4. Microbiological Clinical Correlations and the Perio-Systemic Link
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Periodontal Disease are….
Infections caused by microorganisms that colonize the tooth surface at or below the gingiva
About ____species are able to colonize the oral cavity, the sulcus is ______ sterile
________ between the established microbiota and the host causes disease
________ leads to the destruction of the periodontium
About 700 species are able to colonize the oral cavity, the sulcus is never sterile
Disequilibrium between the established microbiota and the host causes disease
Inflammation leads to the destruction of the periodontium
4 Categories of Periodontal Health
Pristine Periodontal Health
No BOP
No Clinical signs of inflammation
No Periodontal Loss
No Histological signs of inflammation (never happens in real patients)
Clinical Periodontal Health
No BOP
No Clinical signs of inflammation
No Periodontal Loss
Signs of Histological inflammation (normal)
Periodontal Stability → Goal for periodontitis patients
No BOP
No clinical signs of inflammation
Reduced Periodontium
Control of Modifying factors (diabetes, smoking, etc)
Periodontal Disease Remission/Control
Decreased Inflammation
Cannot fully control modifying and pre-disposing factors
Health vs. Stability
Health: means the patient has minimal recession and has NEVER had periodontal disease
Stability: healthy state in a patient that was previously diagnosed with periodontal disease
Main etiology of periodontal disease?
What are the local factors that can increase the risk of periodontal disease?
Bacterial Plaque
The local factors include overhanging margins, open contacts and crowding
Describe the 3 Phases of Plaque Formation
Formation of the Pellicle:
All surfaces are normally covered with glycoprotein pellicle in the tooth surface as well as tissue surfaces and fixed/removable surfaces (but since epithelial tissue sloughs off, plaque doesn’t form there)
pellicle structure determines which bacteria can attach
Initial adhesion/attachment of bacteria
Gram + bacteria are usually the primary colonizers and coat the most coronal tooth surface
Adhesins on bacteria attach to pellicle
Colonization and plaque maturation
Co-aggregation: primary colonizers let secondary colonizers adhere to them
Gram - bacteria are usually the secondary colonizers and coat soft tissues as well as the most apical tooth surfaces
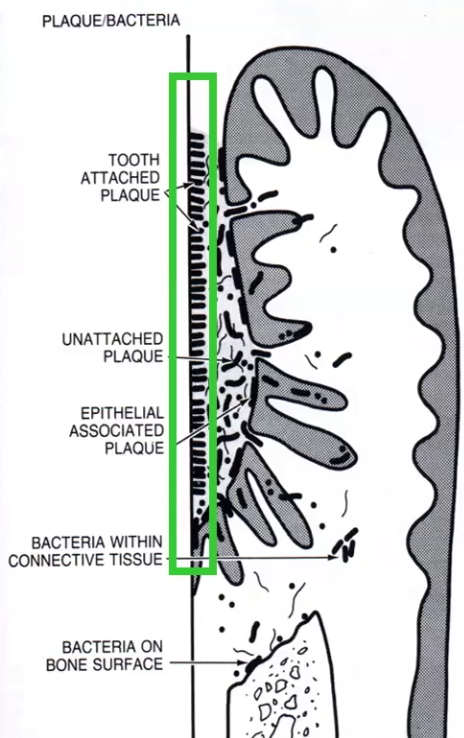
What are the 2 Plaque Hypothesis
Non-Specific plaque hypothesis: periodontal disease results when bacterial proliferation exceeds threshold
Not true bc people with a lot of plaque sometimes do not have periodontal disease
Specific Plaque Hypothesis: periodontal disease results from specific bacteria found in dental plaque that is different than dental plaque from healthy sites
May be bc of susceptible host
You can have no plaque and still have periodontitis bc the host has aggressive pathogenic bacteria
Describe all the complexes: Yellow, Green, Purple, Orange, Red
Primary Colonizers:
Yellow: S. mitis, S. Oralis, S. Sanguis, S. Gordonii, S. intermedius
Green Complex: E. Corrodens, Capnocytophaga. A.a
Purple Complex: V. Parvula, A. odontolyticus
Secondary Colonizers:
Orange Complex: F. nucleatum, P. intermedia, P. nigrescens, P. Micros, E. Nodatum, C. Rectus, C. Showae
Red Complex: T. denticola, P. gingivalis and B. Forsythus
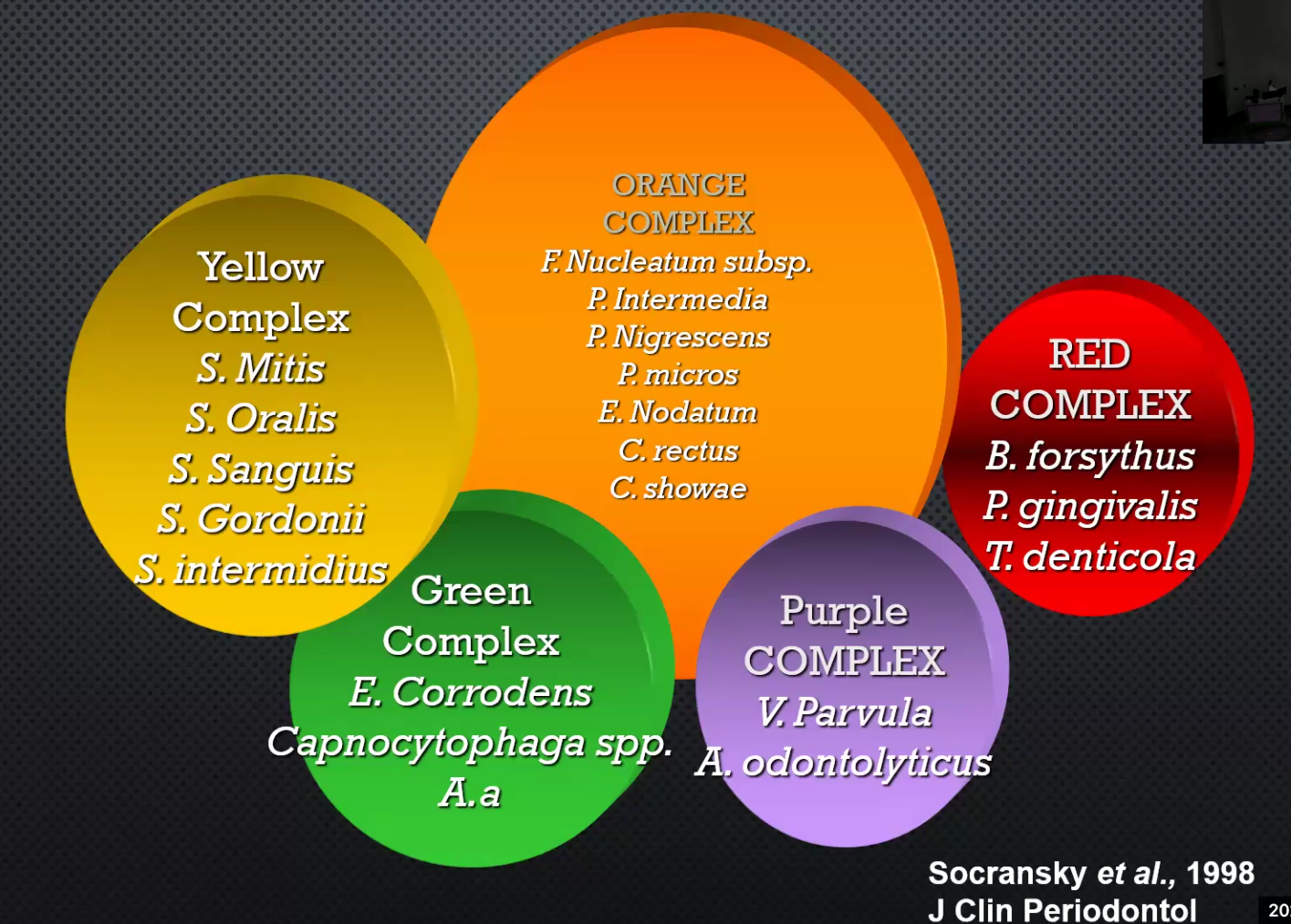
If you find the red complex bacteria, what does that mean with regards of progression of the disease?
The disease is very far along the progression
In regards to a Healthy periodontium, which would predominate?
Gram-positive or Gram-negative
Facultative anaerobes or Anaerobes?
Which 2 species would make up 40% of isolates?
Gram positive
Facultative anaerobes
Actinomyces and Streptococcus species dominate
Actinobacillus Actinomycetemcomitans (A.a)
What complex
Virulence factors
Morphology and physiology
Linked to
Green
Gingival tissue invasion, Collagenase, Endotoxin
Gram negative and facultative anaerobe
Aggressive periodontitis, edocarditis, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and alzheimer’s disease
P. Gingivalis
What complex
Virulence
Morphology and physiology
Linked to
Red
Subverts host immune system, abscess formation, keystone pathogen (central to disease progression)
Gram negative anaerobe
Chronic periodontisis, athersclerosis, alzheimers and cancer
P. Intermedia
What complex
Morphology and physiology
Linked to
Orange
Gram negative anaerobe
Pregnancy gingivitis and necrotizing periodontal disease, systemic endocarditis
Fusobacterium Nucleatum
What complex
Morphology and physiology
Linked to
Orange
Gram negative anaerobe, opportunistic most abundant in oral cavity
Alzheimer’s disease