Chem - 1B Matter and Change
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Chemistry
the study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter, the processes that matter undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany these processes
physical science
All chemistry deals with chemicals - any substance that has a definite composition
Energy
the ability to move or change matter
Periodic Table
where elements are organized
groups/families: Vertical columns of the periodic table (18)
periods: Horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table
zigzag line on the periodic table separates
metals (left) and nonmetals (right)
Types of Elements
Metals
Nonmetals
Metalloids
Metals
elements that are good electrical conductors and good heat conductors
Most are:
solid at room temperature
malleable (can be hammered or rolled into thin sheets)
ductile (can be drawn into a fine wire)
silvery or grayish white luster
Nonmetals
elements that are poor conductors of electricity and heat
Most are:
gases
one is a liquid (bromine)
solids include carbon, phosphorus, and sulfur, and are britter
Metalloids
elements that have some characteristics of both metals and nonmetals
Elements located on staircase between metals and nonmetals
All are solid at room temperature, less malleable but not very brittle, semiconductors of electricity
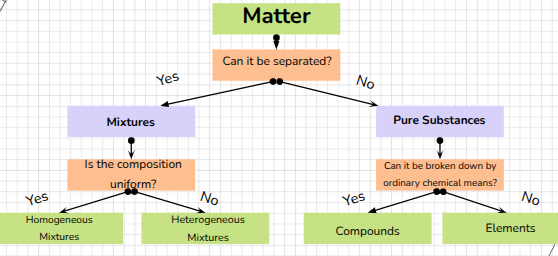
Matter
anything that has mass (measure of the amount of matter) and takes up space
Atom
the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element
Element
pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances
made of one type of atom
Compound
a substance that can be broken down into simple stable substances
Mixture
a blend of two or more kinds of matter, each of which retains its own identity and properties
Types of mixtures
Homogeneous
Heterogenous
Homogeneous
Mixtures uniform in composition also called solutions
ex:
salt water
iced tea
maple syrup
Heterogenous
Mixtures that are not uniform throughout
ex:
chocolate chip cookie
salad
boba
Classification of matter
Extensive Properties
Depend on the amount of matter that is present like volume and mass
ex:
Volume
Mass
Intensive Properties
Does not depend on the amount of matter present
ex:
Color
Melting Point
Density
Conductivity
Chemical Properties
Relate to a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform one substance into different substances
ex:
Burning Charcoal + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxide
Chemical Changes
Changes in which one or more substances are converted into different substances
Also called Chemical Reactions
Reactant → Products
ex:
Carbon + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxide
How do you know a chemical change has occurred?
color change (cooking)
formation of a precipitate (chunky mik)
formation of a gas (baking soda + vinegar)
evolution of energy as light (glowstick)
evolution of energy as heat (burning wood)
Physical Properties
Characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance including melting point and boiling point
Physical Changes
Change that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance
ex
melting
grinding
cutting
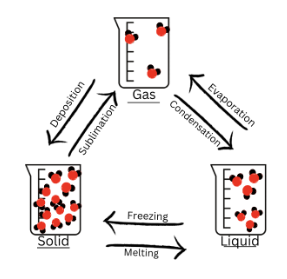
Change of State
a physical change of a substance from one state to another (ripping up paper)
What are the states of matter?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
Solid
definite volume and definite shape
Very high density because particles are extremely close together
Incompressibility since they are so tightly packed
Low to no diffusion (millions of times slower than liquid diffusion)
Form crystal structures or amorphous solids
Crystal
A type of solid where there is a 3D arrangement in a fixed pattern and includes gemstones
Amorphous
A type of solid that lacks definite pattern
includes glass and plastic
Liquid
Definite volume, but an indefinite shape
takes shape of the container
Higher density than gases due to close arrangement of particles (medium density)
Attraction between liquid particles caused by intermolecular forces
Less compressible than gases
Liquids will diffuse together
Liquids have surface tension - force that pulls adjacent liquids together
Capillary action - attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
Gas
No definite shape or volume
Can expand to fill any volume
Gas particles glide past each other because they don’t attract
Extremely low density
Highly compressible (can be squished together to make smaller volume)
Gases will mix together automatically
Diffusion - spontaneous mixing caused by random motion
Effusion - process by which gas particles pass through a tiny opening
Plasma
a high-temperature physical state of matter in which atoms lose most of their electrons, particles that make up atoms
Surface tension
force that pulls adjacent liquids together
Capillary action
attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
Diffusion
spontaneous mixing caused by random motion
Effusion
process by which gas particles pass through a tiny opening
Chart of Solid, Liquid, Gas + their Properties
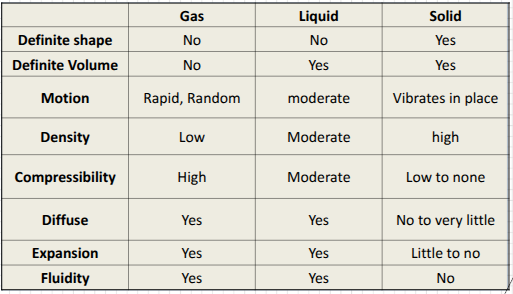
Diagram of Change of State
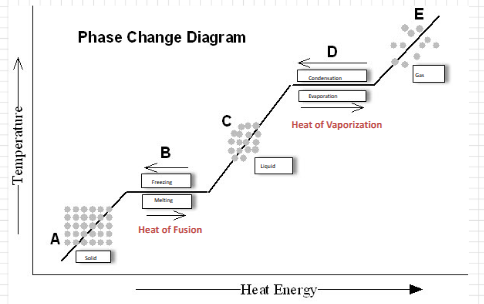
Phase Change Diagram
What does the Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter state?
particles of matter are always in motion
Kinetics = movement
Molecular = molecules, particles, things
5 Assumptions of the Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter (KMT
Gas particles are very tiny but have huge space between them (they take up more space than necessary)
Collisions between gas particles and between particles and container walls are elastic (no net loss of total kinetic energy)
Gas particles are in continuous, rapid, random motion
There are no forces of attraction between gas particles
The temperature of a gas depends on the average kinetic energy of the particles of the gas (move faster at higher temps)
Ideal vs. Real Gas
Ideal gas = Is a hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all the assumptions of the KMT (kinetic-molecular theory)
Real gas = is a gas that doesn’t behave completely according to the assumptions of the KMT
At very high temperatures and low pressures real gases act most like ideal gases
Barometer
a device used to measure atmosphereic pressure
Manometer
a device used to measure the pressure of an enclosed gas sample
are pressure and volume indirectly or directly related?
indirectly related
are volume and temperature indirectly or directly related?
directly related
are pressure and temperature indirectly or directly related?
directly related
Accuracy
measuring near true value
Precision
getting consistent results
explain how a student can be accurate, precise, or both
A student can be accurate if they have a low percent error
A student can be precise if they get the same answer more than once
A student can be both if they consistently get the correct answer multiple times