Functional Groups/Isomers/Microscopic Images - Kam
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
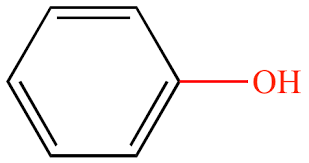
Hydroxyl: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
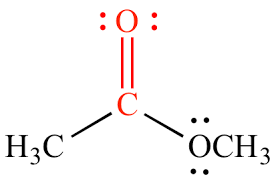
Carbonyl: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
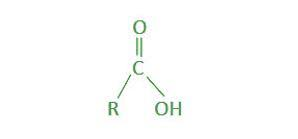
Carboxyl: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
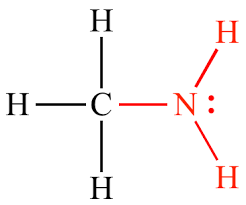
Amino: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
Sulfhydryl: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
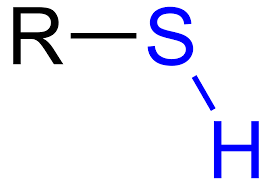
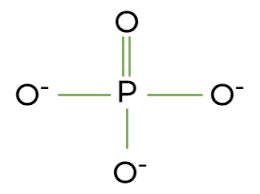
Phosphate: Polar/Hydrophilic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
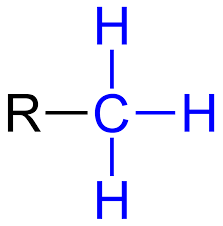
Methyl: Nonpolar/Hydrophobic
What structure is this, its stance in water and charge
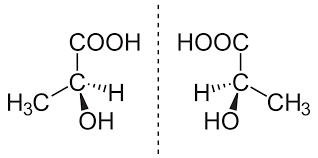
Enantiomer
Mirror images of each other (Have to have asymmetric carbon that has 4 different components attached to it).
Structural
Different covalent arrangements of their atoms.
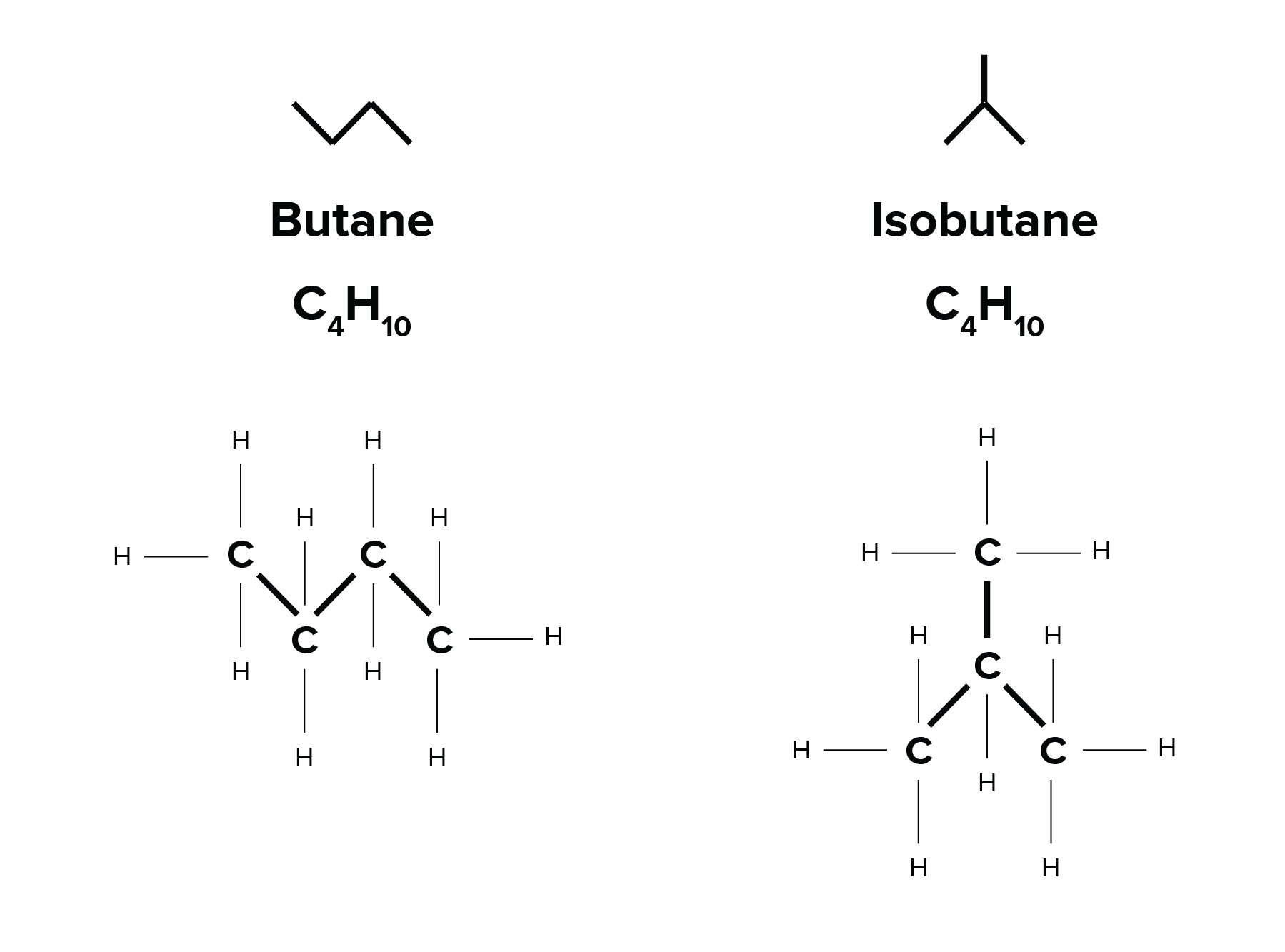
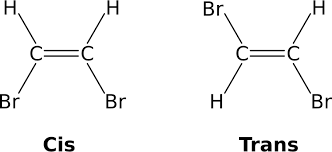
Geometric (Cis/Trans)
Same covalent arrangements but differ in spatial arrangements (Have to have a double bond, cis = same side, trans = oppo side).
Rough ER: protein synthesis, folding, modification (like glycosylation), and transport
What is this & its function

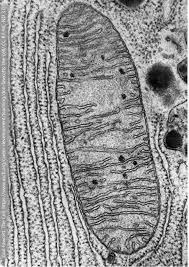
Mitochondria: generating most of the cell's supply of ATP for energy through cellular respiration & converting nutrients into usable fuel
What is this & its function
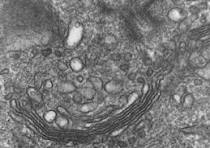
Golgi Apparatus: cell's post office, receiving proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), modifying and sorting them, and packaging them into vesicles for delivery to their final destinations, like the cell membrane, lysosomes, or outside the cell for secretion (e.g., insulin)
What is this & its function
Smooth ER: lipid and steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, detoxification of drugs/poisons, and calcium storage
What is this & its function
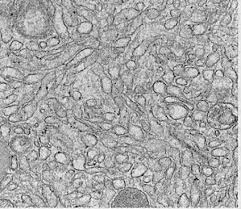
Cytoskeleton: provide cells with shape and structural support, facilitate internal organization and transport (moving organelles/vesicles), enable cell movement, and play crucial roles in cell division and signaling
What is this & its function
Chloroplast: capture sunlight to perform photosynthesis, converting light energy, water, and CO2 into glucose (food) and oxygen
What is this & its function

C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
Cellular Respiration Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis Equation