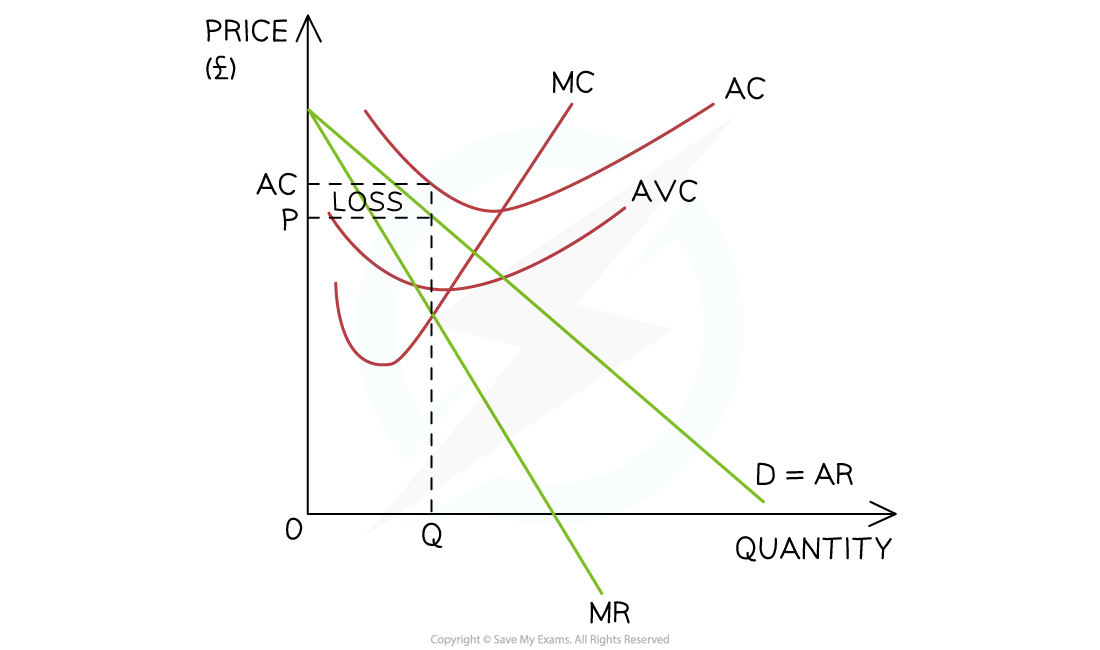3.3 revenues, costs and profits
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
definition of economic long run
when all factors of production are variable
definition of economic short run
when at least one factor of production is fixed
what is the law of diminishing marginal productivity
if a variable FoP is added to a fixed FoP, eventually productivity will start to decrease
what is average product
output per unit of input
what is marginal product
additional output produced by an additional unit of input
what are fixed costs + examples
costs that don’t change with output e.g. salaries, factory machinery
what are sunk costs
costs that can’t be recuperated when businesses leave the market (part of fixed costs) e.g. advertising
what are variable costs
costs that vary with output e.g. wages, raw materials
total cost formula
total fixed cost + total variable cost
total variable cost formula
average variable cost x output (Q)
average total cost formula
total cost / output
average fixed cost formula
total fixed cost / output
average variable cost
total variable cost / output
marginal cost formula
change in total cost / change in output
difference between economists and accountants
economics take opportunity costs into account
what is total revenue
price x quantity
average revenue formula
total revenue / output
marginal revenue definition and formula
extra revenue received from the sales of an additional unit of output
change in TR / change in Q
relationship between total revenue and PED
when PED elastic if there is a decrease in price TR will increase
if PED inelastic if there is a decrease in P TR will decrease
representation of where diminishing marginal returns begin on a graph
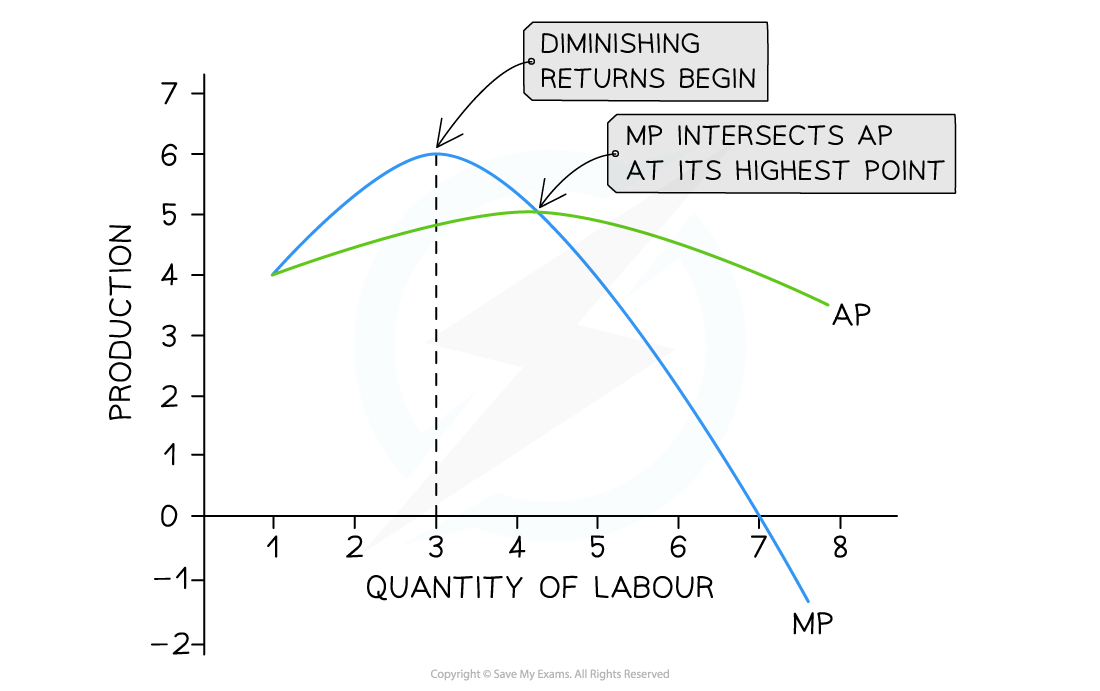
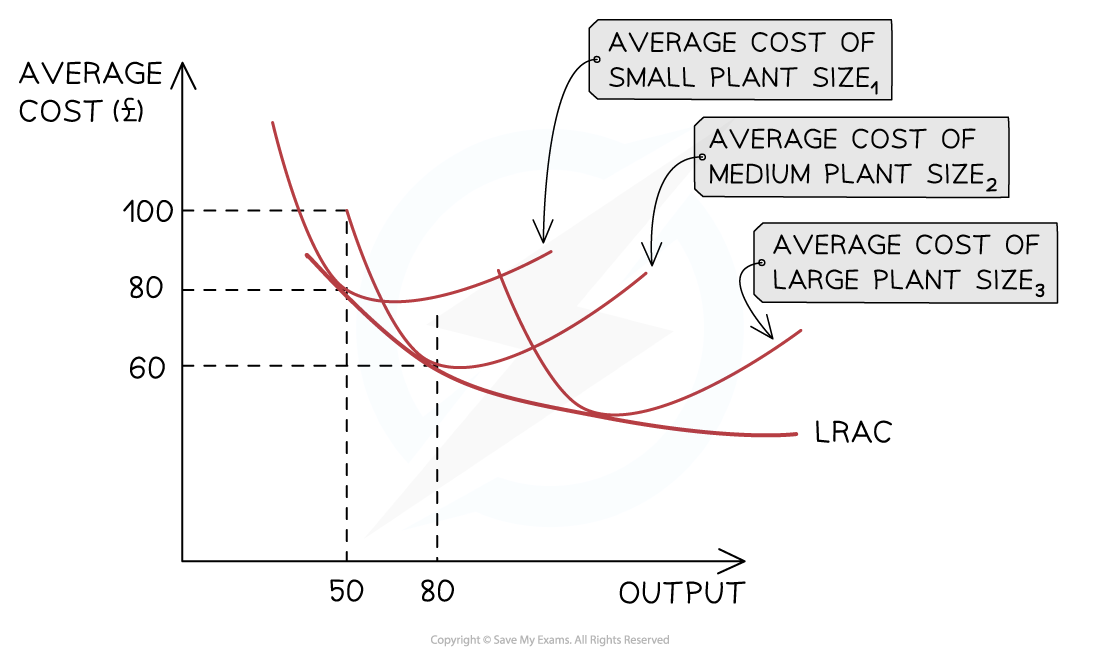
diagram of relationship between short run and long run average cost curves
types of economies of scale
financial economies - lower IR for larger firms
managerial economies - larger firms can employ specialist managers = effeciency
marketing economies - larger firms spread costs of advertising on large number of sales
purchasing economies - bulk discounts on raw materials
technical economies - spread costs of new machinery over more units sold = lower AC
risk-bearing economies - spread risk of failure through diversification
types of diseconomies of scale
management diseconomies - managers work in own interest not the firms
communication diseconomies - inefficient communication
geographical diseconomies - communication challenges in widespread operation bases
cultural diseconomies - culture clash in the workplace = decreased productivity
what is the minimum efficient scale
lowest cost point on a long run average total cost curve
lowest possible cost per unit that a firm in an industry can achieve in the long run
minimum efficient scale on a diagram

what are internal economies of scale
result of the growth in the scale of production within a firm
what are external economies of scale
when there is an increase in the size of an industry in which the firm operates
what are examples of external economies of scale
geographic cluster - firms move closer to major manufacturers
transport links - lowers LRAC
skilled labour - lower labour costs - larger geographic cluster = larger pool of skilled labour
fabourable legislation - when govs support certain industries to achieve their wider objectives
what is the profit maximisation point
MC=MR
what are explicit costs
costs which have to be payed e.g. wages and raw materials
what are implicit costs
opportunity costs
need to be considered when deciding if more profit can be made elsewhere
profit formula
total revenue - total costs
normal profit
TR = TC (breakeven)
just enough to cover costs
when do supernormal profits occur
when TR>TC
when do losses occur
when TC>TR
when should firms shut down in the short run (SR shut-down profit)
if AR is higher than AVC the firm should keep producing
the firm should shut down if selling price (P/AR) doesn’t cover AC (e.g. in diagram)
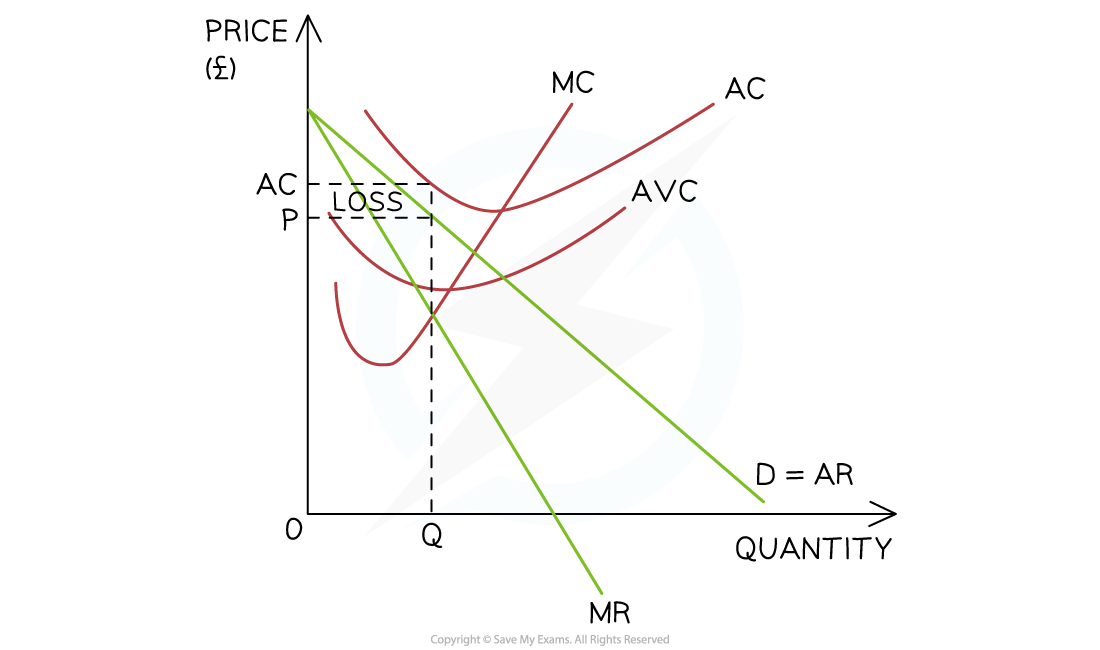
when should firms shut down in the long run (long-run shut-down profit)
if LRAR is higher than LRAC
if AR is less than or equal to AC the firm should shut down
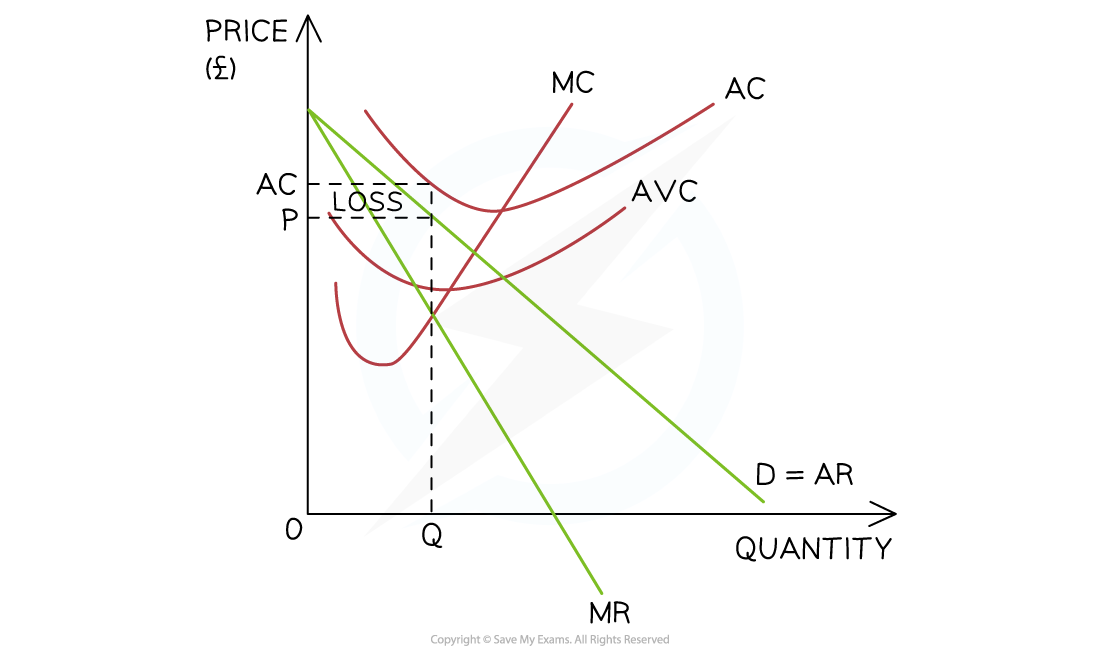
what is supernormal profit
AR > AC
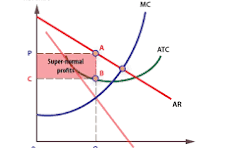
what is normal profit
AC = AR
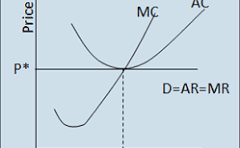
what is a loss
AC > AR
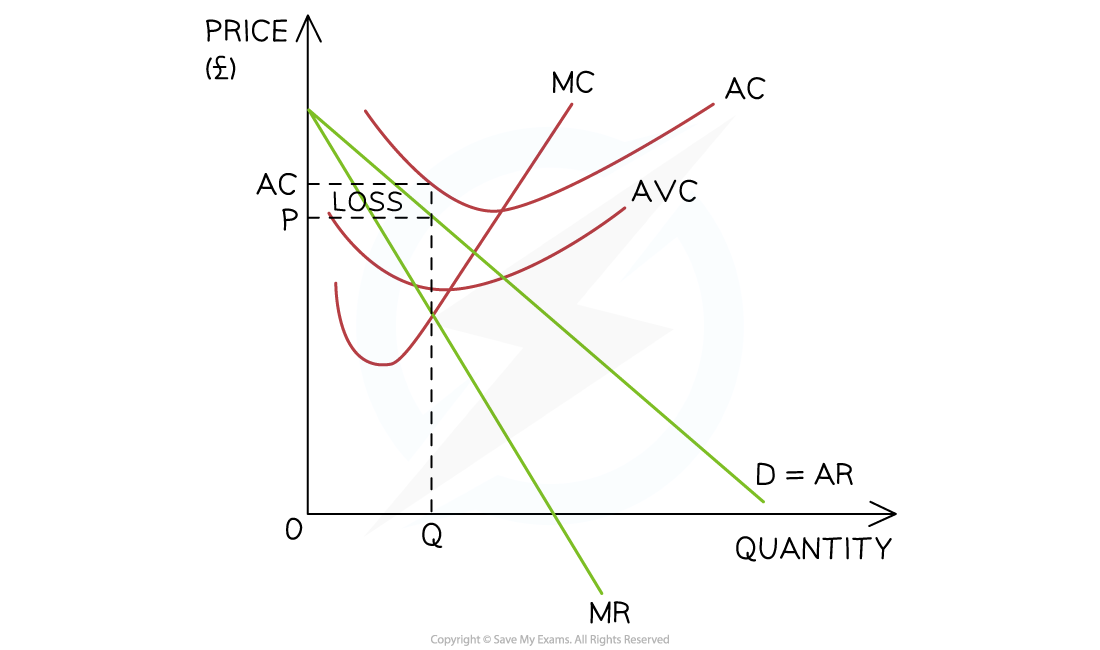
what is the short run shut-down point
when AVC = AR
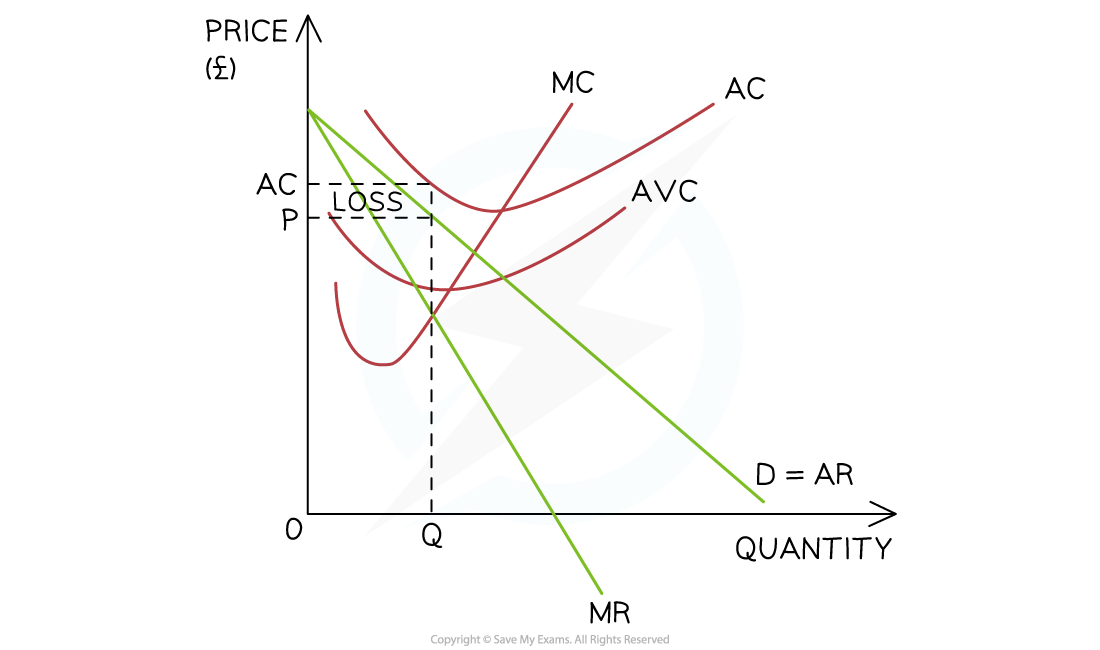
what is the long run shut down point
when AC > AR