3.2 Cerebral Cortex
most part prominent part of the mammalian brain
cerebral cortex
outer surface cerebral cortex cells
gray matter
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
most part prominent part of the mammalian brain
cerebral cortex
outer surface cerebral cortex cells
gray matter
axons of cerebral cortex outer surface cells located in
extending inward = white matter
how do neurons communicate to other hemisphere
2 axon bundles
Corpus callosum
smaller, anterior commissure
is the anterior commissure the only commissure
no, there are several others that serve as pathways across the midline to link subcortical structures
corpus callosum & anterior commissure
bundle of axons that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
how does the cerebral cortex of primates differ from other mammals
larger cerebral cortex
more folding
more neurons per unit volume
primates
monkeys, apes, humans
what are similar about mammal brains
same brain subareas in the same locations
what brain area has the same constant percentage across mammal species
cerebellum
10 - 14%
laminae
layers of cell bodies that are parallel to the surface of the cortex and separated from each other by layers of fibers
how many laminae in cerebral cortex
6
lamina V: inner pyramidal layer
long axons to the spinal cord and other distant areas
thickest in motor cortex
greatest control of muscles
large pyramidal cells
Lamina IV: internal granular layer
receives axons form sensory nuclei of thalamus
main site for incoming sensory info
prominent in the sensory areas (visual, auditory, somatosensory)
absent in motor
small cells
molecular layer, lamina I
mostly dendrites & long axons
external granular layer, lamina I
small pyramidal cells
pyramidal cell layer, Lamina III
pyramidal cells
multiform layers, lamine VIa & VIb
spindle cells
cerebral cortex columns
groups of cells perpendicular to the surface of the cortex and to its laminae
nature of cells in specific columns
similar functions
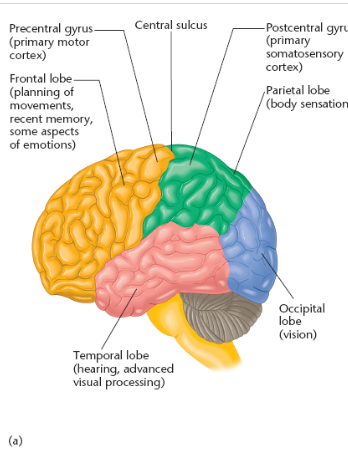
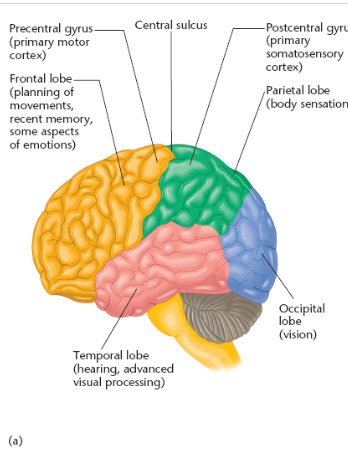
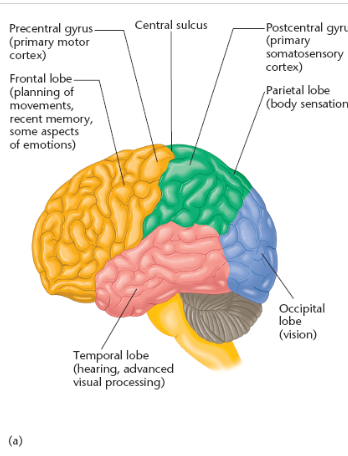
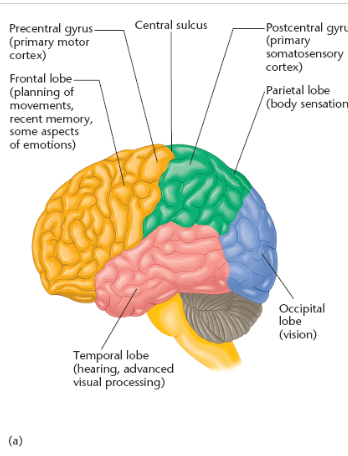
name and locate the cerebral cortex lobes
name and locate the columns in the cerebral cortex
occipital lobe
visual information
occipital lobe location
posterior (caudal) end of the cerebral cortex
other names for occipital lobe
striate cortex
primary visual cortex
destruction of striate cortex causes
cortical blindness in that related part of visual field
ex: damage in Rhemi causes blindness in left visual field
how can those w eye damage induced blindness have visual dreams & scenes
intact occipital cortex
previous visual experience
relationship of eyes and visual cortex
eyes = stimulus
visual cortex = experience
parietal lobe
receives sensations from
touch receptors
muscle-stretch receptors
joint receptors
location of parietal lobe
between occipital lobe & central sulcus
central sulcus
deep groove in the surface of the cerebral cortex
local anesthesia
anesthetizing the scalp but leaving the brain awake
simulation of postcentral gyrus during local anesthesia result
tingling sensations on opposite side of body
postcentral gyrus aka
primary somatosensory cortex
postcentral gyrus/ somatosensory cortex
4 bands of cells
parallel to central sulcus
name and identify location of interpreting sensations in the somatosensory cortex
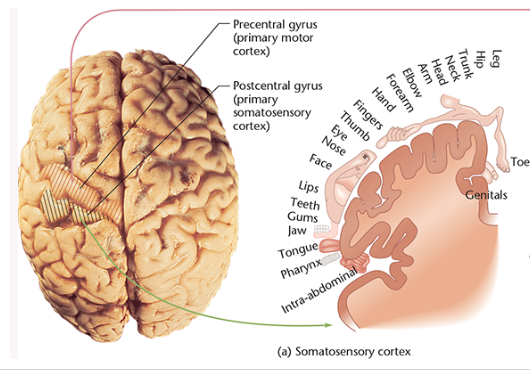
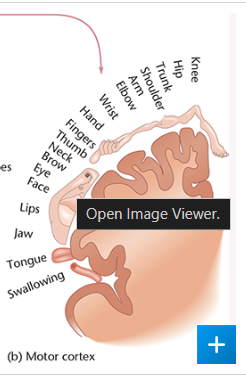
precentral gyrus aka
primary motor cortex
name and identify location of interpreting sensations in the motor cortex
parietal lobe
spatial & numeric information
ex: counting w our fingers
monitors all the information about eye, head, and body positions and passes it on to brain areas that control movemen
temporal lobe function
primary cortical target for auditory information
vision → perception of movement and facial recognition
emotion and motivational behaviors
temporal lobe location
lateral portion of each hemisphere, near temples
which temporal lobe is essential for understanding spoken language?
left
tumor in temporal lobe
elaborate auditory or visual hallucinations
tumor in occipital lobe
evokes simple sensations like flashes or lights
Klüver-Bucy syndrome
a behavioral disorder caused by temporal lobe damage
temporal lobe damage in previously wild and aggressive monkeys results in
failure to display normal fears and anxieties
picked up snakes
put almost anything into their moths
lighted matches
frontal lobe contains what cortexes
primary motor cortex
prefrontal cortex
frontal lobe extends from __ to _
central sulcus to anterior limit of the brain
precentral gyrus function
specialized to control fine movements → moving a finger
where is the precentral gyrus located
posterior portion of the frontal lobe
contralateral vs ipsilateral
contralateral (opposite side)
ipsilateral (same side)
precentral gyrus aka
primary motor cortex
prefrontal cortex location
anterior portion of the frontal lobe
which one is larger, prefrontal cortex or precentral gyrus?
prefrontal cortex
prefrontal cortex function
responds mostly to the sensory stimuli that signal the need for a movement
horizontal section of the brain looks like
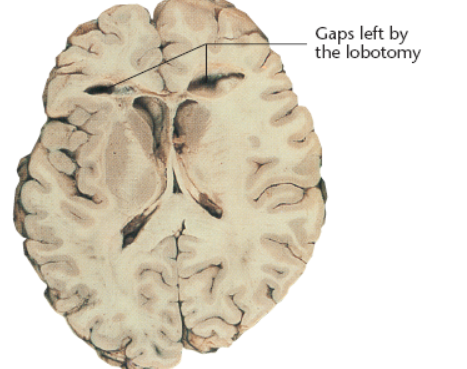
prefrontal lobotomy
surgical disconnection of the prefrontal cortex from the rest of the brain
thought it would help patients who experience psychiatric disorders
consequences of prefrontal lobotomy
apathy
loss of planning ability
loss of taking initiative
memory disorder
distracted
loss of emotional expressions
reduced social norms (manners, etc)
impulsive → failed to adequately calculate probable outcomes due to behavior
prefrontal cortex regions and primary functions
posterior: movement
middle zone: emotions, cognitive control (ex: obj recognition), working memory
anterior: decision-making
prefrontal cortex damage
delayed response task → respond after a delay
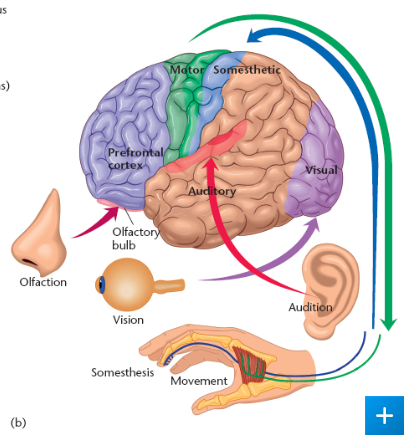
binding problem
question of how various brain areas produce a perception of a single object
where do neurons respond to more than one sensory system
superior colliculus
cerebral cortex function
elaborating sensory information