1.1 - 1.5 The Brain + Sleep
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
vocab from study guide, modules, and videos
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
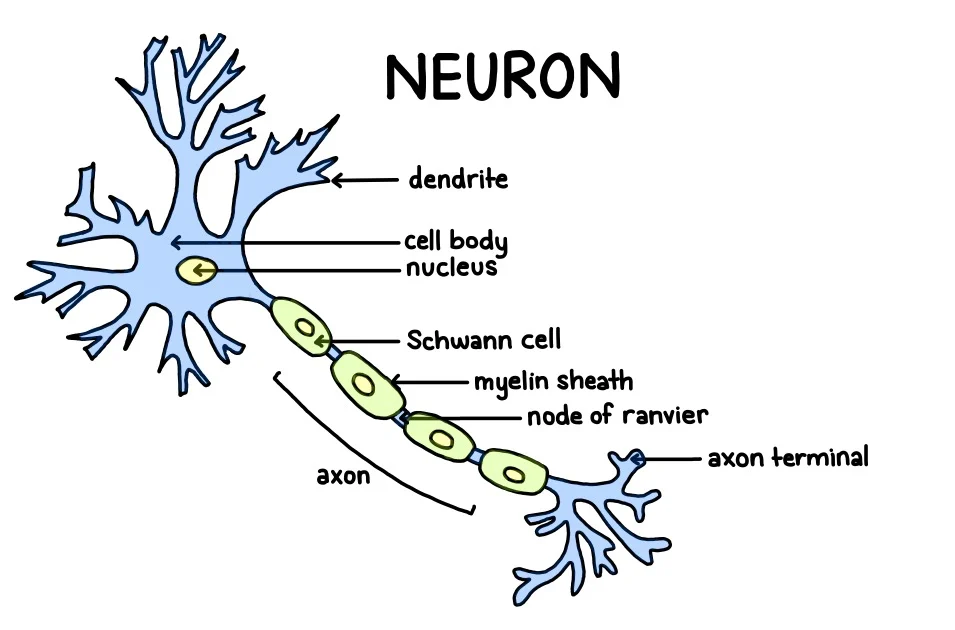
neuron
cell that sends and receives messages
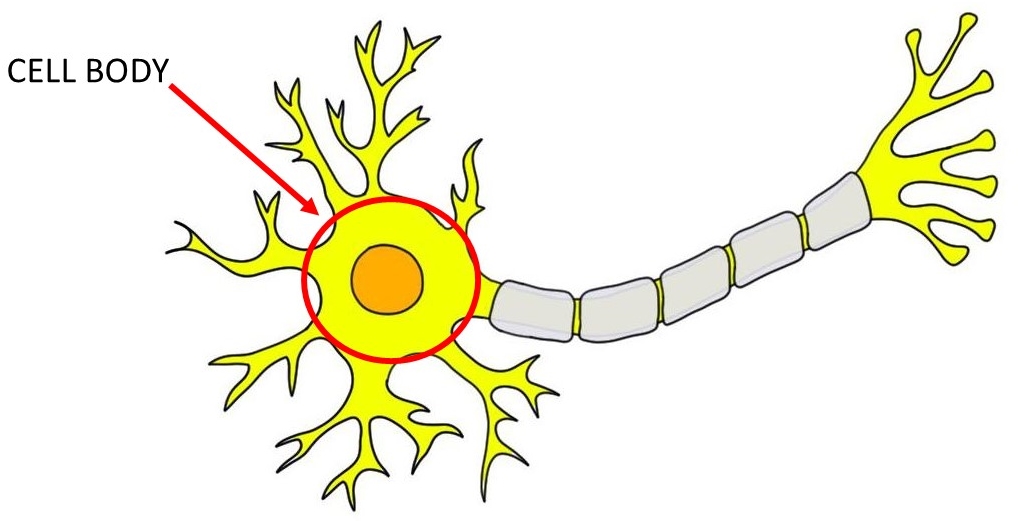
cell body
the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cell’s life-support center
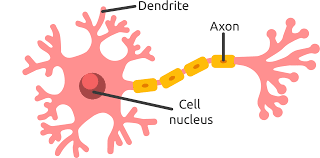
dendrites
receive messages from other neurons and cells, conducting impulses toward the cell body
interneurons
a neuron which transmits impulses between other neurons
axon
sends messages to other neurons, muscles, or glands
myelin sheath
fatty layer that speeds up neural signals
gilal cells
support neurons and help with learning and memory
action potential
an electrical signal a neuron fires
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
excitatory neurotransmitters
encourages neurons to fire
inhibitory neurotransmitters
prevents neurons from firing
refractory period
the brief resting time after a neuron fires, neuron can’t fire
all-or-nothing response
neuron fires fully or not at all
synapse
the tiny gap where one neuron sends signals to another
reuptake
a neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
substance P
pain neurotransmitter
nuerotransmitters
chemicals that cross the synapse to signal the next neuron, and tell the next neuron whether to fire
agonist
increases or mimics neurotransmitter action
antagonist
a molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord; decision maker of the body
Peripheral Nervous System
made up of subsystems; carries messages between body and CNS
Somatic Nervous System
controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
Automatic Nervous System
controls involuntary movements like breathing and digestion
Parasympathetic Nervous System
calms the body down following stress, “rest and digest”
Sympathetic Nervous System
prepares “ fight or flight” responses during stressful situations, puts the body in survival mode
Dopamine
involved in reward and motivation
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter that increases heart rate and focus
GABA
Calms the nervous system
Endorphins
natural pain relieving neurotransmitters
Seratonin
mood stabilizing neurotransmitter
Oxytocin
bonding and love hormone
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that helps muscle movement
Melatonin
sleep hormone
Leptin
hormone that reduces appetite
Ghrelin
Hormone that stimulates appetite
Adrenaline
fight or flight hormone
glumate
main excitatory neurotransmitter for learning and memory
EEG
record’s brains, electrical activity, using electrodes on scalp
lesion
destruction of brain tissue
reflex arc
an automatic response without conscious thought
MEG
measures magnetic fields from brain’s electrical activity
PET
shows brain activity by tracking glucose use during tasks
MRI
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue, scans show brain anatomy
fMRI
shows brain activity and function by tracking blood flow, also shows structure
brainstem
oldest part of the brain; controls automatic survival functions
medulla
the base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
amygdala
deals with fear and aggression
limbic system
involved in emotional making and memory
hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system; place a role in forming new memories but does NOT store memories
reticular activating system
regulates consciousness, filters sensory information and controls the sleep-wake cycle
microelectrodes
records single neuron activity
motor neurons
carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
endocrine system
the body’s slower communication system; glands release hormones into the bloodstream
adrenal glands
glands above the kidneys that release epinephrine and norepinephrine to arouse the body during stress
thalamus
relay station for sensory information (except smell)
reticular formation
network in brainstem and thalamus; regulates arousal and alertness
optogenetics
control neurons with light
sensory neurons
information from the five senses travels towards the brain
Brain’s Job
interprets the message to make the next decision
Spinal Cord’s Job
carries messages between the brain and the body
Occipital lobes
back part of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
Temporal lobes
sides of the cerebral cortex above the ears that processes auditory information, mostly from the opposite ear
cerebral cortex
main control and information-processing center
frontal lobes
front part of the cortex; handles speaking, muscle movements, planning, decision making
parietal lobes
top-middle part of the cortex; processes sensory info like touch and body position
Somatosensory Cortex
front part of the parietal lobes that register and processes body touch and movement sensations
Association areas
cerebral cortex regions involved in higher mental thinking; learning, remembering, and speaking, but NOT basic or sensory tasks
nuerogenesis
the formation of new neurons