Photosynthesis
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 12 Biology U3 AOS 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Photosynthesis
the process of using energy from the sun to convert water + CO2 into glucose and oxygen
Organisms that can photosynthesise are autotrophs (plants/algae)
Chlorophyll (green pigment) is needed and located in chloroplasts
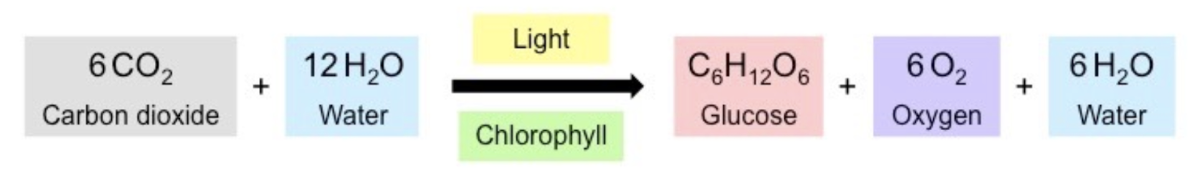
Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 12H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
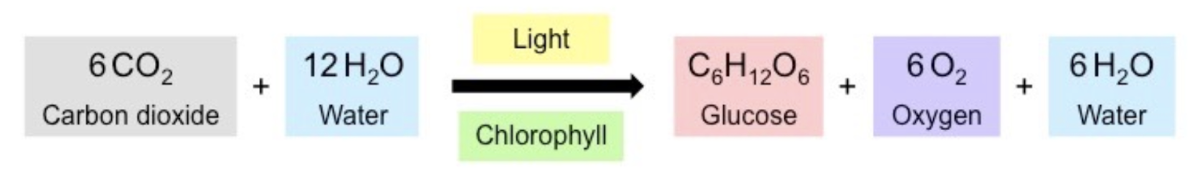
Worded Equation for Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water → Glucose + oxygen + water
Chloroplasts
a plastid in green plant cells, containing chlorophyll and the location in which photosynthesis takes place
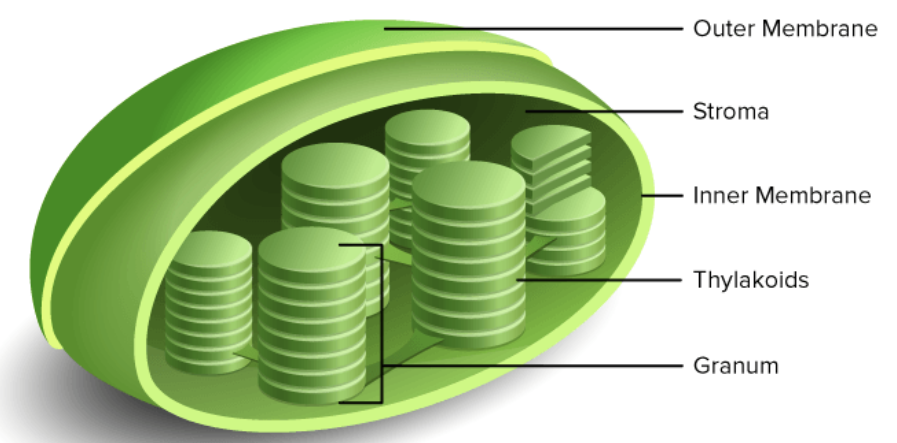

Stroma
all the space in chloroplasts
Stomata
tiny pores on the surface of leaves
OPENS to allow CO2 in the atmosphere to diffuse into the lead
CLOSES to prevent water loss in dry conditions
Thylakoids
individual discs where chlorophyll is specifically located
Granum
one stack of thylakoids
Grana
multiple stacks of thylakoids
Light Dependent Reaction (LDR)
the initial stage of photosynthesis, occurring at the thylakoid membrane
Purpose → to generate high energy coenzymes NADPH and ATP to power the second stage
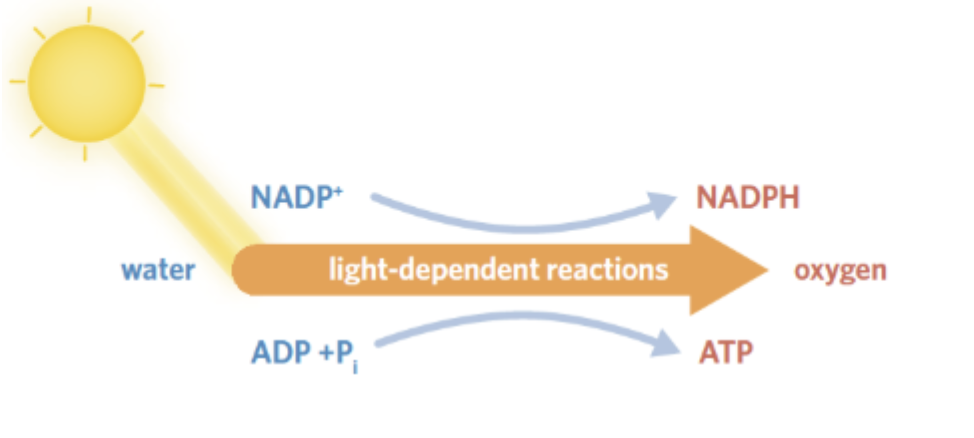
INPUTS of LDR
H2O (water)
NADP+
ADP + P
OUTPUTS of LDR
O2 (oxygen)
NADPH
ATP
Light Independent Reaction (LIR)
the second stage of photosynthesis, occurring at the stroma
Purpose → to use chemical energy (NADPH + ATP) produced from LDR to convert CO2 into glucose
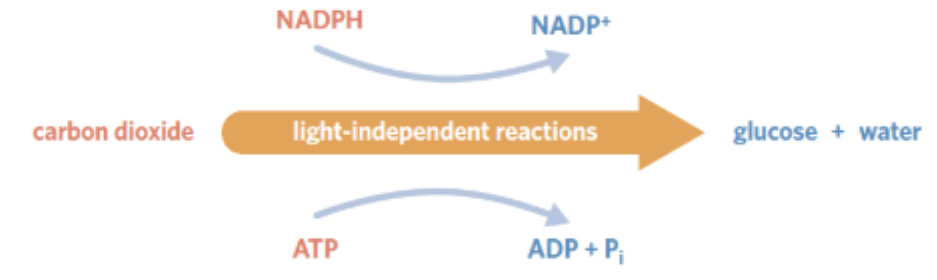
INPUTS of LIR
CO2
NADPH
ATP
OUTPUTS of LIR
Glucose
H2O
NADP+
ADP + Pi
Carbon Fixation
when inorganic CO2 is converted into organic molecules (Carbohydrates) which are of more use to cells
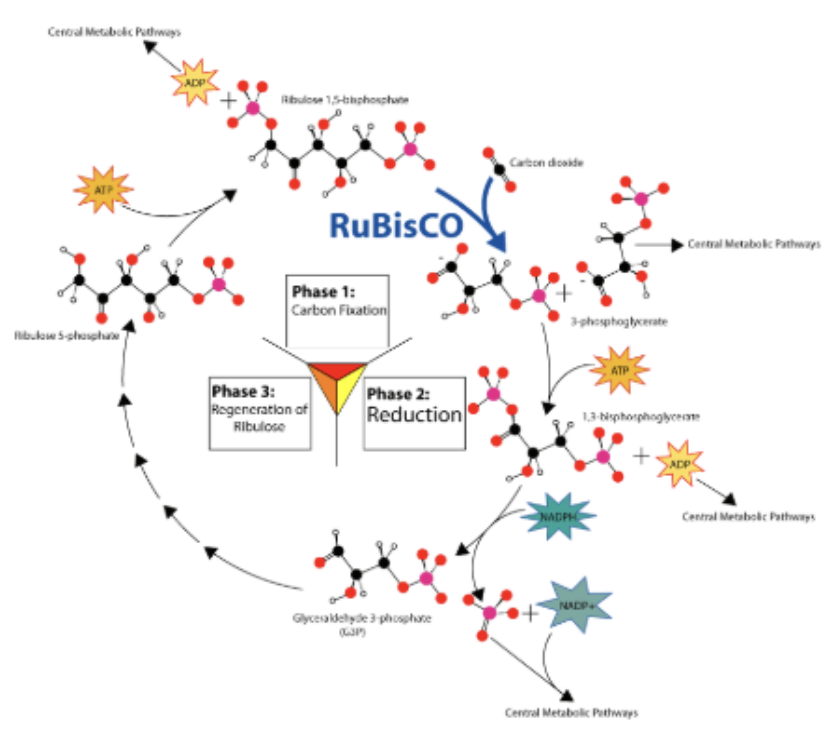
Rubisco
an enzyme that catalyses the 1st step of the light INdependent reaction (carbon fixation)
BINDS to CO2 and ATTACHES it to a sugar
FIXES CO2 into organic 3-PGA molecules → initiating Calvin Cycle
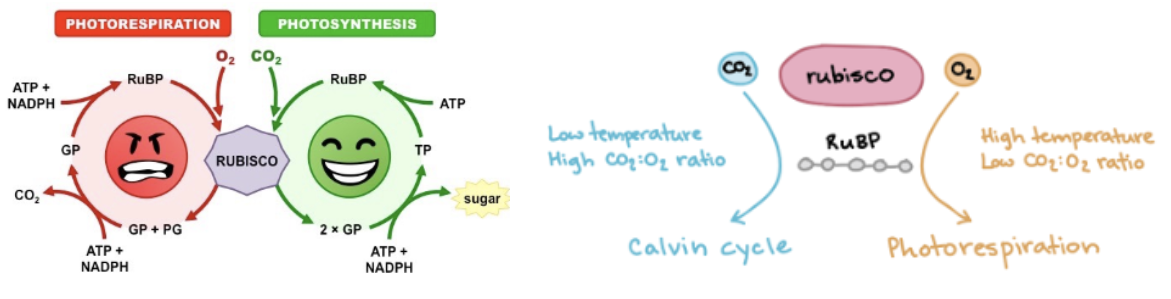
Disadvantage of Rubisco
Has an AFFINITY to bind to CO2 and O2, meaning Rubisco is not specific to CO2 so it can bind O2 to active site
SLOW
Photorespiration
an unwanted + wasteful process in plants
Rubisco is more likely to pick up O2 at higher temps and when O2 concentration is higher than CO2
C4 + CAM plants in higher temperature regions have ADAPTATIONS to reduce photorespiration
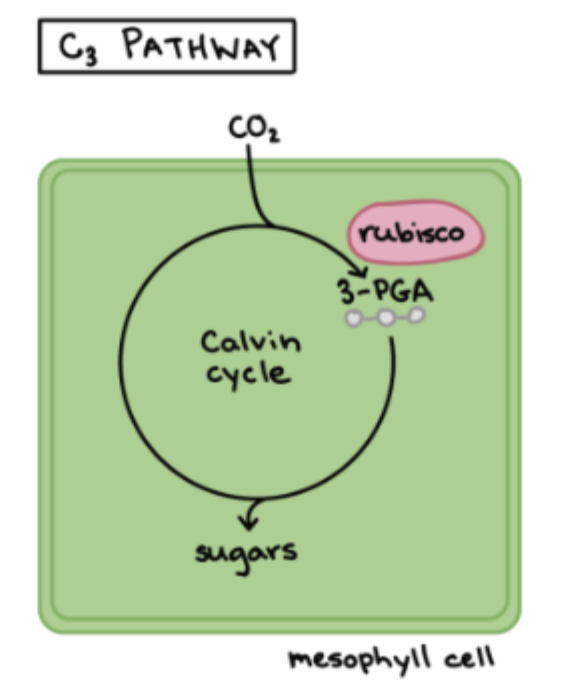
Features of C3 Plants (Standard Photosynthesis)
NO adaptations to limit photorespiration → when the weather is hot + dry as Rubisco will pick up more O2
CO2 is fixed DIRECTLY from the air
Photosynthesis decreases
Photorespiration increases
Features of C4 (Hot + Dry) Plants — Adapted Photosynthesis
Involves TWO cells (mesophyll cell and bundle-sheath cell)
CO2 is fixed in the mesophyll cell + Calvin Cycle in bundle-sheath cell → separated over space
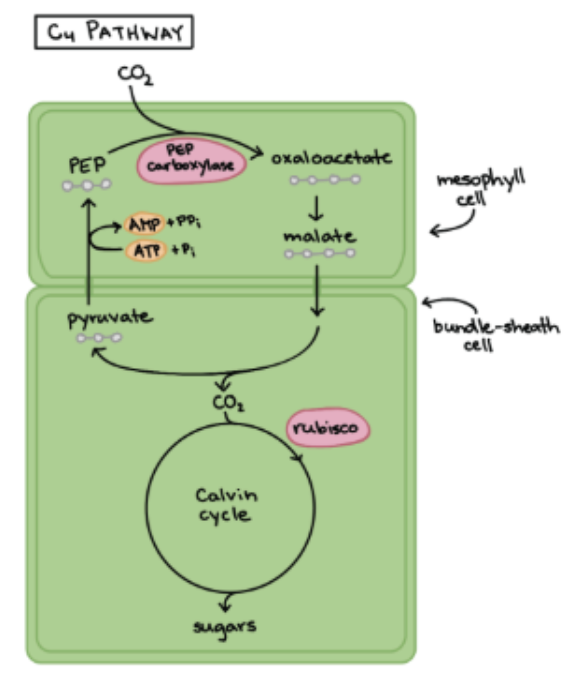
Advantage of C4 Plants
Mesophyll cells constantly pump CO2 into bundle-sheath, keeping CO2 concentration high + lowering chance of Rubisco picking up O2
BUT costs additional ATP
Photosynthesis increases
Photorespiration decreases
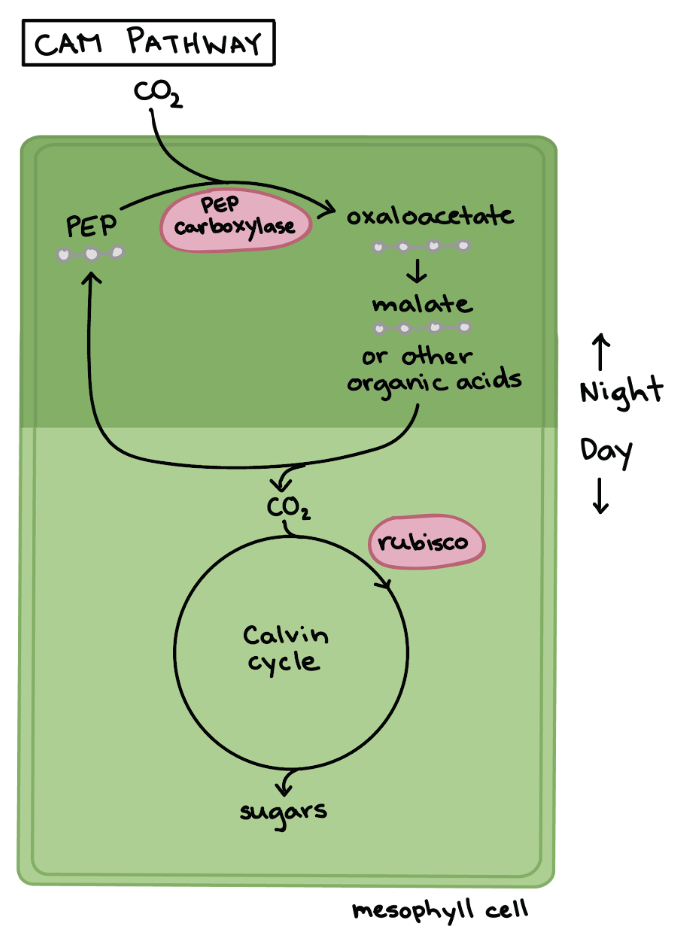
Features of CAM (Desert) Plants — Adapted Photosynthesis
CO2 is initially fixed when stomata are OPEN at NIGHT
Released from storage (NOT cell) into the Calvin Cycle during DAY
Stomata remains CLOSED during DAY to reduce water loss + keeping O2 concentration low → Rubisco attaches to CO2 more
Photosynthesis increases