OCD
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
OCD
obsessive compulsive disorder
- a condition characterised by obsessions and/or compulsions
behavioural, emotional and cognitive
behavioural characteristics of OCD
Compulsions
- repetitive, compelled to repeat behaviours to reduce/manage anxiety produced by obsessions (e.g., hand washing)
Avoidance
- avoid situations that they feel may trigger their OCD, may interfere with normal life (e.g., avoid going outside to avoid dirt)
obsession
A persistent, unwanted thought or idea that keeps recurring
COGNITION (in the mind)
Cognitive characteristics of OCD
Obsessive thoughts
- recurring negative/unpleasant thoughts (worry about oven on)
Cognitive coping strategies
- ways of coping with obsessive thoughts, relieves the thoughts but with often unusual behaviour
Insight into excessive anxiety
- sufferers are aware that obsessions/compulsions are irrational (Requirement for diagnosis of OCD)
emotional characteristics of OCD
Anxiety + Distress
- powerful overwhelming anxiety, frightening obsessive thoughts, urge to repeat behaviour causing distress
Accompanying depression
- low mood, lack of enjoyment, completing compulsions can bring some relief from depression but is temporary
Guilt + Disgust
- guilt over minor moral issues and disgust about certain objects or themselves
compulsion
an unreasonable need to behave in a certain way to prevent a feared outcome
BEHAVIOUR
Requirement for diagnosis of OCD
acknowledgement/awareness that the obsessions or compulsions are irrational
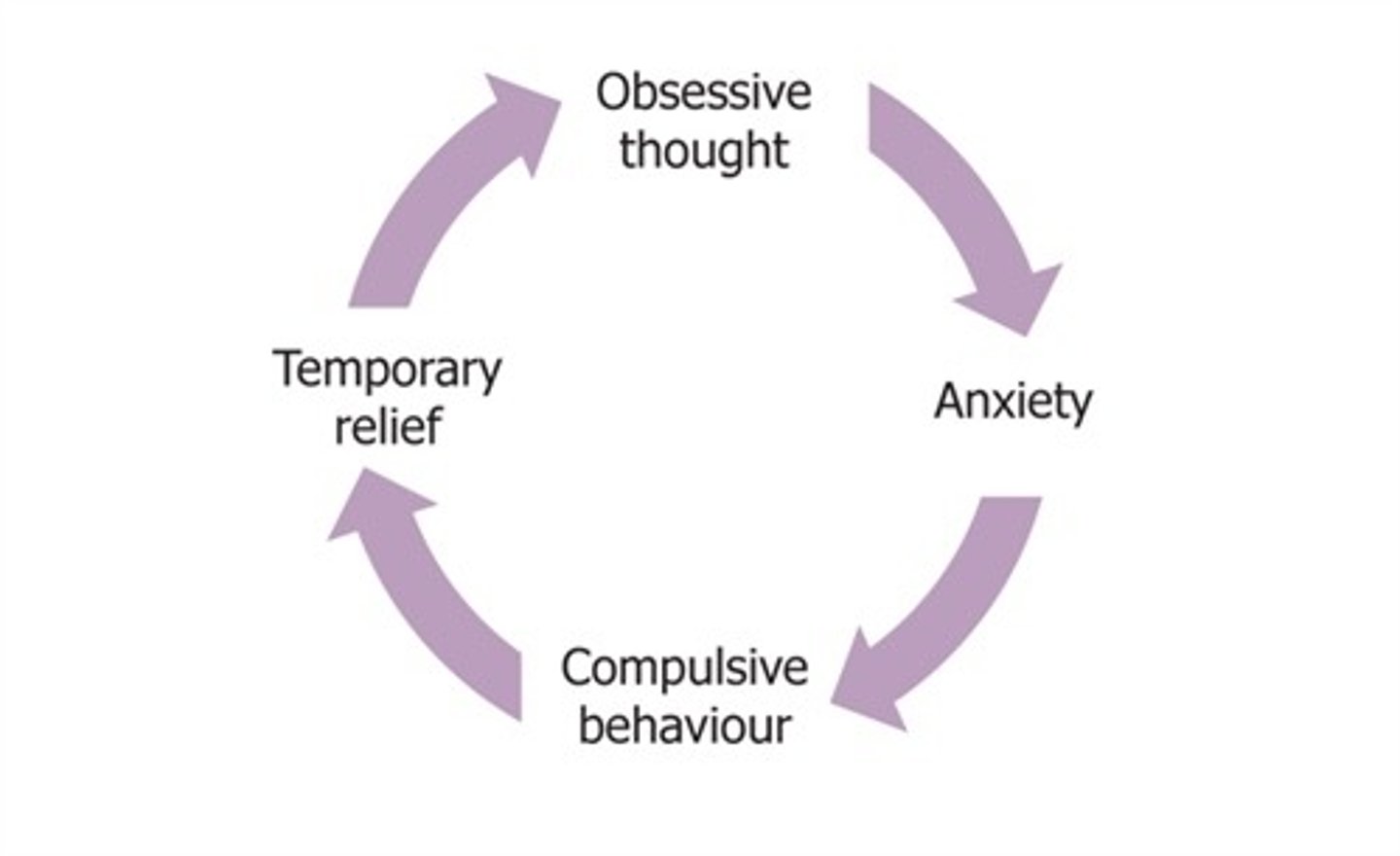
the cycle of OCD
1. thoughts/obsessions
2. anxiety + distress
3. compulsions
4. temporary relief
Explaining OCD
Biological approach
- genetic and neural
Biological approach
a perspective that emphasis the importance of physical processes in the body
e.g., genetic information and neural function
Genetic explanation definition
genes make up chromosomes and consists of DNA which codes for physical features of an organism (eye colour, height) and psychological features (mental disorders, IQ)
genes are transmitted from parents to offspring (inheritance)
Genetic explanation of OCD
individuals receive specific genes which may increase an individuals vulnerability to developing OCD
- large body of evidence to suggest biological component, LEWIS (1936), of his sample:
37% had parents w/ OCD and 21% had siblings w/ OCD
biological vulnerability from inherited genes, not certainty
- candidate genes
- diathesis stress model
the diathesis stress model
proposes a disorder may develop when biological vulnerability is joined with an event
Genetic makeup make people more vulnerable to conditions, but an environmental trigger is needed before the condition develops (e.g., divorced parents)
Candidate genes
genes which increase vulnerability to developing OCD
- involved in regulating serotonin and dopamine systems
OCD = POLYGENETIC
- causes by several genes
Taylor, 2013, suggested up to 230 different genes involved
- genes studied are involved in regulating mood, serotonin + dopamine
create a vulnerability to OCD
SERT gene and the COMT gene
(and cause the neural explanation)
SERT gene
Associated with the transport of serotonin (serotonin transporters)
mutation to this gene causes an increase in transporter proteins at a neurones membrane, leads to an increase in the re-uptake of serotonin, causes lower levels of serotonin in synapses
decreased serotonin levels = increased vulnerability
COMT gene
helps to regulate the function of dopamine
one variation which causes a higher level of dopamine and is more common in patients with OCD than without
increased dopamine levels = increased vulnerability
Neural explanation definition
the view that physical and psychological characteristics are determined by the behaviour of the nervous system, in particular the brain as well as individual neurones
the neural explanation of OCD
genes associated with OCD are likely to affect the levels of key neurotransmitters + the structure of the brain
role of serotonin + dopamine = neural, but imbalances = genetic
affects decision making systems and the structure of the brain
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that transmit nerve impulses from one cell across the synapse to another cell
responsible for relaying information
lower levels of serotonin, normal transmission of mood relevant information doesn't occur, so mood and cognition affected
role of dopamine
associated with feelings of pleasure and reward
dopamine addictions become more frequent as you become obsessed with an action
role of serotonin
called the happy hormone
key hormone involved in regulating mood, well-being and feelings of happiness
Decision making systems
OCD is associated with impaired decision making, linked to abnormal functioning of the:
1. lateral frontal lobes of the brain
&
2. the prefrontal cortex
lateral frontal lobes of the brain (OCD)
several regions in the frontal lobe may have abnormal circuits
frontal lobes = responsible for logical thinking + decision making
prefrontal cortex (OCD)
responsible for primitive behaviours + decision making
overstimulation would lead to an exaggeration of these behaviours (e.g., repetitive hand washing)
Genetic explanation strength
P: good supporting evidence for the suggestion that a vulnerability for OCD is altered genetically
Ex: best sources of emphasising importance genes = twin studies, monozygotic twins share 100% of DNA, provides evidence for a genetic link
Ev: e.g., Nested et al,2010, conducted review of previous twin studies examining OCD, research showed 68% of identical twins were both diagnoses, compared to 31% of non-identical twins, very strong genetic component
Ext: Billet et al,1998, used a meta-analysis of 14 twin studies of OCD, found on average MZ twins were x2 more likely to develop OCD if twin also had OCD, chances were lower for DZ twins
L: research supports idea that there are inherited genes which increase vulnerability to OCD
Genetic explanation weakness
P: criticised as being biologically reductionist, suggestS the presence of a gene means OCD is predetermined in individual
Ex: environment could also trigger development, with combination of candidate genes increasing biological vulnerability -shown by diathesis-stress model
Ev: research by CROMER et al (2007) supports this, found that over 1/2 patients who'd experienced traumatic events had OCD, OCD = more severe in patients who'd experienced >1
Extra: bio approach doesn't consider cognitions + learning - some psychologists suggest OCD may be learnt through classical conditioning and reinforced through operant negative reinforcement
L: suggests environment is more influential than originally thought when it comes to developing OCD
Neural explanation strength
P: supporting evidence for the role of neural mechanisms
Ev: some antidepressants (fluoxetine) work purely on serotonin systems, increase levels which reduces symptoms of OCD
Ex: suggests serotonin system has role in development of OCD
C: casual link between serotonin + OCD may simply be co-morbidity as many patients also develop depression, likely to disrupt system
- weakness = too many candidate genes individually contributing, difficult to identify influence on development
L: important to consider because suggests we can't rely on the use of drugs to relieve symptoms of OCD
Neural explanation weakness
P: theory = limited by issues with regard to cause and effect for neural explanation
Ex: should not assume the neural mechanisms = sole cause of OCD
Ev: despite evidence suggesting various neurotransmitters + brain structures don't function normally with OCD + linked to abnormal behaviour - research shows other areas are involved at times, therefore not one area of brain consistently influencing the development
Ext: furthermore, abnormal behaviours previously thought to be caused by fault decision making systems in the prefrontal cortex + linked to OCD may have developed because of OCD
L: therefore, psychologists may argue that biological approach lacks validity as research implies there is no casual link between the disorder + brain structure, + specific genes increase vulnerability
approach to treating OCD
the biological approach
Drugs used in treatment of OCD
1. SSRI's
2. SSRI's + CBT
3. Tricyclics
4. SNRI's
drug therapy for mental disorders aims to
increase/decrease levels of neurotransmitters in the brain or to increase/decrease their activity
SSRI's
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- work on serotonin system in brain, serotonin is released by certain neurones in brain
- serotonin is released by presynaptic neurones, travels across the synaptic gap + doesn't fully go to the post-synaptic neurone as its often reabsorbed in presynaptic neurone
SSRI's prevent serotonin being reabsorbed by presynaptic neurone
- effectively increases serotonin levels in synapses
- means message is passed on to the postsynaptic neurone
-- a type of antidepressant (fluoxetine), can take 3-4 months of daily use to have impact
SSRI's + CBT
drugs reduce anxiety to point where patient is able to engage more effectively with CBT
Some patients respond best with CBT alone, whilst others benefit from daily fluoxetine
alternatives to SSRI's (Tricyclics)
when SSRI's are not effective after 3-4 months, dose can be increased or combined with other drugs
= tricyclics
- older type of antidepressant
- same effect as SSRI's, but more side effects
- used as last resort if don't respond to SSRI's
SNRI's
Serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors
- increase the level of serotonin and noradrenaline in the brain
- newer drugs, second line of defence for people who don't respond to SSRI's
Biological approach to treating OCD Strength
P
A strength of the biological approach to treating OCD s that they are both effective in treatment and cost.
EX
Randomised drug trials and research support the effectiveness of SSRI's and these drugs are often cheaper than cognitive behavioural therapy or other forms of psychological treatments, meaning they could be offered to a wider range of patients.
EV
For example, Soomro et al. (2008) conducted a review of the research examining the effectiveness of SSRI's and placebos in treating OCD. Their study concluded that SSRIs were more effective than placebos as 17 studies showed significantly better results for the SSRI's.
C
However, some psychologists believe that drugs are overused in the mental health system as a way of distracting ourselves from our problems and avoiding psychological treatment because these drugs are seen as a "quick fix".
LB
Nevertheless, research has shown that typically symptoms decline significantly for around 70% of the patients and there are alternative drug treatments available for the remaining 30% who don't respond to SSRIs, proving that drug treatments are effective in treating the majority of patients.
Biological approach to treating OCD Weakness (1)
P
A weakness of the biological treatment for OCD is that the drugs used can have side effects.
EX
Although evidence suggests drugs like SSRIs are effective, some patients may experience side effects including blurred vision, erectile dysfunction in males, tremors, and possible weight gain.
EV
In recent years, the NHS suggested that 1 in 100 patients taking these drugs may suffer from disruption to blood pressure and heart rhythm, such as palpations, and may become more aggressive.
EXT
As well as this, some drugs such as BZ's are renowned for being highly addictive and causing long term memory impairments, so can often only be prescribed for short treatment.
LB
Consequently, this weakens the use of drugs because patients may be less willing to take them and therefore their OCD symptoms may return.
Biological approach to treating OCD Weakness (2)
P
A criticism of the biological approach to treating OCD could be unreliable for drug treatment.
EX
Although SSRI's are fairly effective and any side effects will probably be short term, their use can be seen as controversial
EV
For example, some psychologists believe the evidence favouring drug treatments is biased because the research is sponsored by drug companies who do not report all the evidence (GOLDACRE 2013)
EX
This suggests that the data on effectiveness of drugs may not be trustworthy.
EXT
Furthermore, whilst there is evidence of a biological component to OCD, some case of OCD have no family history of the disorder, and many cases show that OCD can arise from traumatic events that trigger the development of OCD. Therefore, it may be more appropriate to treat individuals with psychological therapies like CBT instead of resorting to drugs.
LB
This is important when considering how appropriate drug therapies are to treat disorders such as OCD, due to their reliability and their effectiveness.