Androgens/Antiandrogens
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Androgens
_______ —> primary secreted androgen in men (______ ______) and women ( ______ ______ and ______ ______ )
______ and ______ (DHEA) —> weak androgens —> can be converted to ______
testosterone, Leydig cells, corpus luteum, adrenal cortex
androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone, testosterone
Androgen Synthesis and Secretion
hypothalamus —> ______ from its pulse generator
GnRH acts on the ______ ______ to stimulate the release of gonadotropins —> ______ and ______
pulsating GnRH secretion causes an ______ in LH and FSH, while continuous GnRH secretion causes ______ in LH and FSH
during the 1st trimester, the ______ produces ______ —> which mimics LH activity
stimulation of Leydig cells results in increased ______
Leydig cells produce about ______% of male testosterone, while the adrenal cortex contributes about ______%
in females, approximately ______% of testosterone comes from the adrenal cortex via DHEA
GnRH
anterior pituitary, FSH, LH
increase, decrease
placenta, hCG
de novo testosterone biosynthesis
95, 5
50
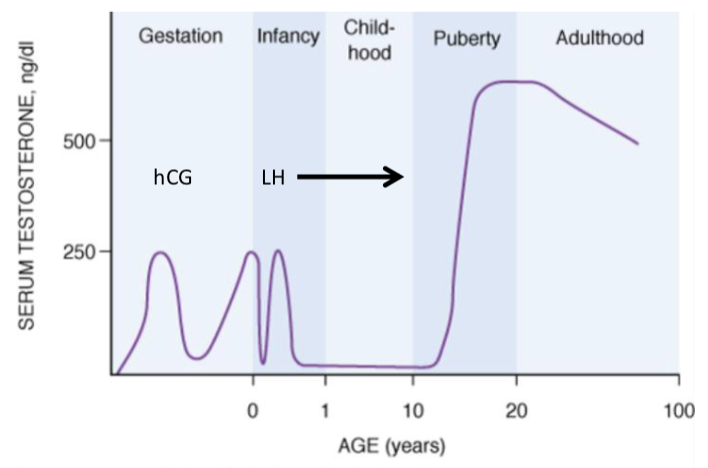
Male Serum Testosterone Concentration
during gestation, testosterone production is stimulated by ______
during infancy, testosterone levels briefly rise due to ______ stimulation
testosterone levels remain low during childhood because the ______ axis is inactive
at puberty, testosterone production sharply increases in response to elevated ______ levels
in adulthood, testosterone levels remain high but gradually ______ with age
daily testosterone secretion is ______ and ______ —> occurring about every ______ hours
testosterone levels are highest at ______ and ______
hCG
LH
hypothalamic-pituitary
LH
decline
diurnal, pulsatile, 2
8 AM, 8 PM
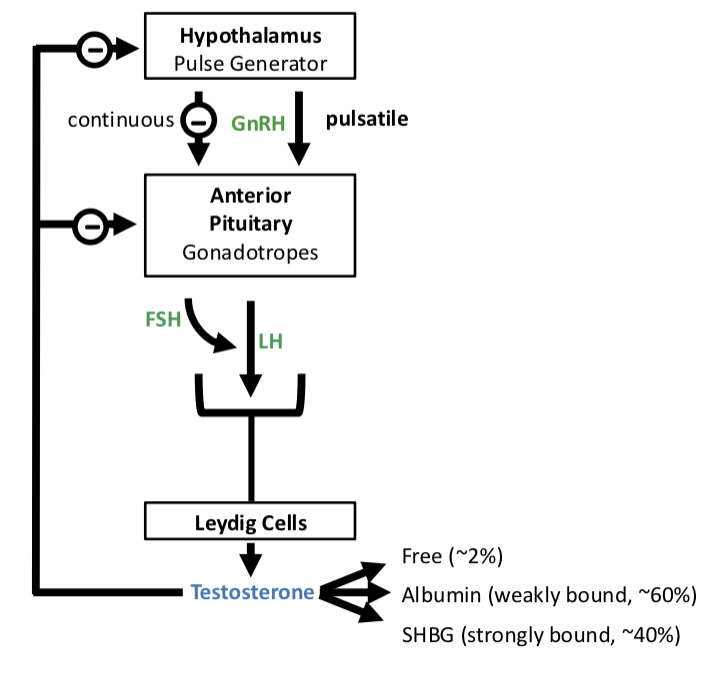
Testosterone Binding
free testosterone (____%) —> active form that diffuses into tissues
albumin-bound (~____%) —> weakly bound, still bioavailable
SHBG-bound (~______%) —> strongly bound, biologically inactive
2
60
40

Metabolism of Testosterone —> active and inactive metabolites
Testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme ________.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is about ________ as abundant as testosterone but is a more potent androgen.
Testosterone is converted to estradiol (E₂) by the enzyme ________.
A ring into a phenol group.
The two active metabolites of testosterone are ________ and ________.
5a-reductase
1/10
aromatase (CYP19)
dihydrotestosterone (DHT), estradiol
Direct and Indirect Effects of Testosterone
DHT binds to ______ receptors to exert its effects on external genitalia and hair follicles.
External genitalia → differentiation during ________ and maturation during ________.
Hair follicles → increased growth during ________.
Adult → contributes to ________ diseases.
Testosterone directly binds to ______ receptors in internal genitalia, skeletal muscle, erythropoiesis, and bone.
Internal genitalia → ________ development during gestation.
Skeletal muscle → increases ________ and ________ during puberty.
Stimulates ________ and supports ________ maintenance.
Estradiol binds to ________ receptors, mainly affecting bone and libido.
Bone → ________ closure and increased ________.
Contributes to ________.
androgen
gestation, puberty
puberty
prostatic
androgen
wolffian
mass, strength
erythropoiesis, bone
estrogen
epiphyseal, density
libido
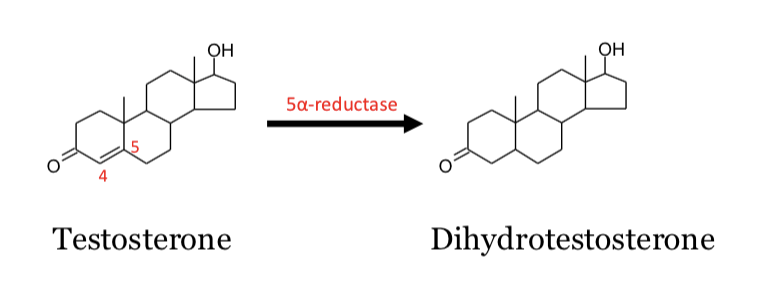
Dihydrotestosterone
the affinity of DHT for the androgen receptor is ______ than that of testosterone
the conversion of testosterone to DHT involves the reduction of the ______ double bond
greater
4,5-
Effects via the androgen receptor —> In Utero
formation of male ______ —> testosterone and external ______ —> dihydrotestosterone
internal, genitalia
In Utero Deficiency
caused by ______ or ______ receptors
results:
first trimester —> degree of deficiency determines the degree of ______ characteristics
third trimester —> results in ______ genital development
the role of androgens during infancy is ______
CYP17, dysfunctional
female
incomplete
unknown
Effects via the androgen receptor —> Puberty
promote ______ capability
cause drastic effects of a variety of ______ simultaneously
increased ______ production —> acne
increase ______ growth
increase ______ mass and ______
promote ______ growth
stimulate ______ —> inc. Hgb and Hct
______ changes like aggressiveness
reproductive
tissue
sebum
hair
muscle, strength
bone
erythropoiesis
behavior
Deficiency in Puberty
______ (increase/decrease) traits —> on previous flashcard
______ —> breast tissue enlargement due to relative estrogen excess
decreased
gynecomastia
Effects via the androgen receptor —> Adulthood
maintains adult ______ characteristics
contributes to ______ ______ ______
linked to ______ issues
benign prostatic hyperplasia —> ______ in prostatic cells converts testosterone to DHT
prostate cancer —> testosterone is not the cause, but the cancer ______ on testosterone
male
male pattern baldness
prostate
5a-reductase Ⅱ
depends
Adulthood Deficiency
regression of testosterone effects depends on the ______ and ______ of deficiency
if testosterone deficiency is substantial, ______ symptoms occur first
rapid —> decreased ______ and ______
gradual —> decreased ______ mass, ______, ______ and ______ ______ density
degree, duration
rapid
libido, energy
muscle, Hgb, Hct, bone mineral
Effects via the androgen receptor —> Senescene
testosterone ______ and SHGB ______ gradually with age
results in decreased —> (4)
decrease, increase
energy, libido, muscle mass and strength, bone mineral density
Effects via the estrogen receptor
conversion of testosterone to estradiol results in _____% of estrogen in males —> rest directly from ______
promotes fusing of ______
may play a role in regulating ______
a deficiency of estradiol during ______ prevents ______ closure —> individuals develop ______ limbs compared to the ______
85, testes
epiphysis
libido
puberty, epiphyseal, long, trunk
Testosterone — PK Issues
testosterone is ______ absorbed orally but rapidly ______ by the liver
because testosterone undergoes extensive ______ metabolism, most formulation are designed to bypass this effect
to avoid first-pass metabolism, testosterone preparations are given through alternative routes such as ______, ______ patch, and ______ ______
readily, metabolized
first-pass (hepatic)
IM, transdermal, topical gel
Testosterone Esters
are formed by adding a substituent to the ______ group on the testosterone molecule
examples of testosterone esters —> (2)
act as ______ that are converted to active testosterone through ______ ______ in vivo
compared to testosterone, these esters are more ______ and are usually dissolved in ______ for IM injection every ______ weeks
after injection, testosterone levels are initially ______ than normal but drop to ______ levels before the next dose
17a-OH
testosterone enanthate, testosterone cypionate
prodrugs, ester hydrolysis
lipophilic, oil, 2-4
higher, low-normal
Testosterone Toxicity —> Endogenous Doses
has no true “______ ______” but ______ effects such as acne and aggression may occur
mainly seen in the presence of ______ illnesses
increase ______ in someone with erythrocytosis
increase ______ and ______ retention effects in CHF
side effects, puberty-like
concomitant
erythropoiesis
sodium, water
Testosterone Toxicity —> High Dose
decrease ______ size and function due to ______ feedback
______ can occur from testosterone’s aromatization to estradiol
can cause ______ and ______ and ______ retention
in women, and children, high testosterone levels produce ______ male testosterone effects
testicular, negative
gynecomastia
erythrocytosis, sodium, water
Testosterone Toxicity —> Cardiovascular System
According to the FDA, there is a possibility of increased ________ risk associated with testosterone use, despite ________ and inconclusive evidence.
some evidence suggests a higher cardiovascular risk in ______ men
risk is slightly higher in patients with existing ______ ______ disease
the greatest risk occurs with ______ preparations that lead to ______ concentrations of testosterone
cardiovascular risk is unlikely in men who are legitimately ______ and require replacement therapy
cardiovascular, conflicting
older
coronary artery
injectable, supraphysiological
hypogonadal
Testosterone Undecanoate
orally ______, long-acting ______ ester
when given orally (in oil), it bypasses the ______ ______ pass effect by being absorbed through the ______ system
when administered IM (in oil), it provides stable testosterone concentrations for about ______ months
bioavailable, testosterone
hepatic first, lymphatic
2
Testosterone Undecanoate —> Injection
more ______ than other esters
not used in age-related ______ or patients under ______ years old
rare but severe risks can occur soon after injection, including:
pulmonary oil ______ and ______
due to these risks, testosterone undecanoate has highly ______ availability and requires ______ after administration
toxic
hypogonadism, 18
microembolism, anaphylaxis
restricted, monitoring
Alkylated Androgens
modified forms of testosterone with a substituent at the ______ position
orally ______, but are less ______ than testosterone
additional toxicity can occur even at ______ doses
_______ —> may cause ______ by blocking bile flow, and occasionally ______ _____
can cause a decrease in ______ due to increased metabolism via hepatic triglyceride lipase
examples —> (5)
17 a
bioavailable, androgenic
physiological
hepatotoxicity, cholestasis, peliosis hepatis
HDL
methyltestosterone, oxandrolone, stanozolol, fluoxymesterone, danazol
Male Senescene
testosterone therapy in older men has shown evidence for an increase in ______ and ______ and a decrease in ______
decrease ______, ______ ______, and ______
testosterone therapy may worsen ______ or increase the incidence of ______ cancer
bone mineral density, muscle mass, fat mass
mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke
BPH, prostate
Hypogonadism
______ indication for testosterone therapy
monitor for efficacy
______ ______
______ ______ —> normal puberty effects in boys or restoration of male characteristics in adults
primary
serum concentrations
hormone effects
Other Indications
can be used in catabolic and ______ states
generally only effective for this indication in muscle wasting associated with ______
used in ______ transition
goal plasma levels —> ______ mg/day
wasting
AIDS
female-to-male
300-500
Athletic Performance Enhancement
testosterone use for athletic performance is ______ by the FDA because it is not a legitimate indication and has many adverse effects
“anabolic steroids" refer to ______-alkylated agents which are easily detectable and toxic
______ esters or ______ are less detectable
androstenedione (does / does not) work
name two other androgens sometimes used for performance enhancement:
not recommended
17a
testosterone, hCG
does not
DHEA, tetrahydrogestrinone (novel structure)
Inhibitors of Testosterone Secretion
GnRH antagonist inhibit ______, and therefore inhibit ______ secretion
Ketoconazole inhibits ______ enzymes decreasing both ______ and ______ —> although it’s mainly used to reduce ______ levels
LH, testosterone
CYP, cortisol, testosterone, cortisol
Inhibitors of Androgen Action
Androgen Receptor Antagonists
______/______/______/______ —> indicated for metastatic prostate cancer
often used in combination with a ______ analogue
androgen receptor blocker inhibits adrenal testosterone action
GnRH analogue suppresses testosterone release from Leydig cells in the testes
______ weakly inhibits androgen receptors as a side effect of its intended ______
common side effect —> ______
5a-reductase inhibitors
______/______ —> block conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
indicated for ______ and ______ ______ ______
adverse effects include ______ and ______
flutamide, bicalutamide, nilutamide, enzalutamide
GnRH
spironolactone, aldosterone
gynecomastia
finasteride, dutasteride
BPH, male pattern baldness
impotence, gynecomastia