NURS 3444. Exam 5 (Ch 29)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Outline of Contraceptive Counseling Process
1. Establish rapport
2. Identify those appropriate to receive contraceptive counseling
3. Assess medical history and contraindications to methods
4. Initiate contraceptive counseling points
5. Elicit informed preferences for method characteristics
6. Facilitate preference-concordant decision making
7. Counsel about method initiation and use
PATH Pregnancy Questions
- Pregnancy Attitudes
- Timing
- How important is prevention
Combined Oral Contraceptives
contain estrogen and progestin
How do COCs work?
- increase viscosity of cervical mucus
- suppressing ovulation
- thinning uterine lining
COCs and Menopause
Healthy non-smokers may take the pill until menopause
- helps reduce hormonal changes (mood swings anger, etc)
- cannot take birth control if a smoker
Extended cyclin with COCs
84 hormone pills followed by 7 placebo pills
What else can COCs be taken for besides contraception?
- Acne
- Debilitating cramps
Contraindications for estrogen-containing birth control
- Migraine with aura
- History of blood clots
- Hypertension
Risks of COCs
- VTE
- CV risk
- Drug interactions
Progestin-only pills (POPs)
Safe for Breastfeeding mothers
- 28 pills no placebos
- must be taken within 3 hour window every day
Why would POPs be prescribed?
estrogen contraindicated
Side effects of POPs
- less regular period
- more breakthrough bleeding
- ectopic pregnancy if occurs
Most effective methods of birth control
- Abstinence
- Bilateral tube ligation
- Vasectomy
- LARC
Contraceptive ring
estrogen and progesterone
- ring in the vagina for 3 weeks and remove for 1 week (to create withdrawal bleed)
- can be removed for intercourse
- can become dislodged during bowel movement
Contraceptive patch
estrogen and progestin
- applied for 3 weeks followed by patch-free week (would create withdrawal bleed)
- rotate sites weekly to avoid skin irritation
Where should contraceptive patch be placed?
Upper back, upper arm, upper buttock, lower abdomen
Where should contraceptive patches not be placed?
breast
Types of emergency contraception (EC)
- medication
- Copper IUC
Levonorgestrel (Plan B)
available OTC or prescription
- most effective if taken within 72 hours
- prevents ovulation
- does not affect an established pregnancy
Ulipristal (Ella)
available by prescription only
- may be used within 120 hours of unprotected intercourse
- works as progestin blocker and may affect an existing pregnancy
What are EC drugs more effective with
normal BMI
Contraceptive Injection
DMPA (depo provera)
- progestin-only injection
- suppresses FSH and LH inhibiting follicle maturation and ovulation
How often is DMPA given?
13 weeks
Benefits of DMPA
- can be used with breastfeeding
- less frequent or scant menses
DMPA side effects
- weight gain
- breakthrough bleeding
Contraceptive Implant
progestin-only
- approved for 3 years
- creates changes t cervical mucus
Common side effects of contraceptive implant?
Unscheduled bleeding
- BMI above 30 may make less effective
Copper IUC
- inhibiting sperm motility
- capacitation
- survival
- phagocytosis
can be used as EC
Progestin IUC
- inhospitable changes to the cervical mucus
- endometrial atrophy
- varibale effects on ovulation
Copper IUC side effect
heavier bleeding
Progestin IUC side effect
decrease menstrual bleeding and spotting
New acute cramping with IUC
can suggest IUC has slipped into the cervix
Diaphragm
Flexible saucer that is placed into the vagina to cover cervix
- does not protect against STIs
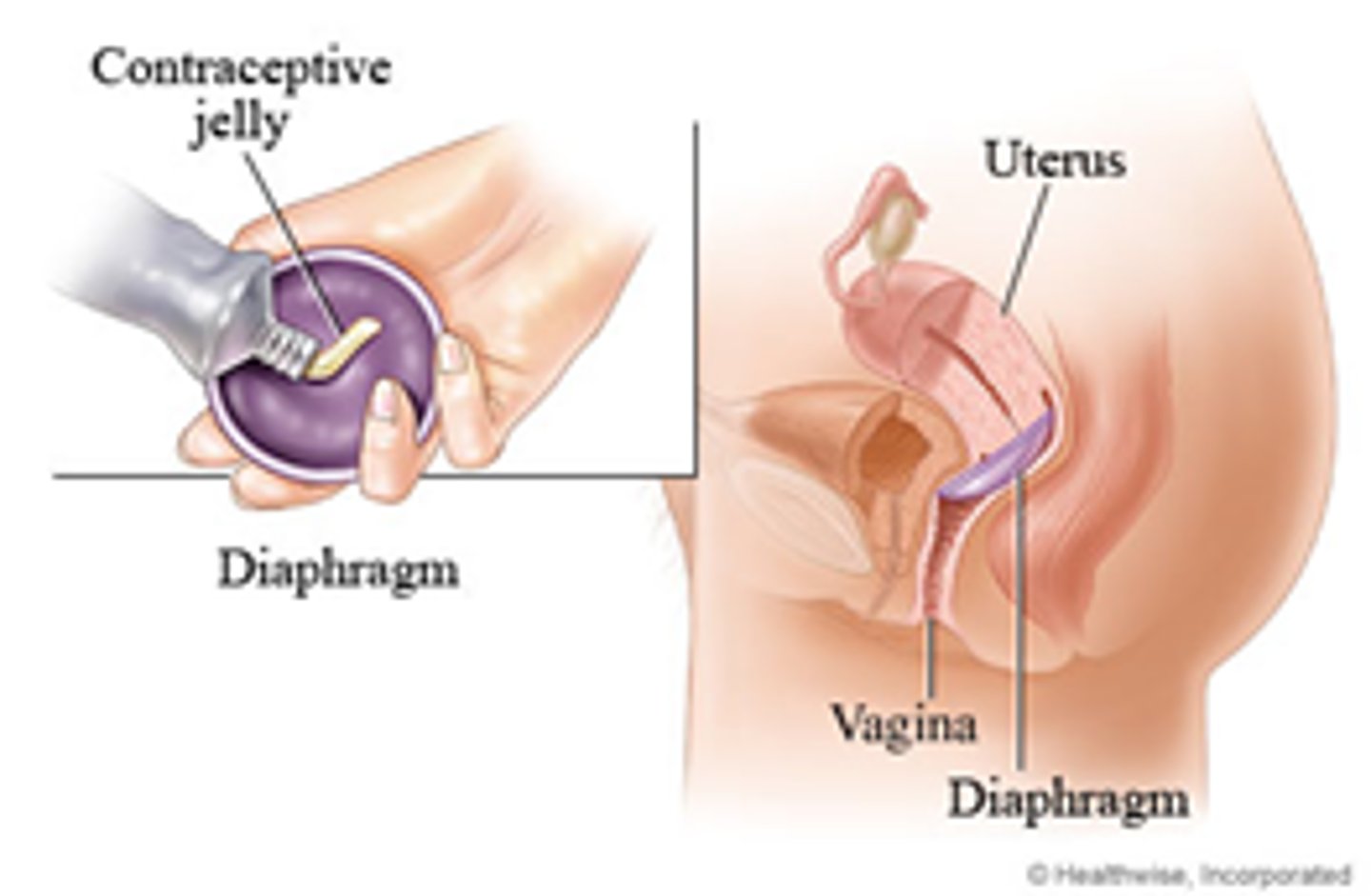
How often is the diaphragm replaced?
every 2 years
Contraceptive sponge
2 inch round, spermicide-infused, foam disk that fits over the cervix
- wet sponge prior to insertion
- must be placed up to 24 hours before intercours
Standard Days method
avoid intercourse on days 8 through 19 of the menstrual cycle
Infertility
defined as lack of pregnancy after 12 months of well-timed intercourse (6 months if the woman is over 35 years old).
What to assess for infertility
- Semen analysis
- Testicular biopsy
- Menstrual cycle
- Hysterosalpingogram
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
test for fallopian tube patency
- X-ray test with contrast to assess if tubes are blocked
Clomiphene citrate (Clomid)
Selective estrogen receptor modulator and common first-line medication to induce ovulation
Progestin-only methods
- POP
- Implant
- DMPA
- IUC
Estrogen-progestin Methods
- COC
- Patch
- Ring
Contraindications with estrogen
- migraine w/ aura
- hypertension
- smoking after age 34
Contraindications with progestin
- current breast cancer
- acute viral hepatitis
Cervical secretion method
avoid cervical intercourse on days when the cervical mucus is consistency that indicates fertility
Symptothermal method
elevate cervical secretions and temperature
- Temperature will slightly dip day of ovulation and rise sharply after ovulation
Spinnbarkeit cervical mucus
looks like egg white
- no sex with that consistency
Intrauterine insemination
Ejaculated sperm is washed to remove prostaglandins and semen proteins and the concentrated in culture media → Sperm then introduced into upper uterine cavity by way of cervix
Invitro fert
- Ovaries are stimulated to maximize oocyte recruitment
- Ovulation triggered with beta hcG
- Oocytes are retrieved by follicle aspiration guided by ultrasound
- Oocytes mixed with cleaned spermatozoa
- Embryo implanted at top of uterine cavity through the cervix (number depends on age, number of oocytes received)
- More embryos transferred → higher likelihood of conceiving
- Embryos may also be frozen