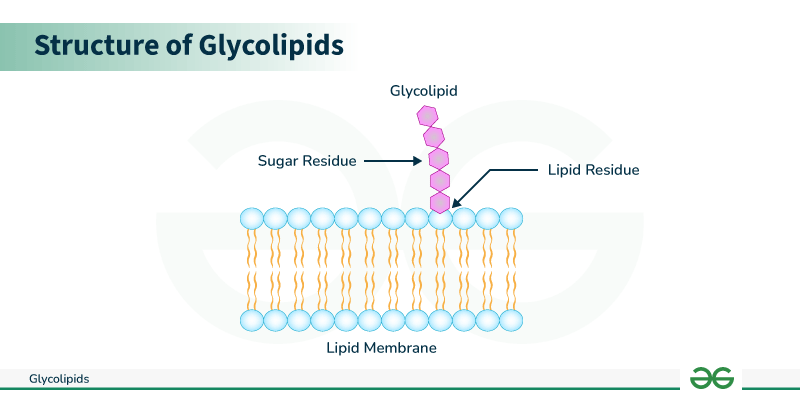
Glycolipids
carbohydrates bonded to lipids
glyco=sugar
Glycoproteins
carbohydrates bonded to proteins
lets a cell recognize another cell
Cell wall
(only plants)
provides: shape/structure, protection, control water intake
consist of cellulose (help plants stay upright)
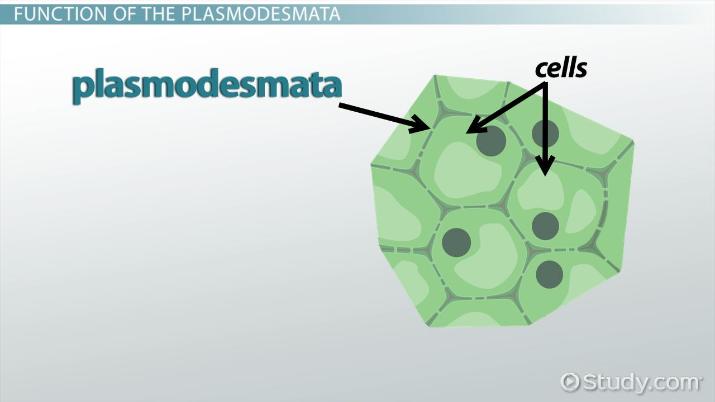
Plasmodesmata
hole-like structures in cell filled w/ cytosol that connect adjacent cells
Selective permeability
some substances can cross membrane more easily than others
small, non polar, hydrophobic molecules have easy passage
large, polar, hydrophilic molecules have hard passage
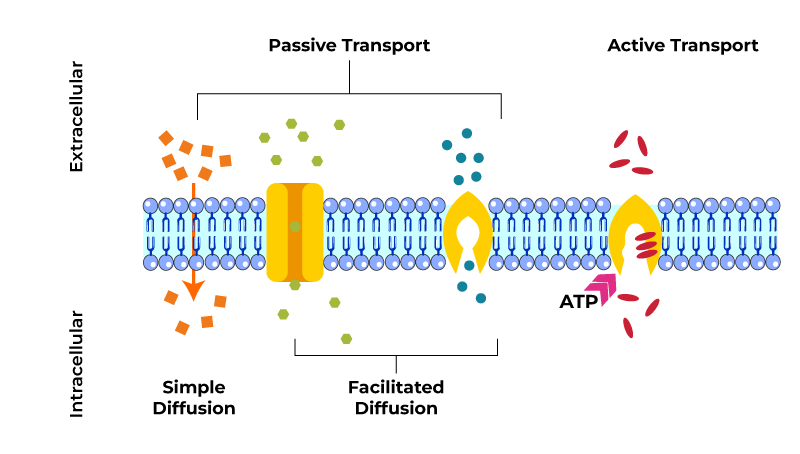
Passive transport
high → low
doesn’t require energy bc solute is moving w/ concentration gradient
import materials, export waste
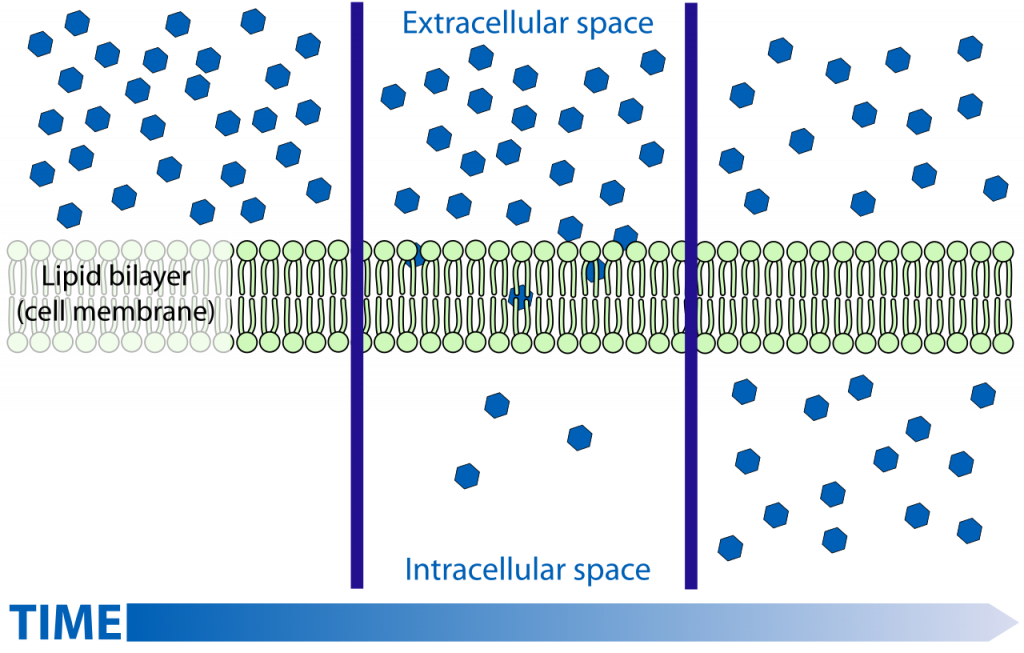
Diffusion
constant motion of molecules
high → low
move DOWN concentration gradient
diffuse across membrane
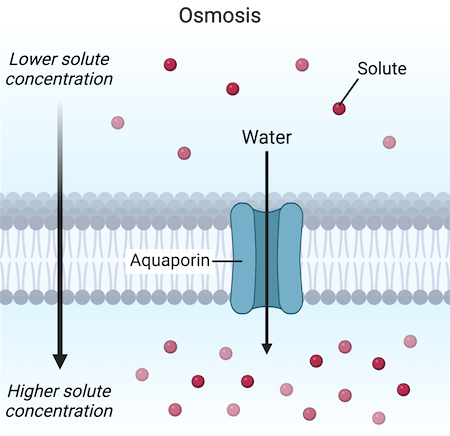
Osmosis
diffusion of water down concentration gradient across membrane (aquaporin)
low → high
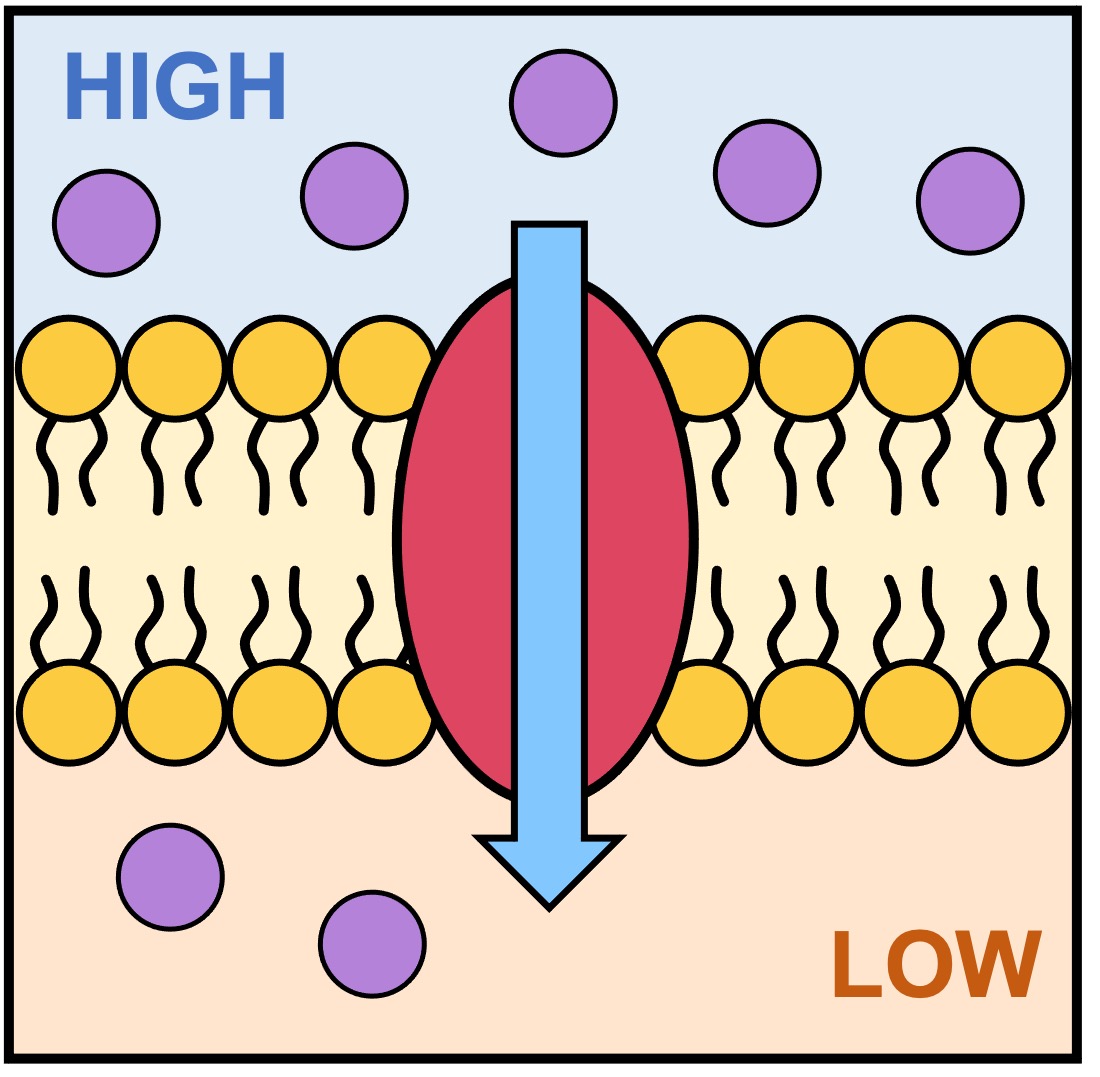
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion of molecules thru membrane via transport proteins
high → low
increases diffusion rate for: small ions, H2O, carbohydrates
transport proteins: channel & carrier
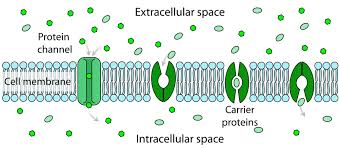
Channel Proteins
provide a channel for molecules & ions to pass
act as a “gate”
hydrophilic
high → low
no energy needed
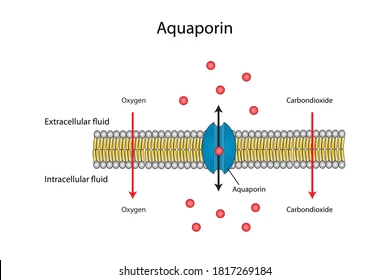
Aquaporins
specific channel protein for water
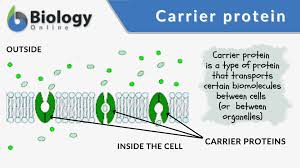
Carrier proteins
undergo conformational changes(shape change) for substances to pass
need energy
low → high
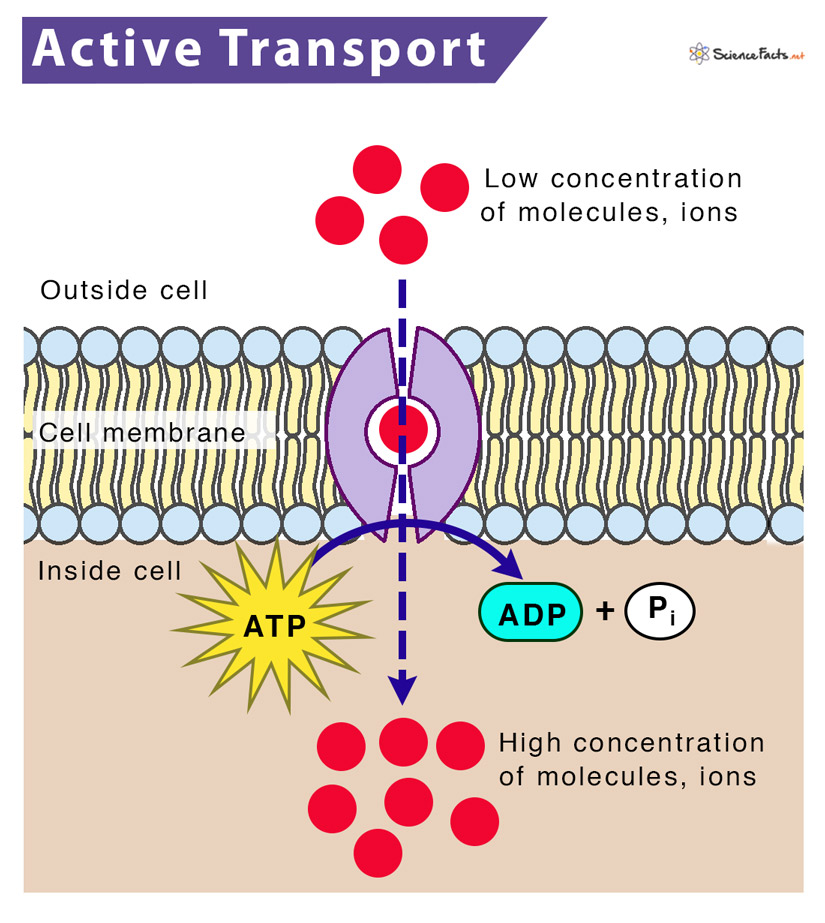
Active transport
needs energy bc solute moves against concentration gradient
Pumps
Cotransport
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
energy source used by cells
Pumps
maintain membrane potential (unequal concentrations of ions across membrane)
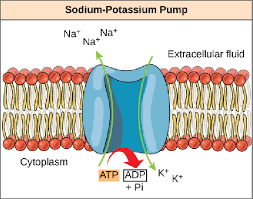
Sodium potassium pump
3 Na+ pumped out of cell
2 K+ pumped into cell
Result: +1 net charge in extracellular fluid
321 NOKIA
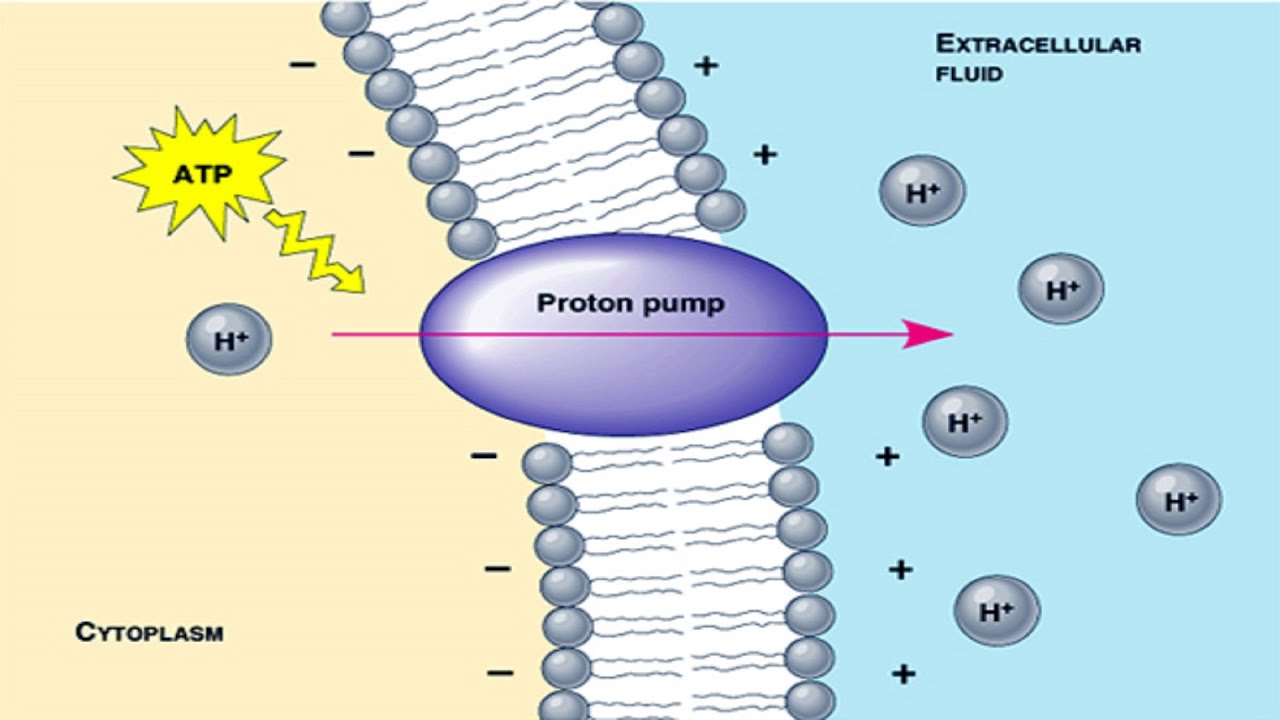
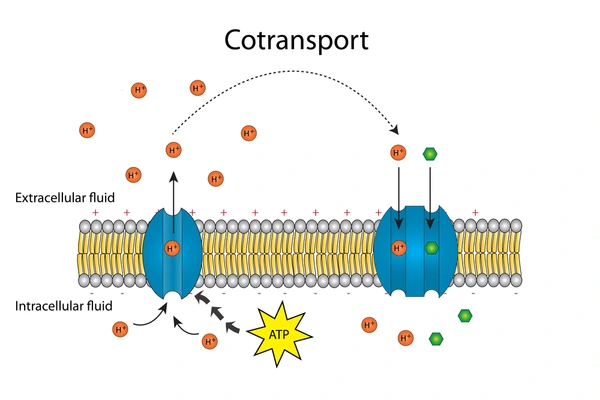
Proton pump
integral membrane protein that builds up a proton gradient
pumps H+ out of cell
Cotransport
coupling of favorable movement of 1 substance w/ unfavorable movement of another substance
favorable movement: downhill diffusion
unfavorable movement: uphill transport
Exocytosis
(exit/OUT) production of molecules via vesicles that fuse to plasma membrane
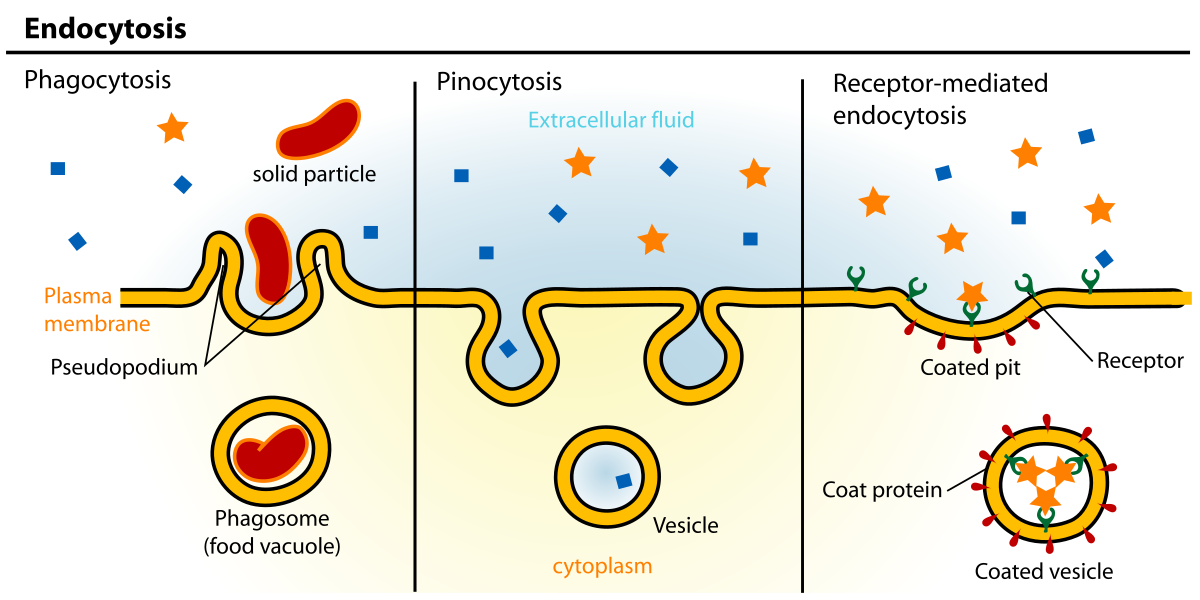
Endocytosis
(enter/IN) uptake of molecules from vesicles fused from plasma membrane
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor mediated endocytosis
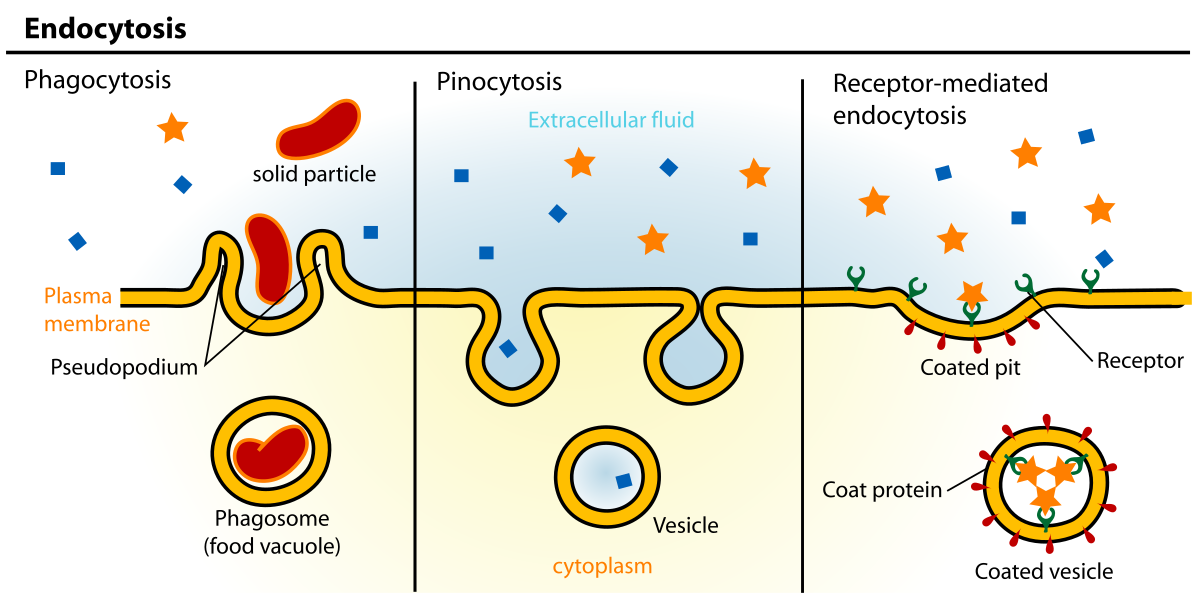
Phagocytosis
cell eats particles later digested by lysosomes
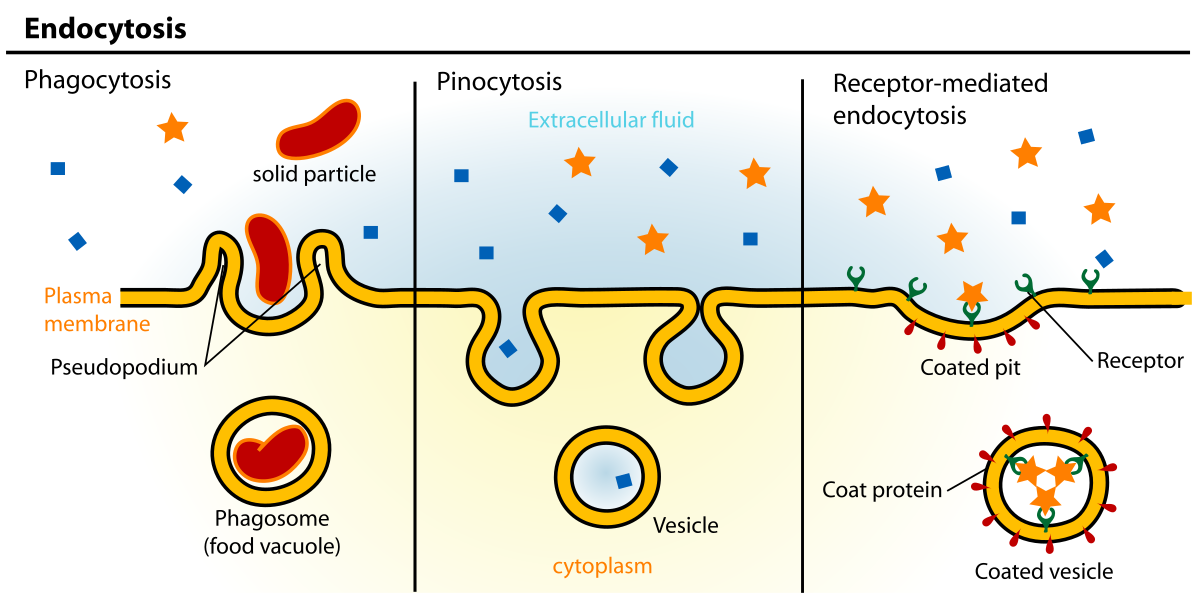
Pinocytosis
nonspecific uptake of extracellular fluid → contain dissolved molecules
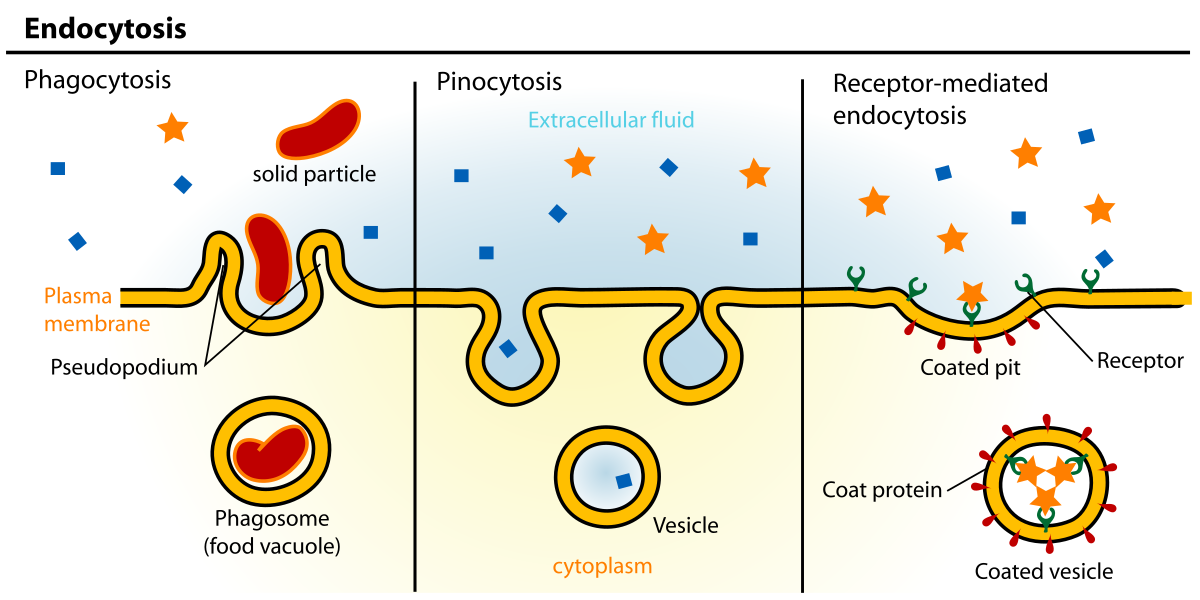
Receptor mediated endocytosis
specific uptake of molecules via solute binding to receptors on plasma membrane
lets cells take BIG amounts of a substance
Tonicity
ability of an extracellular solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
depends on concentration
isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic
Osmoregulation
cells must be able to regulate their solute concentrations & maintain water balance
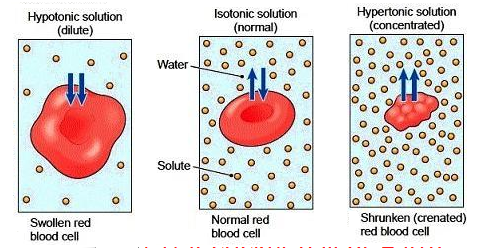
Isotonic solutions
equal concentration
water diffuses in & out of cell at same rate
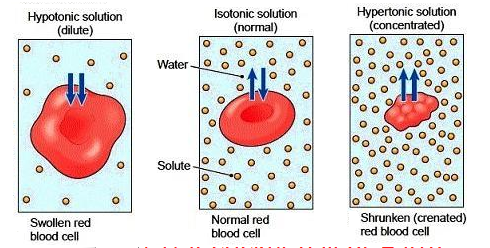
Hypertonic solutions
lose water to extracellular surroundings
SHRINK → die
higher concentration outside cell
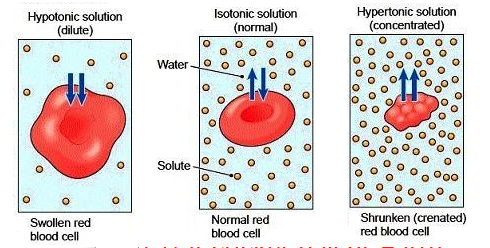
Hypotonic solutions
gain water
SWELL → explode
lower concentration outside
maintain turgor pressure
Water potential
physical property, predicts direction water will flow
high water potential → low water potential
low solute → high solute concentration
high pressure → low pressure
