Diagnostic 3 izadi Test 2
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
timed test that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle through a volume of plasma
-determined by the aggravation of erythrocytes in which plasmatic and erythrocytic factors are involved
moderately elevated ESR
occurs with inflammation but also with anemia, infection, pregnancy, rheumatologist disease, and aging
extremely elevated ESR
(>100 mm/hr.) are infections like TB, collagen vascular disease, malignancy, or metastatic cancer.
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Normal <10 mg/L.
blood test used to measure the level of inflammation in the body; may indicate conditions that lead to cardiovascular disease
high CRP:
• Check for inflammation due to an infection
• Help diagnose a chronic inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
• Determine your risk of heart disease
• Evaluate your risk of a second heart attack
high CRP indicates
inflammation which could be a result of infection, chronic disease, or trauma.
extremely high levels w/ nonclinical findings: non-rheumatic diagnoses, such as infection and malignancy, even in the presence of a previously diagnosed RD.
ESR & CRP
-establishes active inflammation somewhere in body
-opioid reduce ESR & CRP b/c its anti-inflammatory
liver failure
one condition observe to impair CRP production
CRP time taken to increase
increase: 4-6 hours
peak: 36-50 hours
normal: 3-7 days following resolution
ESR time taken to increase
peak: a week
normal: several weeks
Acute phase proteins (APP)
• are a class of proteins whose plasma concentrations increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation.
-response is called acute phase reaction/response
-fever, acceleration of peripheral leukocytes, circulating neutrophils, and their precursors.
hepcidin
• Hepcidin inhibits iron absorption in the intestinal mucosal cells by binding to the ferroprotein and inhibits iron transport by binding to ferroprotein in macrophages. Increased hepcidin during inflammation causes anemia of chronic disease.
anemia of chronic disease
Increased hepcidin during inflammation causes
ferritin
iron storage protein
-to sequester iron to inhibit microbial iron scavenging.
high ferritin
-during malignancy and infection its elevated to reduce free iron available to tumor cells or pathogens
-upregulated by pro inflammatory cytokines
fibrinogen
as a coagulation factor is to promote endothelial repair.
-C3 complement function.
-correlates with ESR.
ANA test
plasma is tested for antibodies that are present in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
-looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder.
nuclear antigens & antinuclear antibodies
antigens are:
-DNA
-RNA
-Histones
-nucleoli
antibodies against:
-anti-DNA
-anti-RNA
-Anti-Histones
-Anti-nucleoli
anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies
• a group of anti-nuclear antibodies the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA.
• Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescence are routinely performed to detect anti-dsDNA antibodies
• They are highly diagnostic of systemic lupus erythematosus and are implicated in the pathogenesis of lupus.
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
blood test used to help diagnose rheumatoid arthritis
-indicates rheumatoid arthritis or another autoimmune disease
rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
• Joint pain
• Joint stiffness, especially in the morning
• Joint swelling
• Fatigue
• Low-grade fever
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
antibody present in most rheumatoid arthritis patients.
-Levels of anti-CCP can be detected in a patient through a simple blood test.
-A positive anti-CCP test result can be used in conjunction with other blood tests, imaging tests, and/or physical examination findings to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis
TORCHeS infections
Prenatal infex that lead to severe abnormalities = most common HEARING IMPAIRMENT & MR
Toxoplasmosis
Other (varicella, listeriosis)
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes Simplex/HIV
Syphilis
STD
An infection transmitted through sexual contact, caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
An infection that causes warts in various parts of the body, depending on the strain.
genital herpes
• A common sexually transmitted infection marked by genital pain and sores.
Chlamydia
A bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs of both males and females
-common sexually transmitted infection that may not cause symptoms.
gonorrhea
• A sexually transmitted bacterial infection that, if untreated, may cause infertility.
HIV/AIDS
• HIV causes AIDS and interferes with the body's ability to fight infections.
Syphilis
A bacterial infection usually spread by sexual contact that starts as a painless sore..
approach to syphilis
-TPHA (treponema pallidum hemagglutination assay
- if positive -> nontreponoma or VDRL (ventral disease research laboratory)
=current or past syphilis
if VDRL negative then FTA-Abs=fluerescent treponema antibody absorption
-if positive then early syphilis
Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA-ABS)
-measures a specific antibody made against treponema pallidum
-should always be followed to confirm a positive RPR and/or VDRL test for syphilis
-test positive for life
approach to viral hepatitis
• If an individual presents with yellow discoloration, the first tests performed should be the AST and ALT.
• Increased AST and ALT indicated viral hepatitis.
• Hepatitis B can measure HBs Ag = acute
HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
-indicates th person is infectious
-found in high levels during acute and chronic infection
-used to make the HBV vaccine
HBcAg (Hepatitis B core antigen)
-indicates acute or chronic infection
-not found with vaccine
HBeAg (Hepatitis B envelope antigen)
-associated with the nucleocapsid gene found during acute an chronic HBV
-presence indicates replication virus and high levels of HBV
high serum bilirubin levels mean what?
blockage
-jaundice
-pale stool
AST/ALT ratio
If HEPATOCYTES are damaged AST and ALT will LEAK into the BLOOD.
"AST": LIVER, BRAIN, PANCREAS, HEART, MUSCLE, KIDNEY, LUNGS
"ALT": ONLY in LIVER. L for LIVER
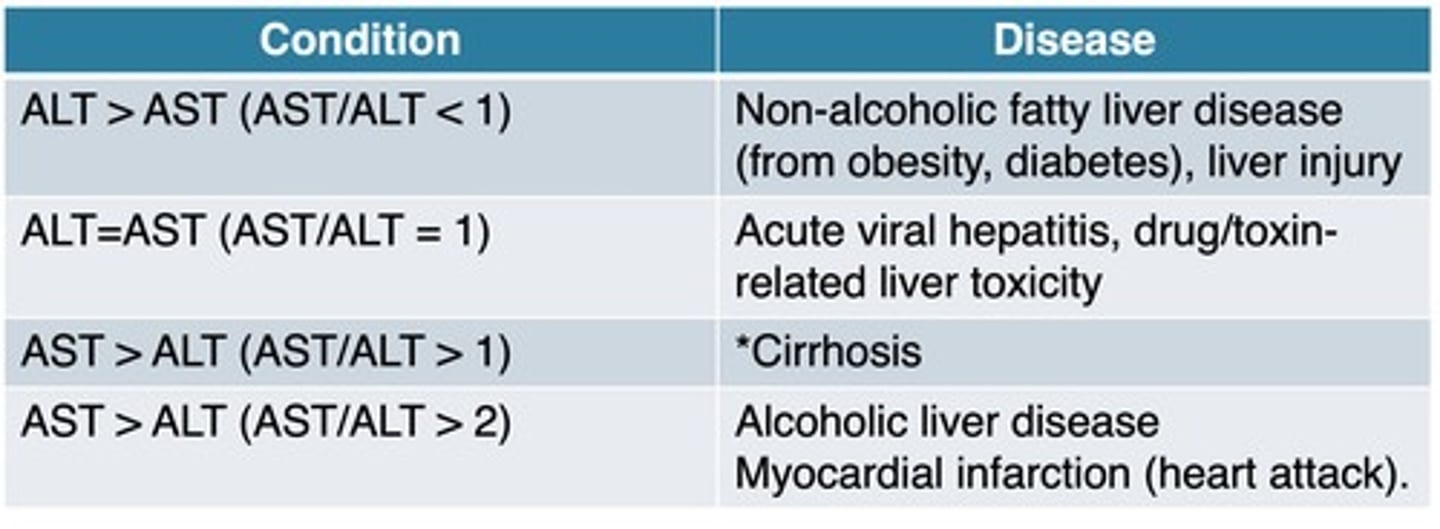
ALT > AST (<1)
-non alcoholic fatty liver disease (diabetes/obesity)
-liver injury
ALT=AST (=1)
-acute viral hepatitis
-liver toxicity
AST>ALT (>1)
cirrhosis
AST>ALT (>2)
-alcoholic liver disease
-chemical hepatitis
-primary biliary cirrhosis
-myocardial infarction
high GGT
-problem is in liver
low GGT
-problem is in RBC or muscle
low albumin means
cirrhosis
high ALP
may be obstruction in bile duct
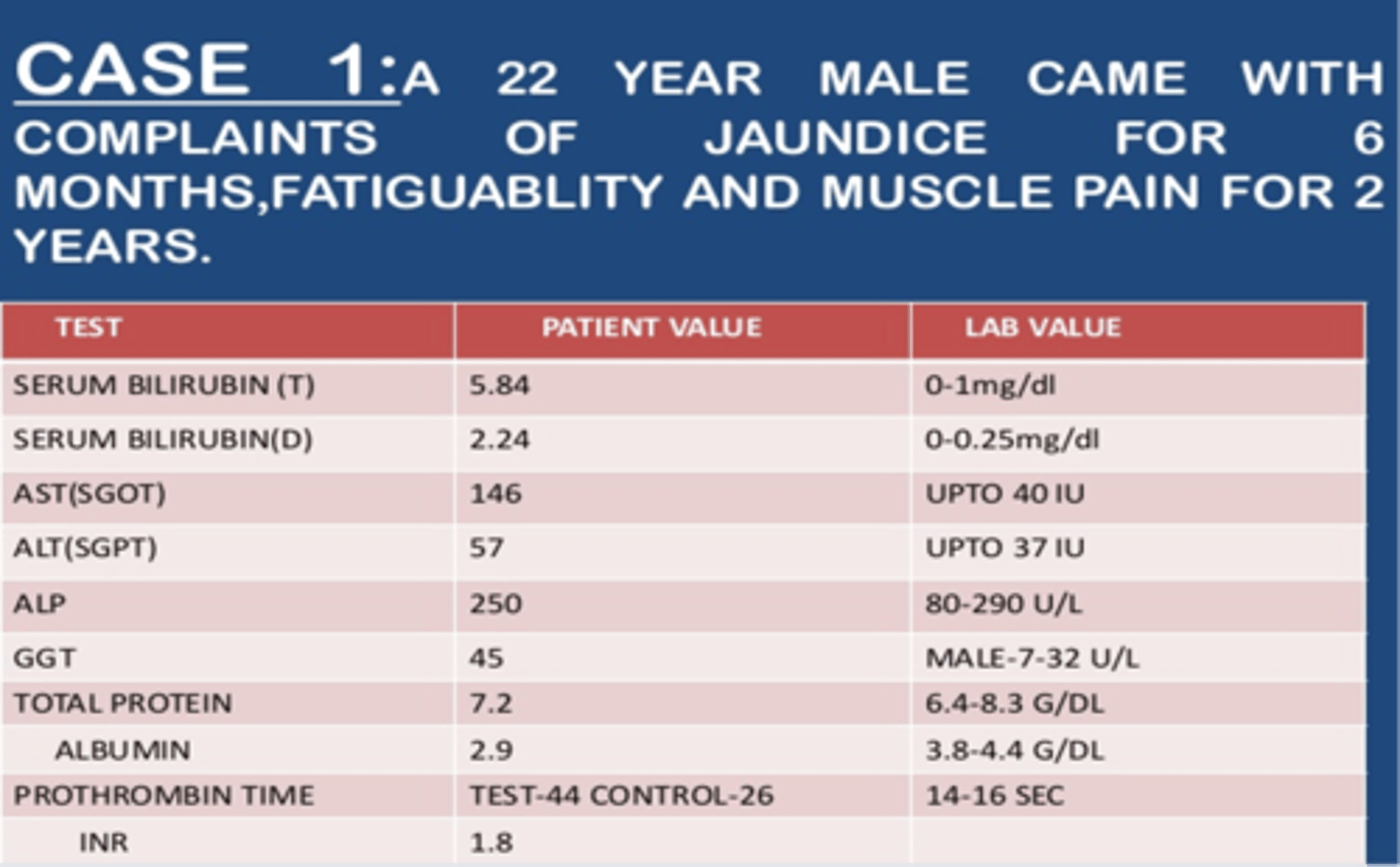
• Serum bilirubin (T) is high
• Serum bilirubin (D) is high
• AST (SGOT) and ALT (SGPT) is high
• AST/ALT = possibility of alcoholic disease
• GGT is high (suggest chronic alcohol use)
• Albumin is low = ?
• Prothrombin time is high
The patient has liver disease due to alcoholism.
-high serum bilirubin (t)
-high serum bilirubin (d)
-AST/ALT =>2 meaning chemical hepatitis
-high ALP = obstruction bile duct
-High GGT = liver problem
-patient has chemical hepatitis or primary biliary cirrhosis

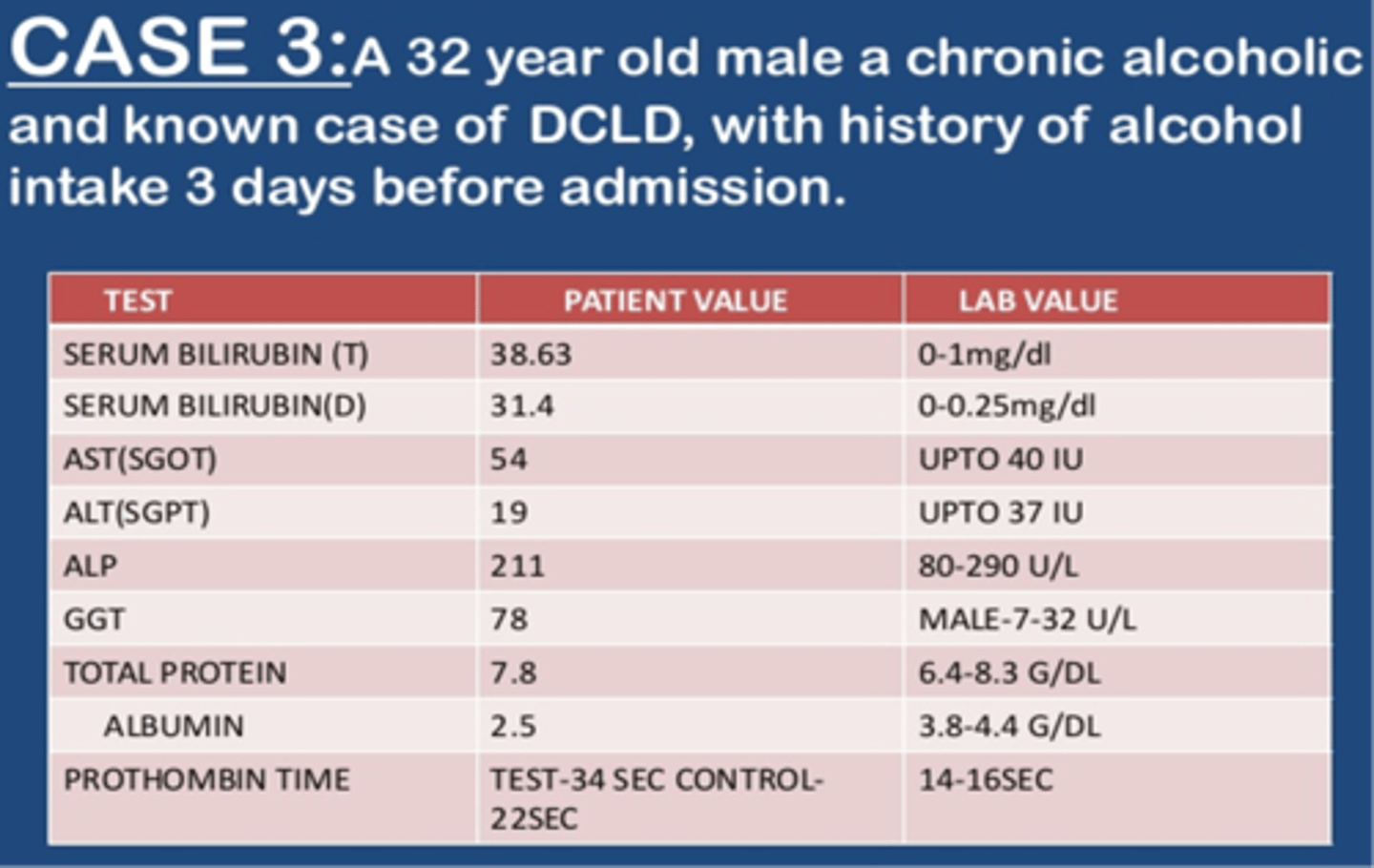
• Serum bilirubin (T) is high
• Serum bilirubin (D) is high
• AST is high
• GGT is high = confirms the problem is in the liver
• Albumin is low = liver cirrhosis for long term
• Prothrombin time is high
• The patient has long-term cirrhosis.
• The patient is not confirmed for having HIV.
• The patient is reactive, but needs a confirmatory test (Western blot test).
• The Western blot test confirms the patient has HIV.
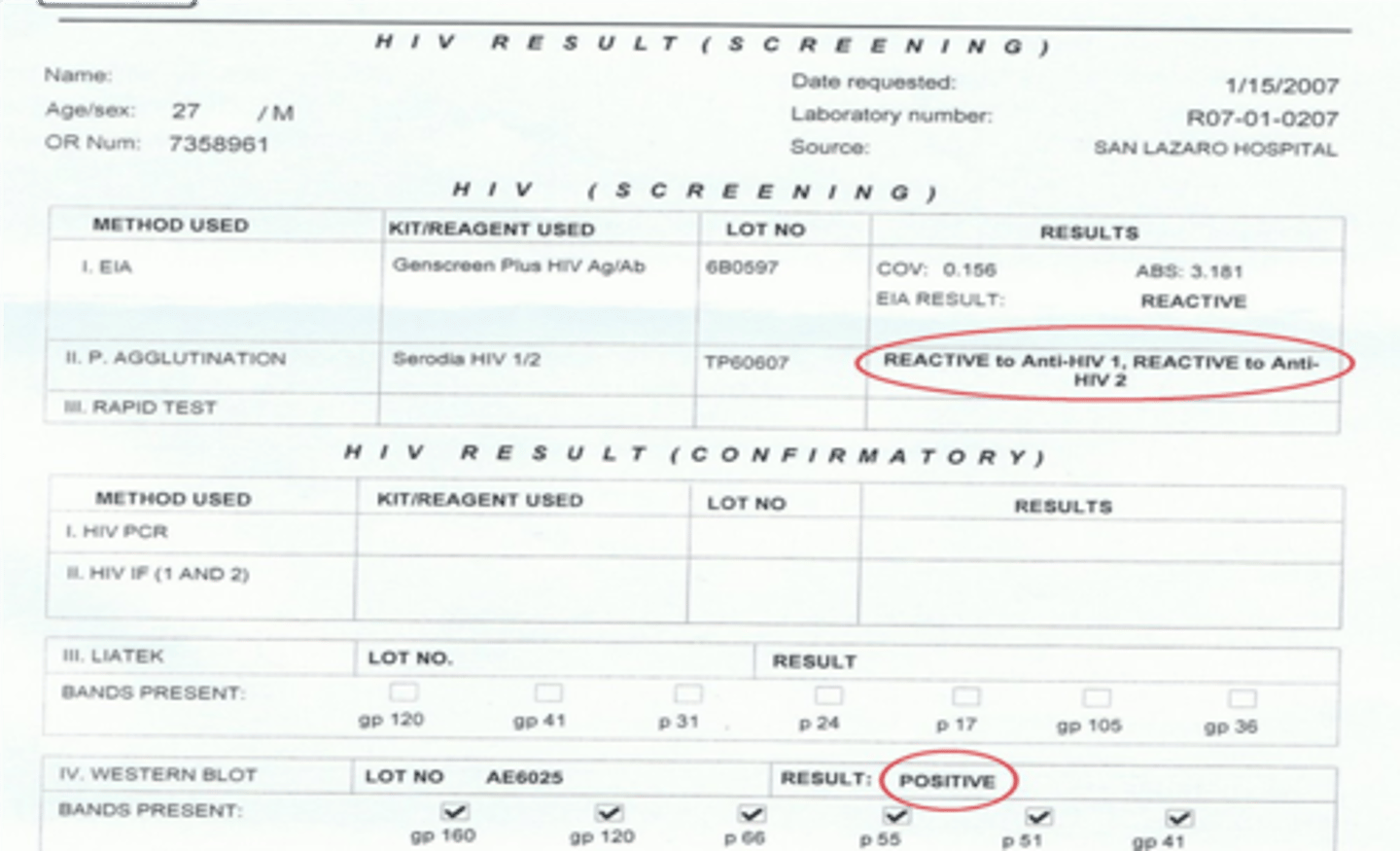
Western blot test
a blood test to confirm the diagnosis of HIV
urine analysis normal values
• Appearance: clear
• Color: amber yellow
• Odor: aromatic
• pH: 4.6 – 8
• Protein: 0 – 8 mg/dL
• Specific gravity: 1.005 – 1.030
• Leukocyte esterase: negative
• Nitrites: none
-Ketones: none
• Bilirubin: none
• Urobilinogen: 0.01 – 1 Ehrlich unit/mL
• Crystals: none
• Casts: none
• Glucose: negative
• White Blood Cells: 0 – 4/low-power field
• WBC casts: none
• Red Blood Cells (RBCs): ≤ 2
• RBC casts: none
pH
ability of Kidney to maintain normal H+ concentration in plasma & extracellular fluids
Specific gravity of urine
• concentration, Kidney ability to maintain homeostasis of fluid & electrolytes
glucose in urine
diabetes; low renal threshold
bilrubin (UA)
liver dysfunction; blood in urine
ketones in urine
fasting, diabetes, dehydration
blood in urine
menstrual, UTI, stones, malignancy
protein (albumin) in urine
dehydration, fasting, kidney disease, UTI, positional
nitrates in urine
produced by bacteria
Leukocyte esterase in urine
WBC, LEUKOCYTE INFECTION
WBC in urine
white blood cells, ↑ in infection, inflammation
RBC in urine
red blood cells; ↑ stones, renal disease, infection
epithelial In urine
squamous, transitional, renal
casts
hyaline, fine/course granular, RBC, WBC, waxy, fatty
crystals in urine
• type formed based on urine pH, presence of inorganic elements, ability to precipitate; normal component w/few exceptions; can indicate type of calculi w/stones
-amorphous urates/phosphates, uric acid, calcium oxalate, triple phosphate, ammonium biurate, calcium phosphate/carbonate
Abnormal Crystals in Urine
cystine, tyrosine, leucine
bacteria in urine
increase with infection
-miscellaneuous: yeast, parasites
normal
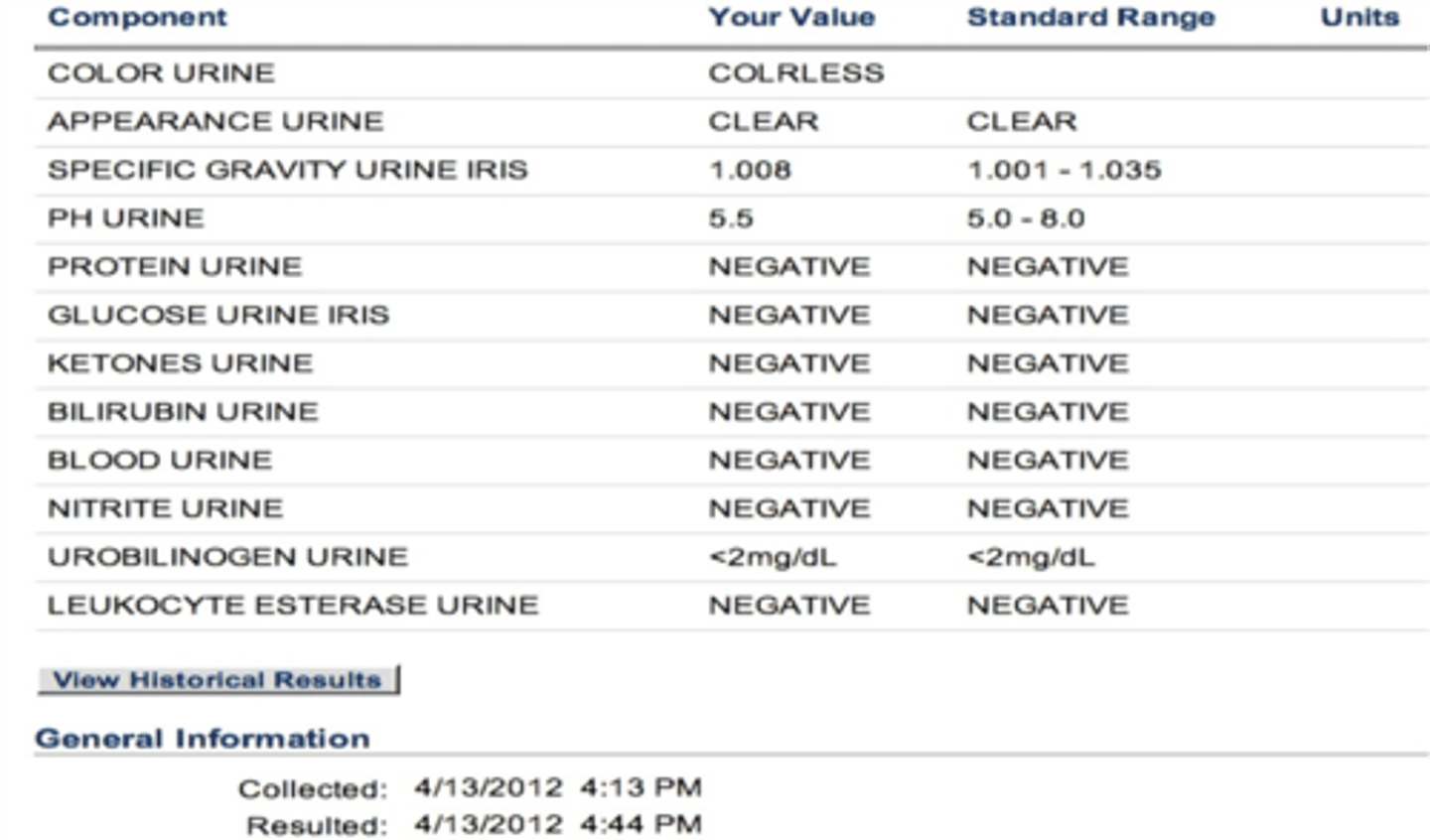
hematuria
increased #s RBCs in urine
• Nephron: glomerulonephritis
• In association w/casts: glomerular
• Extraglomerular: kidney stones, bladder stones, trauma, malignancy, infection, medications
• Interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis, acute cystitis, sickle cell anemia
pyuria
increased #s WBCs (pus) in urine
• Cystitis: UTI
• Pyelonephritis
• Urethritis
- Glomerulonephritis
uric acid
Increased in gout, renal failure, acute fever, chronic nephritis
proteinuria
protein in urine
• Chronic diseases: diabetes, hypertension; sign of kidney damage.
• Transient elevations: infection, medication, exercise, emotional or physical stress; orthostatic; pre-eclampsia
• Diseases: amyloidosis, bladder cancer, CHF, diabetes, drugs, glomerulonephritis, heavy metal poisoning, kidney infection, multiple myeloma, SLE, UTI, polycystic kidneys
E. coli
normal GI bacteria, most common cause of UTI (90%), acute/chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis
symptoms of UTI
-painful urine
-constant urge to urinate
-cloudy urine
-fould odor
-pelvic pain
UTI risk factors
-multiple sex partner
-pregnancy
-menopause
-diabetes
-catheter
-lack of water
Upper UTI
-axcute pyleonephritis
-chronic pyleonephritis
-interstitial pyleonephritis
-renal abscess
-perirenal abscess
lower UTI
-cystitis
-prostatitis
-urethritis
Uncomplicated UTI
UTI without underlying renal or neurological disease
Complicated UTI
UTI with underlying structural medical or neurological disease
recurrent UTI
> 3 symptomatic UTI within 12 months following clinical therapy
reinfection UTI
recurrent UTI caused by a different pathogen at any time
Relapse UTI
recurrent UTI cause by same species causing original utilization w/in 2 weeks after therapy
Pyleonephritis
inflammation of the renal pelvis and the kidney
-white blood cell casts
-(fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting)
UTI babys and infants
-failure to thrive
-fever
-apathy
-diarhea
UTI in children
-dysuria, urgency, frequency
-hematuriqa
-acute abdominal pain
-vomiting
steps for UTI
-urinalysis
-urine culture
nitrite positive
-uti
-bacteria present
• Blood is present = indicates hematuria
• Nitrite is 1+ = bacteria is present, indicates a UTI
• Leukocyte esterase is 3+ = indicates there are WBCs, leukocytes and it could be from an infection
• Bacteria is 3+ = indicates an infection
• WBCs are high = infection or inflammation
• Epithelial cells are high = ?
• A urine culture antibiogram should be performed. The patient has a urinary tract infection.
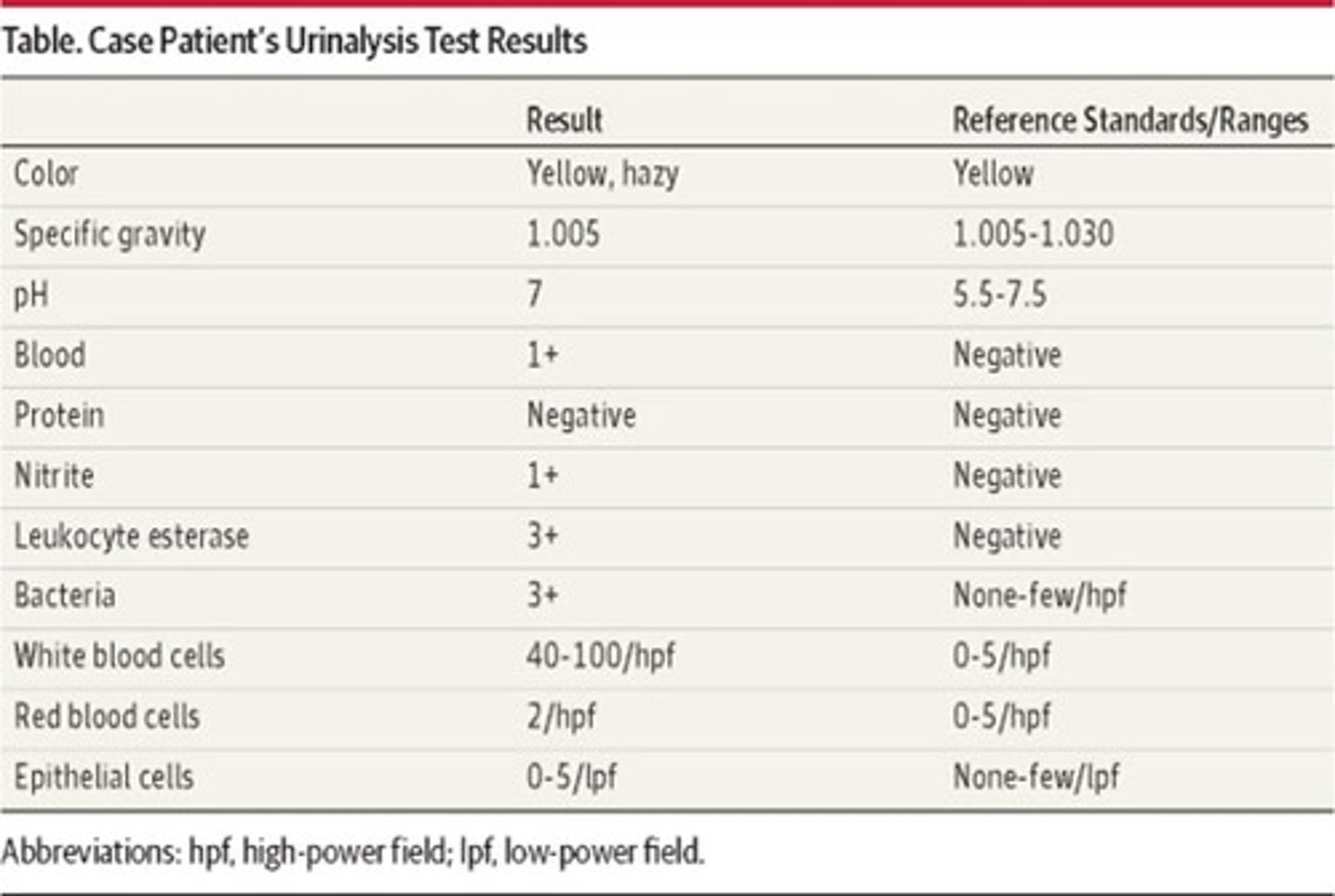
-could just be menstrual period
-trace blood

protein in urine
could indicate dehydration, fasting, kidney disease, diabetes, or UTI
• Leukocyte esterase is positive = indicates there are WBCs, leukocytes and it could be from an infection
• Nitrite is positive = bacteria is present, indicates a UTI
• WBCs are high = infection or inflammation
• RBCs are high = malignancy, kidney stones, menstrual cycle
• Bacteria is many = contamination during sampling or an infection
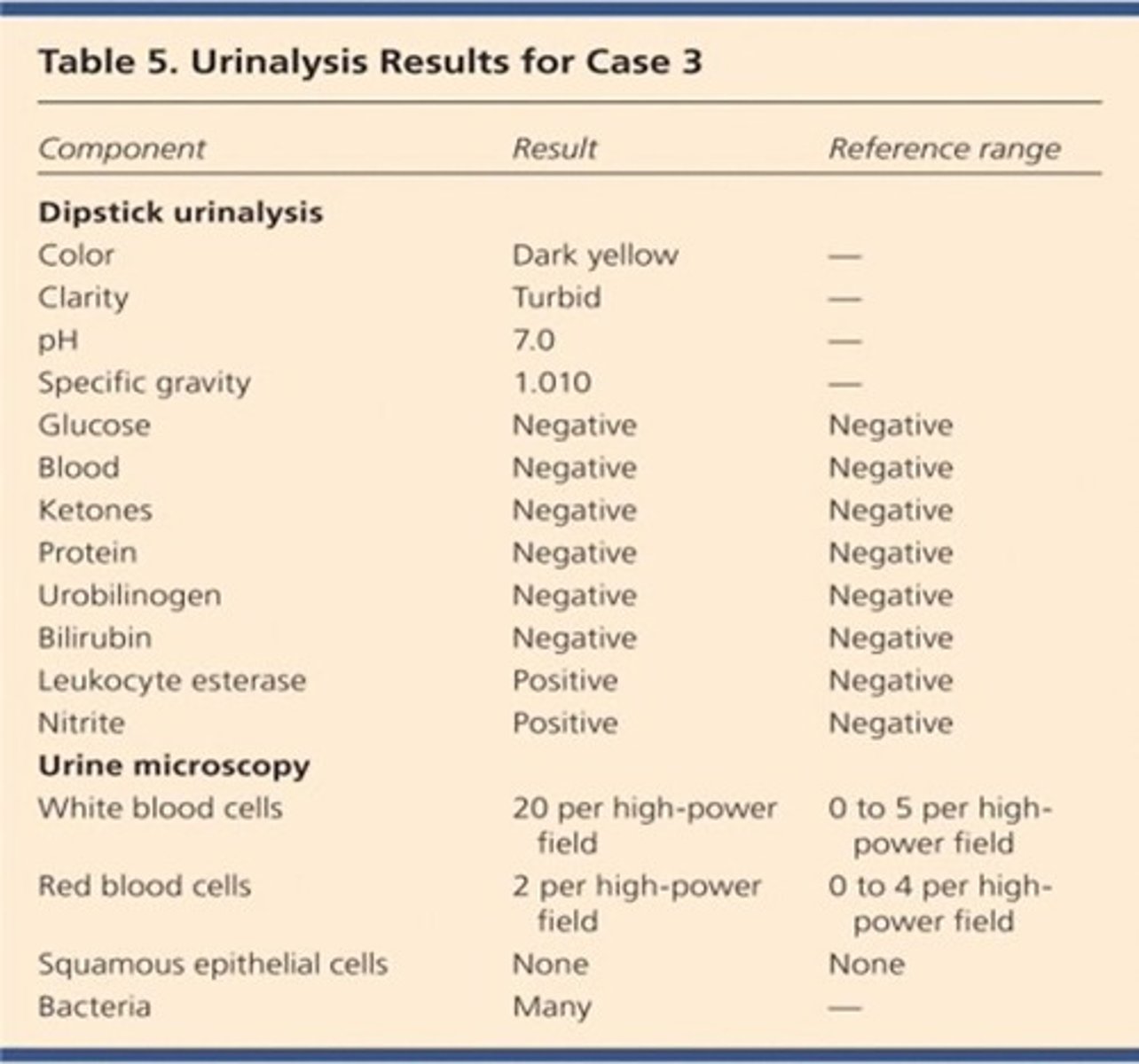
glomerulonephritis urine analysis
-red blood cells and protein in urine or white blood cells
• Blood is 3+ = could indicate menstrual, UTI, stones, or malignancy
• Protein is 2+ = could indicate dehydration, fasting, kidney disease, diabetes, or UTI
• RBCs are high = could indicate stones, renal disease, infection
• Casts are present
• The patient has glomerular nephritis
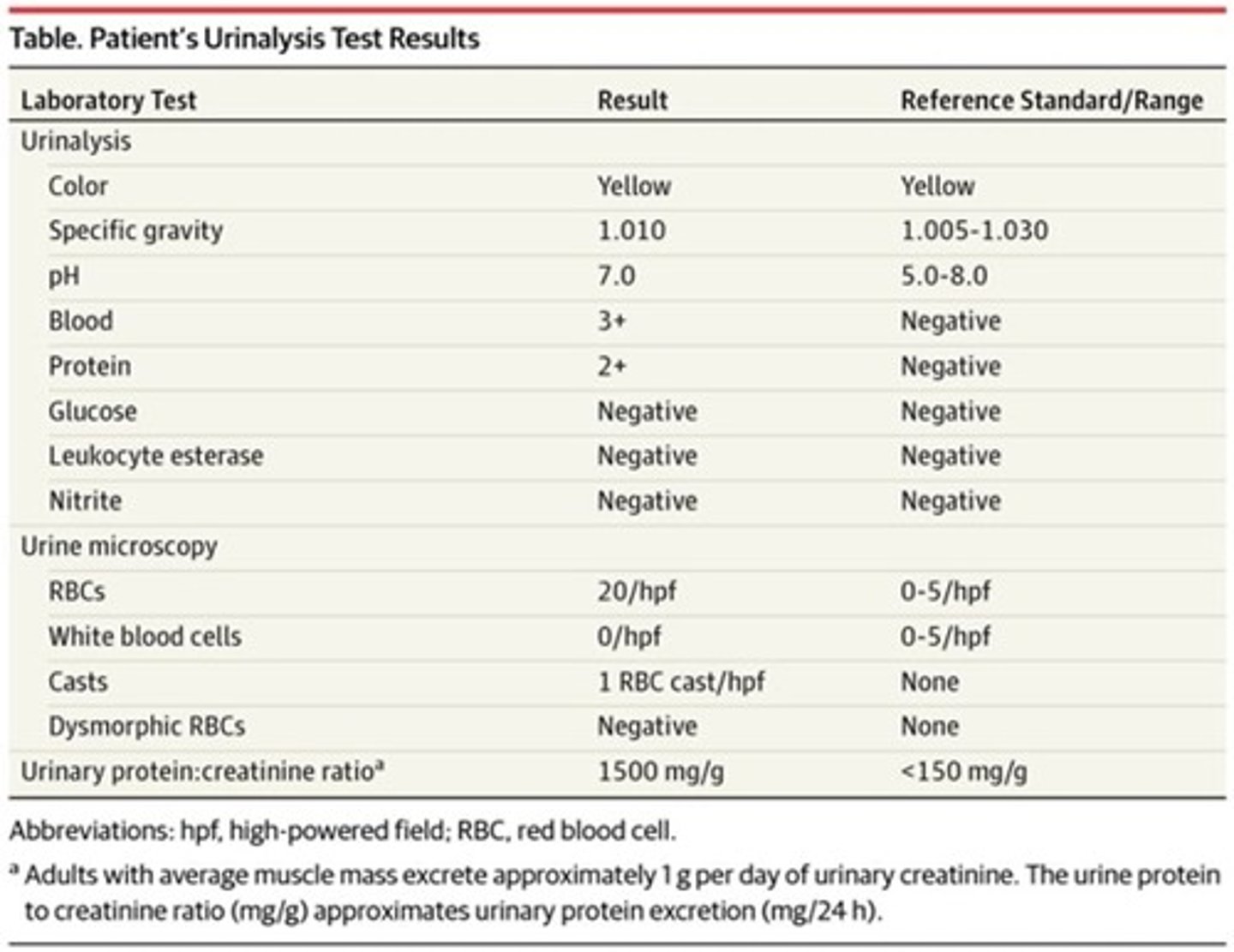
normal (urine)
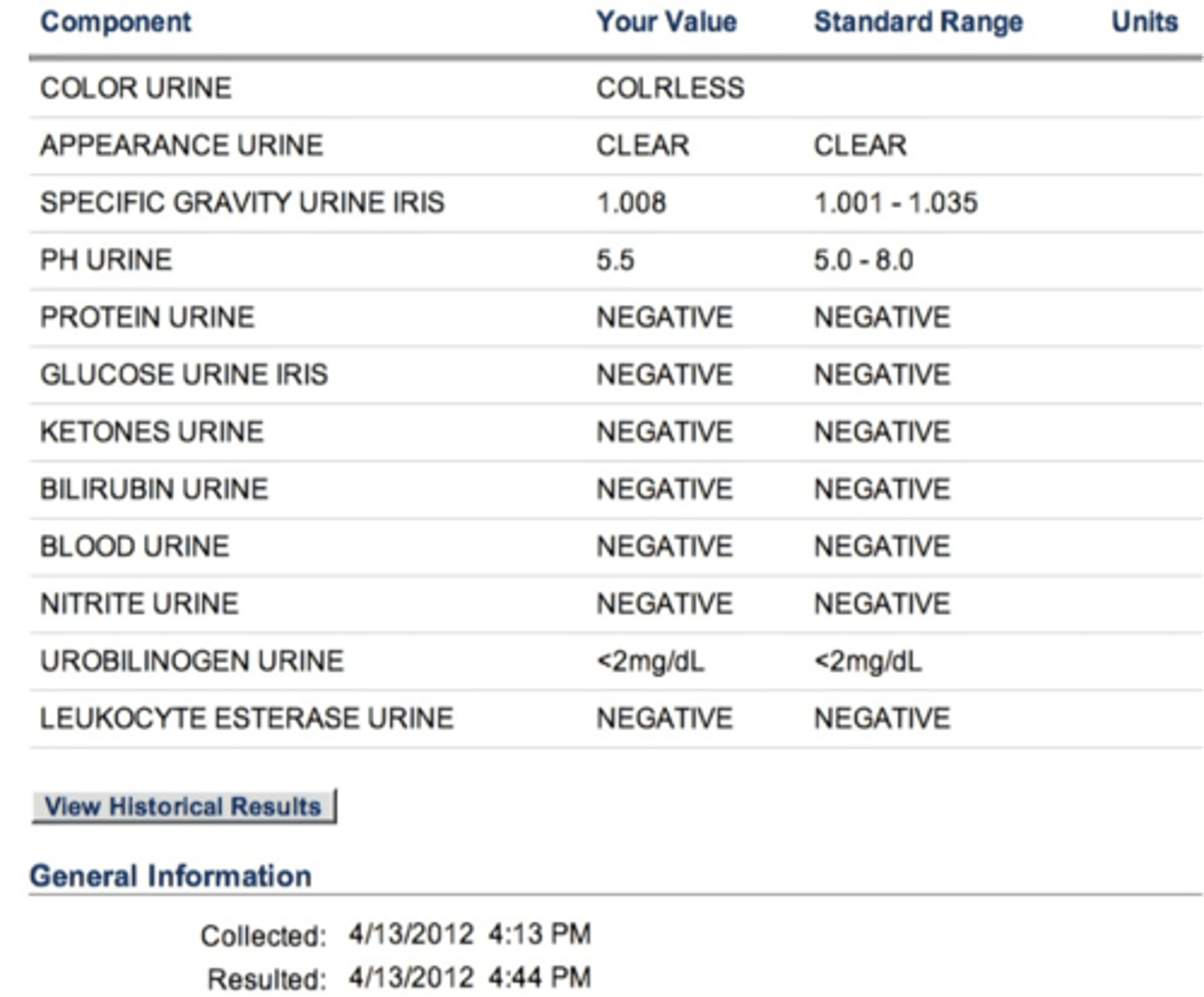
• Few RBCs, severe increase in glucose, protein is 100, bacteria is occasion
• Dd: diabetes or nephrotic syndrome
• Diabetes because of the excreted protein
• Diabetes with the end stage renal failure
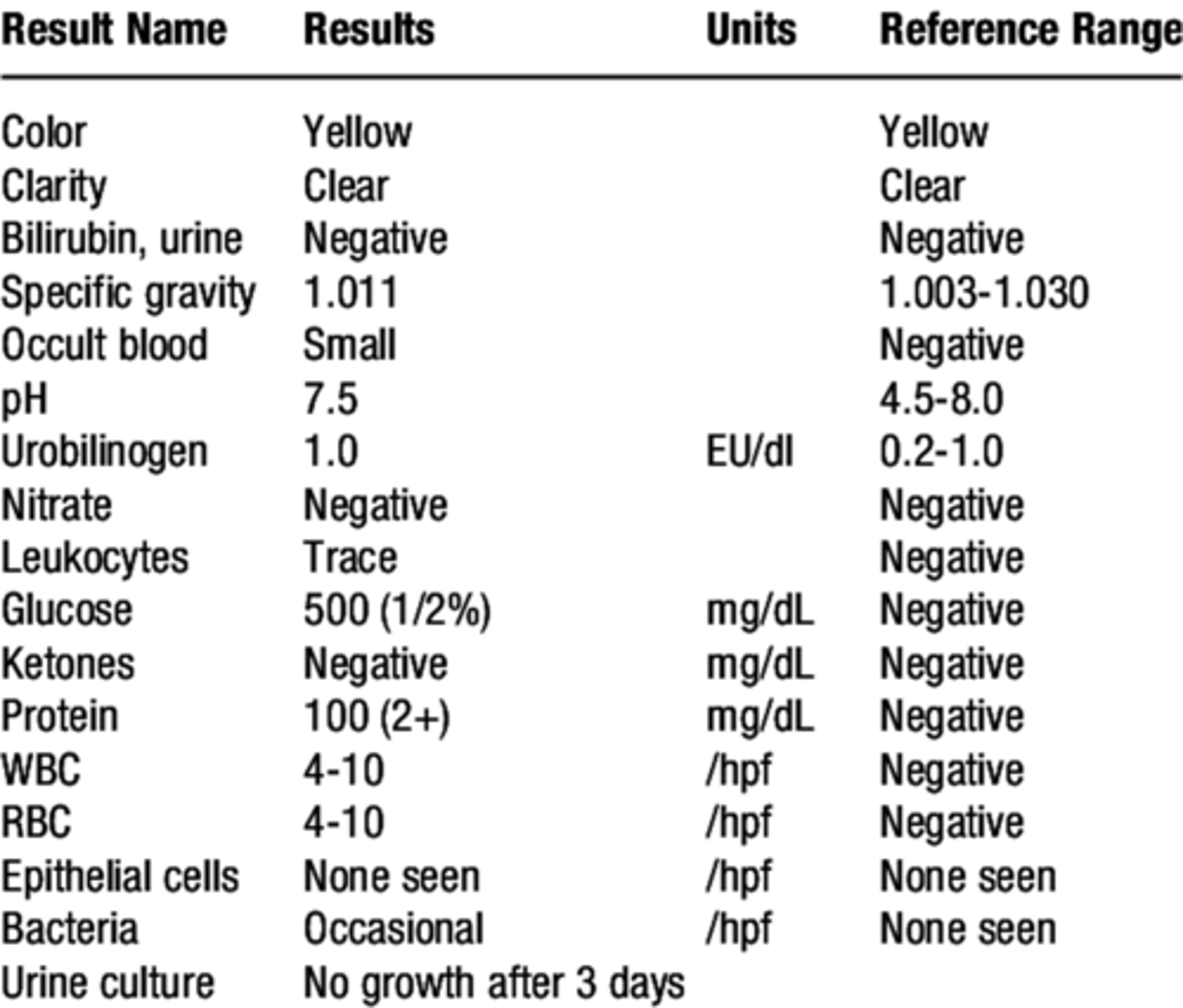
• Bilirubin is 1+
• DD: Increase bilirubin needs a test for liver function. Then you should search for liver diseases.
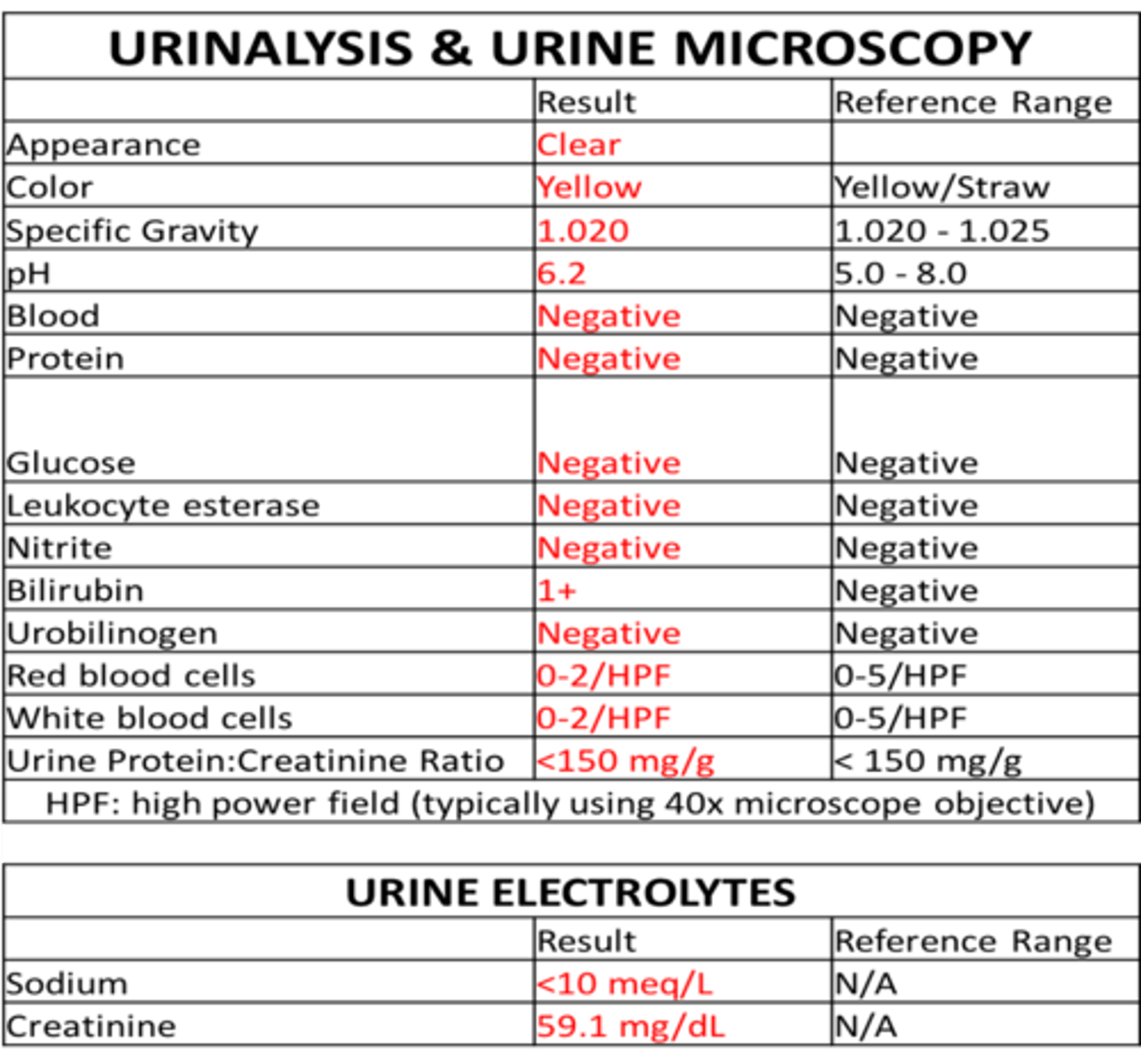
UTI diagnosis
-microscope
-urinalysis
-urine cultue
-images
stool
• Made of ¾ water and ¼ solid.
• included:
• undigested and unabsorbed foods.
• intestinal secretions, mucosa.
• Bile secretion and salts.
• Bacteria and inorganic material.
• Epithelial cells and leukocytes
brown stool color
normal
black stool indicates
-bleeding in the upper GI tract
-drugs