Hematology
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
MCV
rbc size
range: 80-100 fL
MCV (fL) = hct (%) / RBC(10^12/L) x 10
increased MCV
>100 fL = macrocytic
megaloblastic anemia
hemolytic anemia w/ reticulocytosis
liver disease
newborn
decreased MCV
<80 fL = microcytic
IDA
thalassemia
sideroblastic anemia
lead poisoning
MCH
weight of hgb in one RBC
26 - 34 pg
MCH (pg) = hgb (g/dL) / RBC (10^12/L) x 10
increased MCH
> 34 pg
macrocytic anemia
decreased MCH
< 26 pg
microcytic, hypochromic anemia
MCHC
color of RBC
32-37 g/dL
MCHC (g/dL) = hgb (g/dL) / hct (%) x 100
increased MCHC
>37 g/dL = hyperchromic
possible error in RBC or hgb measurement
spherocytes
decreased MCHC
<32 g/dL = hypochromic
IDA
thalassemia
RBC
total # of cells
M: 4.5 - 6.0 x 10^12/L
F: 4.0 - 5.5 x 10^12/L
increased RBC count
M: >6.0 ×10^12/L
F: >5.5 ×10^12/L
polycythemia vera (PV)
decreased RBC count
M: <4.5 ×10^12/L
F: <4.0 ×10^12/L
anemia
hgb
oxygen carrier from lungs to tissues
M: 13.5 - 17.5 g/dL
F: 12.0 - 16.0 g/dL
increased hgb
M: >17.5 g/dL
F: >16.0 g/dL
polycythemia
decreased hgb
M: <13.5 g/dL
F: <12.0 g/dL
anemia
hct
ratio of RBCs to total blood; blood viscosity
M: 41 - 53%
F: 36 - 46%
hct purpose
check for anemia
estimate risk of blood viscosity
RDW
variation in RBC size
11.5 - 14.5%
increased RDW
>14.5%
post-txn
post treatment (iron, B12, or folic acid therapy)
presence of two concurrent deficiencies (iron & folic acid deficiencies)
idiopathic sideroblastic anemia
ANC
absolute neutrophil count
1.5 - 8.0 x 10^9/L
ANC = (WBC) x [(% segmented + % bands) / 100]
increased ANC
>8.0 x 10^9/L = neutrophilia = left shift
> or = 50.0 x 10^9/L = chronic disease (CML) or severe immediate danger (leukemoid reaction)
decreased ANC
<1.5 x 10^9/L = neutropenia
< or = 0.5 x 10^9/L = high risk life-threatening sepsis
plt
initiates hemostasis
150 - 450 x 10^9/L
increased plt count
>450 x 10^9/L = thrombocytosis => clotting risk
decreased plt count
<150 x 10^9/L = thrombocytopenia => bleeding risk
MPV
volume of plt = gauge BM function
7.8 - 10.2 fL
increased MPV
>10.2 fL = BM making new, large plts
WBC
immune defense
4.0 - 11.0 × 10^9/L
WBC count (cells/mm³) = (# cells counted x DF) / (# squares x 0.1 mm³)
increased WBC count
>11.0 × 10^9/L = immunosuppression, BM failure
decreased WBC count
<4.0 × 10^9/L = infection, inflammation
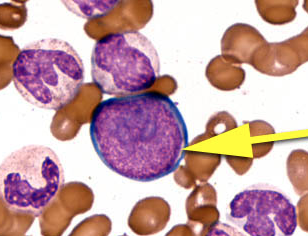
myeloblast
≥20% myeloblasts is diagnostic of Acute Leukemia (AML)
no cytoplasmic granules
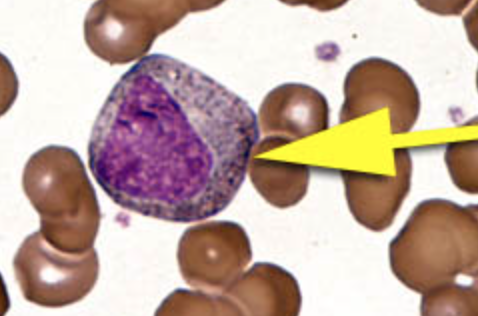
promyelocyte
≥20% myeloblasts is diagnostic of Acute Leukemia (AML)
primary granules containing myeloperoxidase
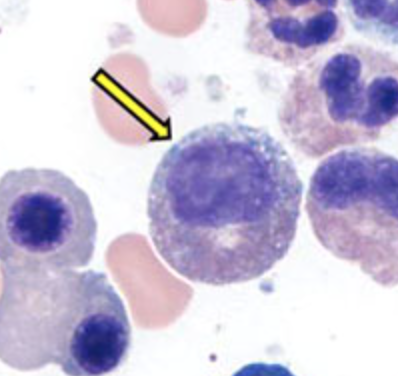
myelocyte
severe marrow release or chronic leukemia (CML)
first stage where granulocyte types can be differentiated (neut, baso, eos)
secondary granules containing alkaline phosphatase & lysozyme
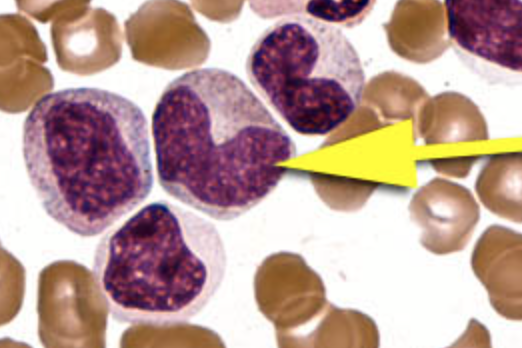
metamyelocyte
kidney bean shape
indicates a significant marrow response (infection/inflammation)
secondary granules
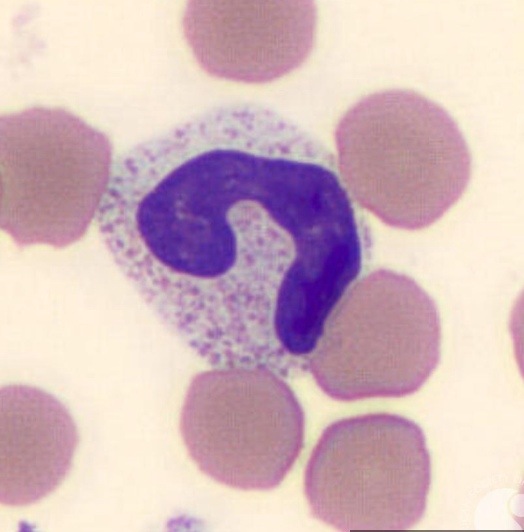
band neutrophil
0 - 0.7 × 10^9/L
no segmentation
secondary granules
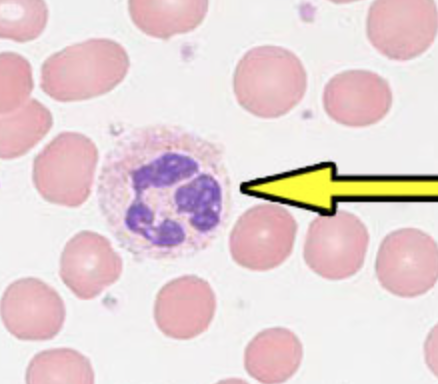
segmented neutrophil (PMN)
2.5 - 7.0 × 10^9/L
bacterial
increased = neutrophilia => acute bacterial infection, physical stress, or inflammation
decreased = neutropenia => chemotherapy, severe sepsis, BM failure
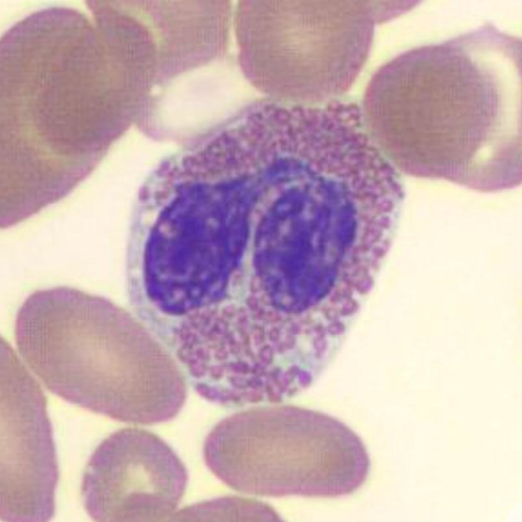
eosinophil
0 - 0.4 × 10^9/L
parasitic & allergic
increased = eosinophilia => NAACPP
decreased = eosinopenia => acute stress/high corticosteroids
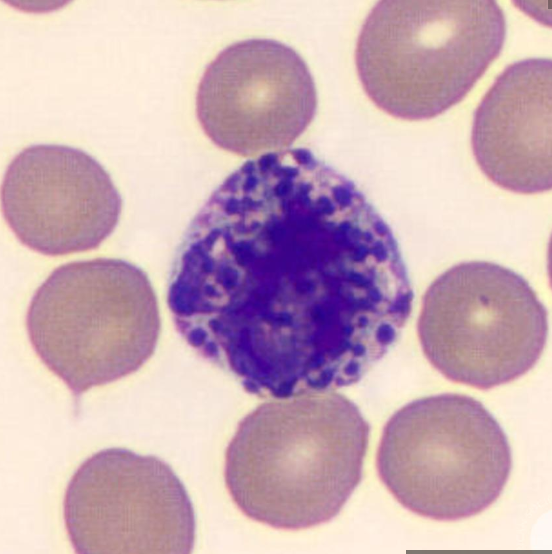
basophil
0 - 0.2 × 10^9/L
hypersensitivity reaction or allergy
increased = basophilia => CML or hypersensitivity reactions (release histamine)
decreased = basopenia => acute allergic reactions or acute stress
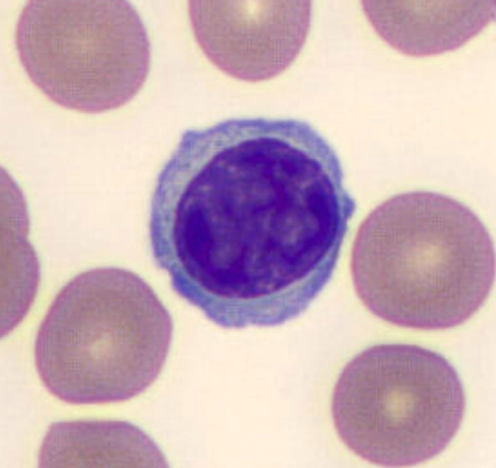
lymphocyte
1.0 - 4.0 × 10^9/L
increased = lymphocytosis => viral infections, whooping cough
decreased = lymphopenia => immunosuppresssion
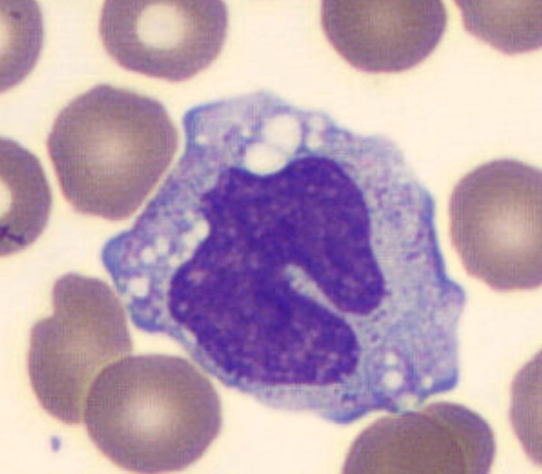
monocyte
0.2 - 1.0 × 10^9/L
increased = chronic infections, recovery phase of acute infections, or malignancy
decreased = BM suppression