Identification of Biomarkers
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
BioMarkers are identified by association studies which link genotype to phenotype
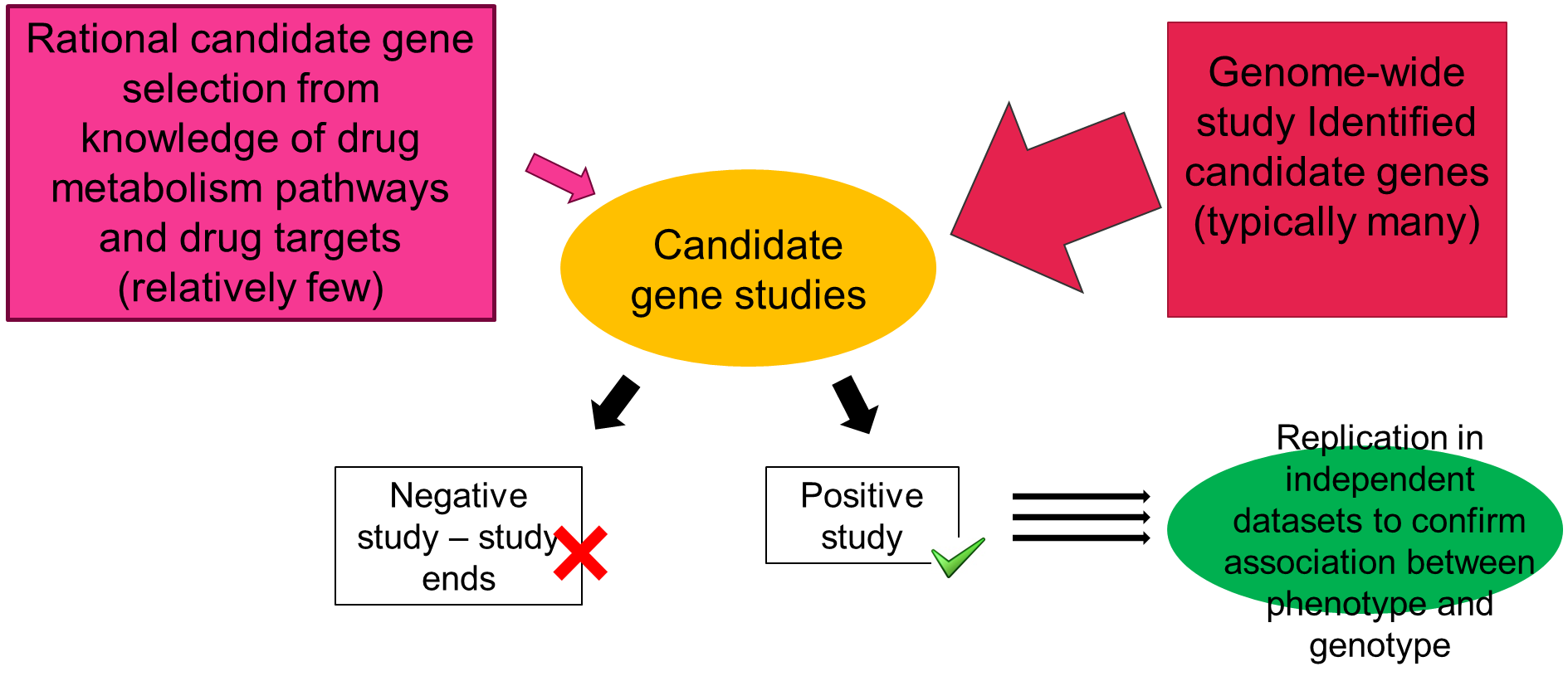
Candidate gene approach
Gene / variation selection | A priori, rational selection of genes increases biological plausibility of finding |
Number of genes variations examined | Small, limits the possibility of false associations |
Genotype technology | Low tech |
Analytical support | Limited |
Number of subjects | Large |
Cost | Low |
Additional benefits | Backed by biology, more targeted and sensitive approach but novel genes cannot be identified |
Candidate gene association studies address questions such as are there variations in a gene that is known to be associated with pathogenesis of a disease OR involved in the ADME of a drug OR in a gene that influences the efficacy of a drug
The genes to be tested are selected on prior knowledge, on the way in which the drugs are metabolised or based on the biological pathway that the drug targets or the pathogenesis of the disease process itself.
It requires that variance are identified and analysed, the variation must be visible. E.g. if we are thinking about the metabolism of the drug, and a gene involved in the activty of the enzyme is not working then that cannot be compensated by the expression of another enzyme as this would not allow you to see the change in phenotype.
A large cohort has to be studied
Example of a Candidate Gene Approach
•Used in the identification of variations associated with Drug induced hypersensitivity
This type of hypersensitivity can occur in weeks of initiating a drug and can be managed by replacing the drug with alternative.
•Can affect the skin as a rash or display as hypersensitivity syndrome with skin blistering and systemic effects (e.g. liver toxicity; renal failure) and can lead to anaphylactic shock and death
•Inappropriate immune reaction where the drug acts as the antigen leading to activation of the adaptive immune response
•Associated with the MHC locus on chromosome 6
Example of a Candidate Gene Approach
•Abacavir (can cause hypersensitivity in 5% of pts) - HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV
•Hypersensitivity syndrome - occurred in ~ 5% of patients
•Candidate gene analysis of MHC alleles for association with this life threatening ADR
•Sequencing of the HLA loci- identification of alleles associated with hypersensitivity to Abacavir in a retrospective study
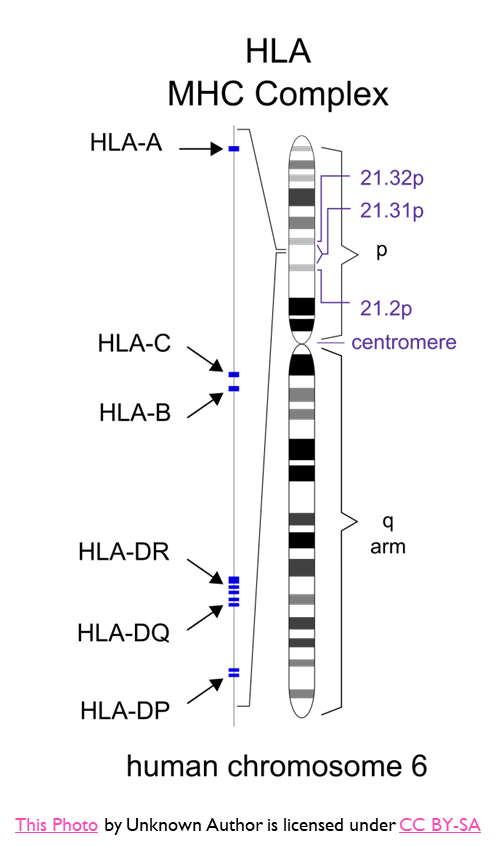
Example of a Candidate Gene Approach
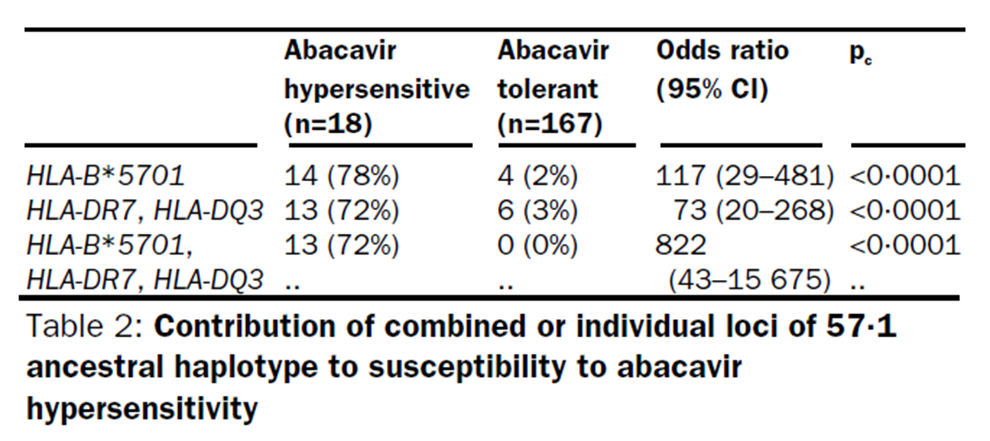
•Combination of the alleles - the HLA-B*5701, HLADR7, HLA-DQ3 when present together were found to be associated with Abacavir hypersensitivity
•Associated with HLA-B*5701 in different populations, allele frequency:
•5% European
•1% in Asian
•< 1% African populations
•Testing for HLA-B*5701 required before use for the first time or re-initiation of abacavir in patients of unknown HLA-B*5701 status who have previously tolerated abacavir
Genome wide association studies
Gene / variation selection | Unprejudiced, analysis of whole genome allows identification of genes previously unlinked to the response |
Number of variations examined | >500, 000 to > 1 million per genome (> risk of false discovery) |
Technology | High throughput |
Analytical support | Sophisticated |
Number of subjects | Possibly modest, depending on strength of association |
Cost | High, requires accurate phenotyping of cohort, additional costs associated with following up large number of positive findings |
Additional benefits | Chance to elucidate novel pathogenic mechanisms |
Genome wide association studies are much bigger and unbiased. They use variations available in databases. They can aid understanding of the physiology of the phenotype being studies and reveal unexpected genetic associations.
Performed using microarrays.
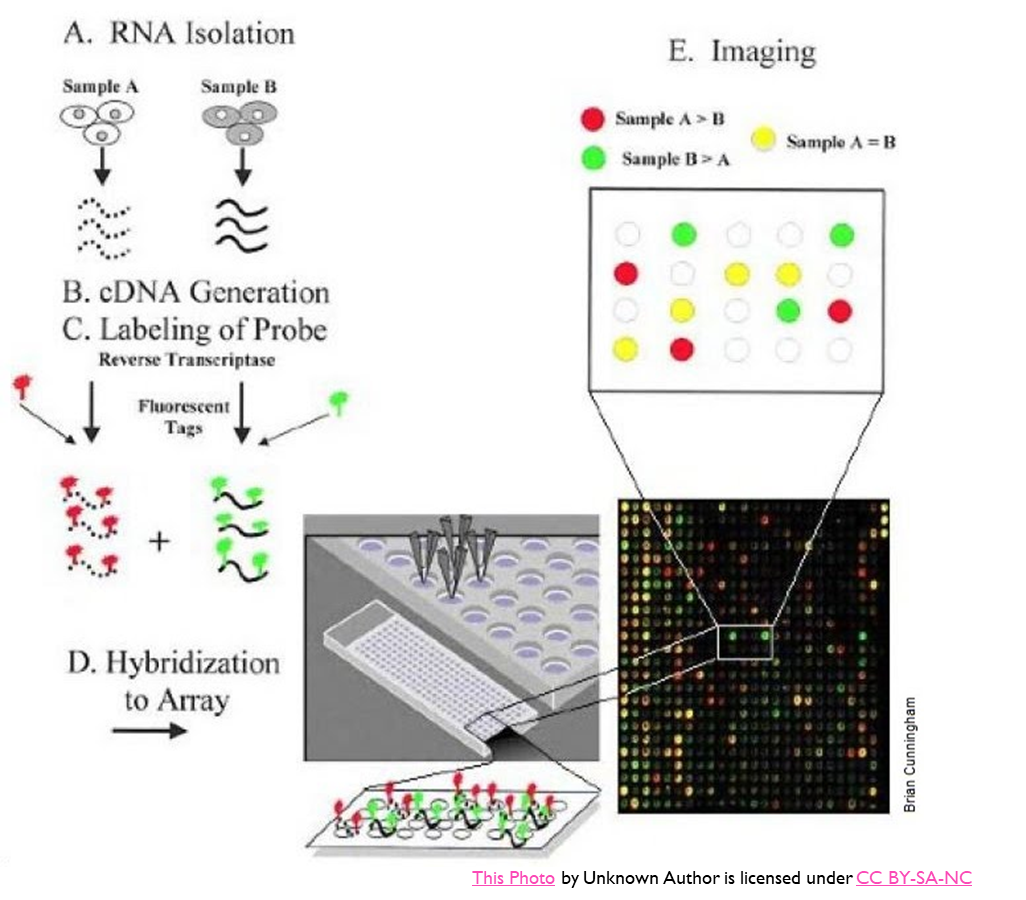
Microarrays
•A microarray is a panel of single stranded samples that collectively represent the DNA to be analysed
•DNA fragments (oligonucleotide probes) are spotted onto a solid support to form a microarray
•Each spot on the microarray has multiple copies of a single DNA sequence.
•The sample is labelled, hybridised against the array and labelled spots are detected
•Used for comparative analysis of expression between 2 samples – gene expression profiling
Example of a GENE Expression Profiling MICROARRAY
•Gene expression profiling in patients with Crohn disease (35) and ulcerative colitis (32)
•Extracted mRNA from CD4+ and CD8+ cells isolated from each patient
•Hydridised against a microarray presenting 28,000 genes identified from the human genome project and the sequence databases (NCBI and ENSEMBL)
•13,250 genes expressed, upregulation of the expression levels of some genes correlated with relapsing disease
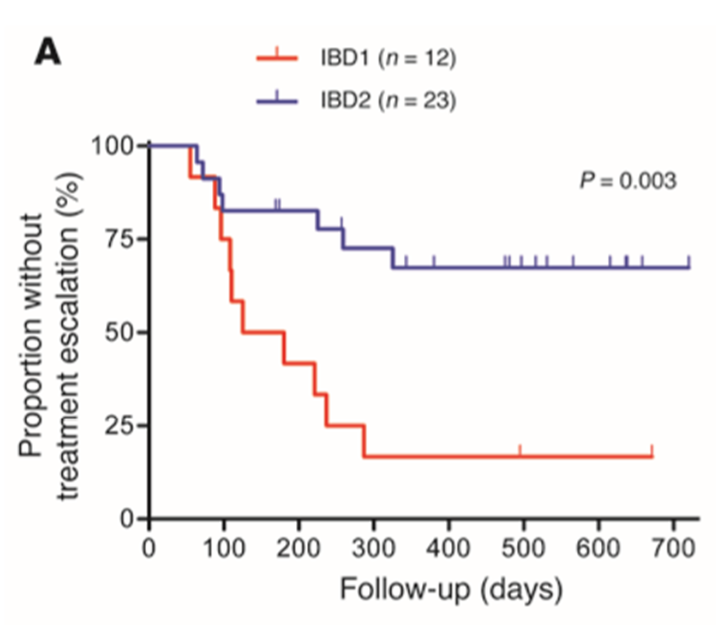
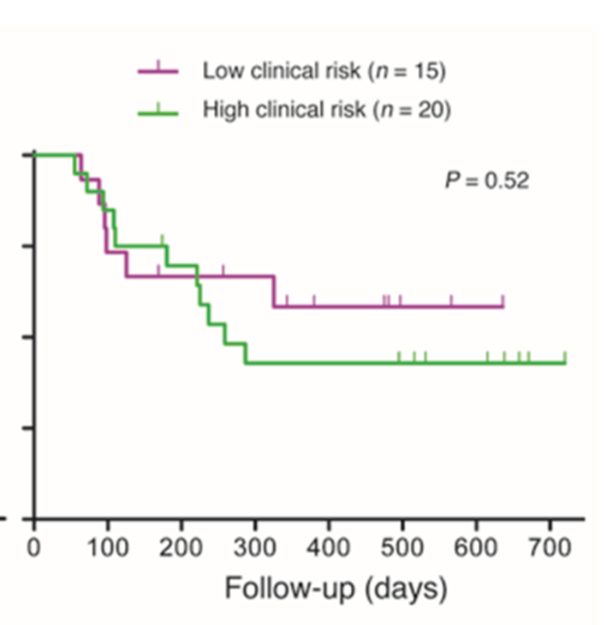
•2 Biomarker signatures identified IBD-1 and IBD-2
Identification of a biomarker Signature
•Identification of a gene set where high expression (IBD1) was an indicator of relapsing disease
•CD patients in the IBD1 and IBD2 groups have significantly different disease courses
•Led to the development of the PredictSURE IBD biomarker assay
Genome wide association studies (GWAS)
•Analysis of a genome-wide set of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in different individuals to identify variations associated with a phenotype.
analyses the DNA of two cohorts for variations that are associated with a phenotype.
The DNA is isolated rather than the messenger RNA. And it is compared against a representative set of single nucleotide variations.
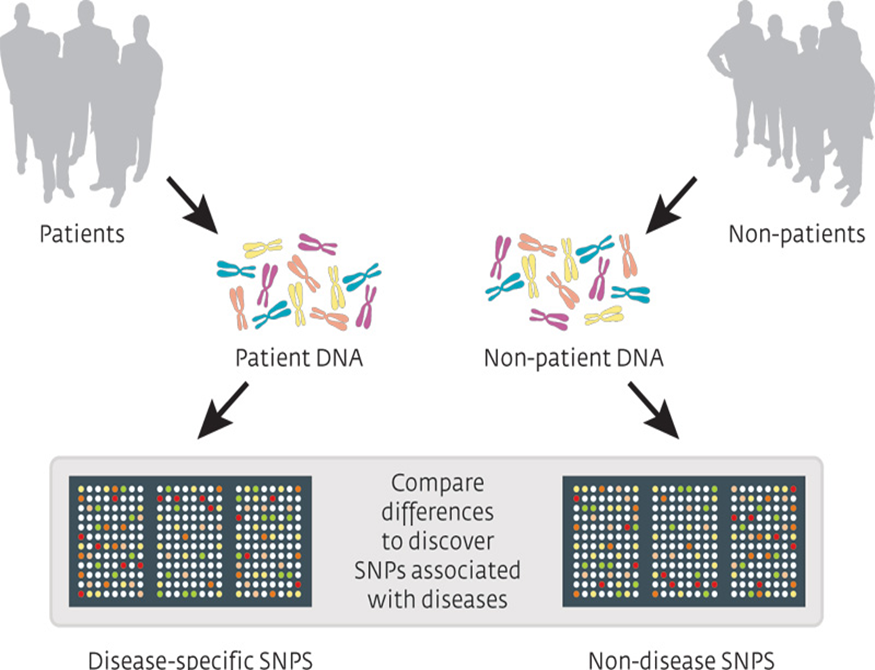
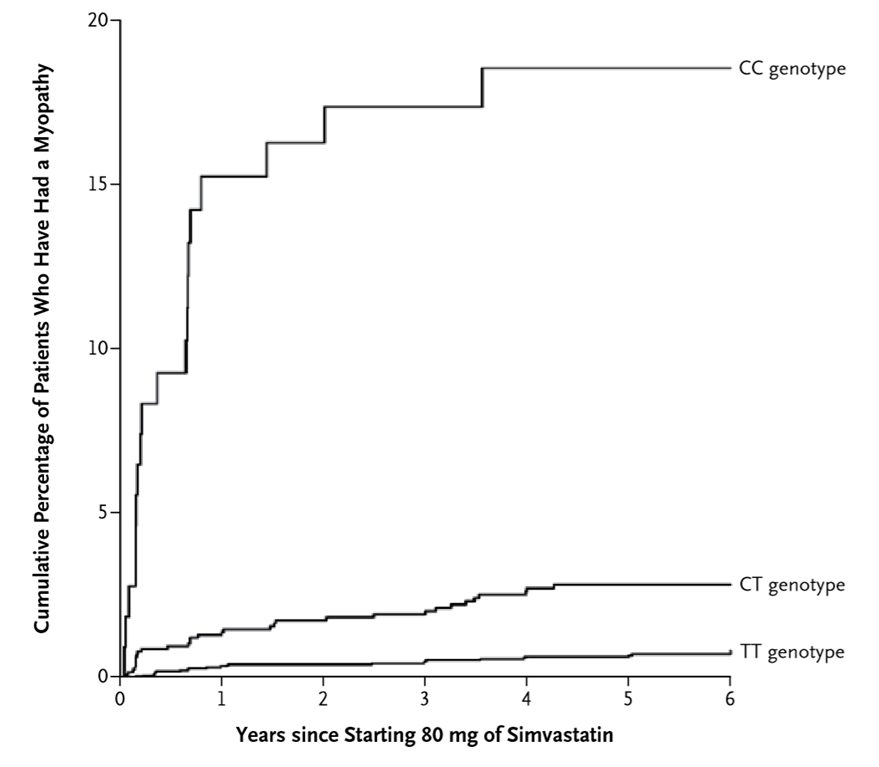
Example of a GENE VARIATION GWAS - incidence of myopathy in those taking simvastatin
•Randomised trial compared the efficacy of simvastatin dose (20-80 mg simvastatin for the prevention of future CV events in patients with prior MI
•Follow up study using the same data including genotyping - a genome-wide association study on simvastatin-induced myopathy v controls in the 80mg cohort
•Identified a SNP (rs4149056) in the solute carrier organic anion-transporter SLCO1B1 (the *5 allele) that were associated with the ADR when present as homozygous C