BIO 120 - 20
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All Tests Combined
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Which four elements are the most common elements found in living matter?
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
When the atoms involved in a covalent bond have the same electronegativity, what type of bond results?
A nonpolar covalent bond
Which of the following statements is true about functional groups?
they include the common carbon partners hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur
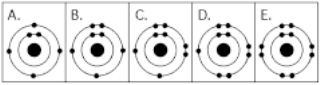
Refer to figure. Which drawing depicts the electron configuration of an atom of carbon?
A
Why is carbon so important in biology?
It can form a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups.
Which of the following statements is true about buffers?
They are composed of weak acids and bases and maintain a relatively constant pH in all living cells and biological fluids.
Which of the chemical groups is not reactive but serves as a recognition tag on the DNA molecule and alters the expression of genes in cells.
methyl
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are:
Nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
Which of the following best describes the logic of scientific inquiry?
If my hypothesis is correct, I can expect certain test results
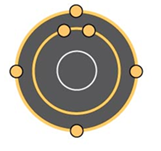
How many valence electrons are represented in the illustrated atom?
4 valence electrons because valence electrons are located in the outer shell of the atom
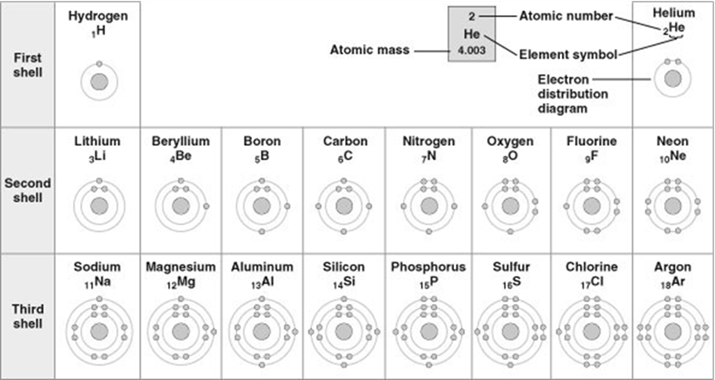
Refer to the table. Which element does not react with other elements?
argon
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because:
The electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
H2CO3 ⇔ HCO3- + H+. Based on this information, which of the following statements is true?
If pH is too low the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction producing more carbonic acid.
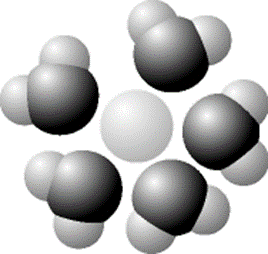
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule (light colored ball in the middle) of the figure above is most likely:
positively charged and hydrophilic
Which of the following statements is true?
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element.
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element.
The hydrogen of a water molecule and the nitrogen atom of ammonia
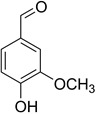
Identify the functional groups in the figure:
hydroxyl and carbonyl
Cohesion, surface tension, and adhesion are the properties of water molecules that:
Are a result of hydrogen bonding
Which of the following properties or processes are exclusive to life?
Composed of cells, metabolism, evolutionary adaptation
Which of the following statements is true about a covalent bond?
valence electrons of two atoms are shared to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms.
A Fat:
Is unsaturated when double bonds exist between the carbons of the fatty acid tails
There is a limit on cell size because:
there is a limited amount of any given substance that can cross a membrane per second
What would be the expected direct consequence of changing one amino acid in a single polypeptide protein consisting of 325 amino acids?
The primary structure of the protein would be changed and the biological activity or function of the protein might be altered.
Which of the following is not one of the three classes of macromolecules composed of similar or identical monomers?
lipids
Channel proteins are used in both passive and active transport.
False
Protein composition of the cell membrane determines cell function.
True
An example of a hydrogen bond is the bond between
The hydrogen atom of a water molecule and the nitrogen atom of ammonia
Simple diffusion occurs as a result of _____, while the energy source for active transport is _____.
the concentration gradient; ATP
If a solute is moving across the membrane against its concentration gradient:
this movement is an example of active transport and takes place through carrier proteins
Which of the following is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
production of secretory proteins
Glycogen is composed of a long chain of glucose molecules that are joined by glycosidic linkages. How is glycogen classified?
as a polysaccharide
The bonding of a fatty acid to glycerol requires which of the following?
removal of a water molecule and formation of an ester linkage
Vinblastine, a drug that inhibits microtubule formation, is used to treat some forms of cancer. Cancer cells given vinblastine would be unable to ________.
separate chromosomes during cell division
Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis breaks down polymers.
Which of the following organelles belong to the endomembrane system?
lysosome, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, plasma membrane
The 20 different amino acids found in polypeptides exhibit specific chemical and physical properties because of different
R groups
_____________ are proteins embedded in the plasma membrane and are involved in transmitting information from the outside environment to the interior of the cell.
Integrins
Animal cells can remain fluid in response to extreme cold by:
increasing the percentage of cholesterol molecules in the membrane
A defect in which of the following intercellular junctions would allow partially digested material to leak passively between the cells of the small intestine into the abdominal cavity?
tight junctions
A phospholipid bilayer with equal amounts of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids displays a specific permeability to glucose. What effect will be increasing the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in the bilayer have on the membrane's permeability to glucose?
Permeability to glucose will increase.
If all hydrogen bonds between amino acids of a protein were disrupted, which levels of protein structure would be affected?
All levels except primary structure
Which of the following is a major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not
A nucleotide is composed of:
a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
When 2 different solutes cross a membrane, the rate of diffusion may be different for each solute because rate is dependent on the concentration gradient of each solute.
True
Which of the following is correct for the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins transported to the Golgi apparatus may be sorted and altered as they move from one side of the Golgi Apparatus to the other.
has a polarity (cis and trans) to its structure
Molecules, such as phosphate, are covalently bonded to proteins as "address labels".
all options are correct
Which of the following structures regulates what enters and leaves the cell?
plasma membrane
Examples of protein tertiary structure bonds include:
side groups (R) forming hydrogen bonds
An example of receptor-mediated endocytosis would be:
the entrance of large quantities of a specific protein into the cell
Which of the following is true for lipids?
representatives include fats, phospholipids, and steroids
Which of the following categories includes all others in the list?
carbohydrate
You are working on a team that is designing a new drug. For this drug to work, it must enter the cytoplasm of specific target cells. Which of the following would be the most important factor that determines whether the molecule selectively enters the target cells and no other cells?
similarity of the drug molecule to other molecules transported by carrier proteins in the target cells
Green onions that are immersed in salt water for several hours become limp and soft. When removed from salt water and placed in tap water the green onions become firm. From this we can deduce that the salt water is a __________________ solution and tap water is a _________________________ solution.
hypertonic; hypotonic
When a potassium ion (K+) moves from the soil into the vacuole of a plant cell on the surface of a root, it must pass through several cellular structures. Which of the following correctly describes the most likely order in which these structures will be encountered by the ion?
cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → vacuole
Leaves are green because
pigments in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts absorb blue and red spectrum light and reflect green.
_______________________ light is used in photosynthesis,
absorbed
Which of the following statements is true about enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
The reaction is faster than the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme
Increasing the amount of enzyme until present in excess would have which of the following effects on the rate of product production and the amount of product produced?
increases the rate of product production and has no effect on the total amount of product
The product of the metabolic pathway bonds to the first enzyme of the pathway at a location other than the active site and no further product is made. This is an example of:
feedback inhibition
The benefit of coupling reactions is
that the net free energy of all reactions is a negative Δ G
Energy forms produced by the citric acid cycle include:
FADH2, NADH, and ATP
Which of the following terms most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
catabolism (catabolic pathways)
Which step in aerobic respiration creates the most ATP?
oxidative phosphorylation
Electron replacement in the photochemical reactions of photosynthesis is the result of which of the following processes?
splitting water molecules
The Calvin Cycle is composed of 3 steps. In the reduction phase:
G3P is shunted off to create glucose and other organic compounds
In aerobic respiration:
pyruvate is converted to Acetyl CoA before entering the citric acid cycle
Which of the following metabolic processes normally occurs regardless of whether or not oxygen (O2) is present?
glycolysis
Which of the following events are associated with chemiosmosis in chloroplasts?
The pH of the thylakoid space increases followed by the production of ATP.
The effect of enzymes on a reaction is:
a higher Δ G
a lower Δ G
Increases the rate of catabolic reactions and has no effect on the rate of anabolic reactions.
Changes a non-spontaneous reaction to a spontaneous reaction
None of the above
None of the Above
Which of the following statements best describes the primary role played by oxygen in cellular respiration?
It serves as the final acceptor for electrons from the electron transport chain.
In allosteric regulation of enzyme activity, a regulatory molecule bonds to the active site.
False
How many total ATPs are created during aerobic respiration?
32
Substrates for respiration can include:
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
What happens to the free energy released as electrons are passed from photosystem II to photosystem I through a series of electron carriers?
It is used to establish and maintain a proton gradient.
Energy released by the electron transport chain during aerobic respiration is used to pump H+ ions into which location in eukaryotic cells?
mitochondrial intermembrane space
Chemiosmosis used to generate ATP during photochemical reactions occurs because:
ATP produced by the electron transport chain following PSII actively transport H+ into the thylakoid space
Which of the following is true about the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH are consumed
During glycolysis:
glucose is converted into pyruvate
Photosynthesis is:
an anabolic process composed of a series of endergonic reactions with a positive delta G.
In aerobic respiration, ATP is generated during:
glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
Cellular respiration is
a catabolic process composed of a series of exergonic reactions with a negative delta G
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; cellular respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules.
Which of the following statements are true regarding NADPH, NADH, and FADH2?
They are electron carriers that are reduced molecules
G1 is associated with which of the following cellular events?
cell growth and organelle replication
Which of the following characteristics do homologous chromosomes exhibit?
They carry information for the same genes.
Colchicine is a drug that blocks the assembly of microtubules. If dividing cells are treated with colchicine, at what stage of mitosis would you predict the arrest of cell division to occur?
prophase
A chromatid:
Contains one copy of the DNA molecule
DNA is a conservative model because after DNA replication is complete the 2 strands of parental DNA reanneal, and the new DNA strand is composed of two DNA strands created during the replication process.
False
Within a double-stranded DNA molecule, adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine, and cytosine forms hydrogen bonds with guanine. What is the significance of this structural arrangement?
It permits complementary base pairing allowing for DNA replication.
Proof reading of DNA that corrects errors in base pair matching is performed by:
DNA polymerase
Why does a new DNA strand elongate only in the 5' to 3' direction during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only to the free 3' end.
Recombination (crossing over) during prophase I of meiosis occurs when:
genetic material of the same gene on non-sister chromatids of a homologous pair is swapped
Independent assortment:
allows for different combinations of non-homologous chromosomes
Tasmanian mongoose has 12 pairs of chromosomes per germ cell, how many chromosomes would there be in a cell at the end of Anaphase I in meiosis I? How many chromatids?
24: 2 chromatids per chromosome
In the cells of many eukaryotic species, the nuclear envelope has to disappear to permit which of the following events in the cell cycle?
attachment of microtubules to kinetochores
Topoisomerase:
relieves the strain on the double-stranded (wound) DNA molecule when replication bubbles form.
The 2 alternating periods of the cell cycle include:
Interphase and M phase
During which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids become chromosomes?
Anaphase
The cell cycle using meiosis for nuclear division:
produces haploid gametes that are genetically similar to the parent cell carrying the same genes, but can have different allele form combinations
DNA polymerase III:
adds nucleotides to the new complementary strand of DNA
Mitosis produces daughter cells that
contains 2 copies of each chromosome and are genetically identical to the parent cell