Medicinal Plants 2 and Mitosis
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Plant meristems
the site of cell growth in plants where cell division, enlargement, and differentiation (specialization) occur
Cell division
the process by which one cell divides into two, has 2 parts: mitosis and cytokinesis
Mitosis
division of the nucleus/the process of nuclear division; consists of 4 stages
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm that separates two daughter nuclei into two cells
begins in late anaphase & is completed by late telophase
Phragmoplast (vesiles, microtubules, and ER) accumulates across the center of the dividing cell
Cell plate forms in the middle of the cell
Cell plate
becomes the the cell wall that separates two new daughter cells and begins to form in early telophase
M (mitotic phase)
dividing phase
Interphase
the non dividing metabolically active stage in which a cell spends 90% of its time in and the stage where preparation for cell division occurs; has three phases
G1 (gap 1) phase
period of intense biological activity: cell is actively growing, organelles increase in size, protein synthesis occurs, respiration occurs
S (synthesis) phase
DNA is duplicated (other sister chromatid is formed)
G2 (gap 2) phase
increase in protein synthesis & final preparations for cell division are completed
Prophase
-Chromatin begins to condense and thicken, forming chromosomes
-Nuclear membrane & nucleolus disappear
-Chromosomes are free in the cytopasm
-Spindle starts to form
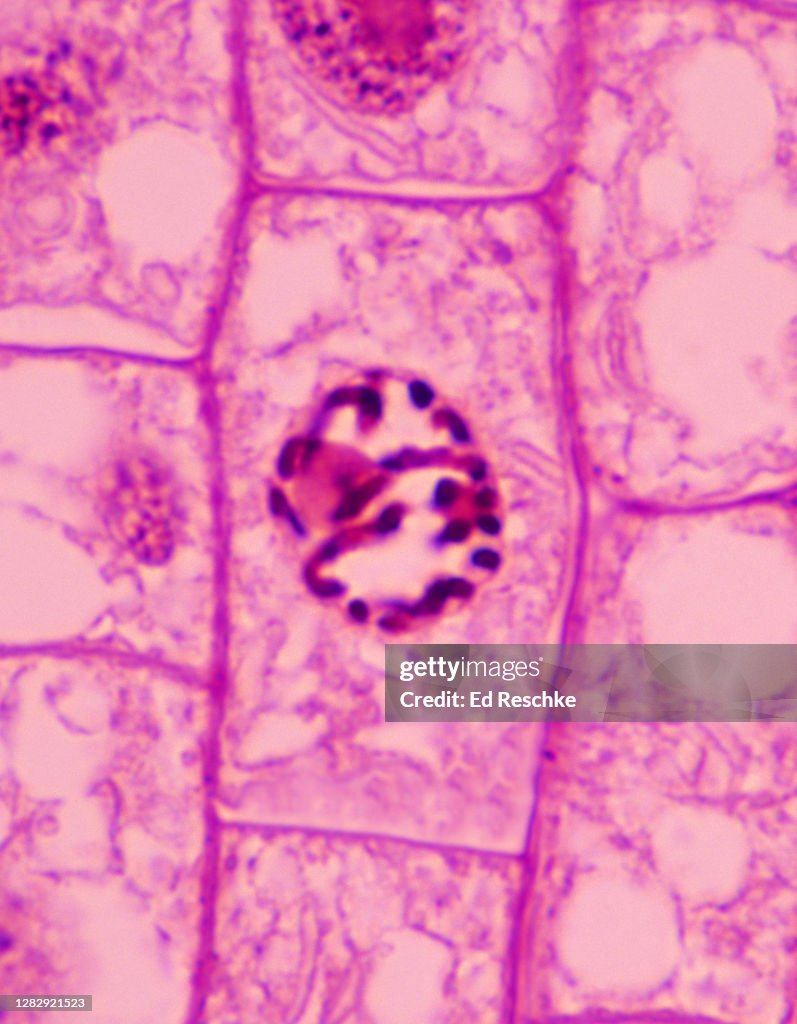
Spindle
a framework of microtubules that pull the chromosomes from the center of the cells to the poles
Microtubules
fibers that act like muscles
Metaphase
-Chromosomes line up on the cell’s equator
-Each centromere is attached to a spindle fiber
-Cell has two poles
-At the end of this phase, centromeres divide

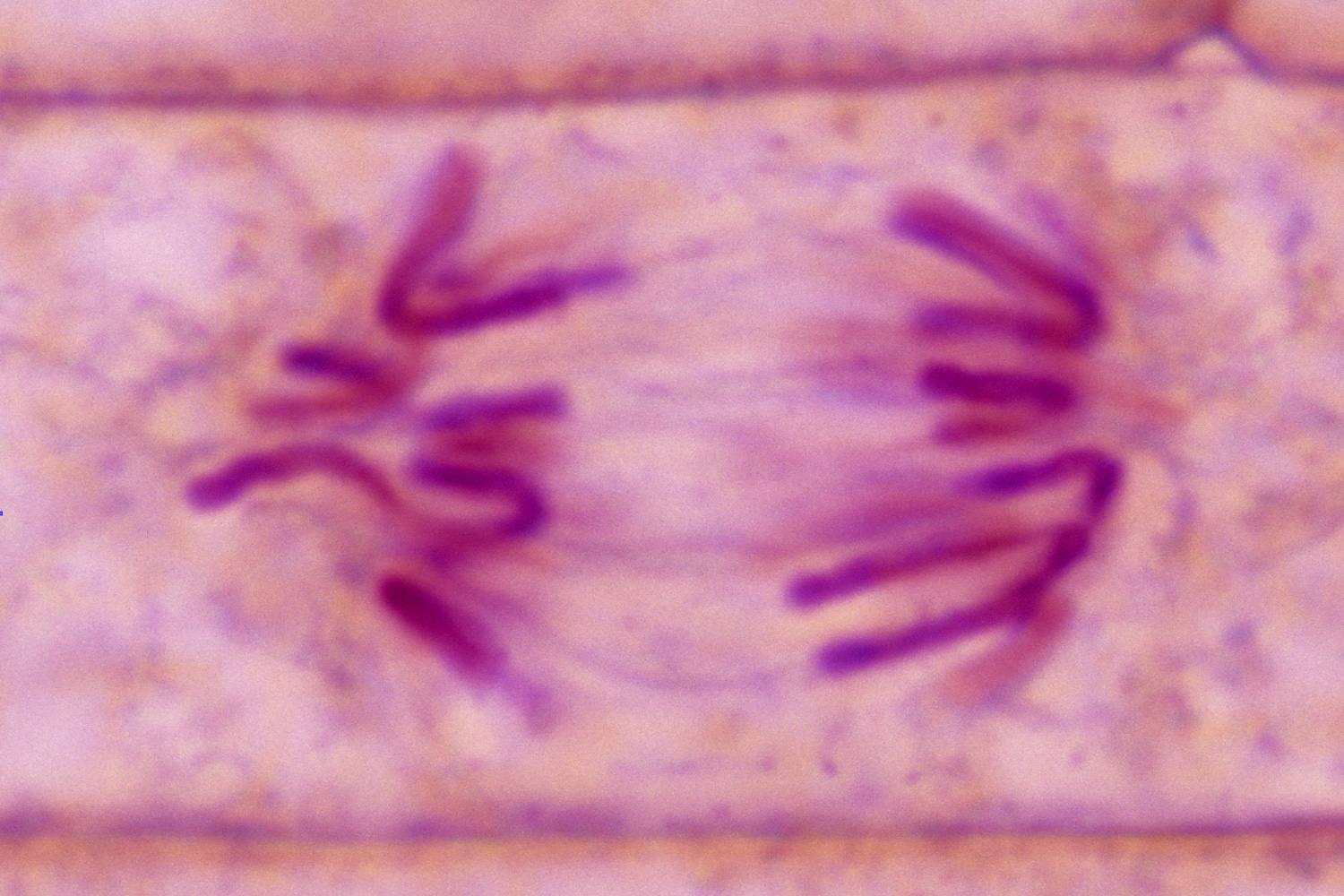
Anaphase
-sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by contraction of the spindle fibers
-each chromatid is now considered one chromosome
-genetic material is divided in 2 identical sets
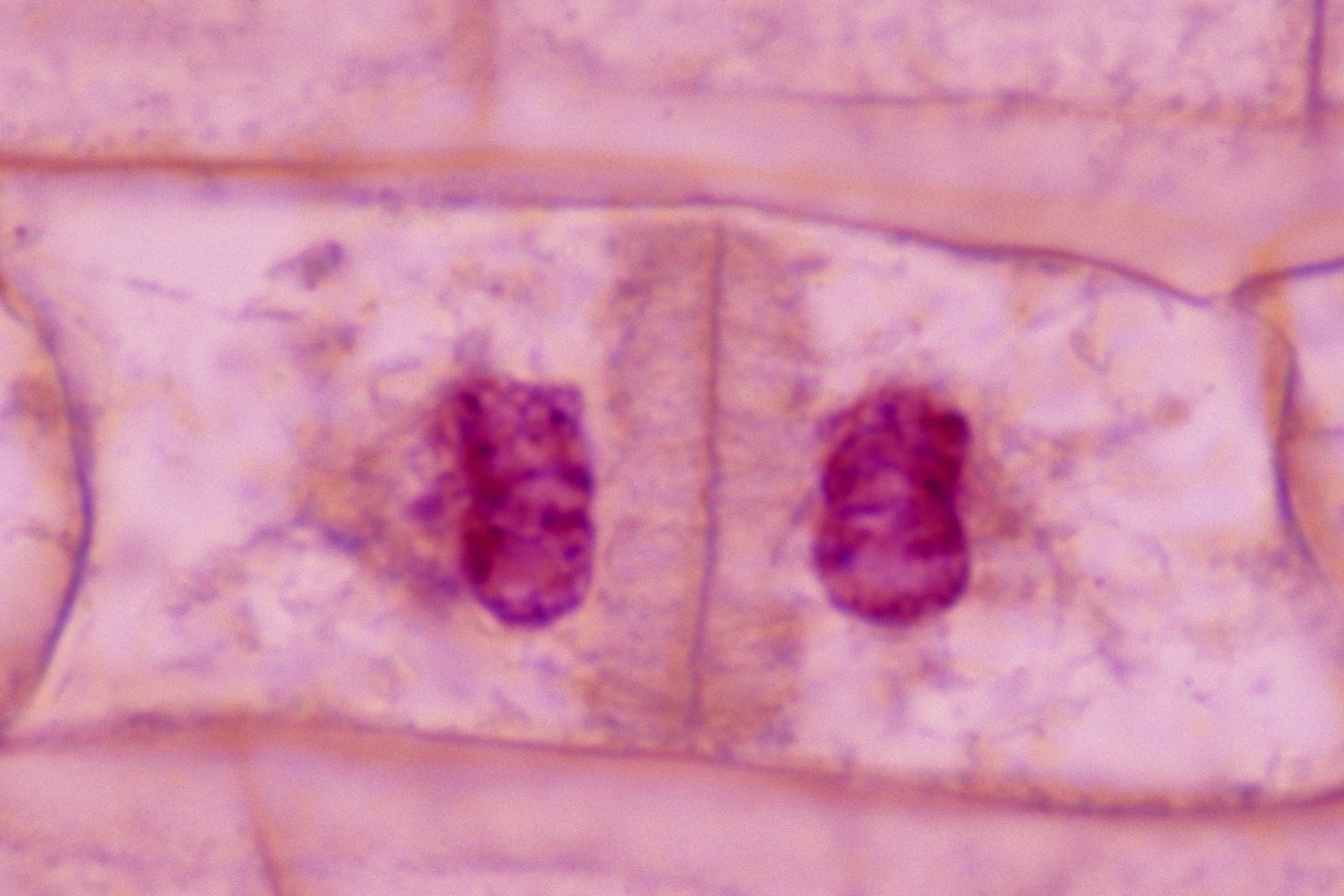
Telophase
-Nuclear membrane reforms
-Chromatids unwind and lengthen: become indistinct
-Nucleolus reappears
-Cell plate egins to appear
Chromatin
DNA & proteins
Chromatids
condensed duplicated strands of DNA
Homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs of the same size & shape that carry genes for the same traits
Madagascar Periwinkle
(Catheranthus roseus) has alkaloids that are used as chemotherapuetic agents for treating cancer and childhood leukemia
the alkaloids act on microtubules to interfere w/ spindle formation & prevent mitosis
Vincristine and vinblastine
useful chemotherapuetuc agents that interfere w/ spindle formation, preventing mitosis from happening
Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia)
the source of taxol
a conifer tree located in forests in the Northwest US
needs shade to grow, is found under canopy layers in forests, and grows slowly
Taxol
an anticancer drug discovered in the 1960s that is an alkaloid that has anti-tumor properties that may help treat women w/ ovarian and breast cancer
it works by biding to and inhibiting the break down of microtubules
Happy Tree
(Camptotheca acuminata) a tree native to Southern China
Contains camtothecin in the bark, an alkaloid w/ anticancer properties for colon & rectal cancers
Chinese skullcap
(Scutellaria baicalensis) used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine
flavons in roots may halt tumors, kill cancer cells, and leave normal cells intact. It has the potential for treating cancer & liver diseases
Mandrake
(Mandragora officinarum) has been used for its anesthetic properties
it looks like a two leg like branches & a protuberance that suggests male genitals
the doctrine of signatures said it made men virile, but it does not
Belladonna (atropa belladonna)
used by Italian and Spanish women to enlarge their pupils and achieve a seductive look (done by rubbing their eyes with this plant)
now used by ophthalmologists b/c it dilates pupils
also stimulates circulation and the sympathetic nervous system