Skull Videos
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
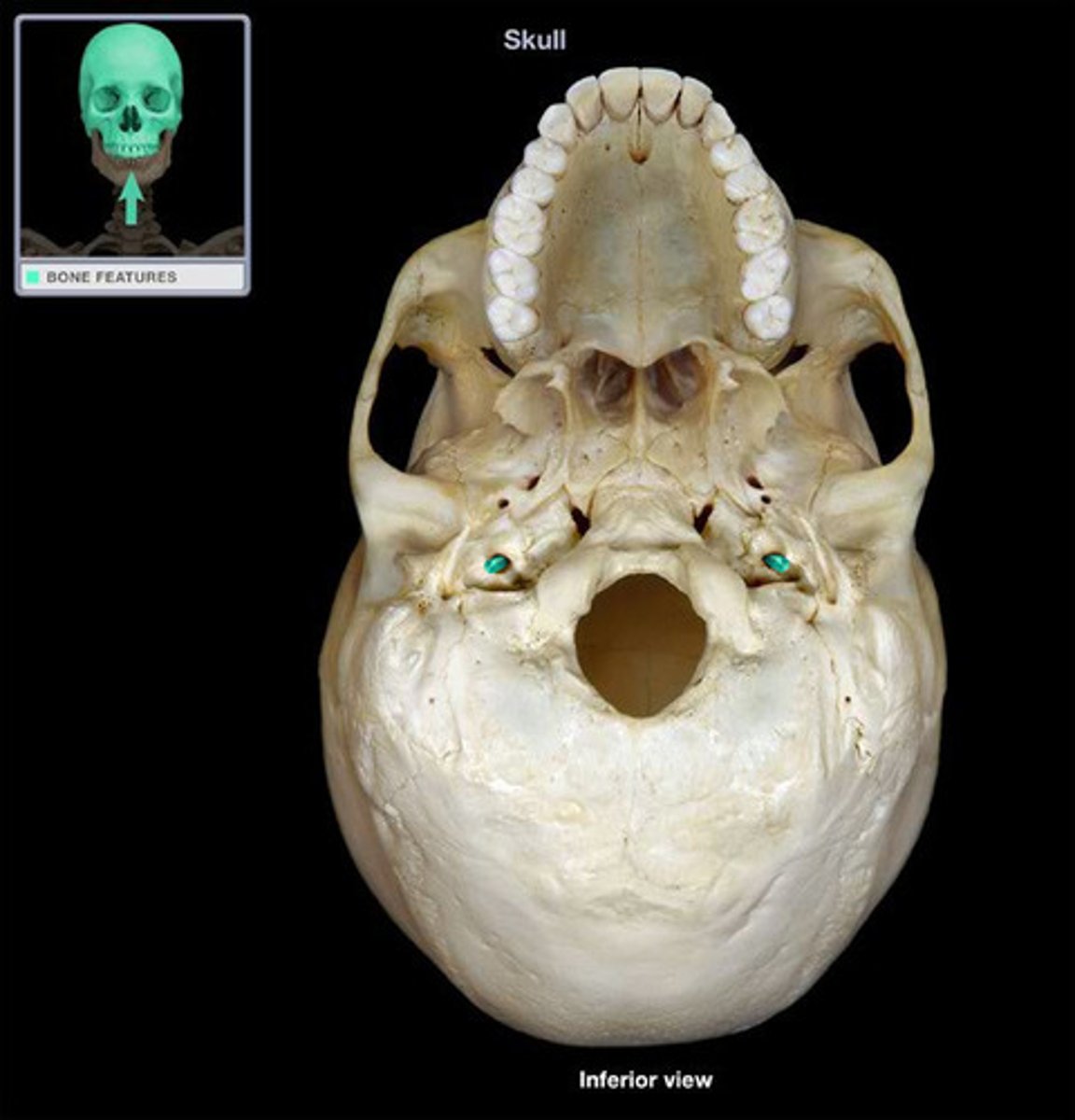
Which foramina lie along sagittal suture and go from scalp to the superior sagittal sinus
emmissary veins
Suture between temporal and parietal bone
coronal suture
suture between parietal bones
sagittal sutures
Impression along lateral wall of skull indicates what
middle meningeal artery
what is a V3 terminal branch of inferior alveolar nerve?
mental nerve
Travels along deep aspect of mandible and attaches mylohyoid
mylohoyid line
Located on deep posterior aspect of mandible. What does superior genio tubercle attach
what does inferior geniotubercle attach
superior - genioglossus
inferior - geniohyoid (C1 via 12)
Most inferior portion of mandible located on the caudal side of the mandible. Depressions
Digastric fossa attaches digastric muscles
Where temporal bone articulates with parietal, frontal, and sphenoid bones is called the what
pterion - weakest portion of skull
trauma to pterion could cause what
bleeding of middle meningeal artery - epidrual hemmoraghe
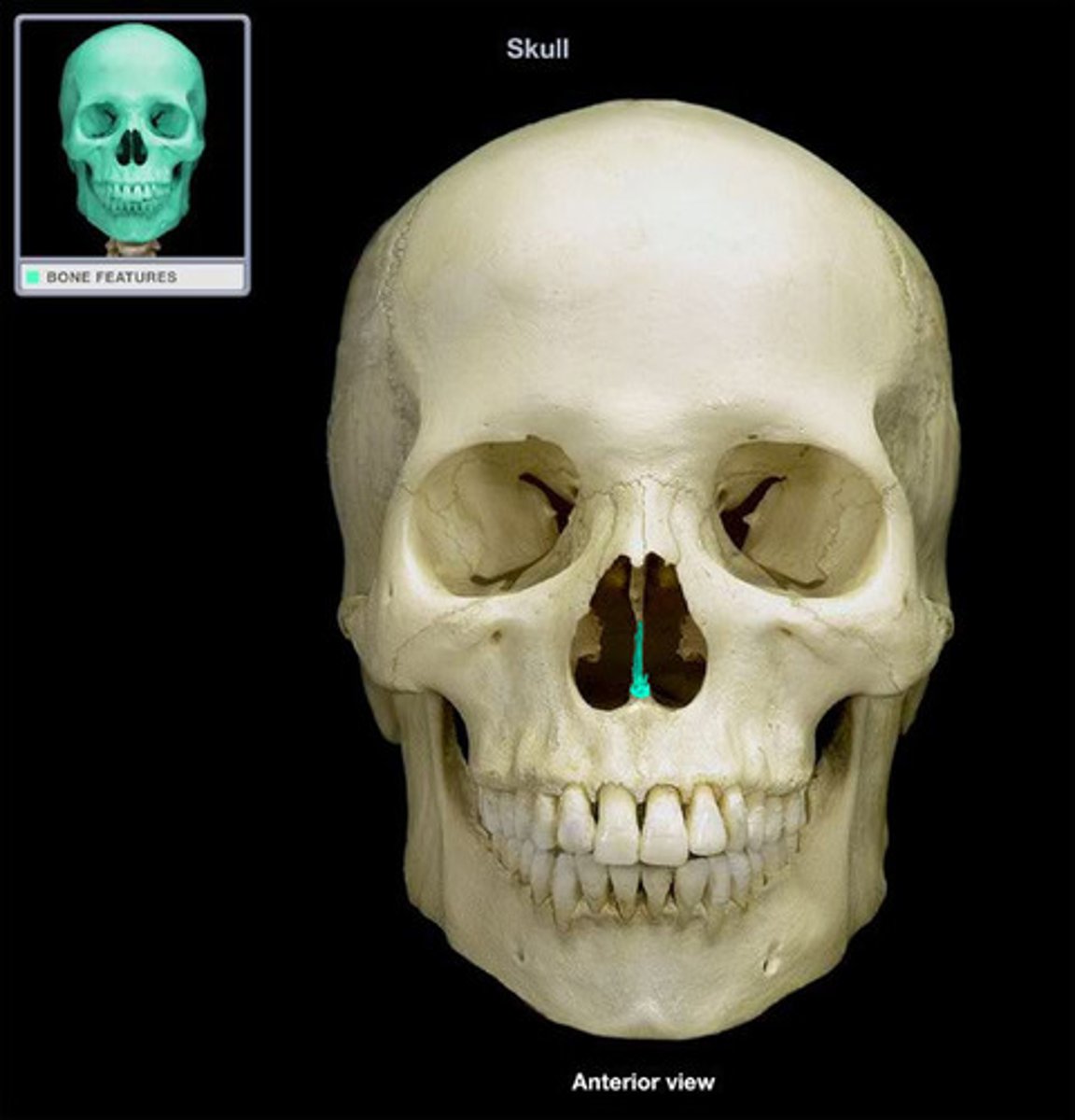
two componets of bony nasal septum
what can you see anteriorly
anteriorly - perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
Bony process on lateral sides of walls of septum - most inferior in nose
inferior nasal conchae
Bony process on lateral side of walls of septum - above the most inferior
middle nasal conahe
The superior and middle nasal conchae are part of what bone
ethmoid bone
The inferior nasal conchae are part of what bone
own independent bone
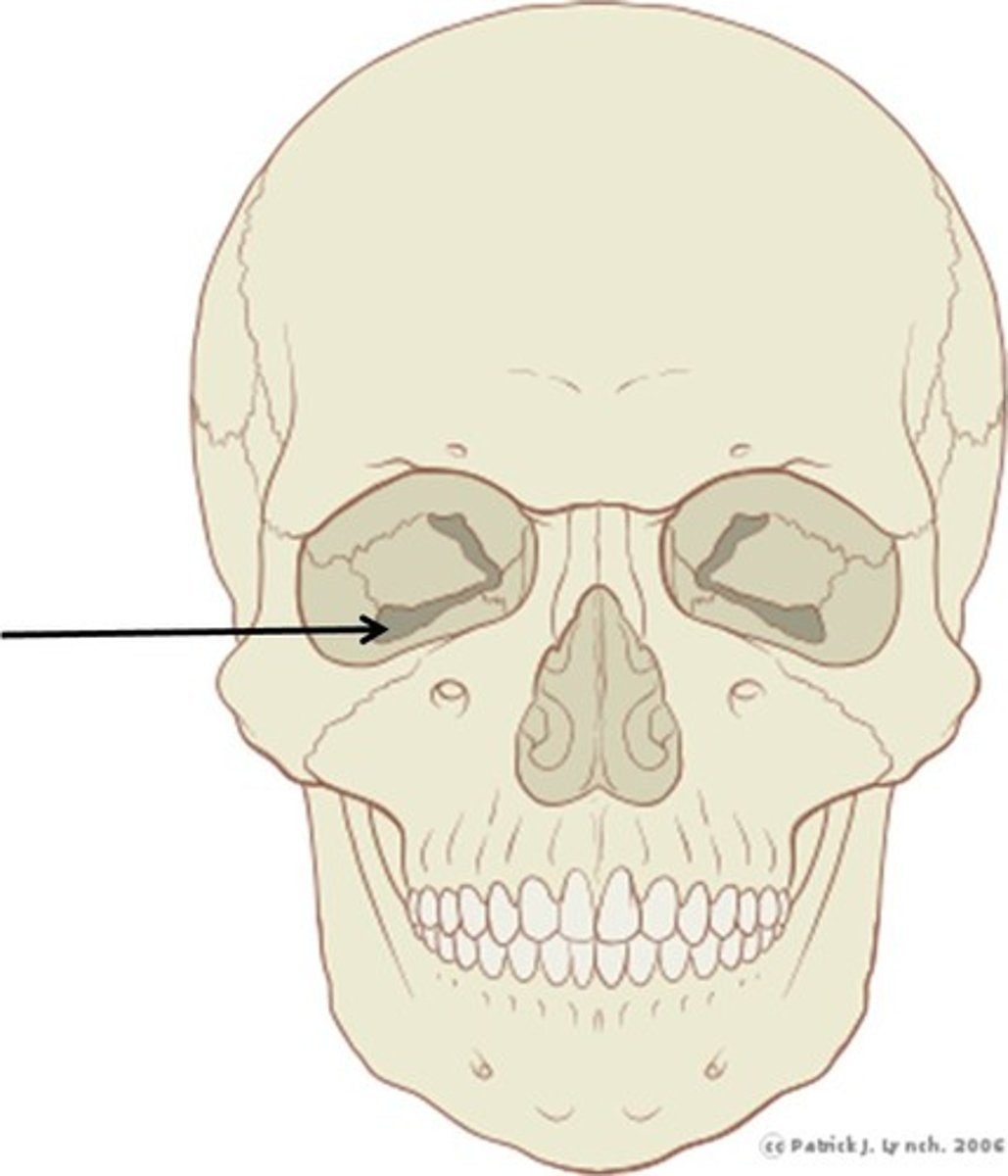
lateral to nasal cavity is what foramen below orbit
infraoribtal foramen - infraorbital nerves and zygomaticotemproal (V2)
Nasal bone articulate with frontal bone
nasion
What region is above nasion
region of frontal bone called glabella
does supratrochlear and supraoribtal come out the same foramen?
no
superior orbital fissure
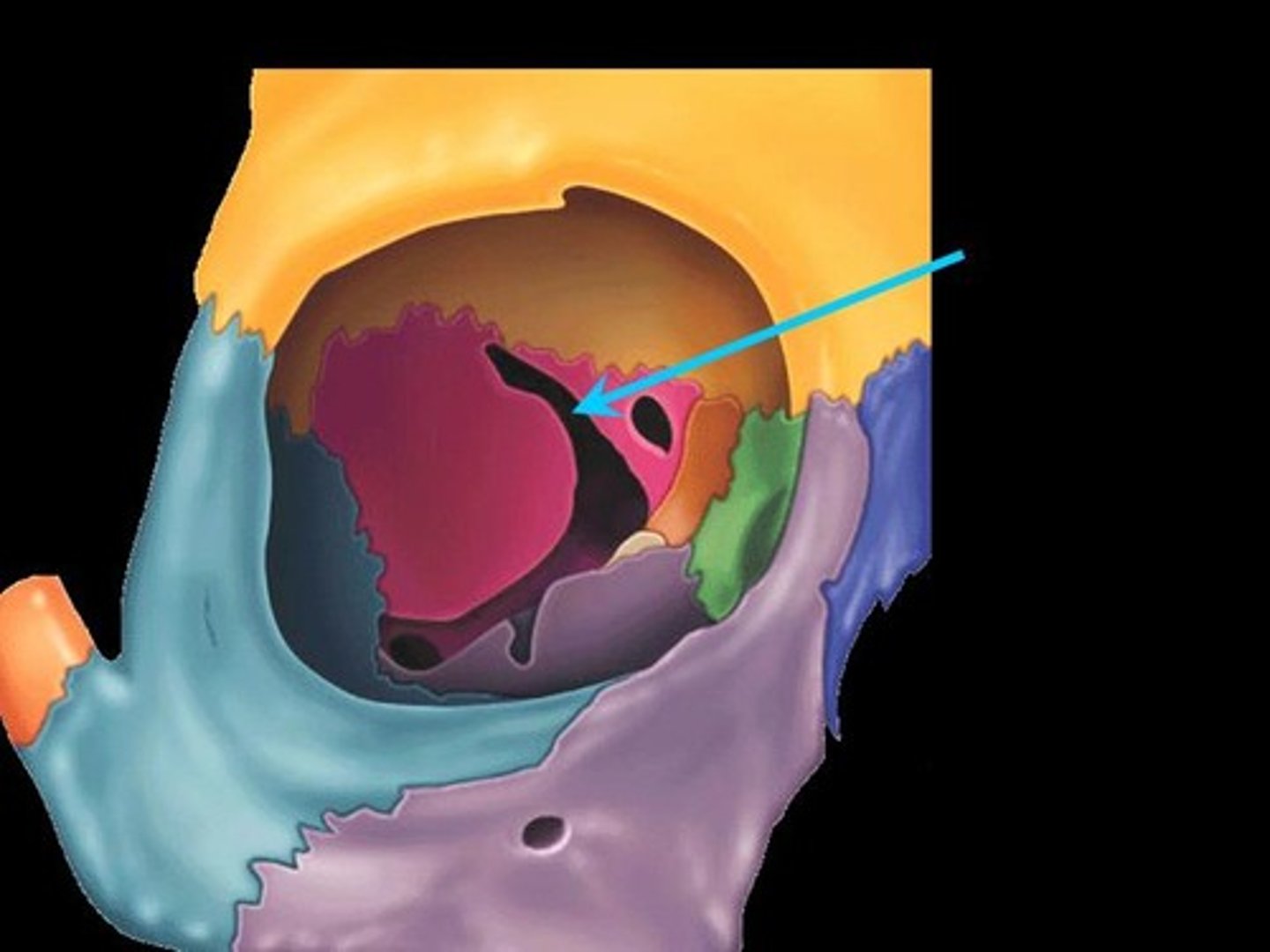
inferior orbital fissure
What canal lies meidally to superior oribtal fissure
optic canal
what divides the anterior and middle cranial fossa
lesser wing of sphenoid
frontal lobes of brain reisde
anterior cranial fossa
middle and posterior cranial fossa are divided by what
petrous ridge of temporal
squamos portion of temporal bone
lateral aspect of skull
temporal lobe resides in what cranial fossa
middle
what resides in posterior cranial fossa
cerebellum
The posterior cranial fossa is separated from the middle and anterior cranial fossa by what structure
tentorium cerebelli
cloeses off posterior cranial fossa except region which midbrain passes through
tentorium cerbelli
crista galli
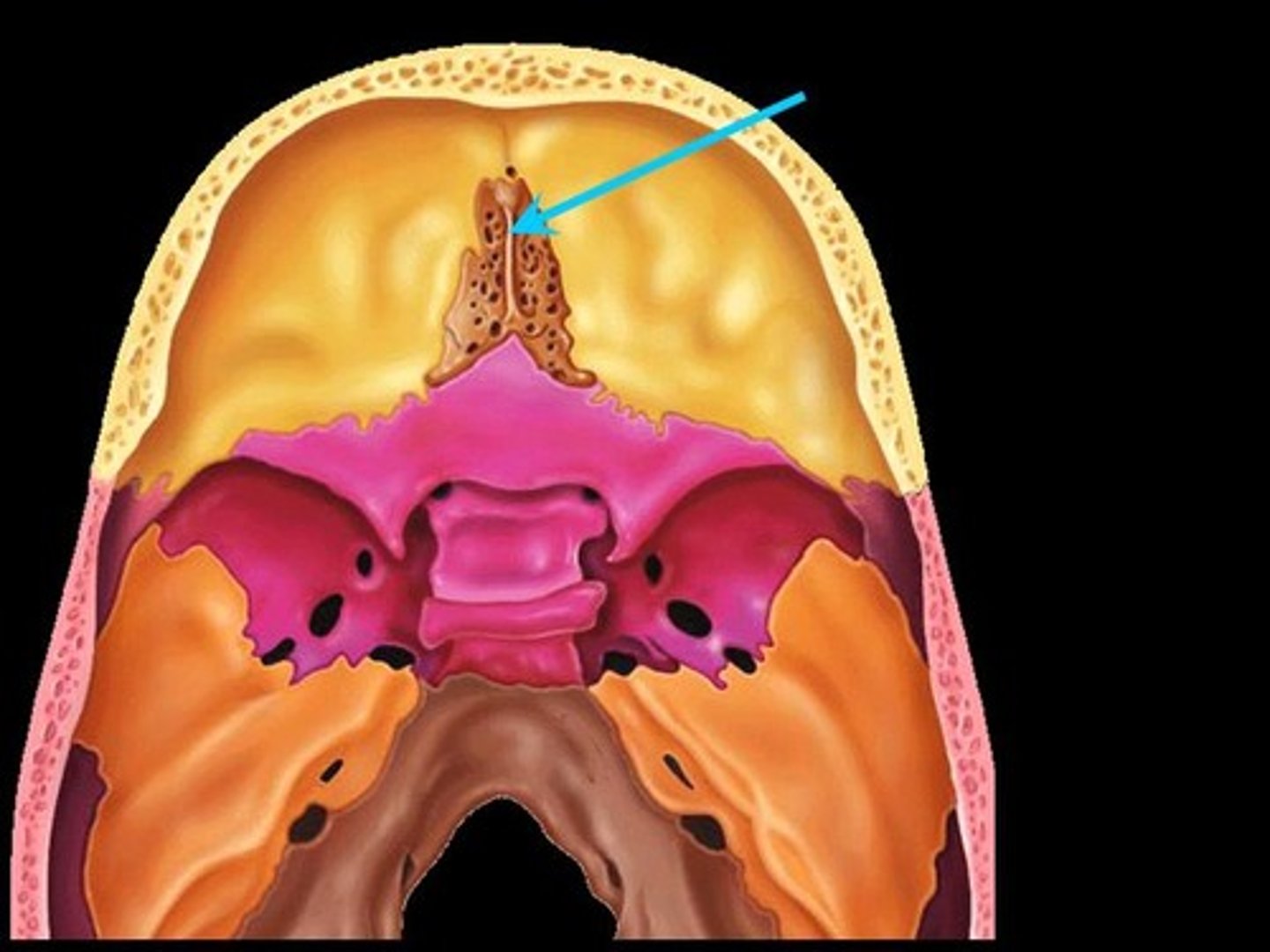
what dural fold attaches to crista galli
falx cerebri
Where do fillia olfactoria transmit from nasal mucous to reach olfactory bulb
cribiform plate of ethmoid bone
clinoid processes come off what bone
sphenoid bone
anterior clinoid process are anterior compartment of what
4 part section of diaphragma sella
diaphrama sella drapes over what
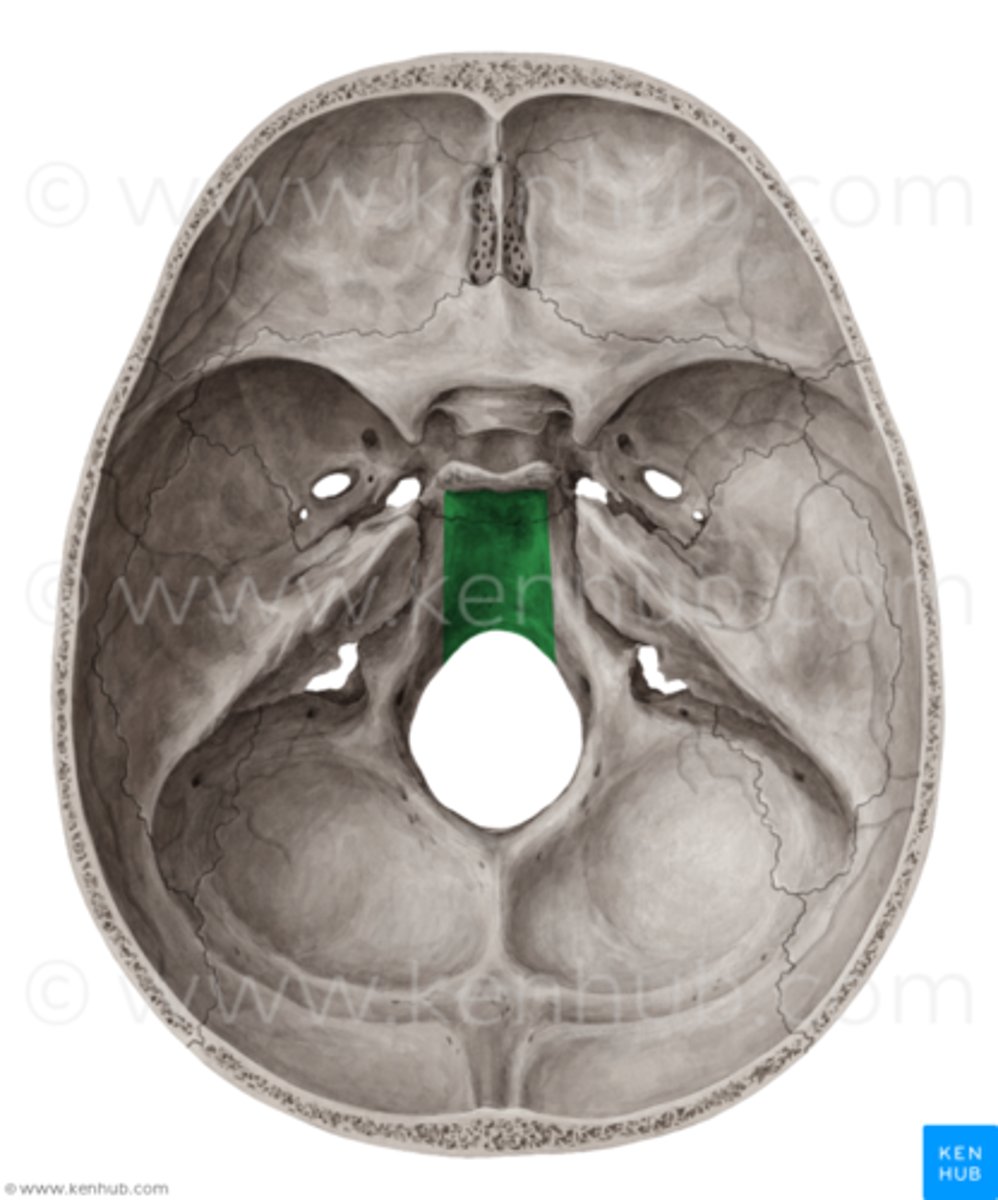
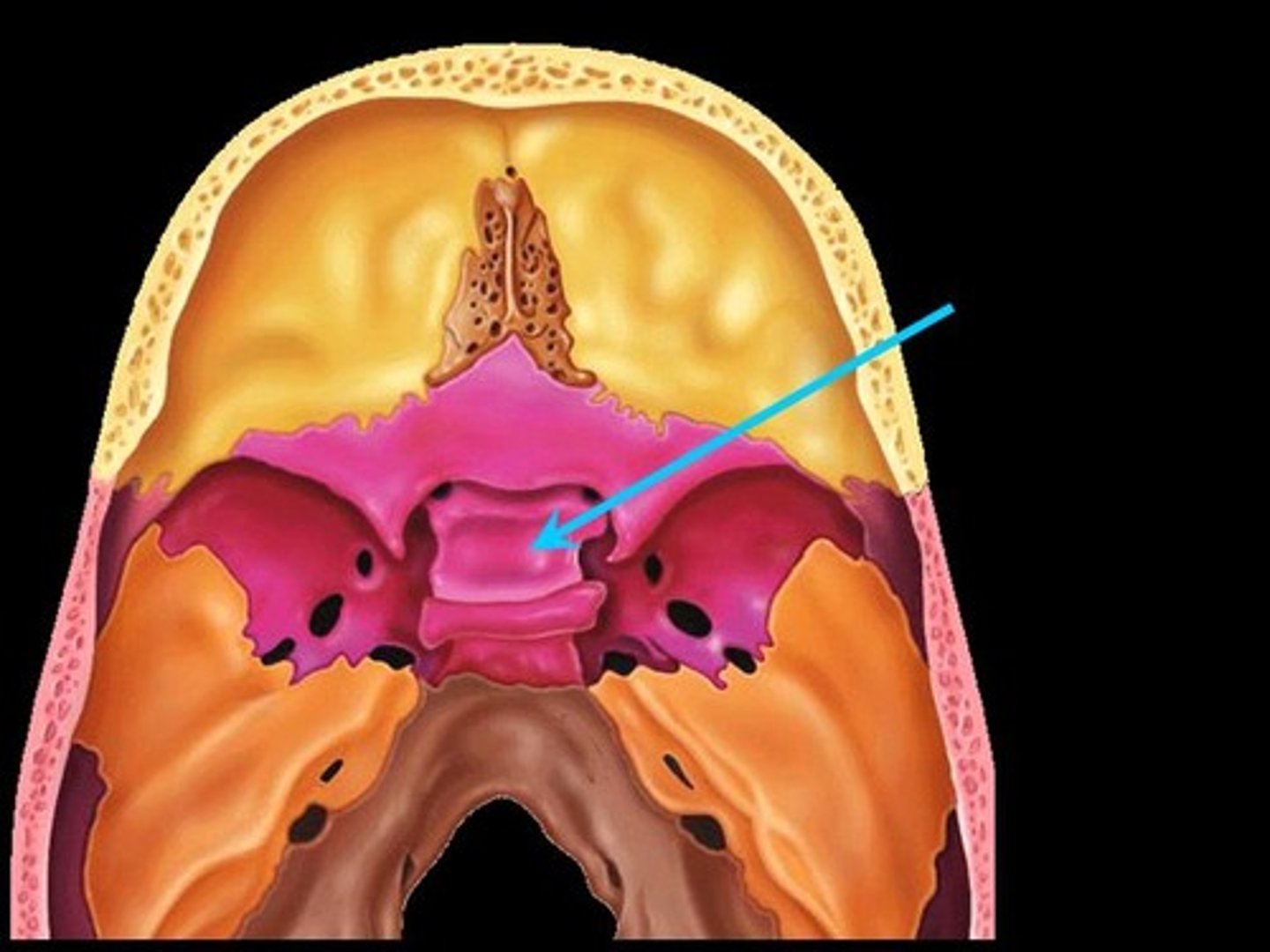
sella tursica
Sight where pituitary gland lives in hypophyseal fossa
sella tursica
Dorsum sella
posterior wall of sella tursica
The dorsum sella is continous with what bony structure
clivus
clivus
the superior orbital fissure lies in what cranial fossa
middle
what foramen lies just lateral and inferior to superior oribttal fissure
foramen rotundrum
Superior orbital fissure
CN 3, 4, V1, 6
foramen rotundrum transmits what
V2 to pterygopalatine fossa
Foramen ovale transmits
V3 out of cranial cavity to ITF
Does ICA go through the foramen lacerum?
Where does it travel?
ICA travels horizontal courses through petrous ridge of tmeporal bone and vertically through cavernous sinus along lateral aspect of sella tursica
Once ICA emerges from diaphragma sella what is it renamed
true cerebral
rise to anterior cerebral and middle cerebral arteries
what cavernous sinus runs along lesser wing of sphenoid and feeds into cavernous sinus
sphenoparietal sinus
two ways venous blood exits cavernous sinus
along petrous ridge of temporal bone - superior petrosal sinus - meets transverse sinus where it becomes sigmoid
inferior runs below petrous ridge of temporal bone to meet sigmoid sinus as it becomes internal jugular vein
Where does greater palatine nerve carrying parasymp to pterygopalatine ganglian exit
foramen rotundrum
lesser petrosal nerves travel along where
floor of middle cranial fossa to exit foramen ovale
carry parasymp to otic ganglion to supply parotid gland
anterior clinoid process
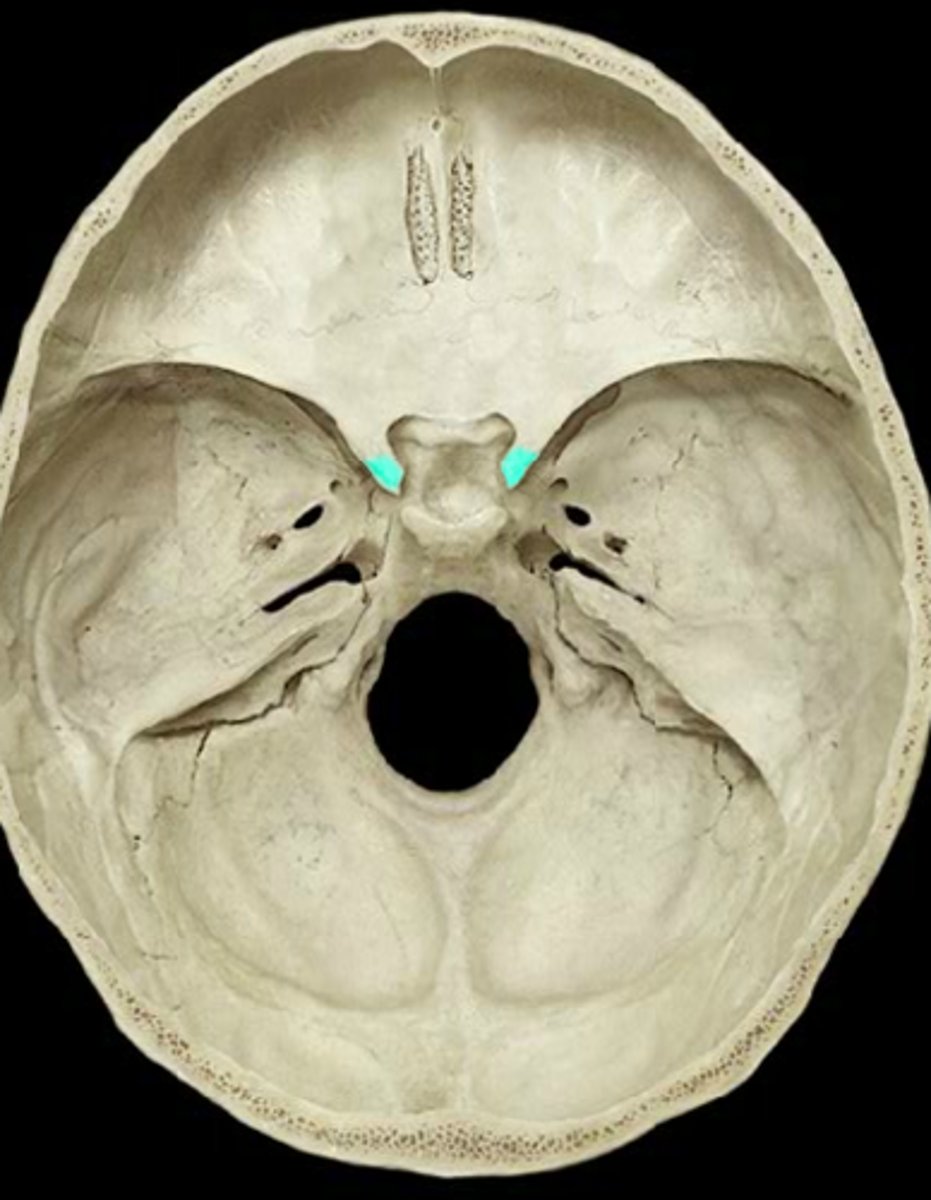
hypophyseal fossa
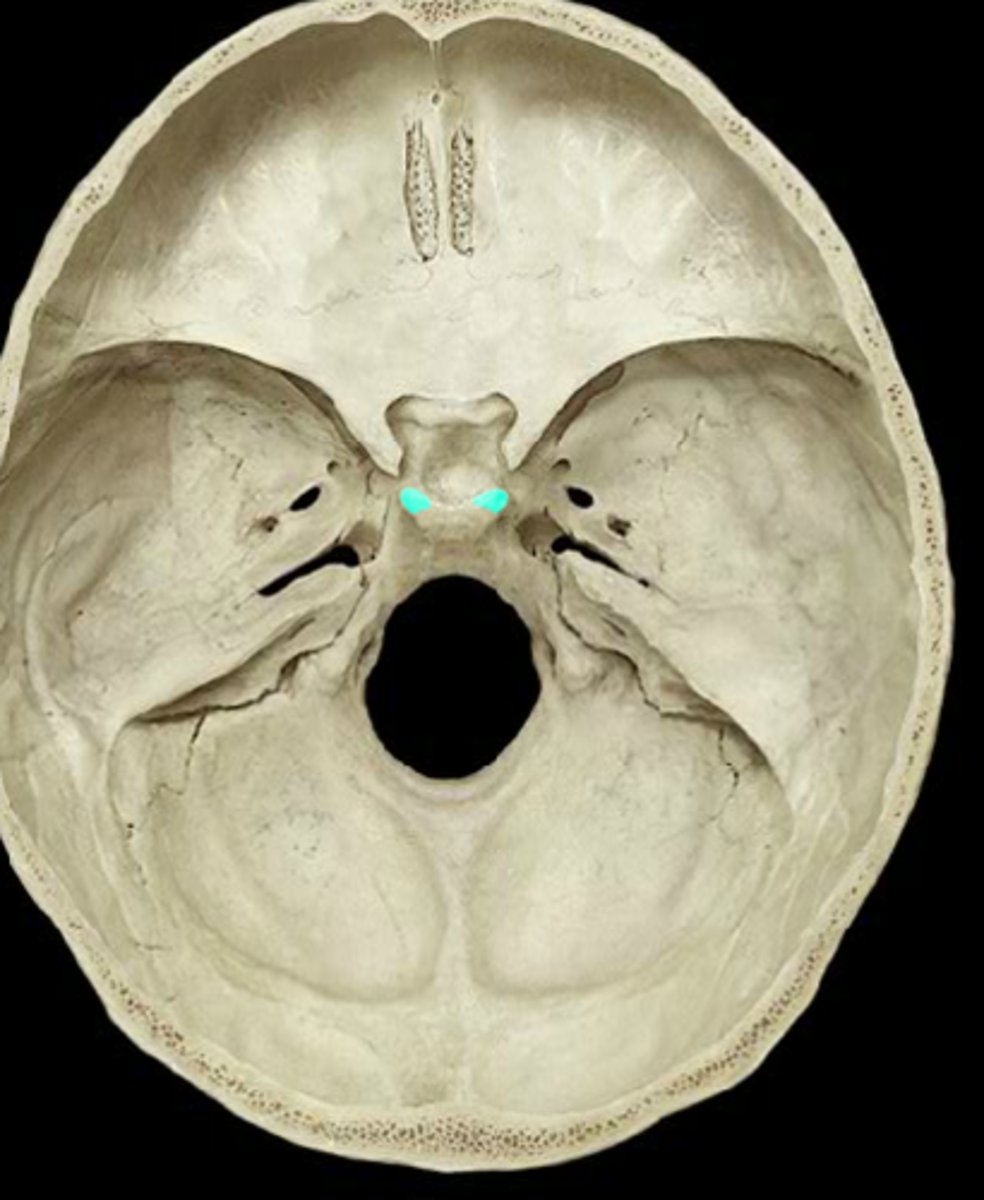
posterior clinoid process
posterior clinoid process
what comese out supraorbital notch
supratroclear nerve (medial)
pterygoid hamulus
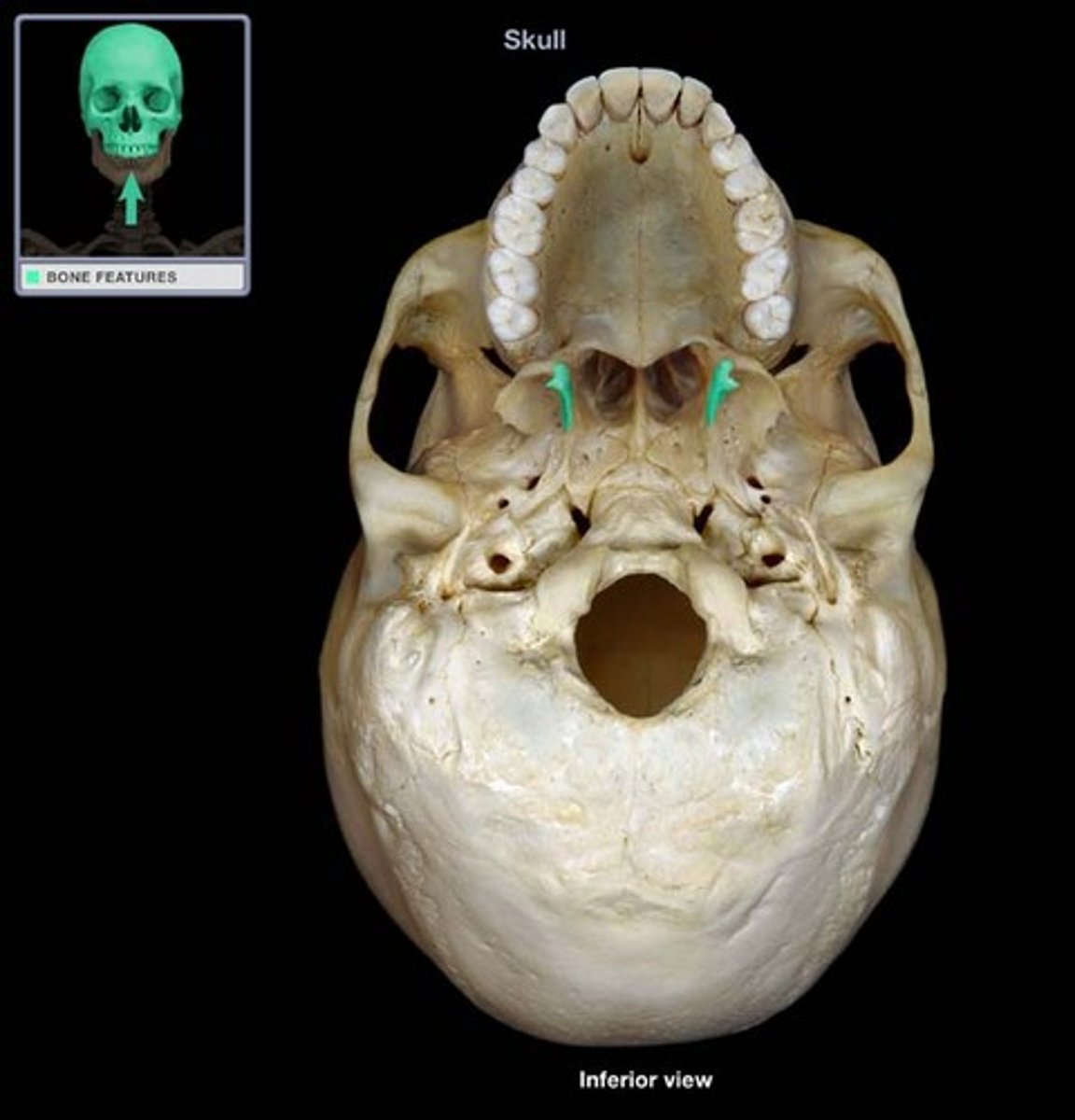
vomer
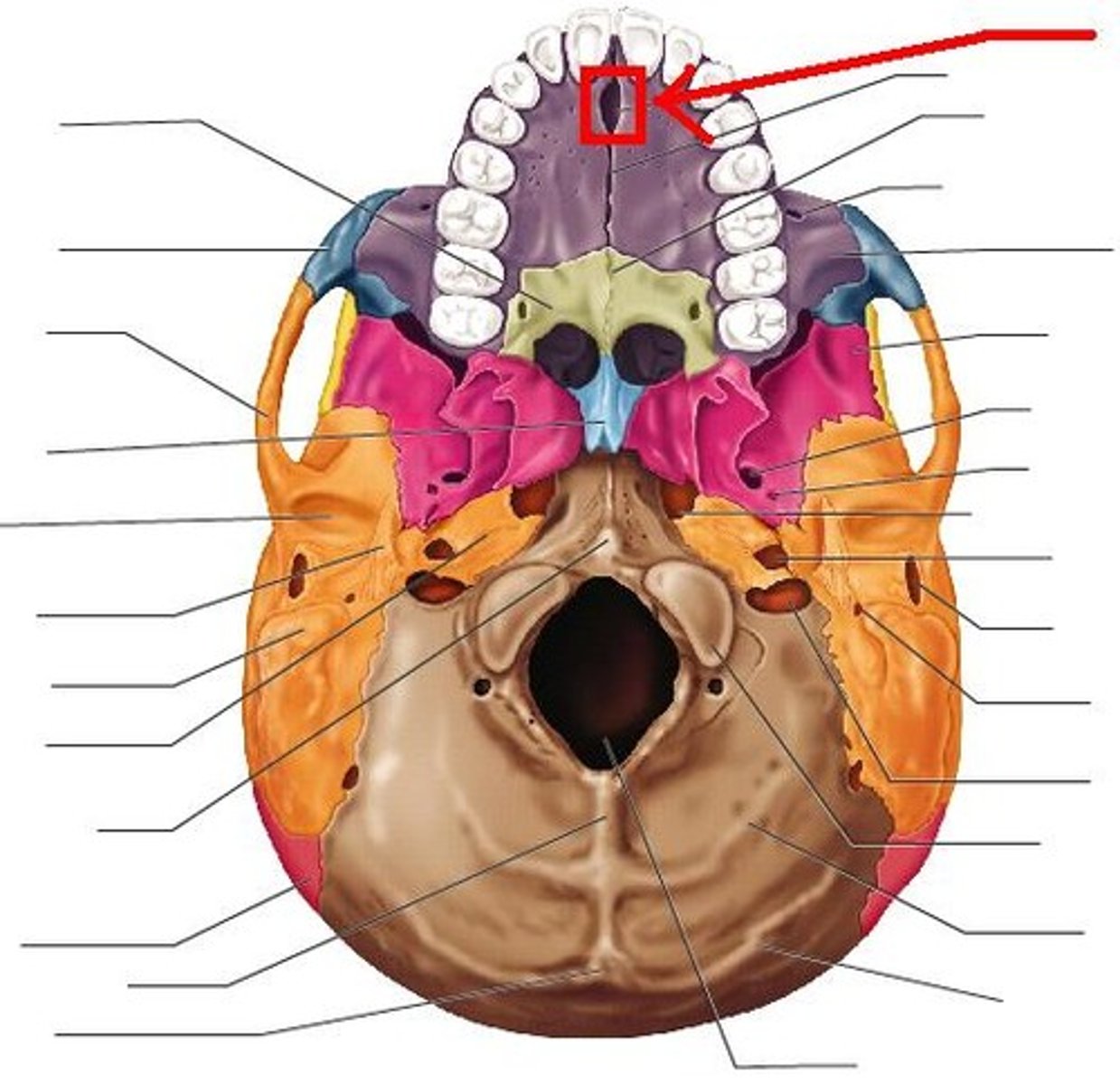
incisive foramen
nasopalatine nerve (V2)
Greater palatine foramen
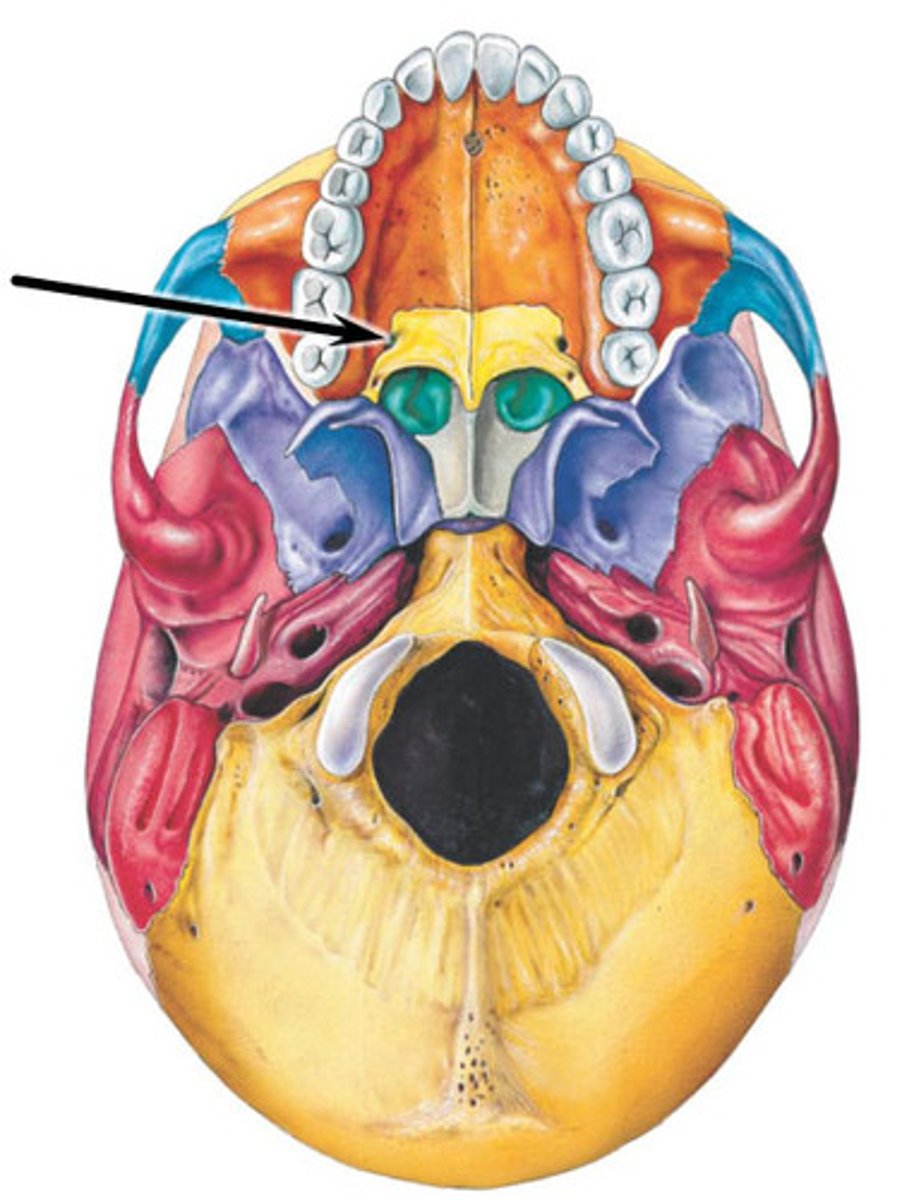
lesser palatine foramen
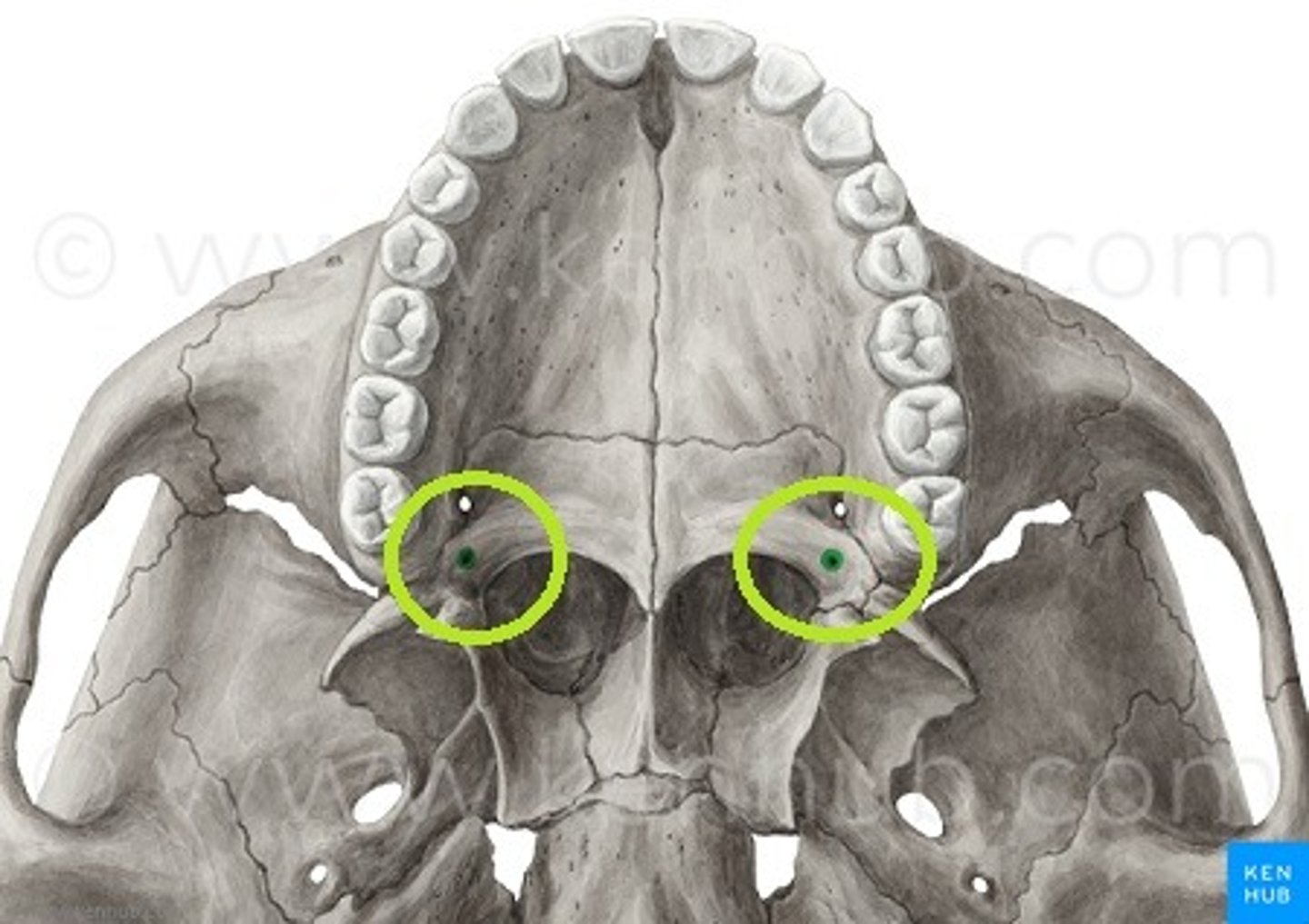
carotid canal