Microbio Lab Quiz 2 (2.1 and 2.2)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Epidemiology
the study of how microbes spread within a group or population
how many are affected
symtoms
how the disease is spread
portal of entry
the way a microbe enters and infects a new host (entrance way)
Examples
Skin (Staphylococcus aureus)
Gastrointestinal tract (salmonella)
Respiratory tract (streptococcus pneumoniae)
Urogenital tract (STDs)
opportunistic pathogen
cause disease when the host’s defenses are compromised
Factors that weaken host defenses
old age
surgery
disease (HIV, cancer, etc.)
Chemotherapy and immunosuppressive drugs
Physical and Mental stress
Normal biota (flora)
normal population of microbes present in an organism (outnumber human cells 10 to 1)
Transient organisms
organism found on the skin for a short period of time but do not grow there
Example: mass transit
contact with contaminated surface but easily removed
some can cause disease
do not stay in the body long because of competition between resident microbes
elimination by the body’s immune system
Vectors
living organisms that transmit disease
Biological vector
an organism in which the parasite undergoes part of its lifecycle (sexual or asexual reproduction) and then transmits the parasite to another organism
Example: female anopheles mosquito (directly biting)
Mechanical Vector
an organism that transmits a parasite but its not part of its life cycle
Example: fleas, ticks (indirectly- carrying disease organisms)
Reservoir of infection
an object that allows a microbes to grow, reproduce, and maintain the ability to infect a new host
nutrient substrate
Examples: burger, soil, and makeup
Fomite
an object that allows a microbe to survive and pass to a new host
any inanimate object
Examples: phone, pen, bathmat —> athletes foot
Hand washing
soap breaks down the oils on your skin allowing trapped bacteria to be washed away
break down the cell membranes of the bacteria
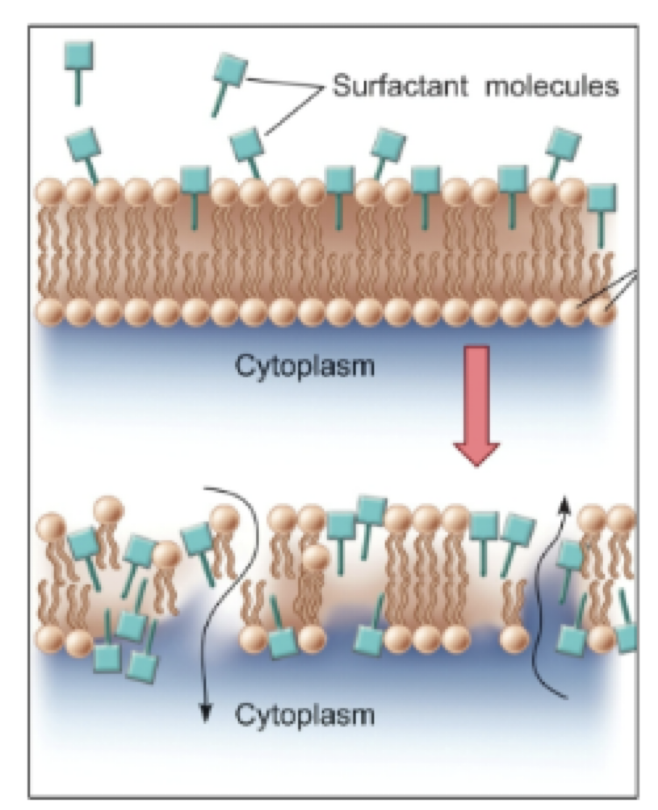
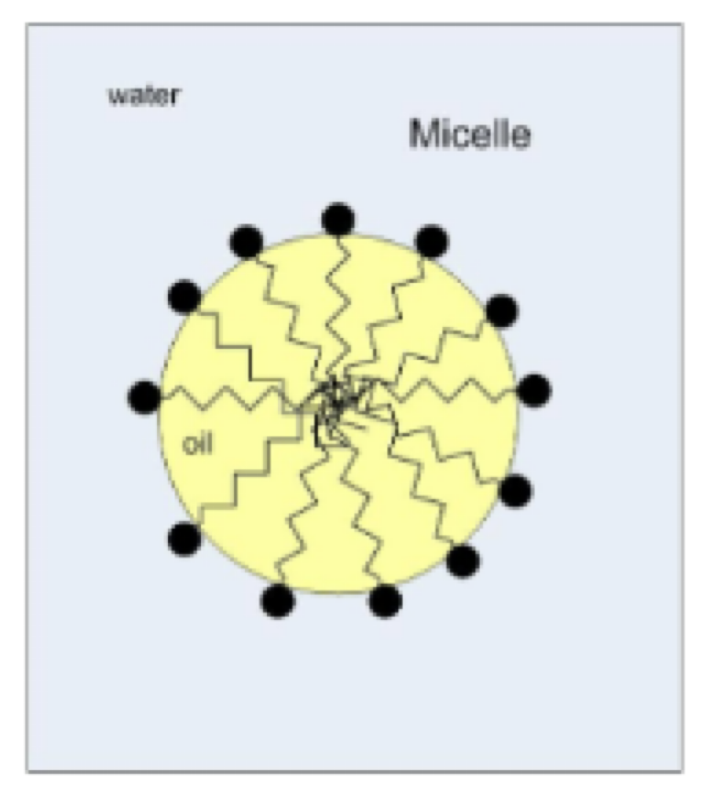
Micelles - Hand washing
spheres of lipids that form in aqueous solutions
Example: a corral
Friction
physically remove emulsified skin oil
Aseptic
chemical that kills microbes (used in hospitals)
Examples: Hydrogen Peroxide and Triclosan
Why do we isolate bacteria?
to isolate a pure bacteria culture
Pure culture
a sample containing a single species of organism
Why do you need a pure bacteria culture?
Carry out biomedical testing
determine antibiotic sensitivity
develop vaccines
determining nutritional requirements
study organism that cause disease
Aspectic technique
Handling microbes and material in such a away that minimizes contamination
Examples: wearing lab coats, hand washing, ulitzing incinerators and cleaning work surfaces before and after transfers
prevents the microbes you re transferring from contaminating the work area or yourself
prevents the microbes on the work area or yourself from being transferred into the samples and then contaminating them
Contamination
presence or possible presence of microbes where they do not belong
Culturing bacteria
agar plates (made from seaweed)
melts at 100 C
solidifies 32-46 C
remains liquid above 46 C
agar is an addictive not media (does not provide food/nutrients for the bacteria)
agar is a solid surface where bacteria can grow —> isolated colonies
Robert Koch
the father of microbiology
invented agar: derived from seaweed
Is bacteria homotrophic or heterotrophic?
heterotrophic
the organisms cannot synthesize their own organic molecules
Growth media
substrate for bacteria to grow in or upon
Complex Media
had a composition that is not definable by an exact chemcial formula
uses extracts from other organism (animals, plants, fungi)
rich in nutrients and support a wide range of bacterial growth
Examples: Tryptic Soy Media
contains enzymatic digests of casein and soybean in an undefined amount that varies batch to batch
Chemically Defined Media
Pure organic and inorganic compounds are added in exact amounts
narrow range of bacteria growth
Enriched Media
contains a complex of organic substances to grow fastidious organiusms
Media which specific nutrients are added: blood, serum, hemoglobin, or special growth factors
blood agar and brain-heart infusion (BHI) agar
Making Media
powdered media dissolved in distilled water
media is dispensed into tubes or bottles according to instructions
autoclave
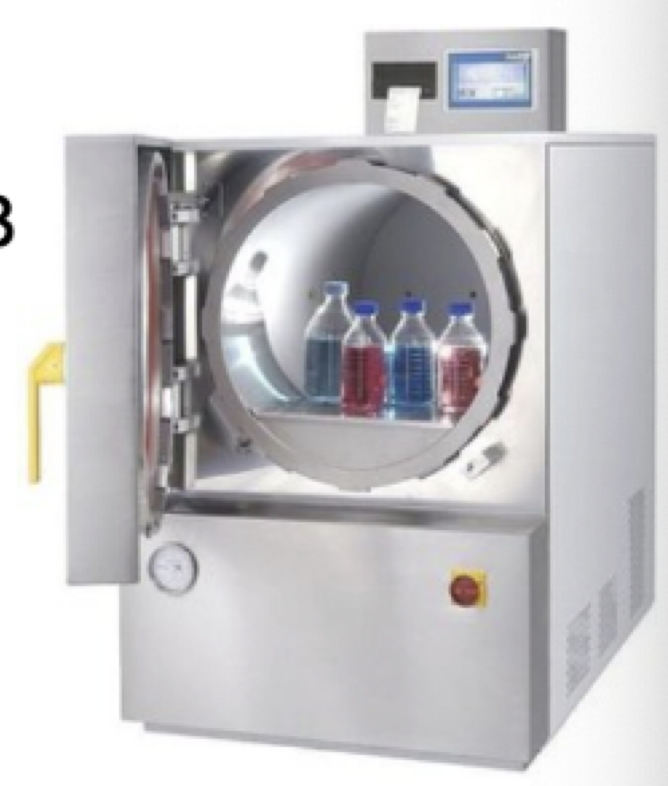
Autoclave
Instrument used to sterilize (Steam B)
Temperature: 121 C
15 lbs of pressure/ square inch (lbs/ in²)
20 minutes: kills all bacteria, fungal spores and viruses

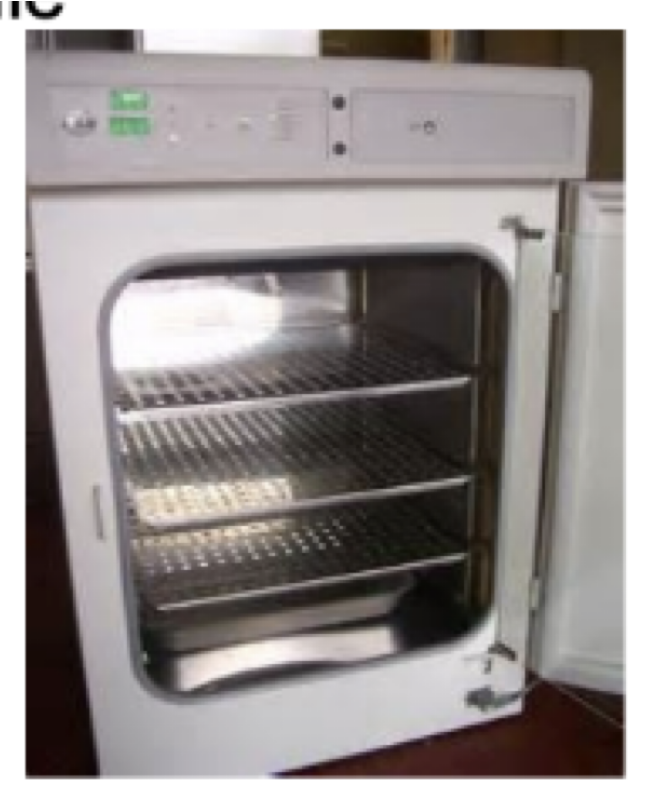
Incubator
holds a constant temperature, used to grow bacterial cultures

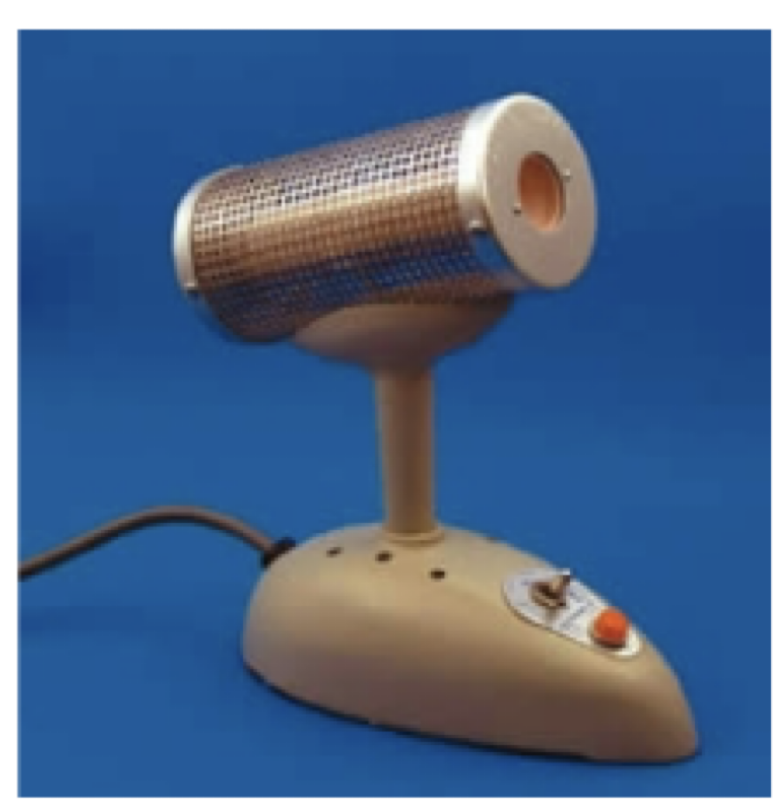
Incinerator
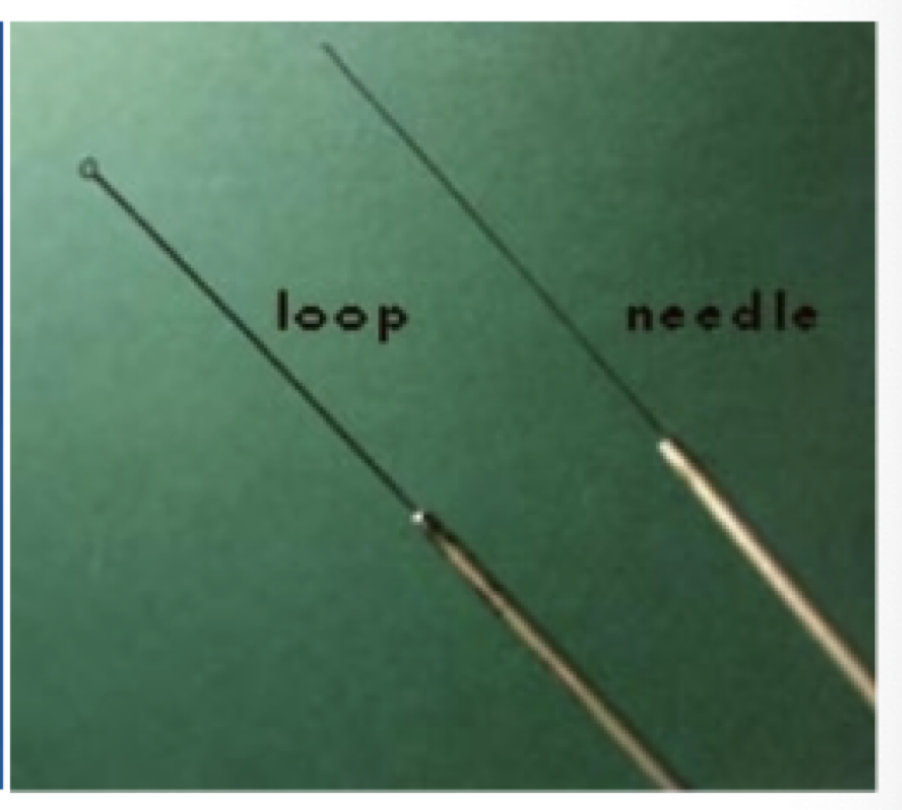
device used to sterilize inoculating tools

tools used to transfer bacteria form a culture to sterile media
inoculating loop
inoculating needle
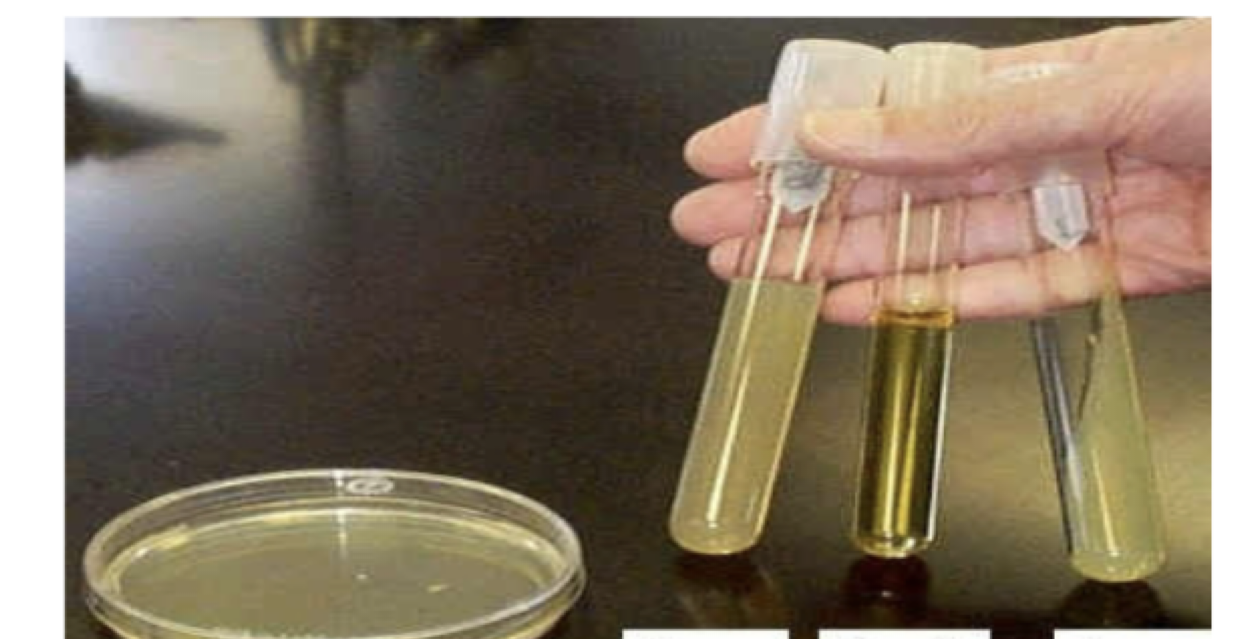
Media forms
agar plate
agar deep tube
broth
agar slant
Streak Plate Isolation
method used to separate a mixed culture and develop isolated colonies
isolated colonies form from a single bacterium
genetically identical
by isolating colonies, further testing can then be carried out
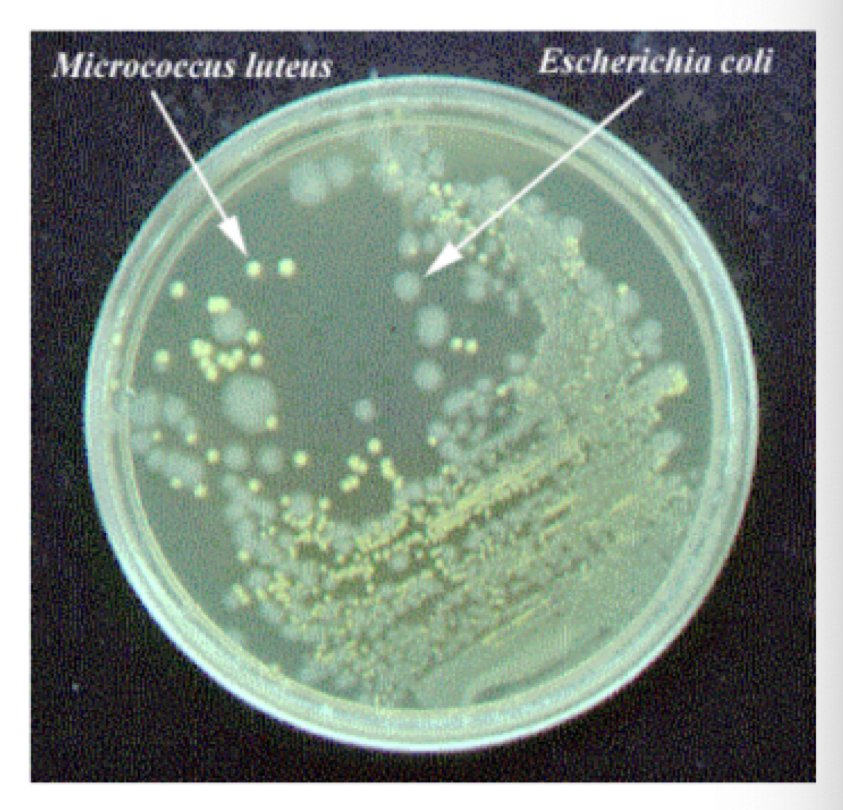
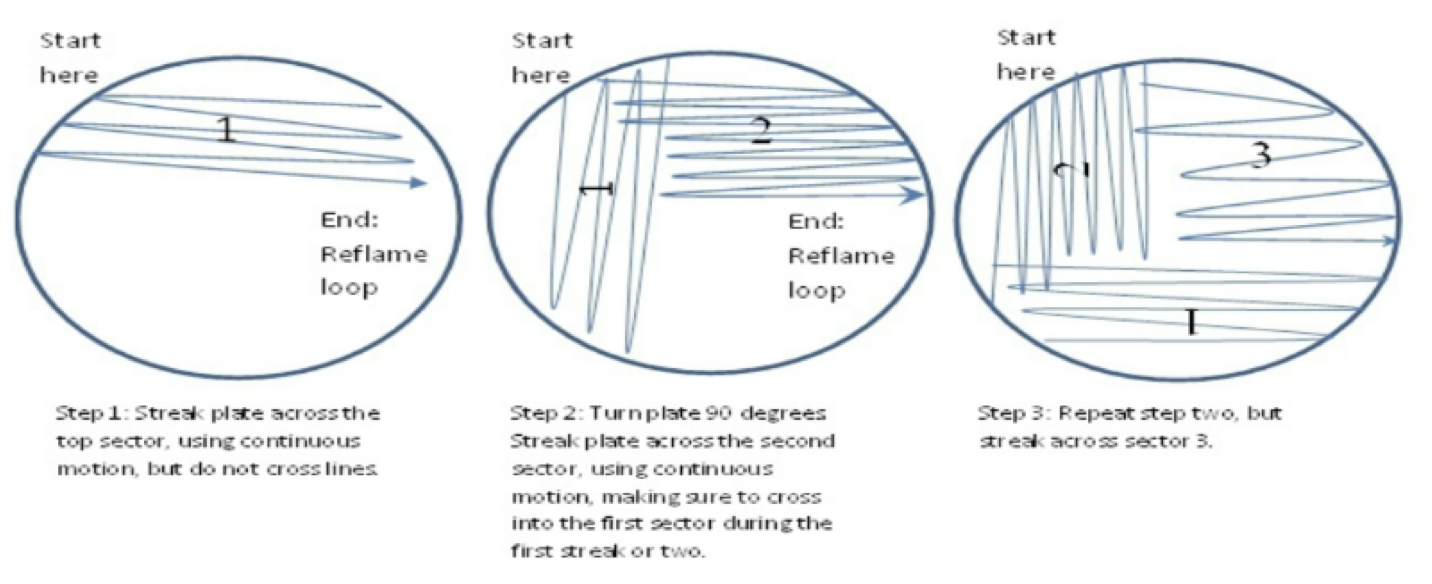
Streak Plate Isolation