Lesson 29: Parasympathetic Nervous System:
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Parasympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy by slowing the heart rate and increasing intestinal and gland activity.
Neurotransmitter at postganglionic parasympathetic nerve terminal
Acetylcholine (ACh) is released at the postganglionic parasympathetic nerve terminal.
G-protein receptor stimulation associated with bradycardia
Muscarinic receptor stimulation is associated with bradycardia.
Preganglionic neuron's origin in the parasympathetic division
The preganglionic neuron's origin is in the cranio-sacral region.
Ganglia location in the parasympathetic system
Most ganglia of the parasympathetic system are located near—or even within—the target effector.
Ratio of preganglionic to postganglionic fibers in many organs
There is a 3:1 ratio of preganglionic fibers to postganglionic fibers.
Effects of the parasympathetic system
The effects of the parasympathetic system tend to be more discrete and localized.
Primary transmitter of all preganglionic neurons
All preganglionic neurons (sympathetic and parasympathetic) synthesize and release acetylcholine (ACh) as their primary transmitter.
Receptors at autonomic ganglia
The receptors at autonomic ganglia are cholinergic: nicotinic.
Primary neurotransmitter of parasympathetic postganglionic neurons
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons synthesize and release acetylcholine (ACh) as their primary neurotransmitter.
Receptors that bind acetylcholine in parasympathetic system
Muscarinic receptors bind acetylcholine in the parasympathetic system.
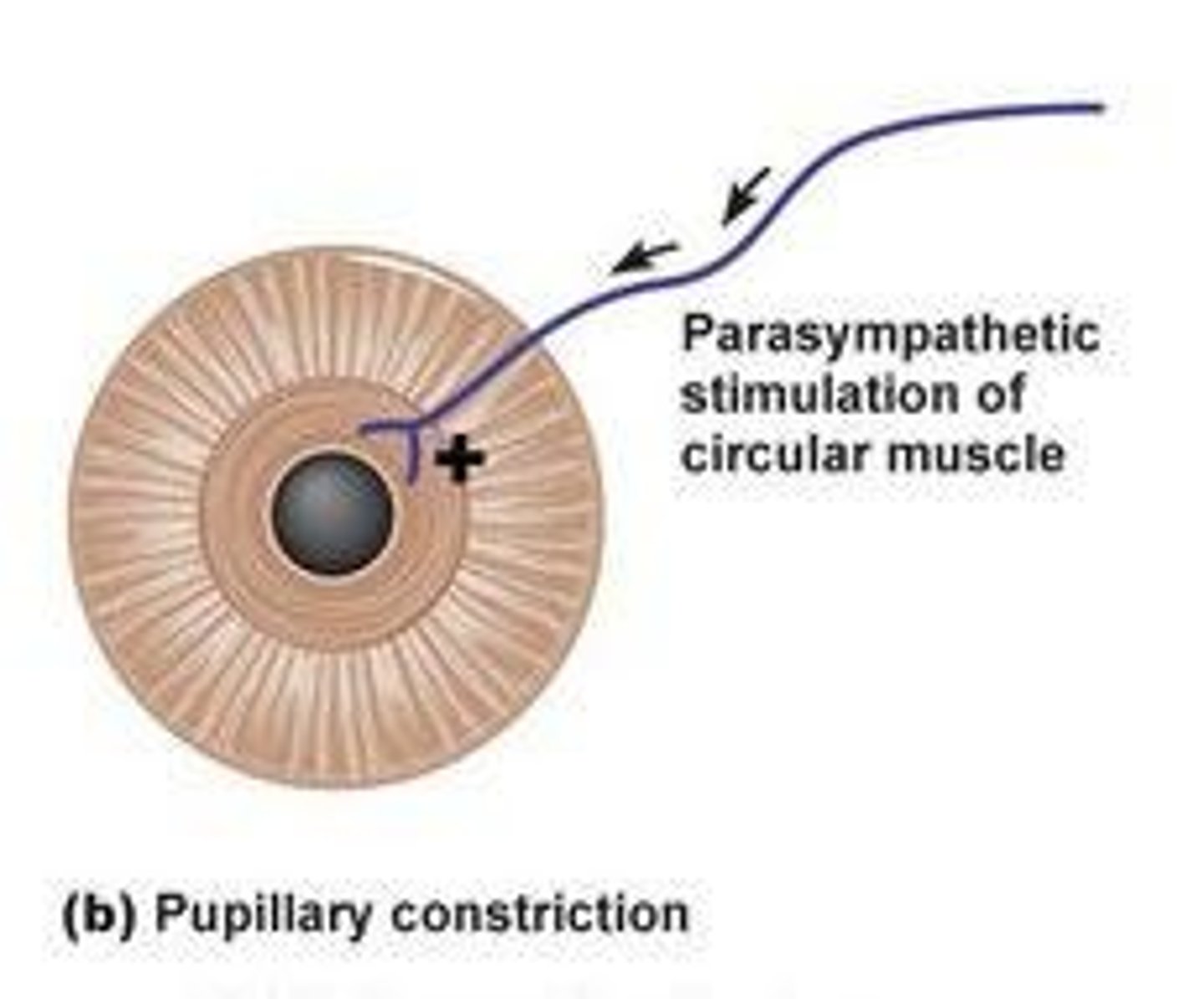
Effects of parasympathetic division stimulation on pupil diameter
Stimulation of the parasympathetic division causes miosis (constriction of pupils).
Effects of parasympathetic stimulation on heart rate
Parasympathetic stimulation leads to a decrease in heart rate.
Effects of parasympathetic stimulation on blood pressure
Parasympathetic stimulation leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
Effects of parasympathetic stimulation on gastrointestinal activity
Parasympathetic stimulation stimulates gastrointestinal activity.
Effects of parasympathetic stimulation on insulin release
Parasympathetic stimulation increases insulin release, leading to lower blood glucose concentration.
G-protein receptor stimulation causing bronchoconstriction
Muscarinic receptor stimulation causes bronchoconstriction.
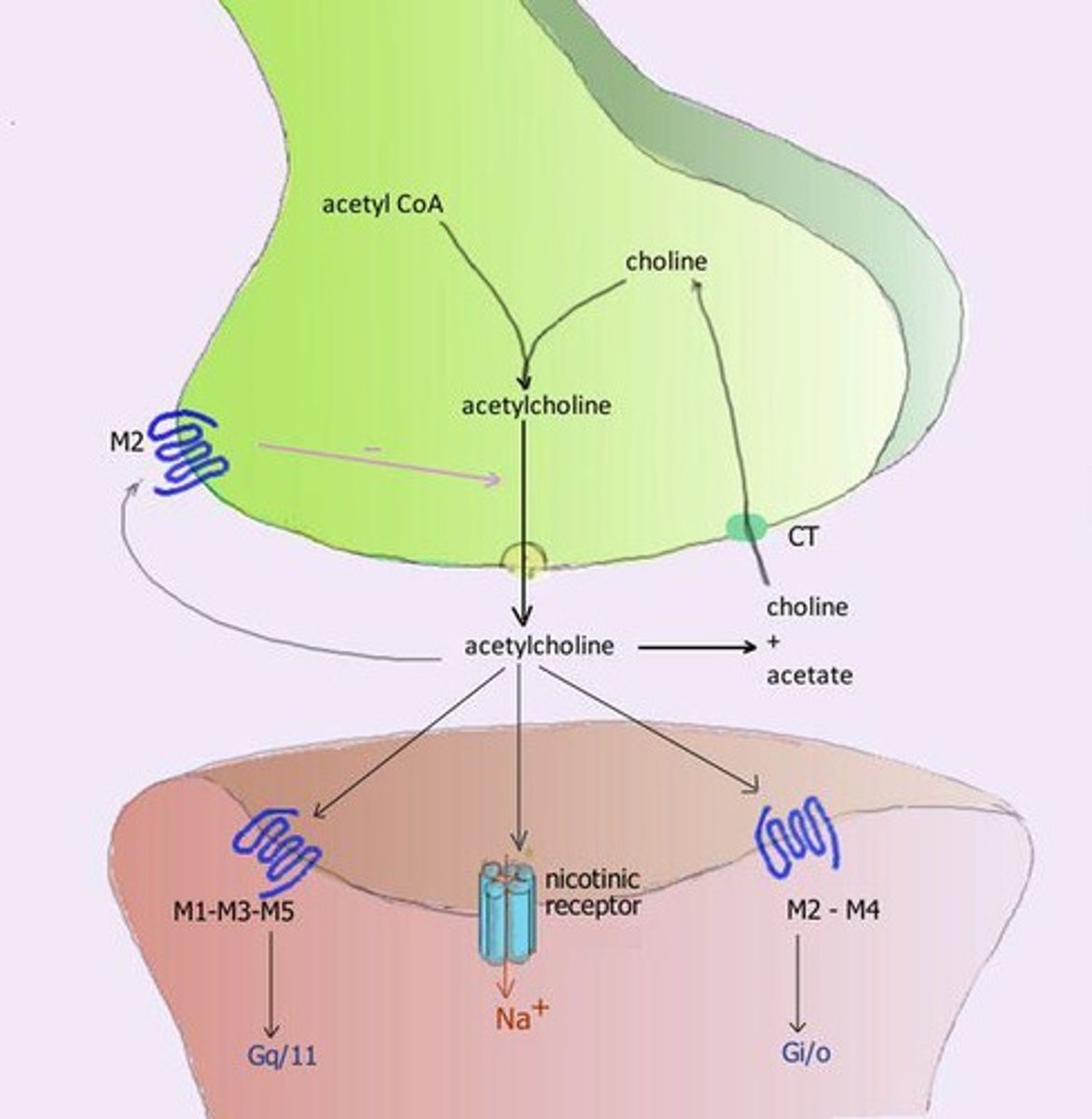
Types of Cholinergic Receptors
ACh possesses both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
Nicotinic receptors
Nicotinic receptors are found in autonomic ganglia, skeletal muscle neuromuscular junction, adrenal medulla, and CNS.
Function of nicotinic receptors
Nicotinic receptors increase cellular permeability to Na+ ions, leading to depolarization and excitation.
Nicotinic muscular receptors (NM)
Nicotinic muscular receptors are found in the neuromuscular junction and lead to depolarization and skeletal muscle contractions.
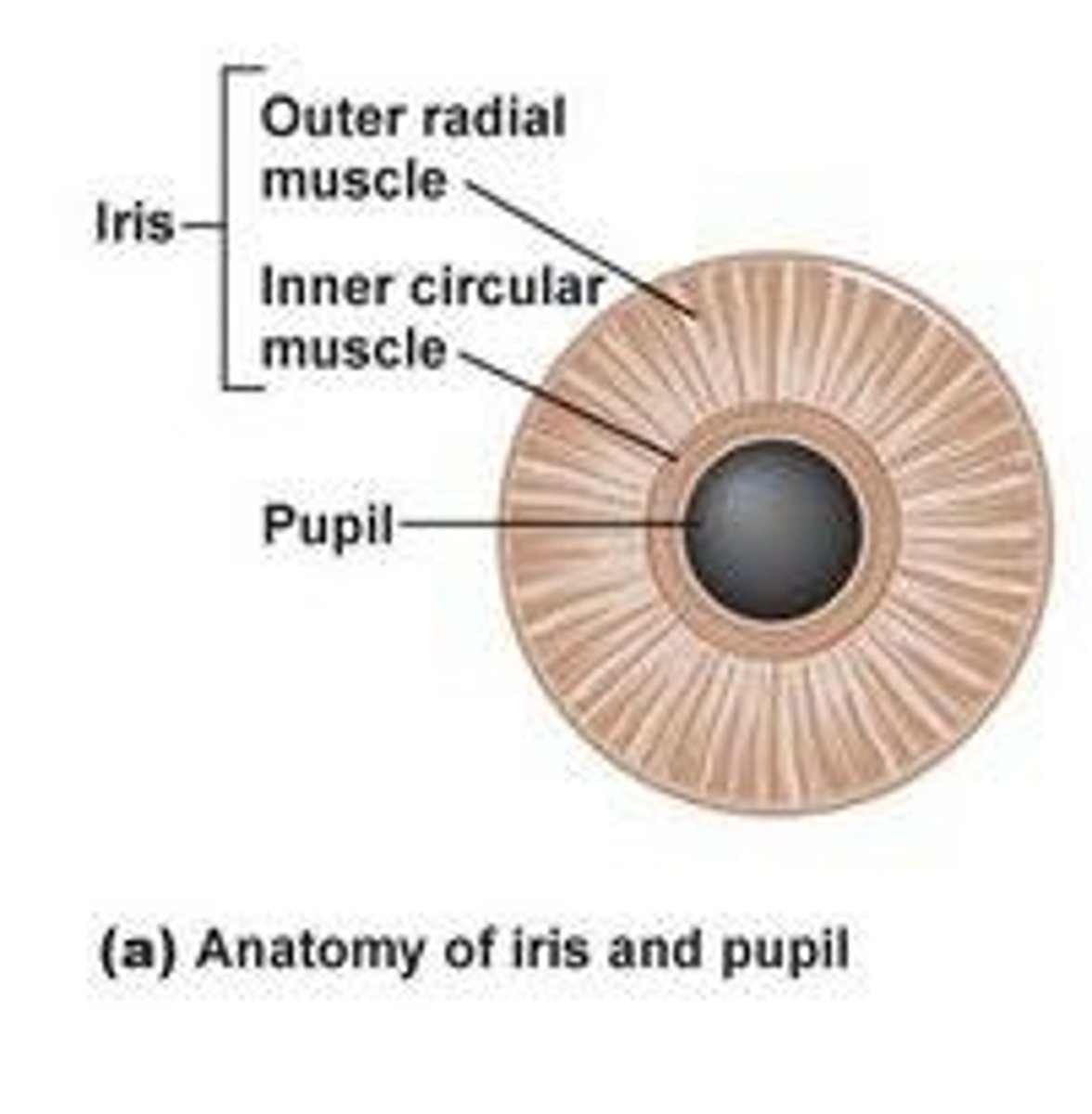
Mydriasis
Mydriasis refers to the dilation of the pupils.
Miosis
Miosis refers to the constriction of the pupils.
Nicotinic neuronal receptors
A type of acetylcholine receptor that is found in the nervous system.
Muscarinic receptors
A type of acetylcholine receptor that is G protein-coupled and mediates various physiological responses.
M1, M3, M5 receptors
Muscarinic receptors that activate Gq protein.
M2, M4 receptors
Muscarinic receptors that activate Gi protein and inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
M3 receptors in vascular endothelium
Non-innervated muscarinic receptors that release nitric oxide, activating guanylyl cyclase and causing vasodilation.
Acetylcholine
A quaternary amine and the prototype for directly acting cholinergic agonists.
Pharmacological effects of Acetylcholine on the cardiovascular system
Produces a rapid fall in blood pressure; brief duration, mainly mediated by the release of endothelial Nitric Oxide, leading to vasodilation.
Effects of Acetylcholine on heart rate
Lowers heart rate and speed of conduction of electrical impulses in the heart.
Effects of Acetylcholine on the eye
Causes miosis, loss of accommodation, and reduces intraocular pressure.
Effects of Acetylcholine on smooth muscle
Increases contraction of the urinary bladder and uterus.
Effects of Acetylcholine on bronchiolar smooth muscle
Causes constriction of bronchiolar smooth muscle.
Intra-arterial injection of Acetylcholine
Leads to excitation and convulsions.
Cholinergic agonists
Also known as parasympathomimetics, they produce acetylcholine-like effects on effector cells.
Direct-acting cholinergic agonists
Activate cholinergic receptors on effector cells.
Indirect-acting choline esters (Cholinesterase inhibitors)
Lead to accumulation of acetylcholine in synaptic junctions, increasing cholinergic action.
Direct-acting parasympathomimetics
Include choline esters like Bethanechol and natural alkaloids like Pilocarpine.
Bethanechol
A direct-acting parasympathomimetic that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors and is resistant to hydrolysis by AChE.
Indications for Bethanechol
Used for GI paralytic ileus and urinary retention associated with bladder muscle atony.
Pilocarpine
A muscarinic receptor agonist used in ophthalmic solutions to treat glaucoma and increase tear production.

Adverse effects of parasympathomimetics
Include bronchoconstriction, bradycardia, miosis, salivation, sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, urinary incontinence, neuromuscular effects, CNS effects at high doses, and uterine contraction.
Pharmacological effect of Bethanechol
Includes urinary retention, increases GI and bladder contractions, mydriasis, and bronchodilation.
Cholinesterase inhibitors (anticholinesterase)
Substances that inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine (ACh).
Irreversible Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Inhibitors that form a stable enzyme-inhibitor complex with AChE, requiring new enzyme synthesis for recovery.
Organophosphate compounds
A type of irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor that interacts with AChE at the esteratic site and causes phosphorylation.
Reversible cholinesterase inhibitors
Inhibitors that temporarily bind to AChE, allowing for the hydrolysis of ACh to resume after the inhibitor is removed.
Physostigmine
An alkaloid from Physostigma venonosum that combines reversibly with AChE to inhibit the hydrolysis of ACh.
Neostigmine
A reversible cholinesterase inhibitor that prolongs the action of ACh and can reactivate the enzyme to hydrolyze ACh.
Pyridostigmine
A reversible cholinesterase inhibitor used therapeutically for conditions like myasthenia gravis.
Edrophonium
A reversible cholinesterase inhibitor used to reverse neuromuscular blockade.
Therapeutic uses of Physostigmine
Used primarily for the treatment of glaucoma.
Therapeutic uses of Neostigmine and Pyridostigmine
Used for the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
Contraindications for Reversible Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Include impaction with obstruction and pregnancy.
Toxicology of Neostigmine
Can cause skeletal muscle weakness, nausea, vomiting, colic, diarrhea, pupil constriction, dyspnea, bradycardia, hypotension, and respiratory paralysis.
Antagonist: Atropine
A competitive antagonist used against cholinergic effects caused by irreversible cholinesterase inhibitors.
Organophosphorous compounds poisoning
Causes cholinomimetic effects such as profuse salivation, vomiting, hypermotility of GIT, defecation, urination, bradycardia, hypotension, severe bronchoconstriction, and muscle paralysis.
Antidote for Organophosphate poisoning
Atropine is used as a competitive antagonist to AChE reactivators like Pralidoxime.
Clinical significance of cholinergic agonists
Includes their role in treating various medical conditions related to the cholinergic system.
Cholinergic antagonists
Inhibits actions of acetylcholine by blocking cholinergic receptors.
Anti-muscarinic
Antagonize muscarinic receptors.
Ganglionic blockers
Antagonize the NN receptor.
Neuromuscular blockers
Antagonize NM receptors.
Antimuscarinic agents (Parasympatholytics)
Inhibits muscarinic actions of acetylcholine and related cholinergic agonists.
Atropine
Prototype antimuscarinic agent, an alkaloid extracted from Atropa belladona.

Scopolamine
An alkaloid extracted from Datura stramonium, also known as l-hyoscine.
Mechanism of action of antimuscarinic agents
Competitive antagonism that prevents ACh binding to these receptors.
Vagolytic effect
Requires large dose to block cholinergic effect, allowing sympathetic action to dominate.
Salivary and sweat glands
Susceptible to small doses of atropine.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Cardiovascular system)
Causes tachycardia, increases cardiac output and blood pressure.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Gastrointestinal tract)
Relaxes GIT, relieves intestinal spasm and hypermotility, decreases secretions.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Urinary system)
Relaxes smooth muscle of the urinary bladder, causing urinary retention.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Bronchioles)
Decreases secretions and causes bronchodilation.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Ocular effect)
Causes mydriasis and cycloplegia (paralysis of the ciliary muscle).
Antimuscarinic drugs - contraindicated in
Increased intraocular pressure.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (Sweat glands)
Causes anhidrotic effect through cholinergic mechanism.
Atropine - Pharmacologic effects (CNS)
Minimal effects, but excess dose can lead to hallucinations, excitement, depression, and coma.
Species sensitivity to atropine
Rabbits are resistant due to atropinase enzyme from the liver.
Therapeutic uses of antimuscarinic agents
Includes antidote for cholinergic agonists, prevention of motion sickness, antispasmodic, and antisecretory agent.
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul-V®)
Preanesthetic use in veterinary medicine; potent antimuscarinic with longer duration of action than atropine.
Homatropine
Ester of mandelic acid used for mydriasis and cycloplegia.

Ipratropium
Used for bronchodilation and available as a nasal spray.
Scopolamine butylbromide (Buscopan®)
Smooth muscle relaxant that does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
Antidote for cholinergic drug poisoning
C. Atropine.
Therapeutic role of glycopyrrolate in horses
Used as a preanesthetic agent.