PSYC 527 Neuro Test 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is Tinbergen’s mechanistic question?
How does this behavior physiologically/neurologically occur?
What is Tinbergen’s ontogenetic question?
How does this behavior develop across the lifespan?
What is Tinbergen’s functional question?
What is the adaptive value or purpose of this behavior?
What is Tinbergen’s evolutionary question?
How did the behavior evolve across species?
What is face validity with animal models?
Does the model have surface similarity to the human condition?
What is predictive validity with animal models?
Does the model respond to treatments the same way humans do?
What is construct validity with animal models?
Does the model accurately capture the theoretical mechanisms underlying the human condition?
Eliminativism
Mental states/folk psychology should be eliminated and replaced with neuroscience. There is no mind beyond the physical (strictest philosophical answer)
Reductive physicalism
Mental phenomena are reduced to physical brain processes
Functionalism
Mental states are defined by their function, not their physical makeup
Substance Dualism
Mind and body are separate substances.
Epiphenomenalism
Mental states are by-products of physical processes with no casual power.
Emergentism
Mental states emerge from physical states but are not reducible to them. The whole is greater than the sum of the parts.
Sympathetic nervous system
Fight/Flight, increases heart rate, blood pressure, inhibits digestion, dialates pupils,
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
rest and digest, slows heart rate, increases digestion
Layer 1 Cerebral Cortex
Dendritic Layer, few cell bodies
Layers 2/3 Cerebral Cortex
Cortical-Cortical Communication
Layer 4 Cerebral Cortex
Input cortex layer, receives sensory input, dense with axons
Layer 5 Cerebral Cortex
output to the cerebral cortex, large pyramidal neurons, and motor control. Bigger somas support axons and action potentials
Layer 6 Cerebral Cortex
Outputs to the thalamus
dlPFC (Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex)
working memory, planning, and conscious attention.
vlPFC (Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex
response inhibition, inhibitory control
dmPFC (Dorsomedial Prefrontal Cortex)
attention, error detection, monitoring emotional stimuli
vmPFC (Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex)
value-based decision making, moral reasoning, emotion-based decisions.
lOFC (Lateral Orbitofrontal Cortex)
learning guided by reinforcement/punishment.
mOFC (medial orbitofrontal cortex)
decision making guided by reinforcement/punishment
Rostral PFC (Rostral Prefrontal Cortex)
higher-order social cognition, multitasking
Hippocampus
memory consolidation, spatial navigation
Amygdala
emotional processing, especially fear/threat
Cingulate cortex
emotional regulation, pain, attention
Mammillary bodies
memory, part of Papez circuit
Parts of the limbic system
Hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate cortex, mammillary bodies
Nucleus accumbens
Part of ventral striatum, central in reward, motivation, reinforcement learning, dopamine pathways.
Parts of Basal Ganglia
globus pallidus, caudate nucleus, putamen.
Basal Ganglia Direct Pathway
stimulates movement (putamen → GPi (globus pallidus internus) → thalamus → motor cortex
Basal Ganglia Indirect Pathway
inhibits movement (putamen → GPe (globus pallidus externus)→ subthalamic nucleus → GPi → thalamus → motor cortex).
Hypothalamus
Primary behavioral functions: fighting, feeding, fleeing, mating. Regulates autonomic nervous system and pituitary gland.
Major stress hormone cascade
CRF → ACTH → cortisol (stress)
Major reproductive hormone cascade
GnRH → LH/FSH → sex hormones
Major metabolic hormone cascade
TRH → TSH → thyroid hormones
Main stress hormones
CRF, ACTH, cortisol
Main reproductive hormones
GnRH, LH, FSH, estrogen, testosterone, progesterone
Oxytocin
bonding, lactation, uterine contractions, social affiliation
Vasopressin
water retention, blood pressure regulation, social bonding, and exits through the posterior pituitary gland.
Tectum
Dorsal midbrain structure containing superior colliculus (visual reflexes) and inferior colliculus (auditory reflexes)
Pons
Contains reticular formation; regulates sleep, arousal, motor control pathways
Astrocytes
Support neurons, maintain BBB, regulate neurotransmitters and give metabolic support
Oligodendrocytes
form the myelin in the central nervous system
Microglia
Immune defense in CNS, remove debris and shuttles other things.
Blood brain barrier
Protective barrier formed by endothelial tight junctions and astrocytes; regulates passage of substances. 3 ways to enter: lipid soluble, active transport, very small molecule.
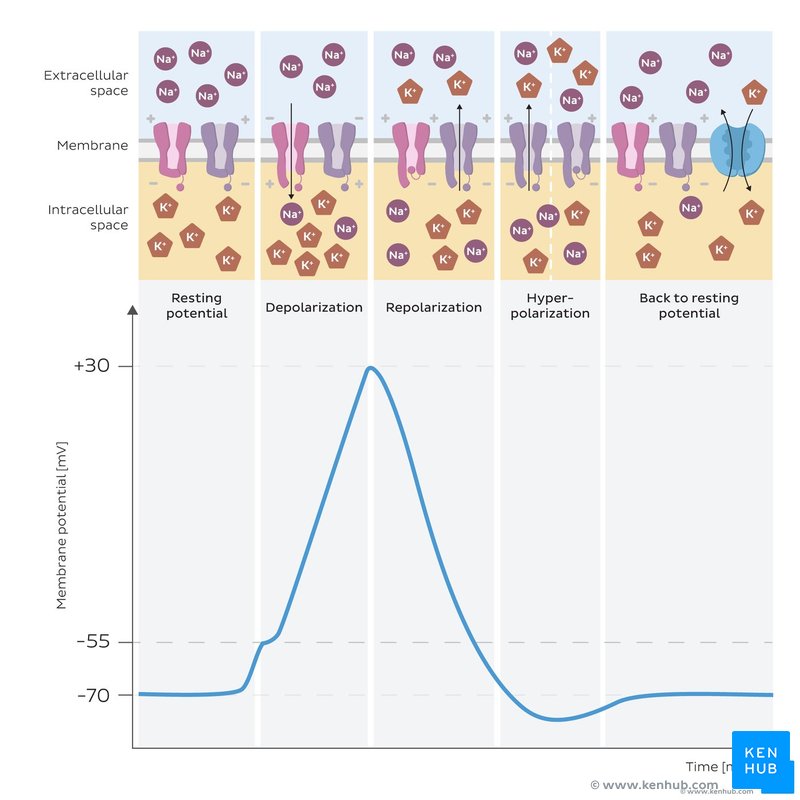
Resting membrane potential
Approximately –65 mV. Maintained by Na+/K+ pump (actively transports 3 Na+ and 2 K+ in per APT) and leaky K+ channels (allows passive movement of K+ out of cell, crucial for resting potential)
Action potential steps
Threshold reached → Na+ channels open (depolarization, Na+ influx).
Na+ channels inactivate, K+ channels open (repolarization, K+ efflux).
Hyperpolarization due to continued K+ efflux. Return to resting state via Na+/K+ pump
Outward rectifying
K+ channels, open during depolarization, allow K+ efflux (repolarization), which slows down the action potential by increasing the refractory period and delaying repolarization
Inward Rectifying
stabilize resting potential, allow K+ influx at negative potentials, speed up refractory period, faster repolarization
Steps of Synaptic Transmission
NT synthesis & transport to the terminal.
2. Action potential reaches presynaptic terminal.
3. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open → Ca2+ influx.
4. Vesicles fuse with the membrane → NT release.
5. NT binds postsynaptic receptors (ionotropic or metabotropic).
6. Postsynaptic potential generated (EPSP/IPSP).
7. NT cleared via reuptake (transporters) or degradation (enzymes).
Ionotropic and metabotropic postsynaptic receptors
Ionotropic – ligand-gated ion channels, fast response (e.g., AMPA, GABA-A).
Metabotropic – G-protein coupled, slower but modulatory (e.g., mGluR, GABA-B).
Agonist
A substance that binds to a receptor and activates it, mimicking the natural neurotransmitter
Antagonist
A substance that binds to a receptor but blocks or dampens its activation
Inverse Agonist
Binds to receptor and produces the opposite effect of an agonist. Ex: clozapine)
Partial Agonist
Binds to receptor and activates it, but produces a weaker response than a full agonist.
Competitive antagonist
Competes with agonist at the same binding site; effect depends on relative concentration.
Noncompetitive antagonist
Binds to a different site and reduces receptor function regardless of agonist concentration
Positive allosteric modulator
Binds at a site distinct from the agonist and increases receptor activity (e.g., benzodiazepines on GABA-A). Increases efficacy
Negative allosteric modulator
Binds at an allosteric site and decreases receptor activity. Decreases efficacy
Acetylcholine
First NT discovered.
Brain regions / pathways: Basal forebrain → cortex & hippocampus (learning, memory). Pons (REM sleep), Neuromuscular junction & autonomic nervous system
Behavioral functions: Learning, memory, REM sleep, muscle contraction
Receptors: Muscarinic (M1–M5): excitatory or inhibitory (metabotropic), Nicotinic: ionotropic, excitatory (Na+ influx). Think about ACh as the knuckles, 1,3,5 are excitatory, 2-4 are inhibitory
Drug examples: Nicotine (agonist, nicotinic), Atropine (antagonist, muscarinic)
Dopamine
Brain regions/pathways: Nigrostriatal system: substantia nigra → striatum (motor control), Mesolimbic system: VTA → limbic system (reward, motivation), Mesocortical system: VTA → cortex (cognition, planning, problem solving)
Behavioral functions: Motor control, reward & reinforcement, motivation, executive functioning
Receptors:
D1 family (D1, D5): excitatory (Na+ channels, phasic firing)
D2 family (D2, D3, D4): inhibitory (K+ channels, tonic firing)
Drug examples: Chlorpromazine (D2 antagonist, antipsychotic)
Norepinephrine
Brain regions / pathways: Locus coeruleus → widespread forebrain targets (arousal, attention, vigilance), Sympathetic nervous system
Behavioral functions: Arousal, vigilance, stress response, appetite regulation (increases hunger)
Receptors:
Alpha-1 (excitatory) → agonist: phenylephrine (decongestant)
Alpha-2 (inhibitory, autoreceptors) → agonist: clonidine (antihypertensive, reduces feeding)
Beta (excitatory) → antagonist: propranolol (reduces anxiety, treats social phobia)
Drug examples: Clonidine (α2 agonist), Propranolol (β antagonist)
Serotonin
Brain regions/pathways: Cell bodies in raphe nuclei (brainstem) → limbic system & cortex, 98% in gut, ~2% in brain
Behavioral functions: Mood regulation, sleep & arousal, appetite, pain modulation
Receptors: 5-HT1 (inhibitory, autoreceptors), 5-HT2 (excitatory), 5-HT3 (ionotropic, inhibitory), 5-HT4–7 (metabotropic, mixed roles)
Drug examples: Buspirone (5-HT1A partial agonist, anxiolytic/antidepressant)
Glutamate
Brain regions / pathways: Widespread in cortex & hippocampus (primary excitatory NT)
Behavioral functions: Excitation, learning, memory, synaptic plasticity
Receptors: NMDA: Ca²+ channel (learning/memory, LTP), AMPA: Na+ channel, Kainate: Na+ channel, Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs)
Drug examples: Ketamine (NMDA antagonist, anesthetic/antidepressant), PCP
GABA
Brain regions/pathways: Widespread in cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum (main inhibitory NT)
Behavioral functions: Inhibition, prevents seizures, regulates anxiety, sleep, and motor control
Receptors: GABA-A: ionotropic, Cl- channel, GABA-B: metabotropic, K+ channel
Drug examples:
Diazepam (Valium, benzodiazepine, GABA-A agonist)
Barbiturates (stronger GABA-A agonists)