BIO120 Test Review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
living things change over time
adaptation arises due to natural selection
What are the two core tenets of evolution?
Heritable variation in fitness
What is natural selection?
Experimental
Theoretical
Observational
Comparative
What are the four types of approaches to studying evolution?
Evolutionary history, evolutionary mechanisms
What are the two branches of studying evolution?
A phenotypic trait that gives higher relative fitness in a population
The processes that allow for the former definition to arise
What are the definitions for Adaptation?
William Paley
Who argued for “The Argument From Design?”
Lemarck
Who argued for “Inheritance of acquired characteristics?”
The idea that the DNA can transfer information to proteins, but never in reverse. It did disprove Lemarck’s idea.
What did August Weissman argue for, and did it disprove Lemarck’s idea?
Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
Who came up with the Theory of Natural Selection?
Uniformitarianism and gradualism
What did Lyell discover?
The idea that the process that shaped the earth in previous eons are the same ones that appear today.
Define “Uniformitarianism”
The idea that quickly reproducing organisms are not swelling in population rapidly for some reason or another.
What was it that Malthus wrote about?
Transformational Evolution (Within generations), and Variational Evolution (between generations)
What were the two kinds of evolution that people believed in?
There must be variation within a population
This variation must be heritable
Some organisms confer better fitness in their environment than others
What are the 3 requirements for natural selection to occur?
Brazil: Geology
Galapagos Isles: Biogeography, Homology
Australia: Biogeography
Darwin’s Garden at the Down House: Domestication
What are the four countries and branches where evidence for evolution was found?
Transitional fossils, species linkages, familiar organisms on fresher strata
How did Geology prove evolution?
Vestigial structures (ex. appendix, dysfunctional wings), homologous structures (ex. altered forelimbs), similar gene composition (500 genes shared)
How did Homology prove evolution?
Colonization from cacti, birds, geographical separation leading to diversity within species and early stages of speciation
How did Biogeography prove evolution?
Artificial selection, maize vs. corn, ancestor to present-day changes
How did Domestication prove evolution?
Mutations
Independent Assortment
Recombination
What are the three sources for Genetic Variation?
Point mutations
“Indels” (Insertions/deletions)
Change in repetition #
Chromosomal rearrangement/inversion
What are the four kinds of mutations?
They can be beneficial, neutral, or deleterious
How can mutations affect fitness?
True
True or False: A phenotype is a combination of both genetic factors AND environmental ones
True
True or False: Mutation rates can be affected by environment
False
True or False: Mutations are deterministic
Stochastic: Random, unpredictable
Deterministic: Predictable, non-random
Define “Deterministic” and “Stochastic”
Preformationism: Genetic material comes from a single parent
Blending Inheritance: Genes mix together irreversibly, like paint
What were the two types of pre-mendelian ideas of genetics, and how did they work?
Genes are discrete particles
Diploid organisms
Fusion of gametes
What did Mendel conclude?
False, some are continuous
True or False: All phenotypic traits are genotypically discrete
Mendelian genetics (discrete variation (few genes of large effect))
Continuous variation (many small genes)
What are the two modern ideas of genetics?
Fischer, Haldane, Wright
Who made the first mathematical model of evolution?
Mutation - increase
Recombination - increase
Genetic Drift - decrease
Positive/Directional Selection - decrease
Purfying/Negative Selection - decrease
Selection Favouring Diversity - increase
Migration - increase within, decrease between
What are the all of the factors influencing genetic diversity, and do they increase or decrease?
The fraction of a population with a gene containing both possible alleles
Define “Heterozygosity”
Proportion of gene loci containing 2+ alleles within a population
Define “Polymorphism”
Morgan - Classical
Muller - Classical
Ford - Balance
Dobzhansky - Balance
Name the 4 key players of evolutionary schools of thought, and which they followed
High heterozygosity, high polymorphism
Heterozygote Advantage
Selection favours diversity
Define the principles of the balance school
Low heterozygosity, low polymorphism, high homozygosity
“Wild-type” is the normal gene
Negative/purifying selection is predominant
Define the principles of the classical school
Richard Lewontin
Who discovered Electrophoresis?
Motoo Kimura
Negative selection removes deleterious traits, positive selection fixes beneficial ones, the only remaining observable traits for genetic variation are selectively neutral
Who coined the ‘neutral theory’, and what are its tenets?
Analyzed organisms for polymorphism
What did Alivia Dey do?
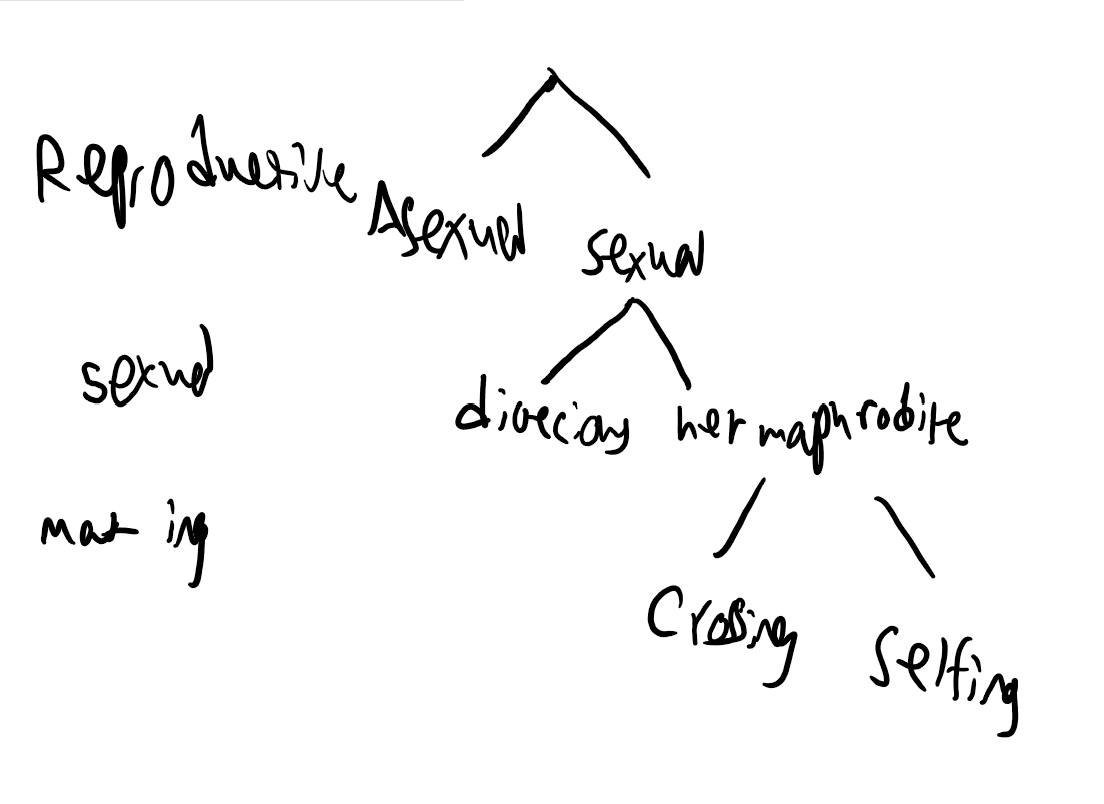
Note: Remember Parthenogenesis Vs. Clonal Propagation
Fill-in-the-blanks for the tree and its categories
False
True or false: Selfing is a process of asexual organisms
Cost of males
50% of genes from females
Transmission bias for asexuals
Time/energy cost to mate/find mates
Risk of STD, predation
Loss of favourable allele combos
List the costs of sexual reproduction
Fixation of positive genes and elimination of harmful ones
Genetic variation improves survivability of species in unpredictable environments
List the benefits of sexual reproduction
Speed of production
2:3 transmission bias
List the benefits of asexual organisms
Accumulation of deleterious traits
More difficult to remove deleterious traits, slower to fix beneficial ones
More likely to go extinct
List the downsides of asexual organisms
Kin recognition
Different flowering times
Self-incompatibility
Dispersal by sex
Delayed maturation
Extra-pair copulation
What are some methods of inbreeding avoidance?
Increases homozygosity
Decreases heterozygosity
Reduces H by 50% per generation
Inbreeding Depression
What are the consequences of inbreeding?
False, inbreeding DEPRESSION changes allele frequencies
True or False: By itself, inbreeding DOES change allele frequencies
Lower fertility
Lower viability
Homozygosity of deleterious alleles
What are the consequences of inbreeding depression?
Disruptive (creates a bimodal graph, can result in speciation)
Directional (increases/decreases overall mean)
Stabilizing (increases frq. average, decreases outliers)
Three types of GRAPHICAL selection
Environment-Organism correlation: Moth color concentration
Genetic Signatures: Relationship between malaria and anemia gene
Long-Term Experimental Evolution (Richard Lenski): Experiment with citrate and e. coli
Methods of linking evolution to ecology + examples
Gene flow refers to the movement of genes from one population or another, migration is the movement of creatures from one population to another
What is the difference between gene flow and migration?
Gene flow: Against
Selection/drift: Towards
Do gene flow/selection/drift work TOWARDS or AGAINST speciation?
FALSE, it is measured using neutral markers
True or False: Gene flow is measured using beneficial genetic markers
Establish to homozygotic populations with distance, score frequency of heterozygotes, relative estimate of gene flow
How is gene flow measured?
Stochastic: Random, unpredictable forces (Ex. Genetic drift, recombination, mutation)
Deterministic: Predictable (Ex. natural selection)
What are “Stochastic” forces and “Deterministic” forces?
A swift decline in population followed by a rebound that generally causes a loss in diversity
What is a Population Bottleneck?
A small subset of a population is separated by geographic region with a small percentage of variation from previous population
What is a founder event?
Local adaptation, Genetic Drift, Phenotypic plasticity
What are the three causes of phenotypic differentiation?
Reciprocal Transplant Study
Name one way phenotypic plasticity is tested for
When a gene spreads so fast that other genes “hitchhike” and increase in frequency as well
Define “Selective Sweep”
Silent mutation: A mutation that does not affect the genome at all
Missense mutation: A mutation that changes the aminoacid that has mutated
Nonsense mutation: A mutation creating a premature stop codon
What is the difference between a silent mutation, missense mutation, and nonsense mutation?
What are methods of maintaining genetic diversity?
Mutation-selection balance
Selection maintaining variation / balancing selection