Clinical Medicine - Nephrology & Genitourinary
1/455
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
456 Terms
Kidneys
regulate blood volume/composition, reguate pH, and produce hormones, excrete waste
Renal corpuscle
glomerulus - filters water and dissolved substances from plasma
glomerulus capsule - receives glomerular filtrate
Renal tubule - proximal convoluted tubule
reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, creatine, acids, and ions by active transport
reabsorbs water by osmosis
reabsorbs chloride and other negative ions by electrochemical attraction
actively secretes penicillin, histamine, creatine, and hydrogen ions
Renal tubule - descending limb of nephron loop
reabsorbs water by osmosis
reabsorbs sodium, potassium, and chloride ions by active transport
Renal tubule - ascending limb of nephron loop
reabsorbs sodium ions by active transport
reabsorbs water by osmosis
secretes hydrogen and potassium ions by electrochemical attraction
Renal tubule - distal convoluted tubule
reabsorbs water by osmosis
Process of urination
visceral sensory fibers relay to the spinal cord (S2-S4) that the bladder wall is stretched
stimulation of parasympathetic nerves causes detrusor muscle to contract and internal urethral sphincter to relax
somatic motor neurons in pudendal nerve causes relaxation of external urethral sphincter and contraction of bulbospongiosus muscles - expels last drops of urine from urethra
What prevents incontinence
mental status
ambulation
physical/muscle issues
outflow issues
Incontinence
involuntary loss of urine or stool in a sufficient amount or frequency which constitutes a social and/or health problem
Is incontinence more common in men/women?
women
Incontinence is related to decreases in
detrusor muscle contractility
maximum bladder capacity
maximum flow rate
ability to withhold voiding with an increase in postvoid residual (PVR)
Complications of urinary incontinence
increased fall risk
nocturia and sleep disruption
hydronephrosis and renal dysfunction from urinary retention
embarrassment/social withdrawal
reduced fluid intake
compromised skin integrity
Types of incontinence
stress - MC
urge
overflow
functional
mixed
Stress incontinence
impaired urethral support from pelvic floor muscle weakness - intrinsic sphincter deficiency
increased intra-abdominal pressure
Urge incontinence
uninhibited bladder contractor due to detrusor hyperactivity
leakage of urine after abrupt urge to void
inability to delay voiding after sensation of bladder fullness is noticed - large or small volume
Overflow incontinence
incomplete emptying due to impaired detrusor contractility, bladder outlet obstruction (BPH or prolapse), or neuropathy
frequent small-volume leakage, weak stream, dribbling, hesitancy, frequency, and nocturia
Functional incontinence
urine loss caused by the inability to reach the toilet because of environmental barriers, physical limitations, loss of memory, or disorientation
urine loss is large/complete
Exacerbating conditions of incontinence
constipation
dehydration or UTI
pulmonary edema, peripheral edema, hypercalcemia, hyperglycemia
COPD/cough
delirium, dementia, depression
spinal cord injury, neurologic issue
urogenital atrophy
Reversible causes of incontinence
DRIPSS
Delirium
Restricted mobility
Infection, inflammation, impaction
Pharmaceuticals, psychological, polyuria
Stones
DDx for incontinence and OAB
DRIPSS
GU malignancy
prolapse
post-surgical
neurologic
3 incontinence questions
during the last 3 months:
-have you leaked urine?
-did you leak with activity, urge, or neither?
-did you leak most often with activity, urge, neither, or both?
Common meds that can cause urinary incontinence
antihypertensives
pain relievers
psychotherapeutics
others
Incontinence physical exam
visual inspection with standing
distended bladder on abdominal exam
rectal exam for hard stool in vault
prostate exam
genital exam for skin integrity, adequacy of pelvic floor, and prolapse
mental status
Incontinence lab workup
exclude metabolic, infectious, and malignant conditions:
urinalysis
urine cytology
renal function (BUN, creatine, EGFR)
serum electrolytes
blood glucose and calcium
Incontinence testing/procedures
bladder US
renal US and/or CT
urodynamic testing
Assessment of post-void residual (PVR)
bladder US
less than 50mL should be present after voiding
more than 200mL indicates dysfunction
Urodynamic testing
probes into urethra and bladder testing muscular contractions
more invasive - last resort done by urology
Incontinence general management
treat underlying or reversible etiologies and prevent constipation
smoking cessation
fluid intake timing and amount (don't restrict fluid)
reduce caffeine, alcohol, and carbonation
prompted voiding
weight loss
pelvic floor exercises
Stress incontinence treatment
general/lifestyle measures
pelvic floor therapy
topical vaginal estrogen
trans or periurethral injection of bulking agents
Urge incontinence treatment
general lifestyle/measures
pelvic floor exercises
1st line: antimuscarinic/anticholinergic - oxybutynin, tolterodine, solifenacin, darifenacin
2nd line: beta 3 agonists: mirabegron and vibegron
botox into detrusor muscle
neuromodulation
surgery - last resort
Anticholinergic/antimuscarinic MOA
inhibiting involuntary detrusor muscle contractions at efferent pathway
Beta 3 receptor agonist MOA
inhibits afferent nerve firing independent of the relaxing effects on the bladder smooth muscle
Overflow incontinence treatment
relief of obstruction (constipation or BPH)
catheterization
alpha-adrenergic antagonists for BPH
micturition maneuvers - suprapubic pressure, Valsalva, double voiding
Pessaries
adds support to vagina and increases tightness of the tissues and muscles of the pelvis
Overactive bladder (OAB)
chronic syndrome of urinary urgency which may be accompanied by frequency, nocturia, +/- small volume of incontinence without UTI or pathology
dx of exclusion
Overactive bladder pathophysiology
multifactorial - true cause unknown
Overactive bladder diagnosis
same as incontinence - rule everything else out
Overactive bladder treatment
general/lifestyle measures
antimuscarinic/anticholinergic agents - oxybutynin
beta 3 receptor agonists - mirabegron and vibegron
Incontinence and OAB - elderly patient considerations
side-effects
drug interactions
renal and hepatic impairment
cost
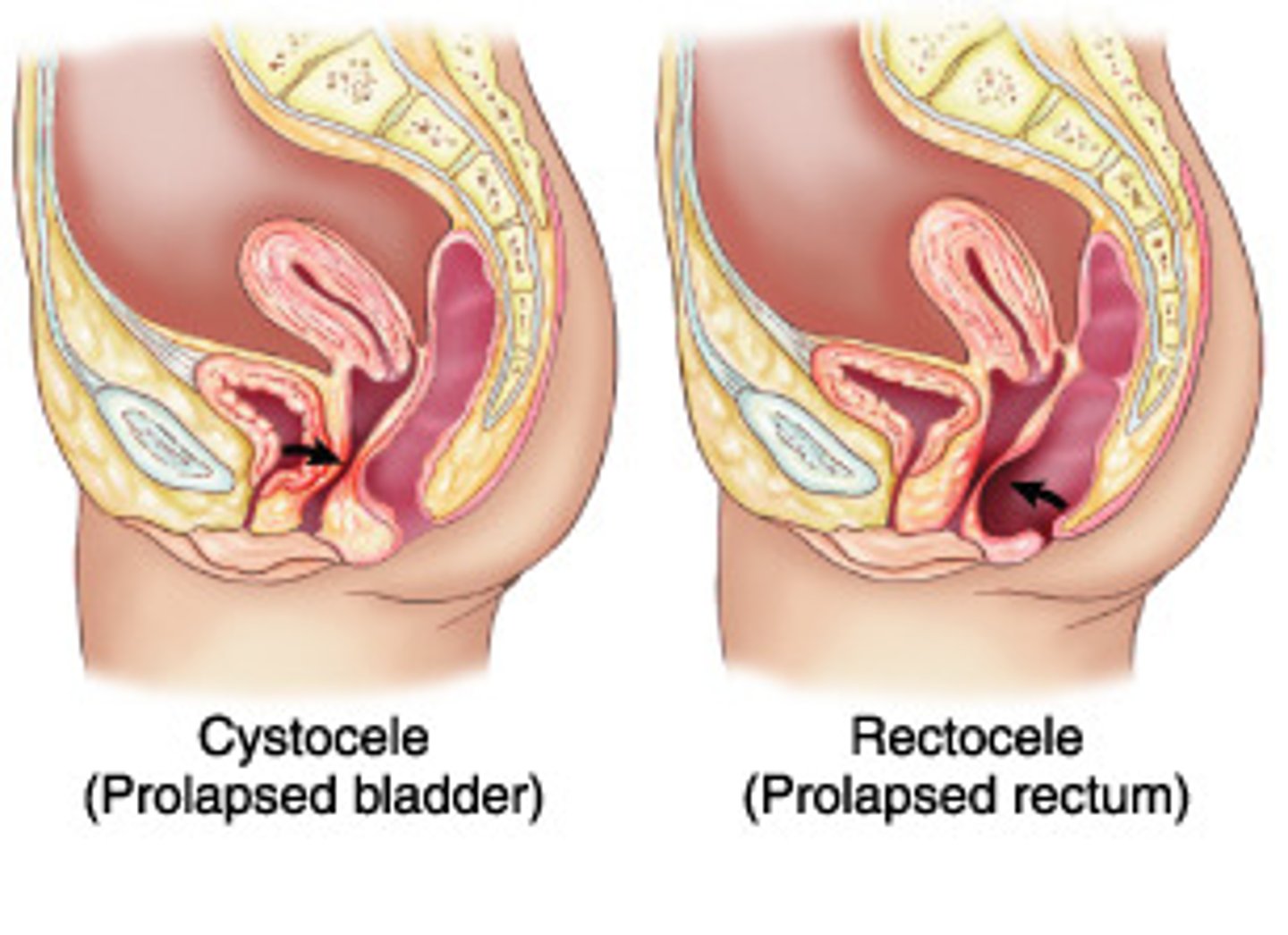
Cystocele
bladder prolapse
vaginal hernia where bladder drops down into vagina causing soft anterior fullness
may be accompanied by urethrocele due to detachment from pubic symphysis during childbirth
Cystocele diagnostics
pelvic exam
US to help further evaluate
Cystocele treatment
improve constipation, weight loss, limit straining
pelvic muscle training
pessaries
only curative treatment: surgery
Clinically significant ejaculation disorders
failure of emission
retrograde ejaculation
premature ejaculation
hematospermia
anorgasmia
Retrograde ejaculation or failure of emission may result from
anatomic abnormalities
functional abnormalities
DM
surgery
urethral strictures
meds - alpha blocker therapy, antipsychotics
MS
peripheral neuropathy
Painful ejaculation etiology
infectious
obstructive
psychological
Hematospermia etiology
idiopathic
secondary to prolonged abstinence
infection or inflammation of the GU tract
self-limiting and typically resolves with 10-15 ejaculations
Anorgasmia etiology
spinal cord injury
psychological factors
dysfunctional sexual techniques
medications (SSRIs)
Ejaculation and orgasm disorders
labs: UA, CBC, BMP, PT, PTT, STD testing
US, CT, +/- MRI
Ejaculation and orgasm disorders treatment
retrograde and failure of emission - reassurance unless trying to conceive
premature - psychotherapy, behavioral interventions (coronal squeeze or start/stop), communication, SSRIs, topical lidocaine, TCAs
painful - NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, abx
Erectile dysfunction
consistent inability to maintain an erect penis with sufficient rigidity to allow sexual intercourse due to arterial, venous, neurogenic, psychogenic causes, or anti HTN or antidepressant medications
Loss of libido may indicate
androgen deficiency
Loss of orgasm if libido and erections are intact
psychological origin
Erectile dysfunction - questions to ask
timing and frequency
normal erections in morning or sleep
hx of dyslipidemia, HTN, neuro, DM, CKD, endocrine, depression, or vascular disease
drugs, alcohol, tobacco
Erectile dysfunction labs
urinalysis
fasting lipids
serum glucose
testosterone
prolactin
free testosterone and LH if testosterone and prolactin abnormal
Erectile dysfunction imaging
duplex US
pudendal arteriography
Erectile dysfunction diagnostic procedures
nocturnal penile tumescence testing for frequency and rigidity
direct injection of vasoactive substances
Erectile dysfunction treatment
PDE-5 inhibitors: sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, avanafil
prostaglandin urethral suppository - alprostadil
injection of prostaglandins into base of penis
testosterone replacement
behavioral therapy
vacuum erection device
penile prosthesis
surgery for venous/arterial disorders
Which PDE-5 inhibitor can be taken daily?
tadalafil - also helps with BPH
Contraindication for PDE-5 inhibitors
nitrates!
Priapism
persistent and painful erection +/- sexual stimulation
may be due to low-flow (veno-occlusive) or high-flow (increased arterial flow without increased venous flow)
Priapism epidemiology
peak ages: 5-10 (consider malignancy or sickle cell) and 20-50 (consider drug use)
Low-flow priapism
more common than high flow
edema of cavernosal trabeculae resulting in stasis, thrombosis, venous occlusion, fibrosis, and scarring
similar to compartment syndrome
High-flow priapism
cavernosal artery rupture leading to arteriocavernous fistula
Priapism etiology
idiopathic: prolonged sexual arousal
secondary: sickle cell, DM, leukemia, solid tumor, spinal cord injury, trauma, ED treatments, cocaine
Priapism treatment
non ischemic: ice packs and analgesia
ischemic: aspiration of corpora, penile injection of phenylephrine/epinephrine, urgent urology consult
If priapism is lasting longer than ____ hours, 90% of men will no longer be able to become erect.
24
Phimosis
fibrous constriction of foreskin preventing retraction
often associated with balanitis and may cause urinary retention
normal in first few years of life
may require elective circumcision
Paraphimosis
retracted foreskin develops a fixed constriction proximal to the glans
penis distal to the constricting foreskin may become swollen and painful or even gangrenous and may result in urinary retention
Paraphimosis management
manual reduction: squeeze glans for 5-10 min to reduce size
ice
urgent or elective circumcision
Balanitis
inflammation of penile head
if foreskin is involved - balanoposthitis
Balanitis S&S
itching, tenderness, pain, dysuria, local edema, erythema
ulceration and lymph node enlargement
superimposed bacterial infections
inability to void
Balanitis etiology
poor hygiene
infectious: MC candida, Neisseria gonorrhea, HPV, herpes, syphillis, HIV, trich, staph aureus, anaerobic bacteria
Balanitis diagnostics
KOH
STD testing
wet mount for trich
Balanitis treatment
topical and/or systemic - antifungals, steroid, abx
hygiene education - retraction and bathing
warm Sitz baths
circumcision consideration
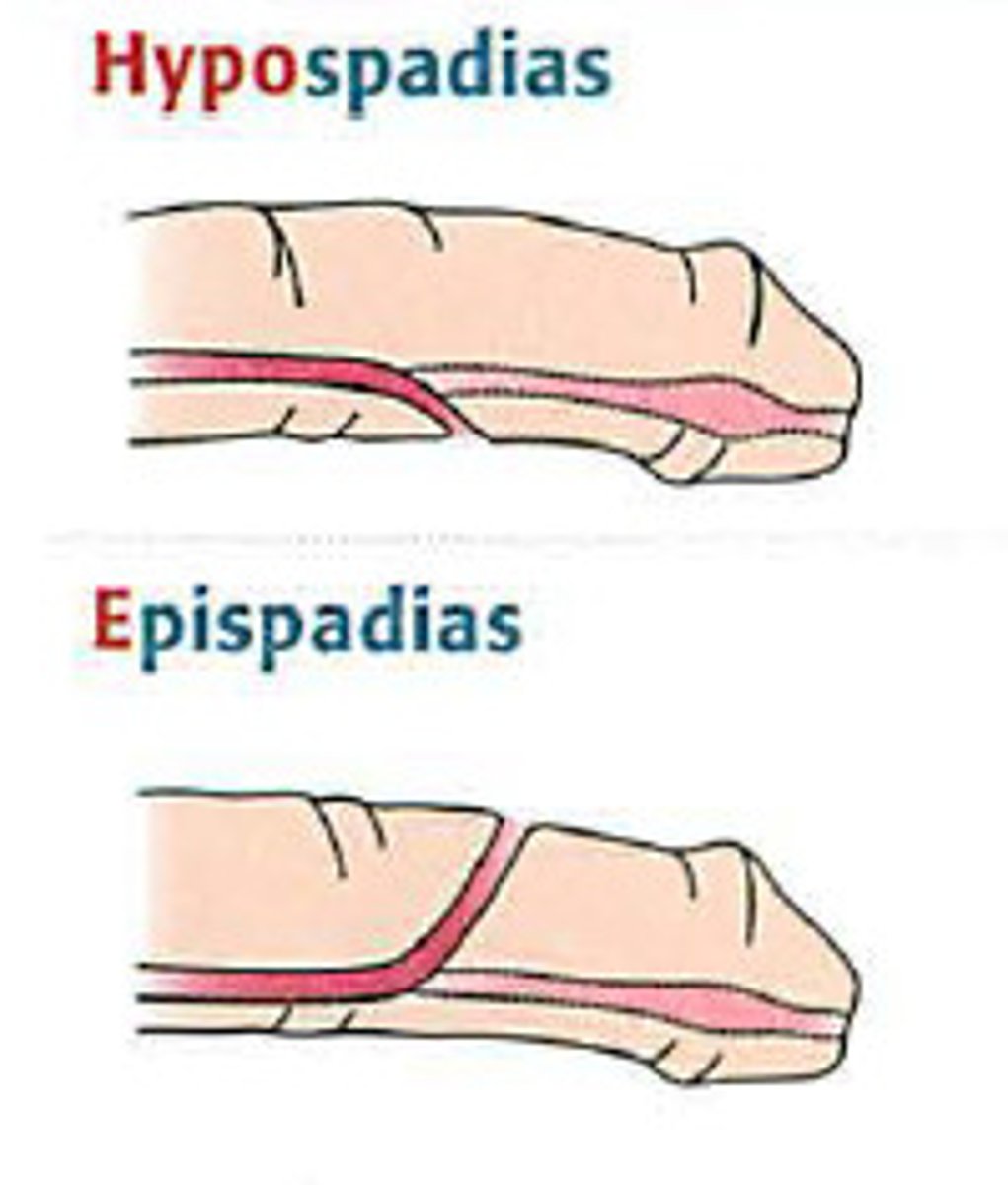
Hypospadias
urethral folds fail to mature in utero - urethral meatus is ventrally displaced on glans on shaft of penis or more proximal at scrotum or perineum
may interfere with urination, ejaculation, and cosmetic appearance
Hypospadias management
do not circumcise because foreskin may be used in repair
IF associated with cryptorchidism or scrotal/perineal locations then workup with US, karyotype, and electrolytes
referral and early repair depending on severity
Epispadias
rare congenital anomaly associated with bladder exstrophy
urethra opens on dorsum of penis with deficient corpus spongiosum and loosely attached corpora cavernosa
Male infertility
inability to conceive after 1 year of unprotected intercourse
Male infertility etiology
testicular defects in spermatogenesis
idiopathic
sperm transport disorders
endocrine - hypogonadism
FSH and LH in men
FSH stimulates Sertoi cells for spermatogenesis
LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone
Male infertility diagnostics
semen analysis
endocrine testing
imaging of accessory glands/ducts
genetic testing
Semen analysis
sample collected after 3-7 days of abstinence and second sample taken at least 1 week apart
looks at volume, pH, concentration, count, motility, morphology, debris, agglutination, leukocyte count, immature germ cells
Male infertility imaging
scrotal US
transrectal US - prostate and seminal vesicles
MRI of head, penis, and scrotum
Low testosterone, high FSH, high LH
primary (hypergonadotropic) hypogonadism
order karyotype
Normal testosterone and LH, high FSH
primary (hypergonadotropic) hypogonadism
seminiferous tubule damage without Leydig cell dysfunction
Low testosterone, but FSH and LH low-normal
secondary (hypogonadotrophic) hypogonadism
High testosterone and LH but normal FSH
partial androgen resistance
Normal testosterone, LH and FSH
further eval
Low sperm count and very low LH in a man who is very muscular
suspicious for androgen abuse
Horseshoe Kidney
MC renal fusion abnormality occurring in 5th-9th week
most fuse at lower poles
2 separate excretory renal units and ureters remain
isthmus can be of renal parenchyma or a fibrous band
asymptomatic or complications later in life
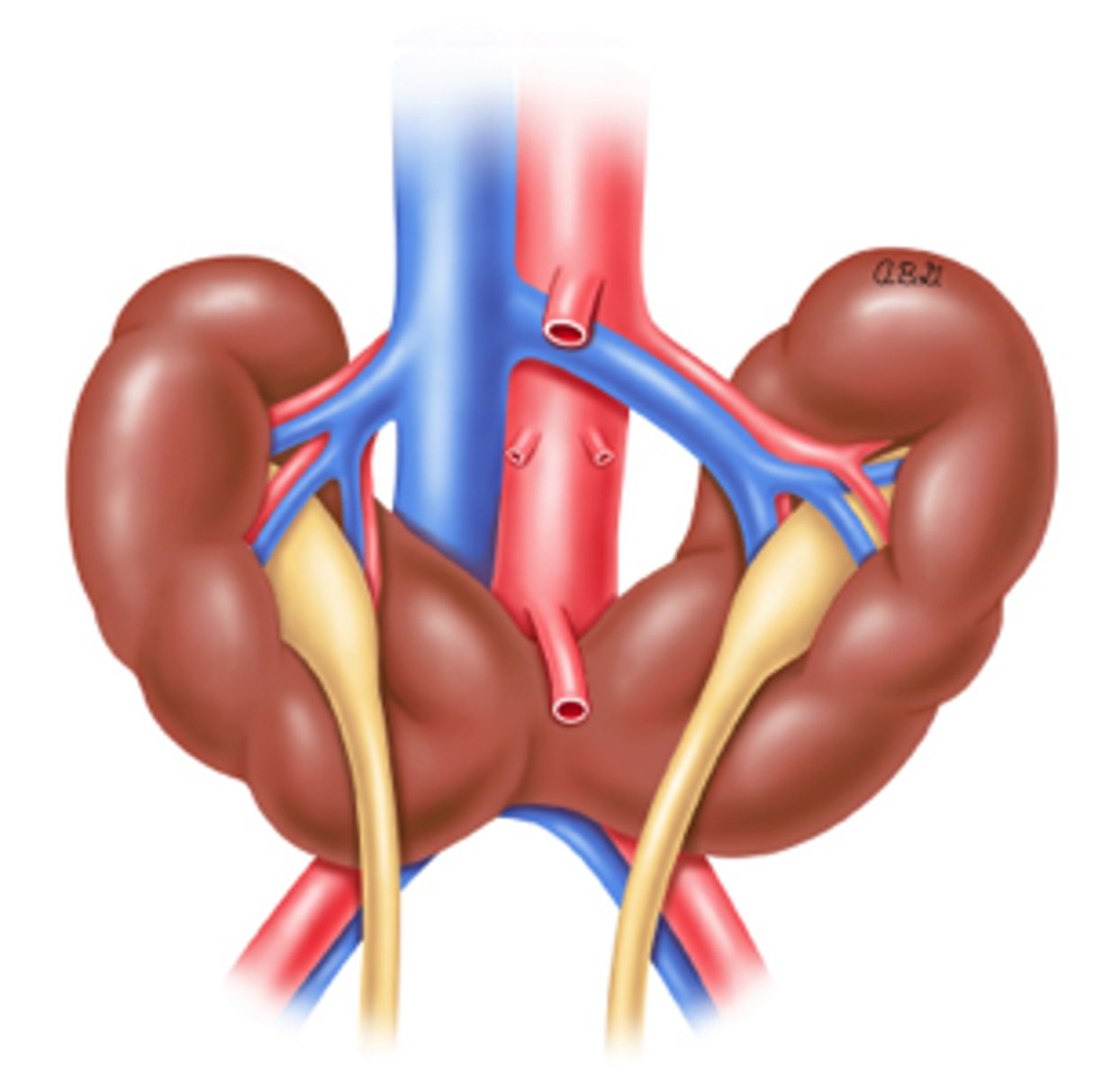
Horseshoe kidney results from
normal embryologic migration of the kidneys
Normal embryogenesis of kidneys
pronephros
mesonephros
metanephros - where permanent kidney is formed
Horseshoe kidney epidemiology
male > females
Horseshoe kidney associated conditions
vesicoureteral reflux
ureteropelvic junction obstruction
nephrolithiasis
cryptorchidism
Turnery syndrome or trisomy 13, 18, and 21
Horseshoe kidney eval
PE often normal
often detected on 20 week anatomy scan
postnatal renal US
voiding cystourethrogram to detect vesicoureteral reflux
creatinine
Horseshoe kidney management
monitor for renal function
US every 2 years
creatinine
blood pressure
urinalysis
Nephrolithiasis
kidney stones
hard crystalline formations in the urinary tract causing pain, NV, urinary symptoms

Nephrolithiasis epidemiology
men > women
Ureteral stones
kidney stones migrate to ureters
Ureteral stones are common at narrow areas like
ureteropelvic junction
ureterovesical junction
crossing at iliac vessels