Chapter 14: Autonomic Nervous System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Autonmic nervous sytem
Involuntary
f: overseas vital functions (ex: heart rate, digestive process)
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight: stimulate
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest: slows/inhibit
preganglonic neuron
connects to CNS autonomic ganglion
Post-ganglion neuron
ganglion to effector site/target
ex: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, GI system
autonomic ganglion
cell body of second cell ( post-ganglion neuron)
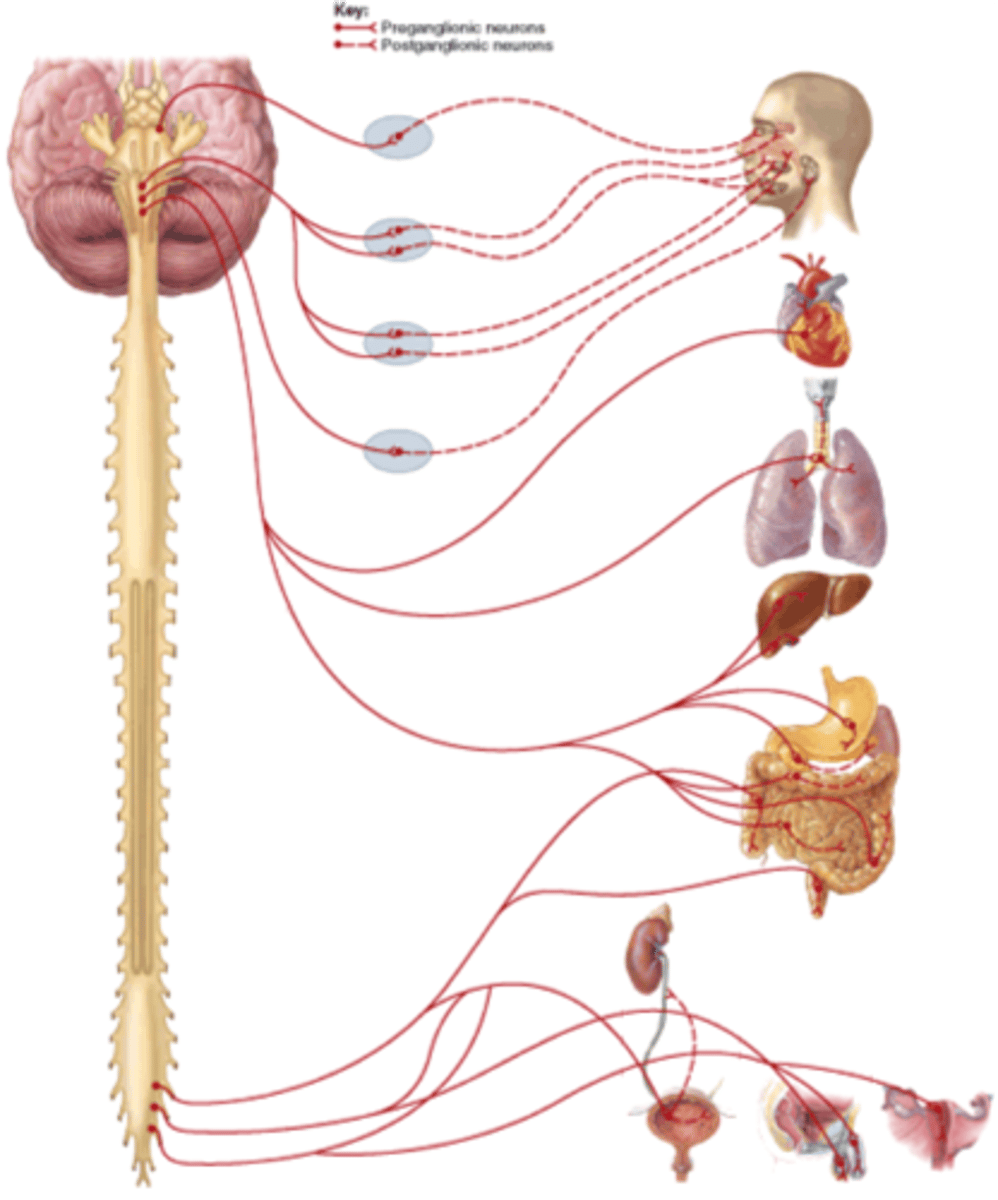
Parasympathetic neurons
origin: craniosacral
preganglionic length: longer
postganglionic length: shorter
autonomic ganglion location: closer to target organ
postganglionic axon neurotransmitter released: ACh
target organ receptor: cholinergic
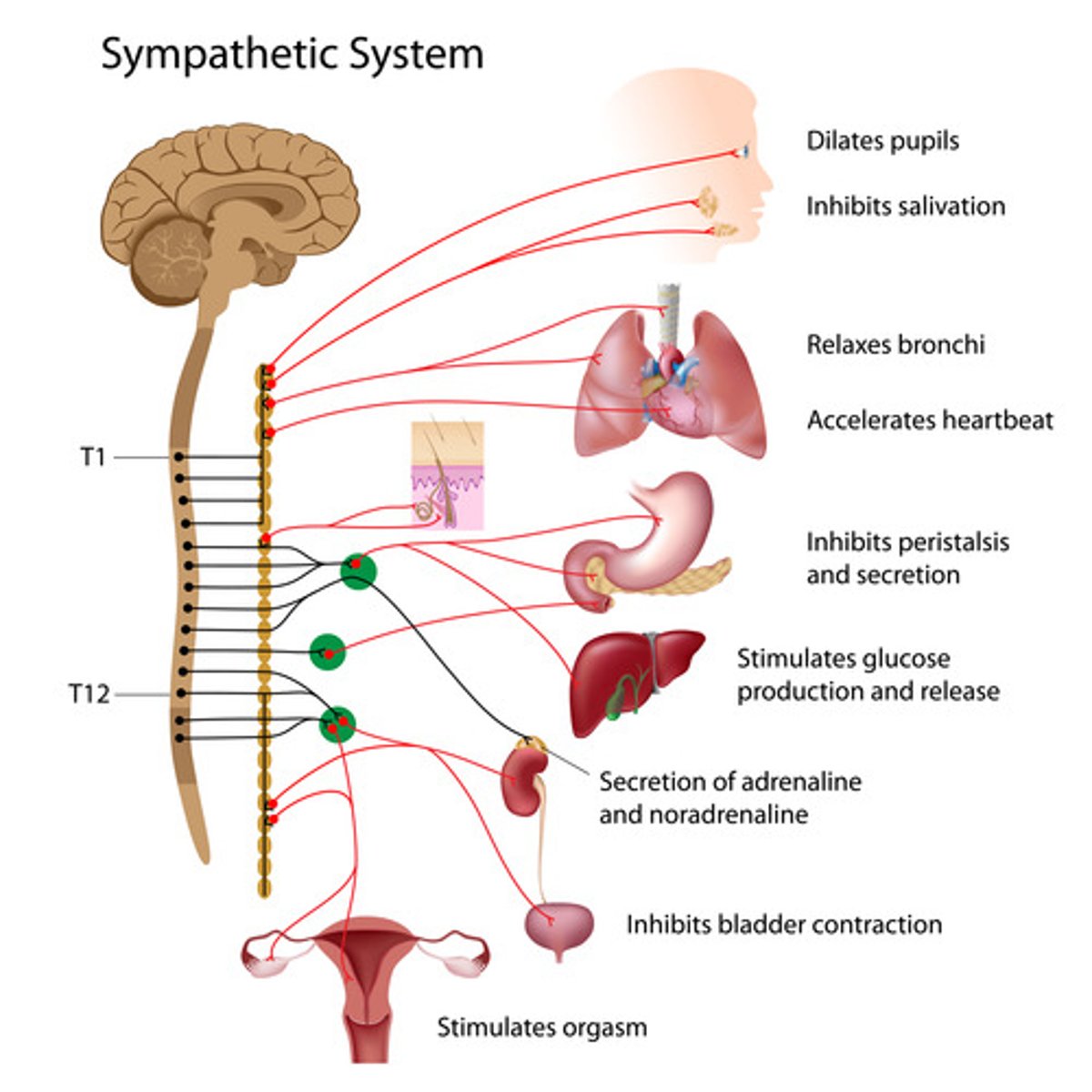
Sympathetic neurons
origin: thoracolumbar
Pre-ganglion length: shorter
postganglion length: longer
autonomic ganglion location: closer to spine
Postganglionic axon neurotransmitter realsed: NE or E
target organ receptor : adrenergic
alpha 1 - excitatory
ex: constrict blood vessel ( smooth muscle) makes muscle excited
beta 1 - exitatory
ex: speeds heart rate ( excites cardiac, kidney)
beta 2 - inhibitory
ex: relaxes airway ( relaxes smooth muscle)
Adrenergic
bind to NE or E
Cholinergic
Bind to ACh
Sympathetic chain
chain of ganglia on eitherside of spinal cord
adrenal medulla
releases hormones into bloodstream when stimulated
collateral ganglion
ganglion near target organ
heart
sympathetic effect : increase heart rate and force of contraction
parasympathetic effect:P decrease heart rate
bronchioles of lung
sympathetic effect: dilation
Parasympathetic effect: constriction
Pupils
sympathetic: dilation
Parasympathetic: constriction
Digestive tract activity and secretion
Sympathetic effect: relaxation ,decrease in secretion
Parasympathetic effect: contraction, increase
Metabolic rate
sympathetic effect: increase
parasympathetic: no effect
Urination
sympathetic: decrease
Parasympathetic: increase
fats/glucose( storage/release)
Sympathetic: increase release of glucose, stimulation of fat breakdown
Parasympathetic: no effect
blood vessels
sympathetic: dilation to skeletal muscles construction to skin
Parasympathetic: little/ no effect
sweat glands
Sympathetic: increase secretion of sweat
Parasympathetic: no effect
step 1: visceral reflex arc
1: sensory signals from the viscera and skin are sent by afferent sensory neurons to the brain to the brain or spinal cord.
step 3: visceral reflex arc
3: motor impulses dome the CNS are sent via efferent motor neurons in cranial and spinal nerves to autonomic
Step 2: visceral reflex arc
2: the stimuli are integrated by the CNS
step 4: visceral reflex arc
4: the autonomic ganglia send the impulses via other efferent motor neurons to various target organs where they trigger a motor response in the target cells
reticular formation
- regulates HR, BP, digestion, metabolic rate, respiration ,urine, sleep/wake, acid-base balance
hypothalamus
- boss of ANS
- instructs reticular formation
- regulates body temp, feeding behavior, fluid intake
visceral reflex arc
-sensory stimulus in an organ leads to predictable visceral motor response