SLP 102 QUIZ 2
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Speech Production
The motor ability (muscles, movement) to produce speech sounds
The subsystems of speech prodcution
respiration, phonation, and articulation
Respiration
Breathing; The power source of speech production
If someone does not have adequate ___________ they won’t have sound
respiration
Phonation
The process of setting the vocal folds into vibration to produce sound
Which subsystem of speech production does voicing relate to?
Phonation
All ______ in English are voiced
vowels
Abducted vocal folds
Apart when breathing and voiceless sounds.
Adducted vocal folds
Together in wave motion for voiced sounds.
What does phonation require to speak?
The larynx (voice box) because we drive air through our voice box to make sound
Articulation
The ability to physically move the tongue, lips, teeth and jaw to produce sequences of speech sounds
Which subsystem of speech production does place relate to?
Articulation
Consonants
Described by place, manner, and voicing
Occlusives
Air flow is stopped to produce the sound
Continuants
Continuous air flow
Stops / Plosives
Made by momentarily ceasing the air stream in the speech tract completely
Example of stops/plosvies
g, d, b, k, t, p
Affricates
Made by rapidly combining a stop and a fricative
Fricatives
Constriction of the airstream
Glides
Articulators must move from one point of contact to another
Liquids
Slight closure of the mouth resulting in vowel-like consonants
Most difficult sound for children to make…
Liquids
Nasals
Activates nasal resonance chambers
Bilabial
lips
Labiodental
lips and teeth
Alveolar
tongue touching ridge behind teeth
Palatal
tongue touching hard palate
Velar
tongue touching soft palate
Glottal
glottis
Voiced sounds
With vibrating vocal cords
Voiceless sounds (unvoiced)
Without vibrating vocal cords
Vowels
the “center” of a a syllable; every syllable needs it
Height (vowel)
how high is the tongue in the mouth?
Backness (vowel)
how far back is the tongue constricted?
Rounding (vowel)
what is the shape of the lips?
Tenseness (vowel)
how tense are the muscles in the speech mechanism?
Phonology
the domain of language
Phoneme
smallest unit of sounds that differentiate the meaning of words
Allophone
one of two or more variants of the same phoneme that don’t differentiate the meaning of words
Phonological process
How children simplify words
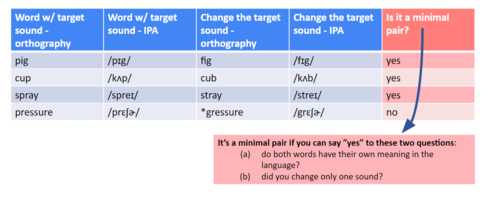
Minimal Pairs
When two words differentiate by one sound
Lexical-semantics
the study of word meanings and the relationships between words
Lexicon
vocabulary
Semantics
the study of meaning in a language
Prelinguistic development (e.g., gesture, intentionality)
a child is learning to control and string together sounds
Phonological development
how children learn the sound system of their language
Undergeneralization/underextension
When a child doesn’t generalize appropriately because of a restrictive schema
Overgeneralization/overextension
Having too generous of a schema
Phonetically Consistent Form (PCF)
Using a certain string of speech sounds to refer to the same thing consistently over time
What are PCF’s
Children’s first expressive “words”
When do PCF’s typically emerge?
Around 9-12 months
Compare speech production and phonology
Both are related to speech sound production
Subjective child observation
Influenced by biases and opinions (bad)
Objective child observation
Based on what is seen, heard, tasted, touched, and smelled (the facts, good)
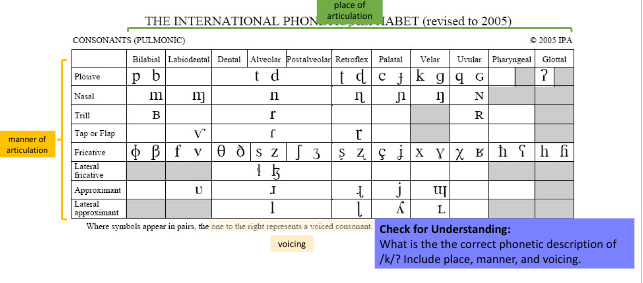
List the voicing, place, and manner of /t/
Voiceless alveolar plosive
Syllable omission
Syllables deleted
What is the IPA symbol for the voiced bilabial stop
/b/
Jimmy exhibits cluster reduction, how might he produce the word “spring” (remove one consonant)
ring
Cluster reduction
Consonant clusters reduced to single consonants
A child says “nana” for the target word “banana,” what phonological process is this an example of?
Syllable deletion
Final consonant deletion
Omit final consonants
A child says “boo” for the target word “boot,” what phonological process is this an example of?
Final consonant deletion
Stopping (A stop/plosive substituted for a fricative)
"fan" becomes "pan"
What is a first receptive word?
Begining to understand what words mean
When does a first receptive word happen?
Around 9 months
Why is the first receptive word important?
Shows their language skills devolping
What is a first expressive word?
The first labels for people, objects, or actions that are familiar
When does a first expressive word happen?
Around 12 months
Why is the first expressive word important?
Allows kids to express their wants and needs
What is the 50 word expressive vocabulary?
Uses and understands at least 50 different words for objects, people
When does the 50 word expressive vocabulary happen?
By 18-24 months
Why is the 50 word expressive vocabulary important?
It's when children start to put words together
Why do we transcribe speech phonetically (i.e., with IPA symbols) vs. orthographically (i.e., with letters)?
IPA is more helpful in representing the sounds more accurately
The role of input/frequency in lexical-semantic development
Influences how likely a child is to acquire a word
Fast mapping
Integrating the word and the referent in the moment
Slow mapping
The process that children gradually learn a word through multiple experiences
Whole object assumption
Words refer to whole objects rather than a part or property of the object
Mutual exclusivity assumption
Different words refer to different kinds of things
Joint attention
Simultaneously attend to two things at once
Tracking co-occurrence probabilities
Noticing over multiple times which words and referents) tend to go together
Novel name nameless category (N3C)
New words refer to new things
Stress and Rhythm
Helps children hear syllables that are stressed or weak
Transition probabilities
Determine how likely it is that certain syllables follow other syllables
How children might overcome lexical-semantics challenges
Learn to identify items, understand their meanings, and learn how the forms connect to the meanings
What makes a word harder to learn
Abstract, multiple meanings, less concrete, hard to visualize
Is “m” or “sh” is more likely to be acquired first?
“m” because it is anterior
Word/form
The sounds we say together to convey a word
Referent/meaning
The entity or idea the word refers to
What sorts of challenges do children encounter as they develop different domains of language?
Understanding receptive language, expressive language, articulation, and syntax
Speech stream segmentation
Dividing speech into segments
Quine’s conundrum
How do we make meaning of a word we don’t know