1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 The Basic Economic Problem
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Basic economic problem
Unlimited wants exceeding finite resources
E.g.
Individual consumer - limited money to spend on goods and services
Individual worker - limited time to enjoy leisure
Producers - limited resources available to produce a good or service
Government - limited revenues available to spend on public services
Scarcity
Insufficient quantity to satisfy everyone’s wants
Economic good
A product which requires resources to produce it and therefore has an opportunity cost
Free good
A product which does not require any resources to produce it and so it doesn’t have an opportunity cost.
E.g. sand, fresh air, seawater, sunlight etc…
Factors of production
The scarce resources used in the production of goods and services.
Land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Any natural resource which is used in production.
E.g. oil, cotton, fertile soil, water, wood
Labour
Human effort used in producing goods and services
E.g. teachers, lorry driver, accountant
Capital
Human made goods used to produce other goods and services
E.g. calculator, power station, printing machines
Problems with constantly running machinery?
Resource depreciation - the wear and tear of a machine (when it is worn down for a long time)
Resource depletion - fewer resources because they are being used up. The consumption of a resource is faster than it can be replenished
Enterprise
The willingness and ability to bear risks and make decisions in business
E.g. Bill Gates
Factor rewards
The payments different factors of production require and receive in order to participate in a productive activity.
Owners of land require payment of rent to supply their resources to firms
Workers supply their labour in exchange for payments called wages
Interest is paid to those who supply or invest capital in firms. (it is what they charge for supplying the money or machinery)
Profit is the surplus left over after all costs have been paid, which rewards entrepreneurs for successfully organising production
Can the economic problem be solved?
No - resources will always be scarce relative to the limitless human wants.
However, we can change the way in which resources are used or increase the quantity and quality of resources, we allow more goods and services to be produced - therefore, wants are satisfied
How easy is it to change how scarce resources are used? Factor mobility
Factor mobility
The ease with which resources can be moved from one productive activity to another (without incurring significant costs or a loss of output)
Occupational mobility
The ability to move factors of production between different productive tasks or uses.
[The education, skills and training of a worker (their human capital) influences their occupational mobility, e.g. a dentist to a plastic surgeon]
Geographic mobility
The ability to move factors of production to different locations.
(Barriers to geographic mobility may include family ties, challenges in securing/affording accommodation in an unknown location)
Improving factor quantity and quality: LAND
How can factor quantity be improved?
Planting and re-growing more trees and plants. Reduce the rate at which they are chopped down
Increase rent to persuade landowners to release their land into productive used
New techniques to improve the extraction amount
How can factor quality be improved?
Reduce the used of chemicals in farming
Invest in technologies to improve the resilience of plants to droughts and infestations
Improving factor quantity and quality: LABOUR
How can factor quantity be improved?
Increase wages to incentivise more people to supply their labour
Increase the retirement age
Improve healthcare to reduce sickness absences and help people live longer
How can factor quality be improved?
Training and education improves workforce skills and quality of goods and services people can produce
Bette working conditions
Reduce working hours so workers have more leisure time
Improving factor quantity and quality: CAPITAL
How can factor quantity be improved?
Producers investing more into capital goods
Increase in interest payments will increase the amount investors are willing to supply to firms
How can factor quality be improved?
Advances and funding into technology continuously improves the speed and accuracy of modern day equipment
Improving factor quantity and quality: ENTERPRISE
How can factor quantity be improved?
Increase the price of goods and services to increase profits and encourage more people to start firms
Lower corporation tax to incentivise people to start a business because they would earn more profit
How can factor quality be improved?
More and better training courses for aspiring entrepreneurs
More and better business advice and support for entrepreneurs
Opportunity cost
The value of the next best alternative foregone.
Consumers - must choose how much of their limited incomes to save and how much to spend
Workers - must choose how to utilise their skills as well as how much of their time should be split between work and leisure
Producers - must choose what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, how much to invest and how to organise their resources
Governments - must choose how best to spend public money and how to finance it, whether that be through borrowing or raising taxes
Production possibility curve/frontier
A curve which shows the maximum output of two types of products and the combinations of those products that can be produced efficiently with existing resources and technology
(Look at image attached for a quick introduction) PPCs involve an opportunity, so in the image, if the country wanted to produce more clothes they have to sacrifice the production of some food.

Shape of a PPC
A straight, linear PPC - Assumes constant opportunity costs. So, the factors of production are perfect substitutes and can do both jobs equally well.
A curved PPC - Indicated the opportunity cost is increasing as more and more of the other product is product
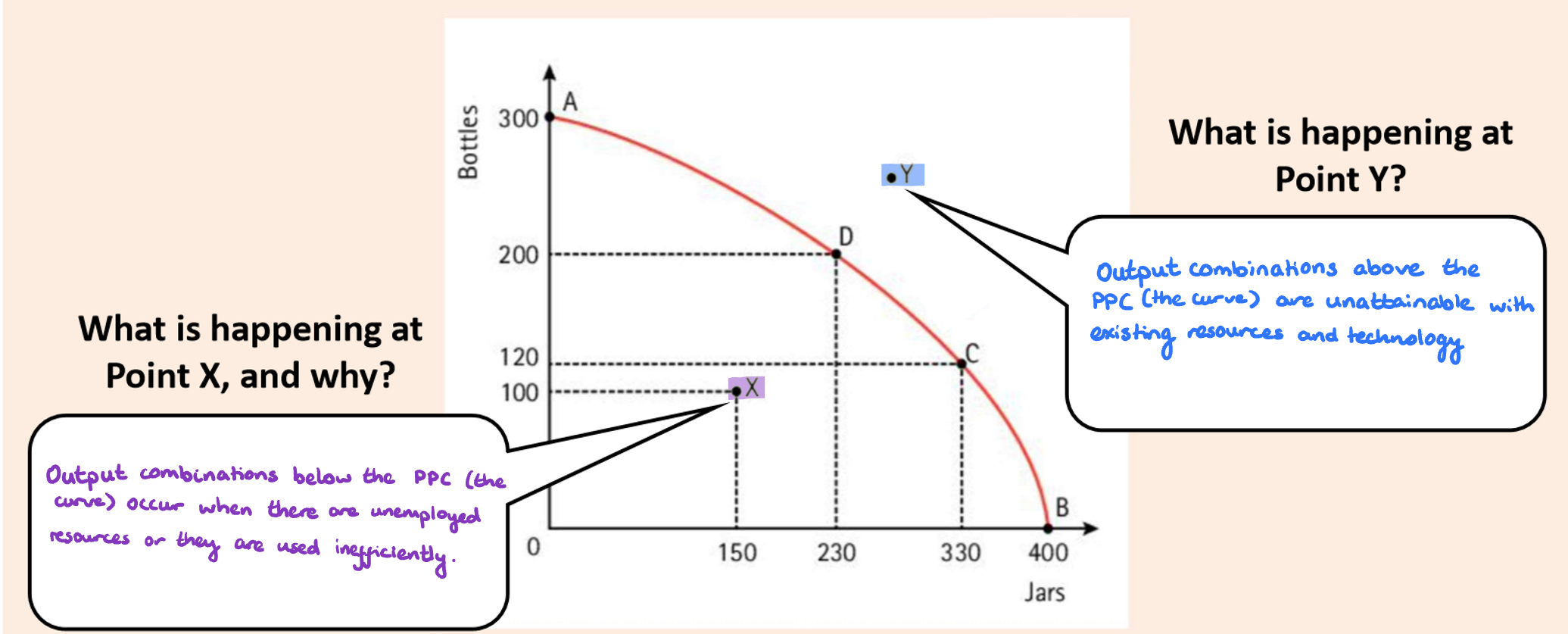
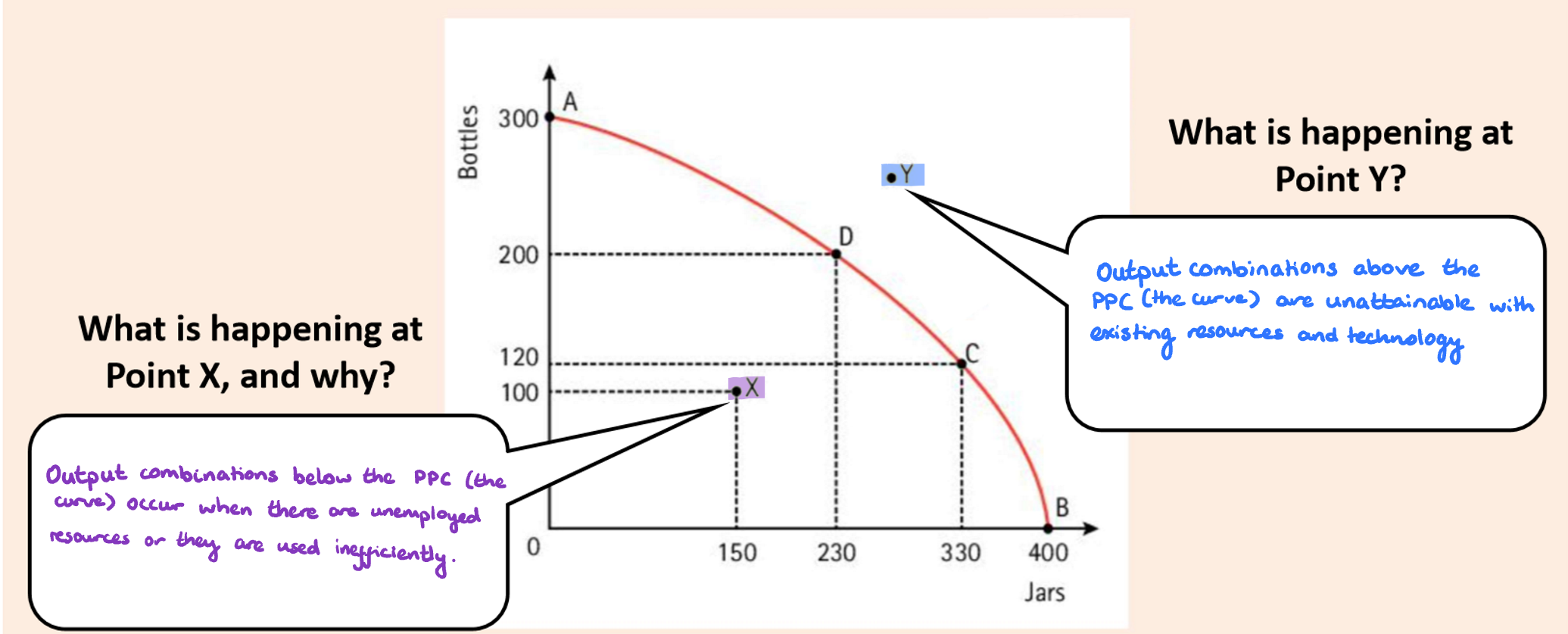
What if a point is above or below the curve?
The curve is the maximum output so if a point is not on the curve we can assume that we have not used everything (below the curve) or we do not have enough for it (above the curve)
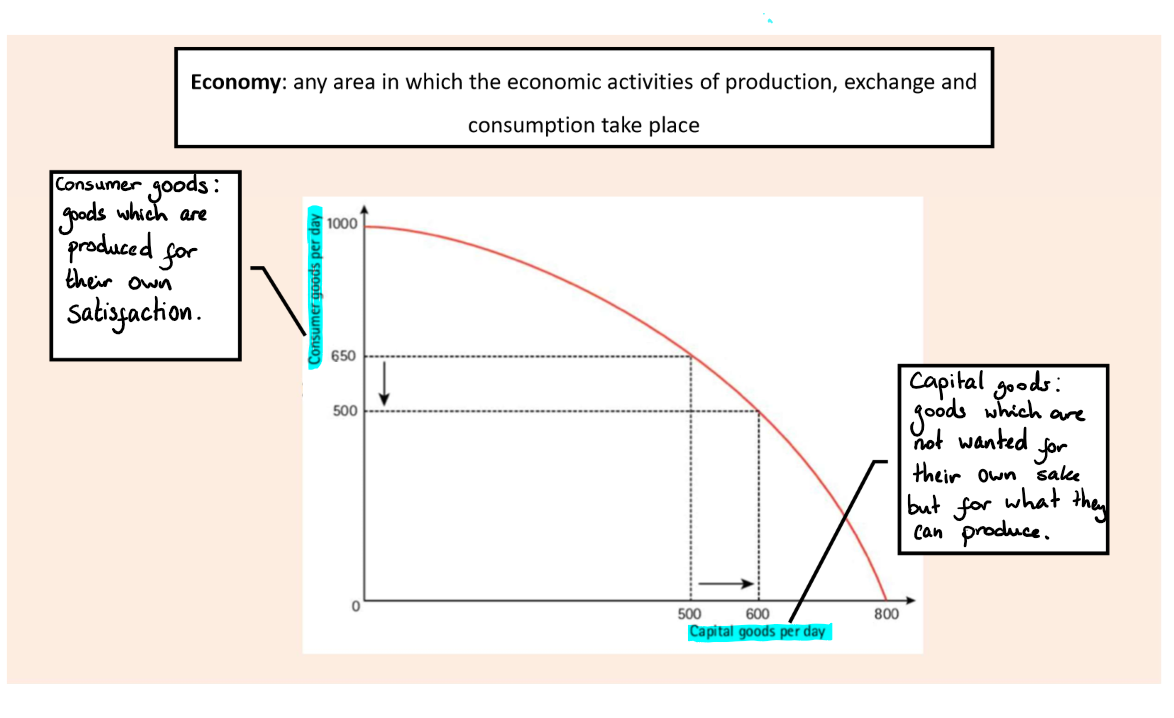
Consumer goods
Goods which are produced for their own satisfaction
Capital goods
Goods which are not wanted for their own sake but for what they can produce
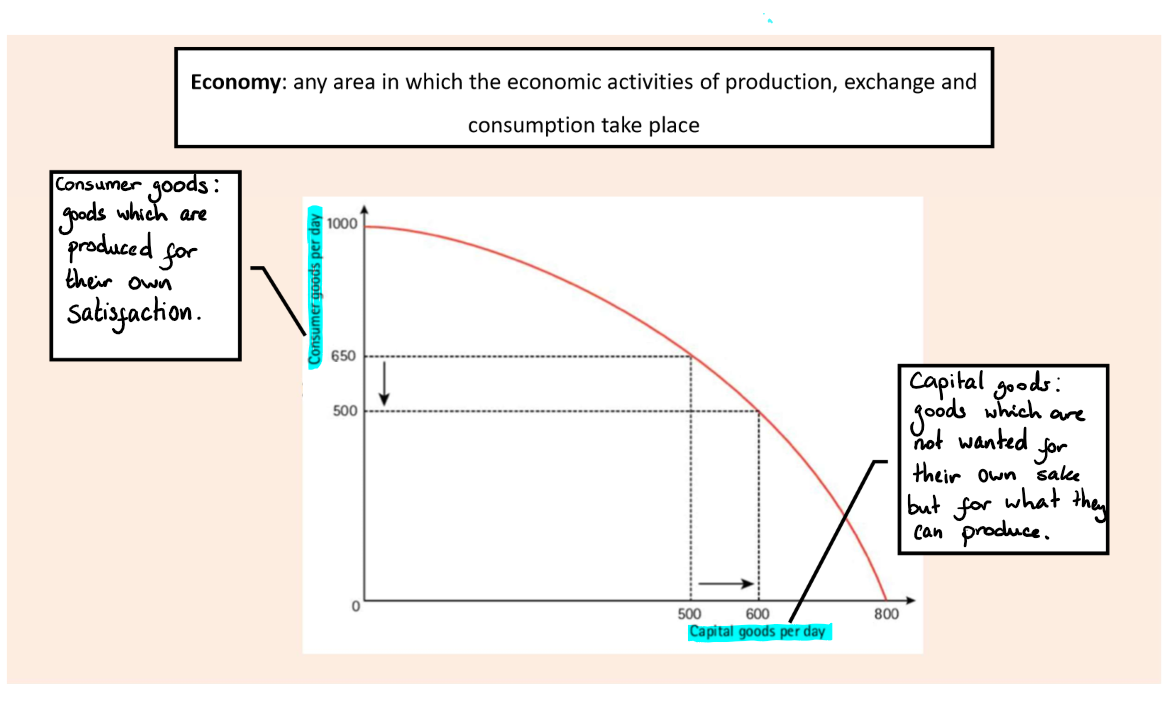
Drawing a PPC
On the y axis - Consumer goods
On the x axis - Capital goods
Look at the image attached
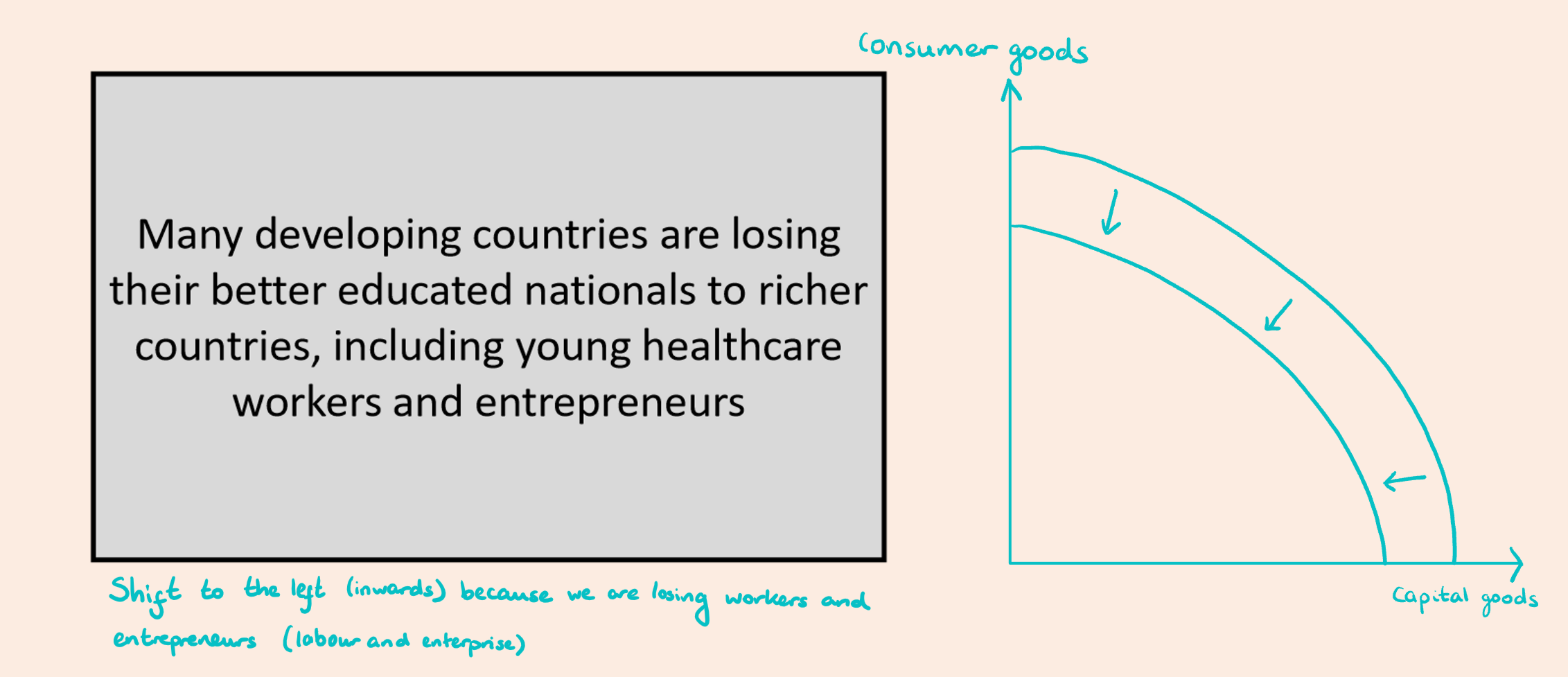
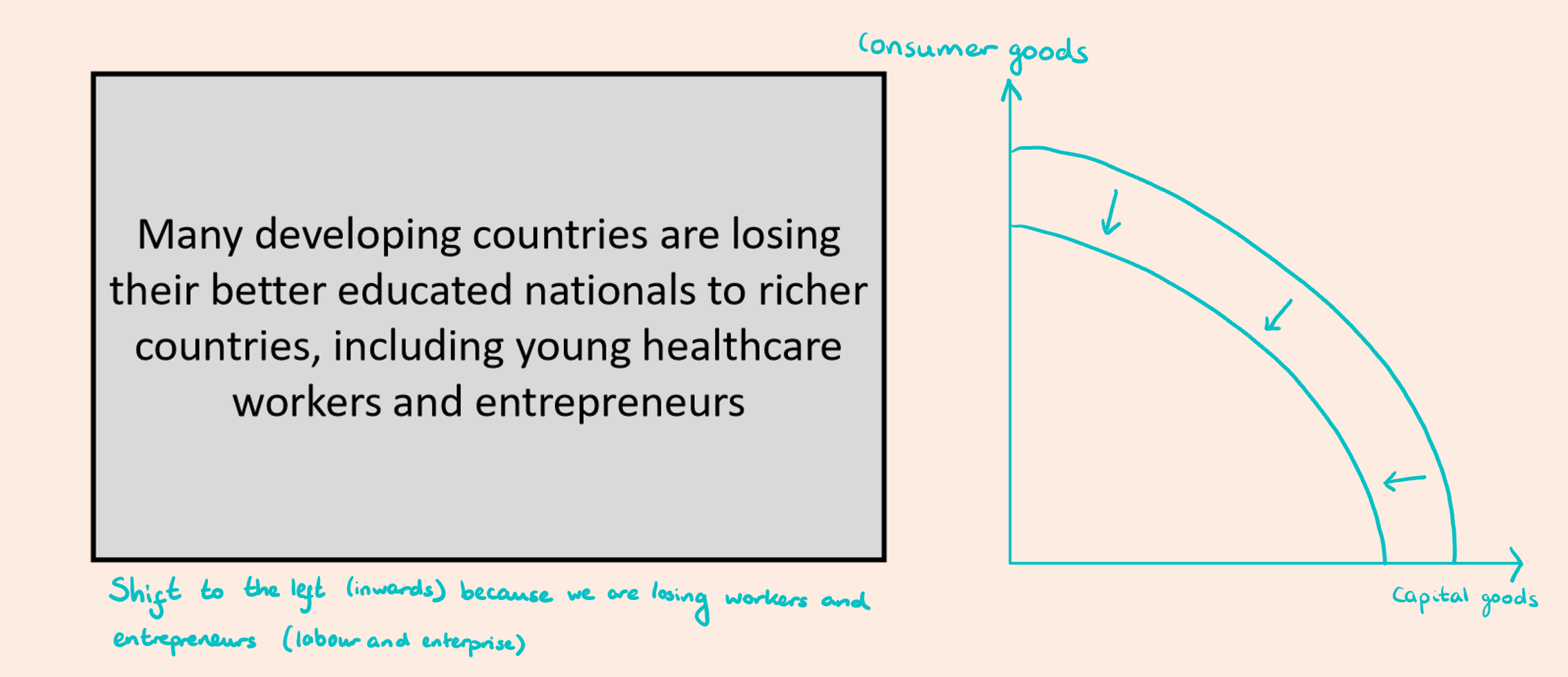
A shift in a PPC
A shift to the right (outwards) indicates an increase in the maximum output
A shift to the left (inwards) indicates a decrease in the maximum output
Look at the image attached
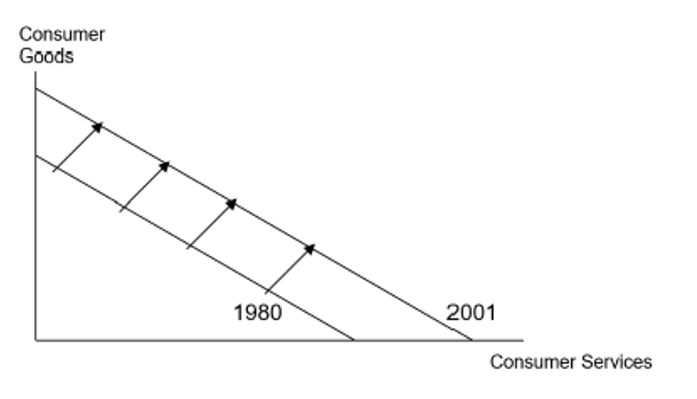
Another example of a PPC shift
Look at the image attached
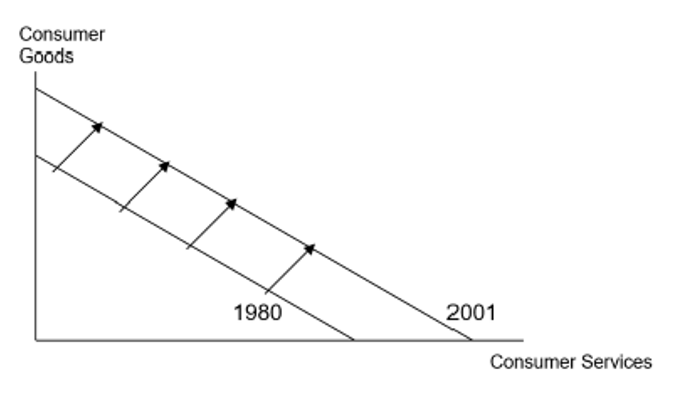
Factors that cause a shift in the PPC
Anything that increases either the quantity or quality of factors of production will shift the PPC outwards
Increase in the size of the labour force
Increase in size of population
Increase in immigration
Increases in quantity and quality of capital
Greater technological progress
Discovery of new natural resources
Etc…
Economic growth means that a country can have more of all goods and services. Over time, increases in inputs or technology can result in an outward shift of the PPC
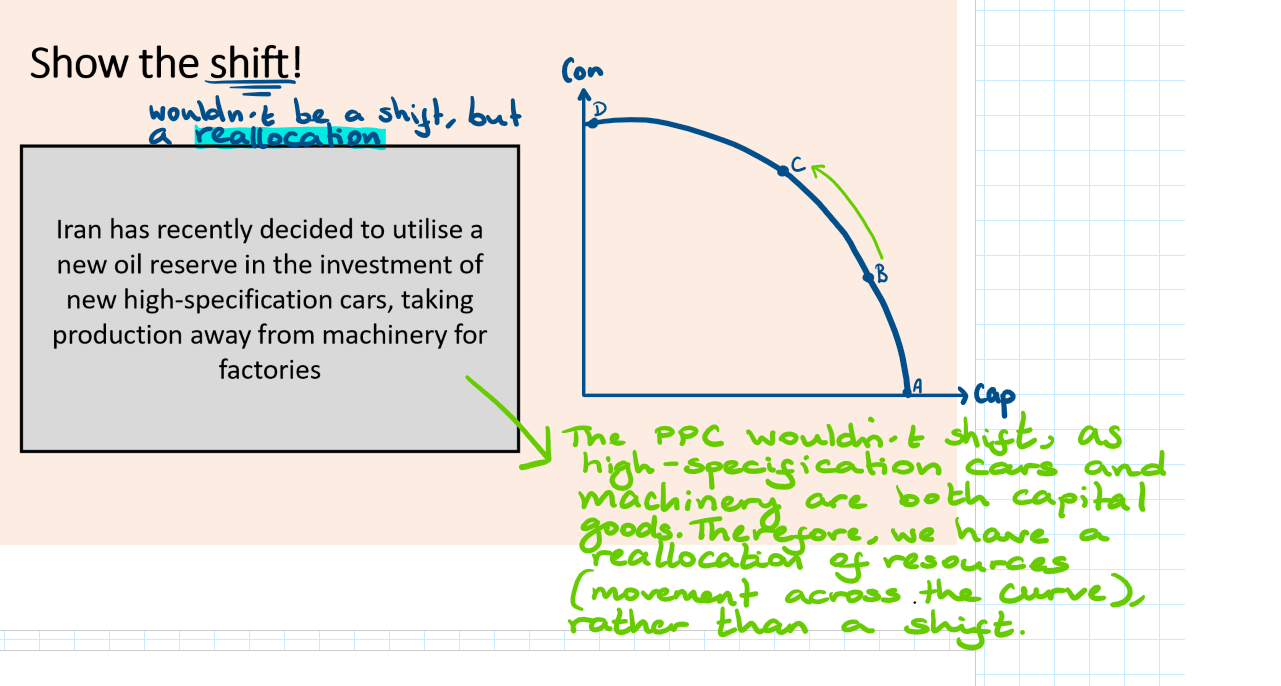
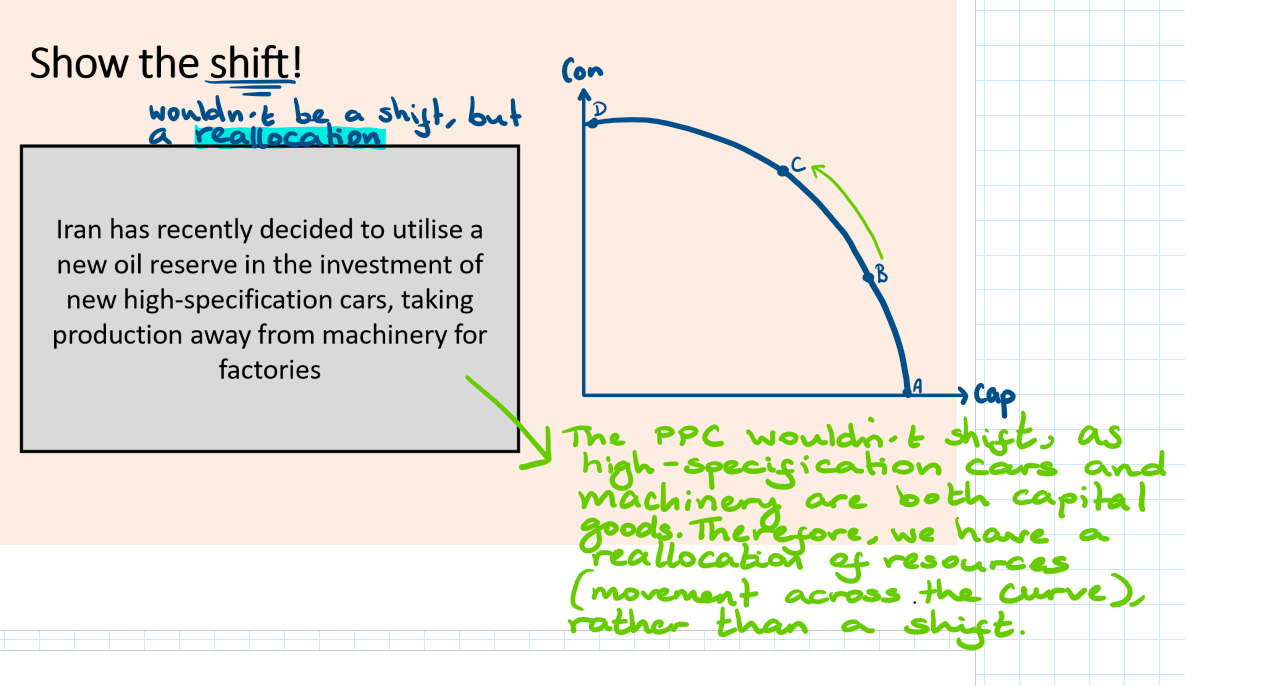
Reallocation of resources on a PPC
Look at the image attached
Movements along a PPC are caused by a reallocation of resources from the production of ones good to the production of another good