estates and interests in land
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what are the fundamentals of land law
1.it is about people and their relationships to land
in the UK all land belongs to the crown so the individuals cant “own” land outright they can only hold estates in land
the legal framework is split between the common law which is legal rights and equity which is fairness based rights
what are devices
estates which are rights to use land for time periods and interests which are rights over land
what are systems
law and equity
land registration
estates in land
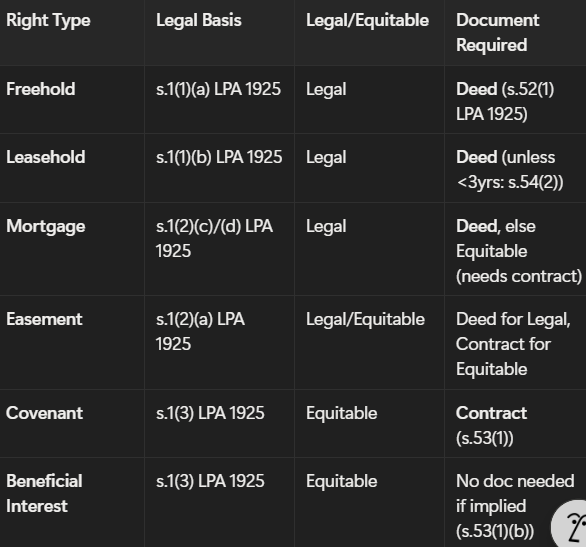
it refers to the legal interest or ownership rights a person has in real property. it includes freehold estates and leasehold estates.
what is a freehold estate name, law, 2 features and example
the name is fee simple absolute in possession
law is s.1(1)(a) LPA 1925
2 features are indefinite duration (perpetual) and immediate right to possess
example: alan owns dun well farm = fee simple absolute in possession
what is a freehold estate name, law, 2 features and example
the name is term of years absolute
law is s.1(1)(b) LPA 1925
2 features are future or present right to possess and fixed duration (can be short)
example: bali rents outbuilding = term of years absolute
what are the two interests in land and their law
legal interests s.1(2) LPA 1925 and equitable interests s.1(3) LPA 1925
(Require Deed under s.52 LPA 1925)
Mortgage – s.1(2)(c)
Easement – s.1(2)(a)
Rentcharge
Right of entry
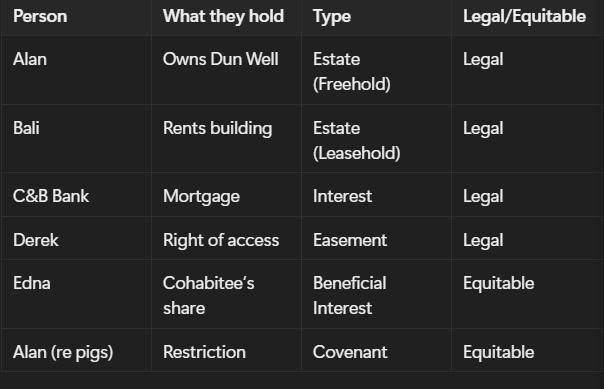
examples
C&B Bank takes a mortgage on the farm – legal interest
Derek has right of access for apples – legal easement
explain legal interests
(Generally require Contract under s.53(1) LPA 1925)
Restrictive Covenant
Beneficial Interest (cohabitee, trust etc.)
Life Estate / Fee Tail
examples:
Alan agrees not to breed pigs = Restrictive Covenant (equitable)
Edna, Alan’s partner, not on title = Beneficial Interest (equitable)
explain equitable interests
give me the authority for each example
s,1(1)(a)
s.1(1)(b)
s.1(2)/(d)
s.1(2)(a)
s.1(3)
s.1(3)