chemistry paper 2 knowledge
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
fluorine
F2
pale yellow
gas
chlorine
Cl2
pale green
gas
bromine
Br2
orange-brown
liquid
iodine
I2
grey (can form poisonous purple vapours)
solid
halogen displacement reactions
Cl- | Br- | I- | |
|---|---|---|---|
Cl2 | yellow/orange solution | brown solution n black ppt | |
Br2 | no change | brown solution n black ppt | |
I2 | no change | no change |
cation flame test
red Li+
yellow Na+
lilac K+
orange / red Ca2+
green / blue Cu2+
cation hydroxide precipitate test
ion | colour of hyd.ppt | dissolves w excess NaOH? |
|---|---|---|
Fe 2+ | green | |
Fe 3+ | orange/brown | |
Cu 2+ | blue | |
Ca 2+ | white | no |
Mg 2+ | white | no |
Zn 2+ | white | yes |
Al 3+ | white | yes |
testing for sulfate ions (SO42-)
few drops of HCl
few drops of BaCl2
if present → white preciptate of BaSO4 (insoluble in HCl)
testing for carbinate ions (CO32-)
few drops of HCl
if present → effervescence as CO2 produced
can be confirmed by limewater
testing 4 Halide ions (Cl-, Br-, I-)
few drops of HNO3
then few drops of AgNO3
if present → precipitate
ion | colour |
|---|---|
Cl - | white ppt |
Br - | cream ppt |
I - | yellow ppt |
choosing reaction pathway
% yield
atom economy
can by-products be used, or toxic?
rate of reaction
possibly equilibrium condition
continuous vs batch process
factor | continuous | batch |
|---|---|---|
cost of factory equiptment | high | low |
rate of production | high | low |
shut-down times | rare | often |
workforce | few ppl needed | many ppl needed |
ease of automation | relatively easily | relatively difficult |
making ethanol - fermentation of renewable raw materials (glucose)
advantages | disadvantages |
|---|---|
cost of raw materials low | rate of reaction low |
conditions (temp n pressure) r moderate | % yield is low - around 15% |
energy requirement is low | product has low purity n needs filtering/fractional distillation |
making ethanol - hydration of non renewable raw material (ethene)
temp 300oC, pressure 60 atmospheres, phosphoric acid catalyst
C2H4(g) + H2O(g) = C2H5OH(g)
advantages | disadvantages |
|---|---|
rate of reaction high | cost of raw materials high |
% yield high - around 95% | conditions (temp n pressure) r high which is £££ to maintain |
product has high purity n no by-products | energy requirement high |
haber process
N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(g)
H = -93kJmol
pressure 200 atm (compromise, higher pressure would be better as fewer mol of gas on right, but expensive n hazardous)
temp 450oC (compromise, lower would be better as forward direction exothermic but then rate too slow)
iron catalyst (doesn’t change equilibrium position. makes reaction faster)
unreacted gases recycled
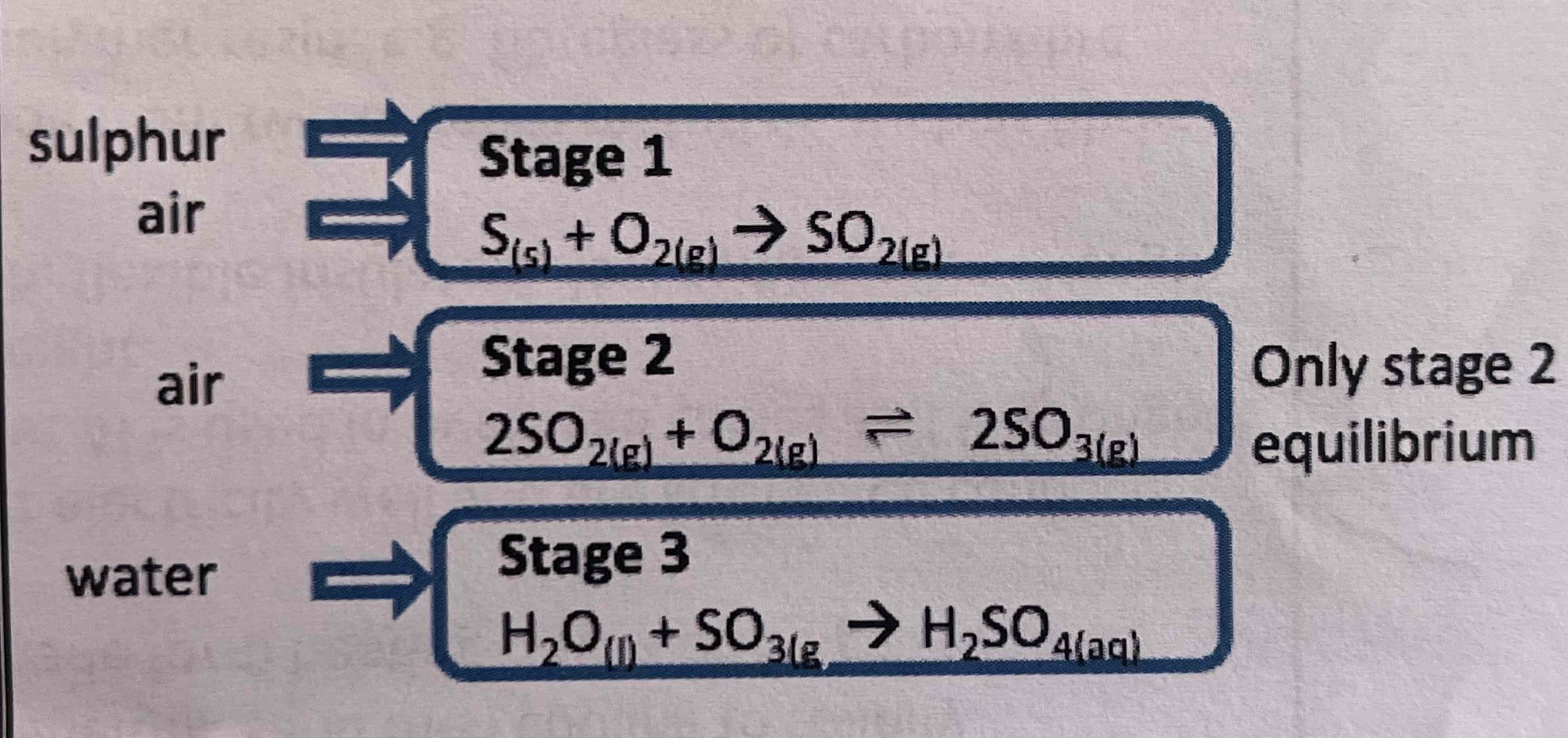
contact process
pressure 2 atm (equilibrium position already lies quite far to right, so only small increase is needed to push gases through converter)
temp 450oC (forward reaction is exothermic so low temp will increase yield but compromise made to achieve reasonable rate and catalyst only works at temps above 380oC)
vanadium (V) oxide catalyst - V2O5
stage 3 v exothermic - would produce hazardous acidic mist
so carried out in 2 stages where SO3 passed through some previously produced H2SO4 to make H2S2O7 (oleum)
this then added to water to make larger vol of H2SO4
steel
Fe
strong
buildings, bridges, cars
duralium
Al, Cu
lightweight
aircraft parts
solder
Sn, Cu
low mp
joining electrical parts
brass
Cu, Zn
strong, resists corrosion
bells, propellers on ships
ceramics
hard non-metallic materials (brick, china porcelain, glass) formed of metals n non-metals in giant lattice
high mp, hard stuff but brittle n poor conductors of heat n elec
glass
made by melting sand then cooling to solidify
Most of the glass we use is soda-lime glass. This is made by melting a mixture of sand (silicon oxide), sodium carbonate, and limestone, then allowing the molten liquid to cool and solidify.
Borosilicate glass is made by heating sand with boron trioxide. Borosilicate glass has a much higher melting point than soda-lime glass.
Glass is transparent, strong and a good thermal insulator, which makes it useful for windows.
clay ceramic
made from heating clay. can be glazed to be waterproof
metals
conduct elec well n r strong
Cu conducts elec well but Al used in overhead cables as its stronger n more lightweight
polymers
tough, flexible insulators, low compressive strength, squash easily
composites
made from 2 or more materials w diff properties, eg fibres embedded in polymer resin. eg. fibreglass or carbon fibre
made from the reinforcement and the matrix (binds the reinforcement together)
concrete
composites of small stones, sand n cement
but low tensile strength (fancy word basically j tension) so reinforced w steel
plywood
layers of wood set at right angles w glue n layer inbetween, so resists bending n strengthens it
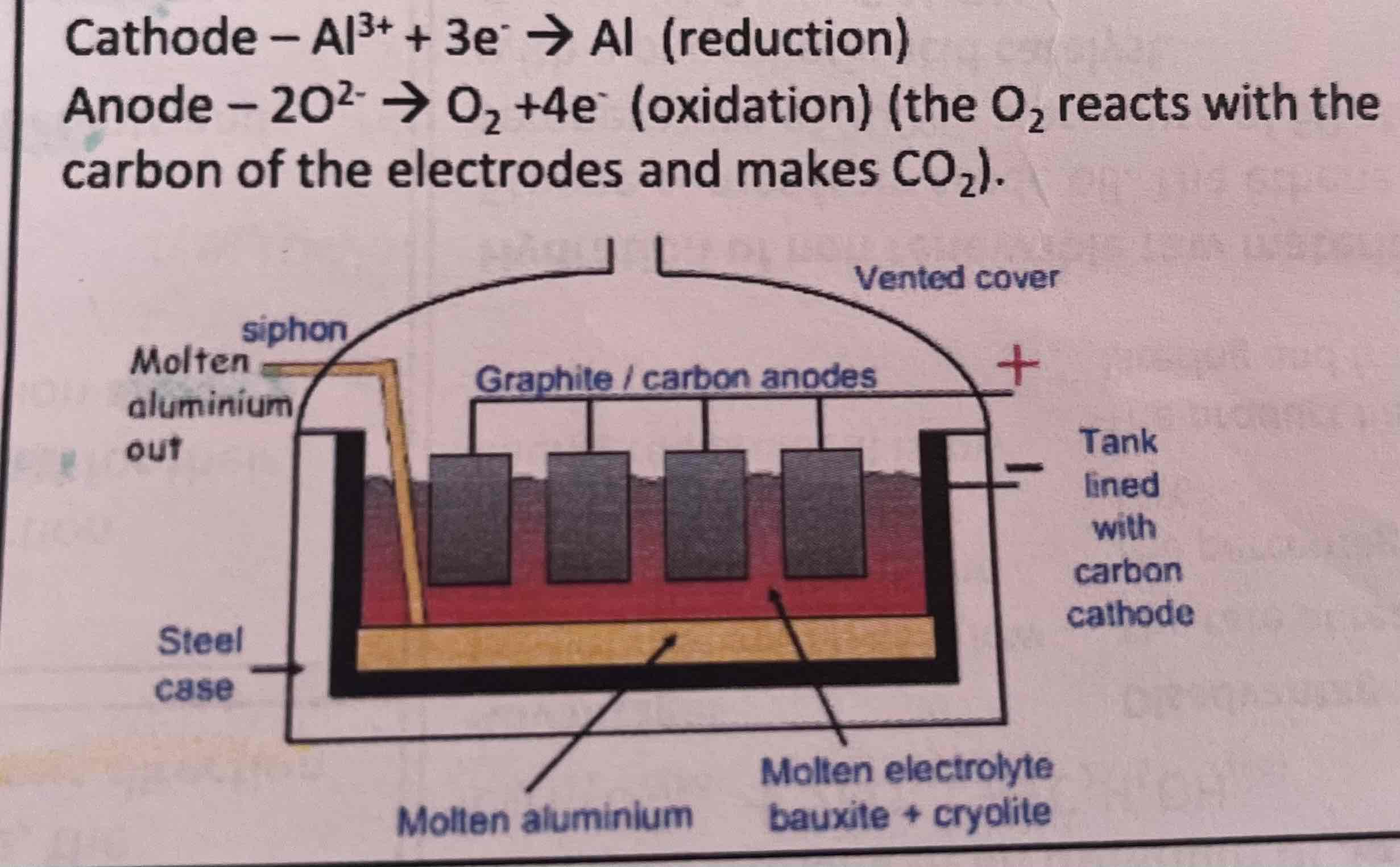
extracting aluminium
aluminium ore (bauxite) contains Al2O3
more reactive than carbon so cannot be extracted in same way as iron or copper
if Al2O3 dissolved in molten cryolite, mp reduced from over 2000oC to 950oC
Al2O3 dissociates from its ions n electrolysis used to extract
carbon monoxide CO
produced from incomplete combustion of fuels containing carbon
toxic, colourless, odourless gas
attaches to haemoglobin - reduces amount of O2 blood can carry - increase chance of heart disease
symptoms - breathing difficulties, drowsiness, even death
particulates
small particles that can settle deep in lungs - breathing problems, bronchitis, increasing chance of heart disease
produced during incomplete combustion n in industrial processes
PM10 r only 10micrometre in diamter (x10-6)
acid rain
formed from NOx produced in high temp of car engines which dissolves in moisture in air, from SO2 produced when ff (which contain sulfur impurities) burned
alternative bio fuels
ethanol from fermentation of plants: | pros | cons |
|---|---|---|
carbon neutral | engines need to be converted | |
only other product is water | not widely available |
biodiesel from veg oil: | pros | cons |
|---|---|---|
carbon neutral | £££ to make | |
engines don’t need to be converted | could increase food prices if farmers grow crops for biodiesel instead of food |
other key terms
lithium oxide Li2O
sodium oxide Na2O
sodium peroxide Na2O2
potassium peroxide K2O2
potassium superoxide KO2
formulas
acid + alk → salt + water
acid + metal oxide → salt + water
acid + carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
alkali metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
metal + oxgen → metal oxide
metal oxide = alk
non metal oxide = acid
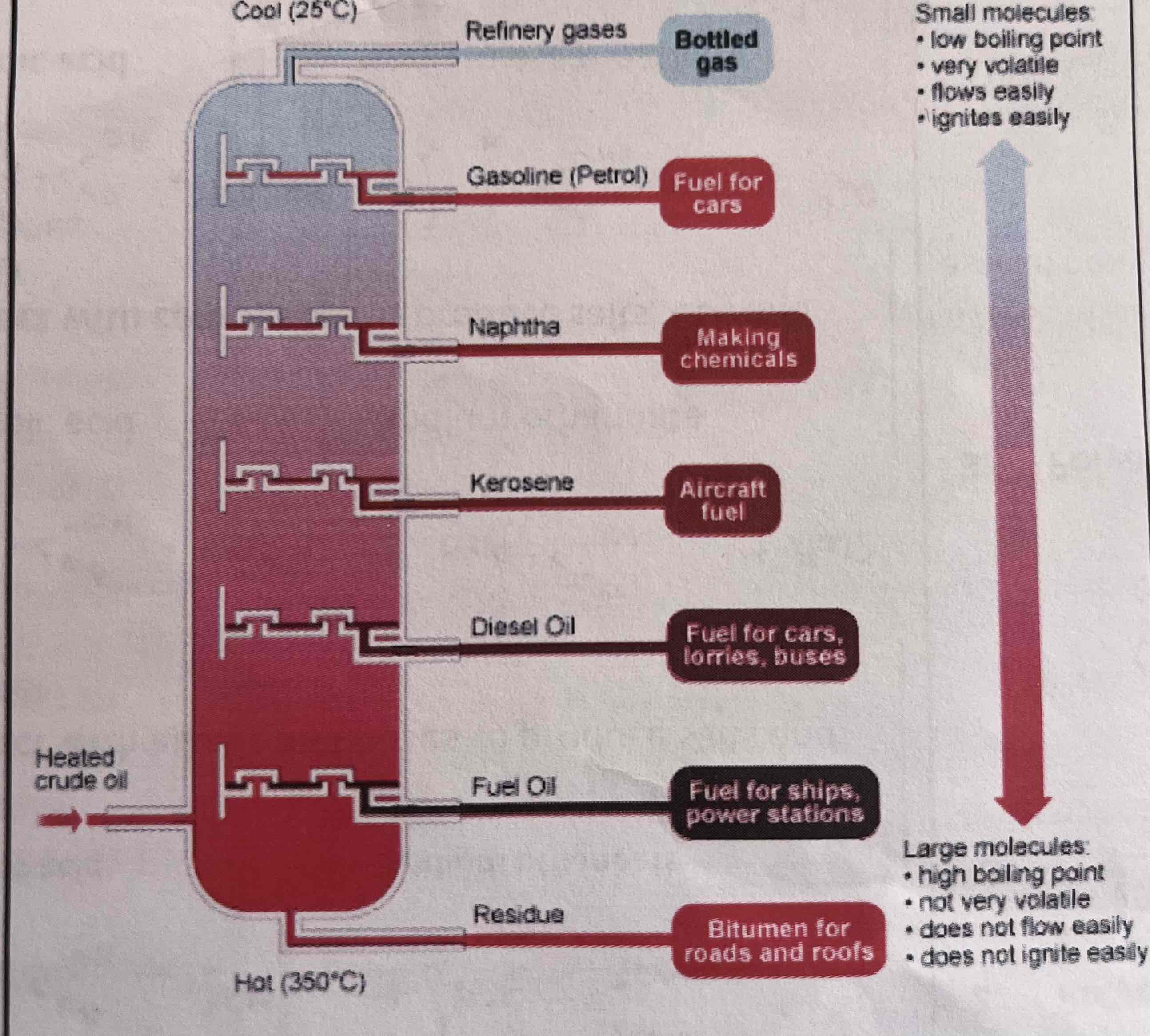
alkanes from crude oil
metal properties
Melting point - the temperature at which a solid melts into a liquid.
Conductivity - how well a material conducts electricity.
Strength - the ability of a material to resist an applied force (it is hard to change the shape of a strong material).
Hardness - how well a material can resist being scratched or indented (hard materials don't scratch).
Brittleness - how easily a material breaks when a force it applied (brittle materials snap easily).
Stiffness - how well a material can resist bending (a stiff material won't bend very much).