Lab Week 10 Nervous tissue, spinal cord, and reflexes
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Two divisions of the nervous system
Central nervous system and Peripheral nervous system
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Sensory receptors and nerves
Sensory versus motor
Sensory: bring information into the brain
Motor: convey info from CNS to muscles and glands, converts plan into action
Three parts of a neuron (nerve cell)
Neuron cell body or soma
Dendrites
Axon
Identify the parts of a multipolar neuron
dendrites, neuron cell body, nucleus, axon hillock, axon, Schwann cell, Node of Ranvier, myelin sheath, presynaptic terminals and collateral axon
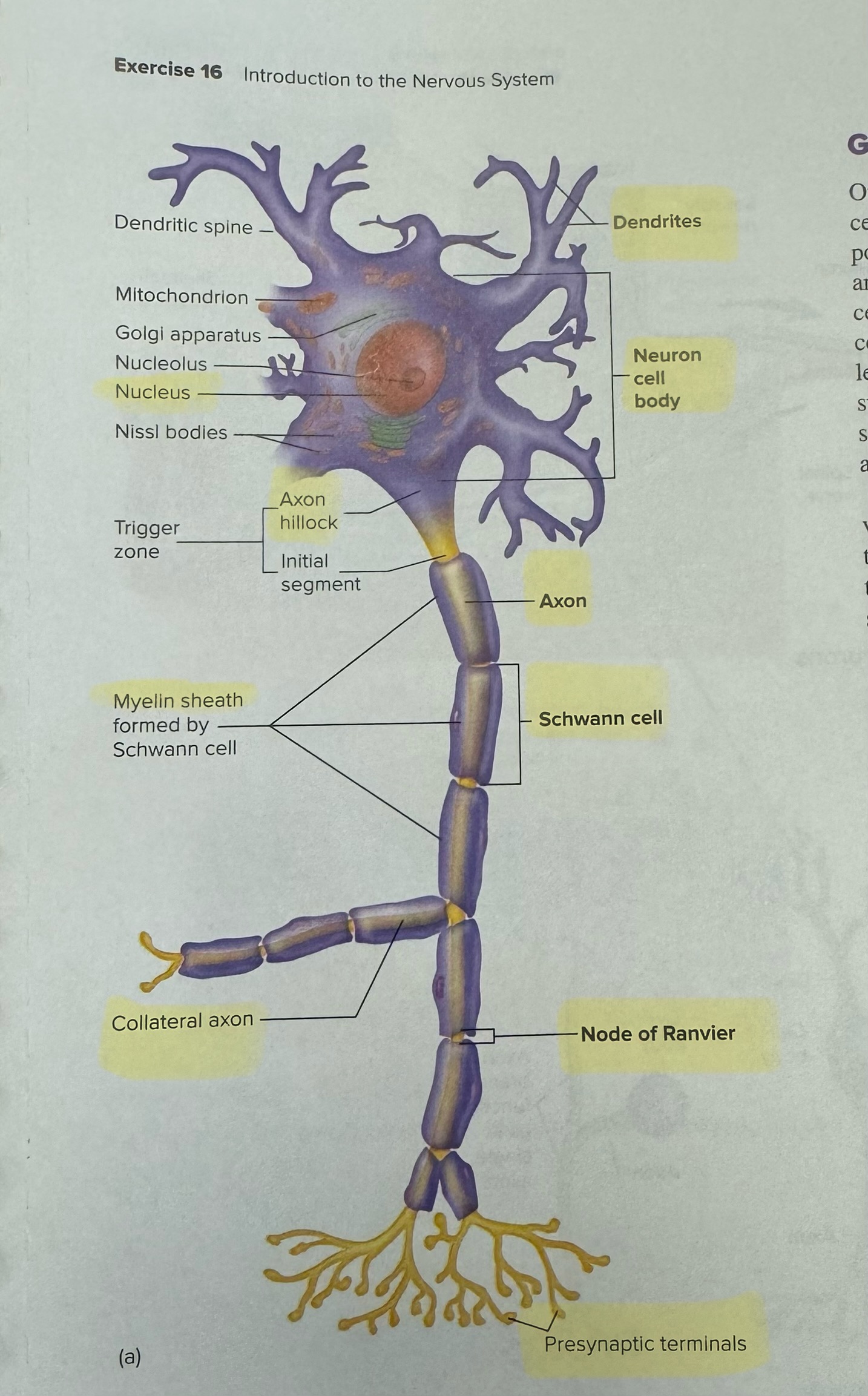
Dendrites (general definition for this and these next few terms)
Cell extensions of the cell body that receive information from other neurons or sensory receptors; conduct currents toward the cell body
Neuron cell body
Or soma, typical cell functions such as protein synthesis and housekeeping
Nucleus
Part of the neuron cell body
Axon hillock
The triangular region of the neuron cell body that is devoid of Nissl bodies, it leads to the axon that exits the neuron cell body
Axon
Arises from axon hillock of the cell body then becomes the initial segment; part of trigger zone where action potentials are generated; ends at presynaptic terminal
Schwann cell
Or neurolemmocytes, the common glia of the peripheral nervous system
Node of Ranvier
The Schwann cells wrap around axon, leaving thin regions between successive cells called this
Myelin sheath
Most long nerve fibers of CNS & PNS are covered by a layer of white fatty material
•protects & insulates
•fibers covered are said to be myelinated
Presynaptic terminals
Neurons transmit information electrochemically along the length of the axon to this
Collateral axon
Branch off of the main axon
Three functional types of neurons
•Sensory or afferent: action potentials toward C N S.
•Motor or efferent: action potentials away from C N S.
•Interneurons: within C N S from one neuron to another.
Another word for neuroglia
Glia
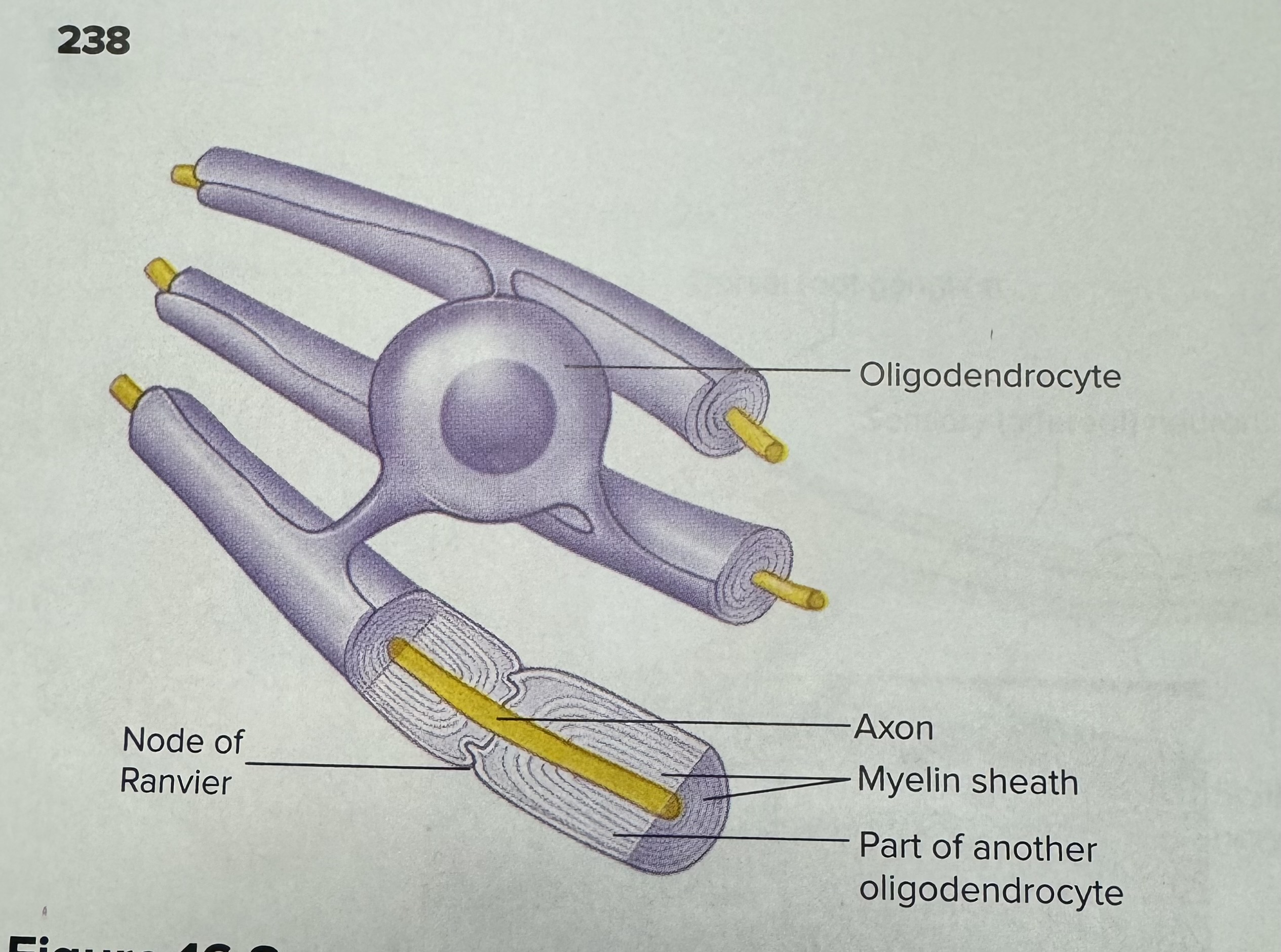
Describe and identify an oligodendrocyte (a type of neuroglia)
Essentially a Schwann cell, but in the CNS, so produces myelin
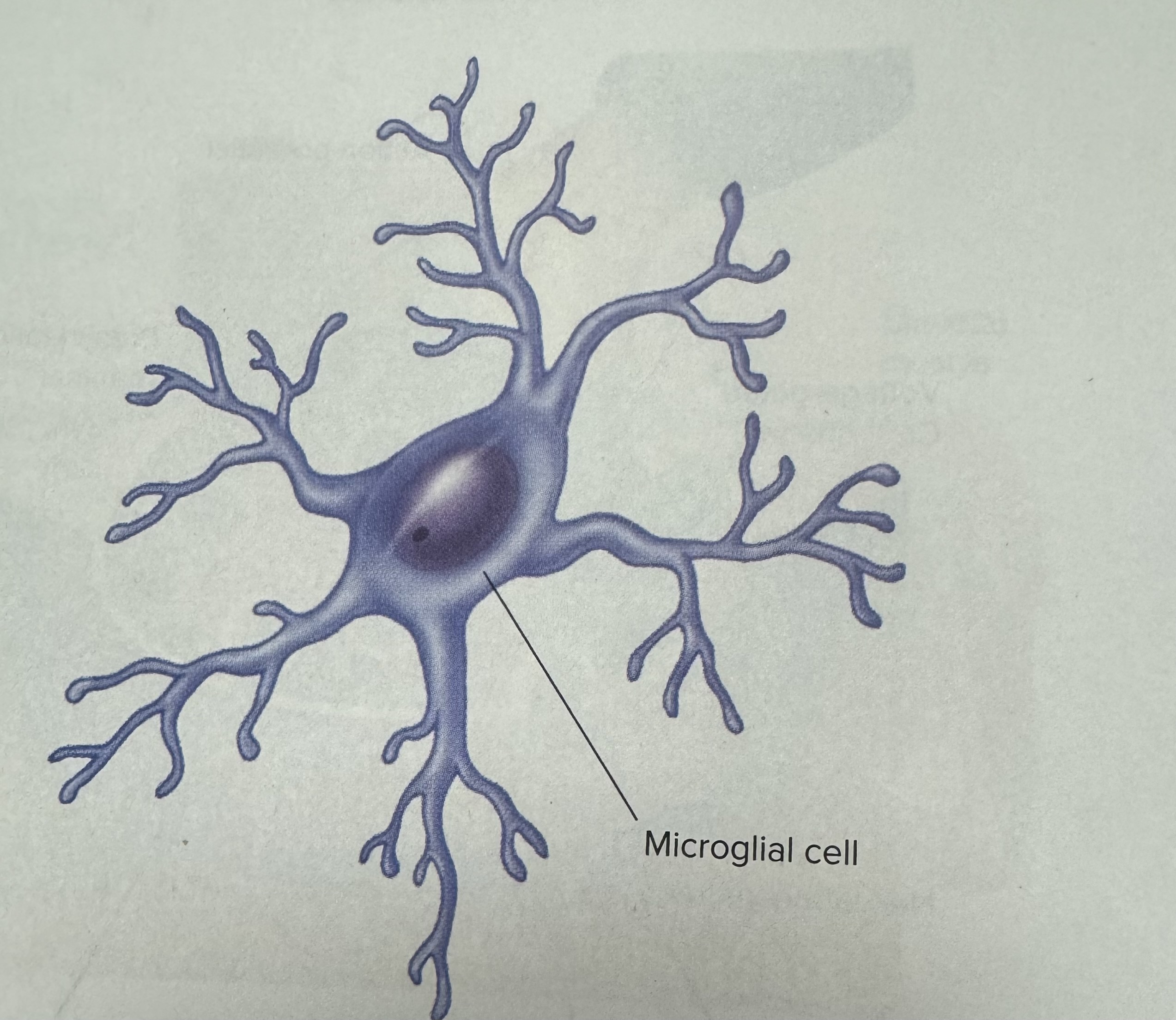
Describe and identify a microglia (a type of neuroglia)
An immunity cell
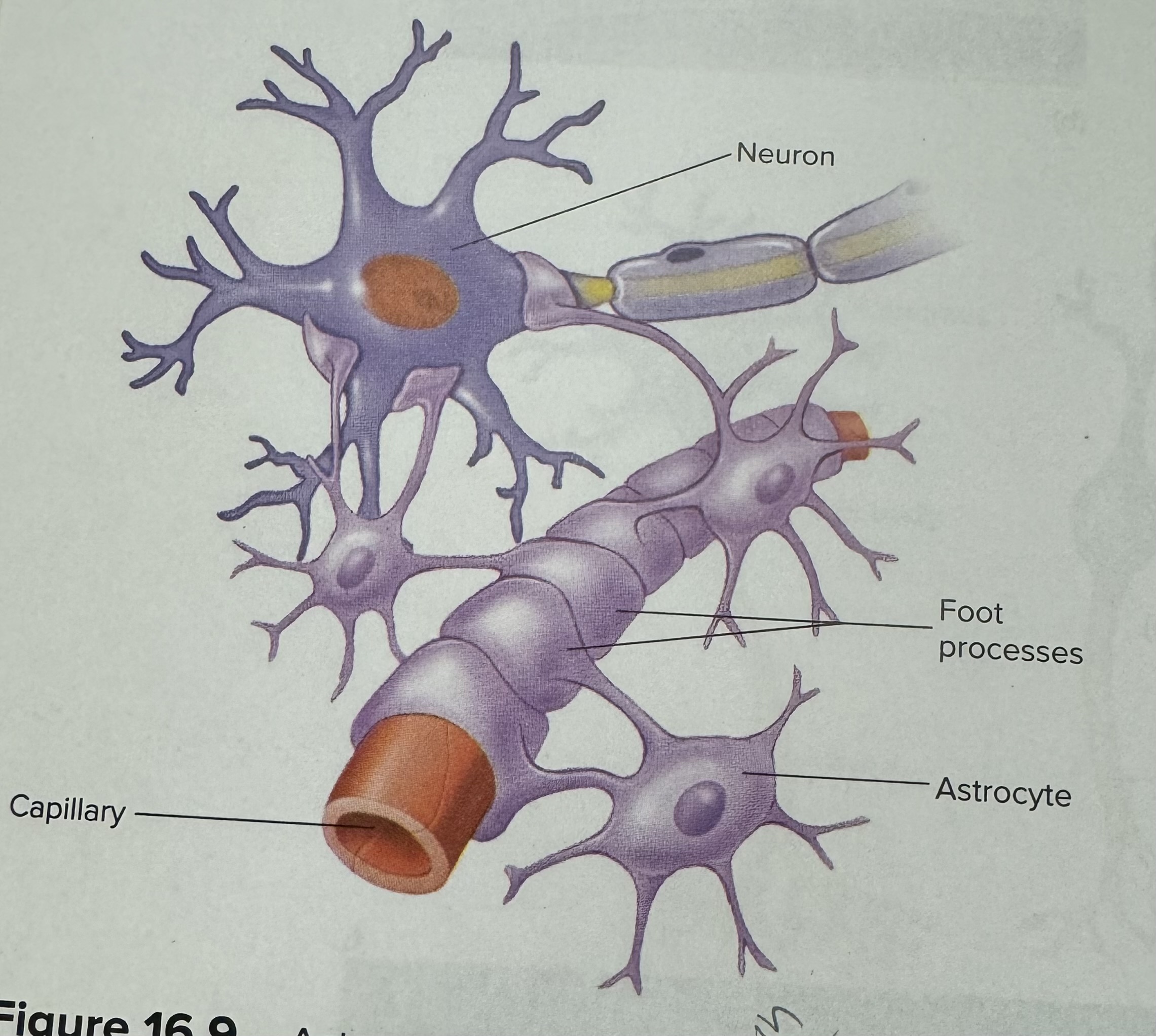
Describe and identify an astrocyte (a type of neuroglia)
Blood brain barrier
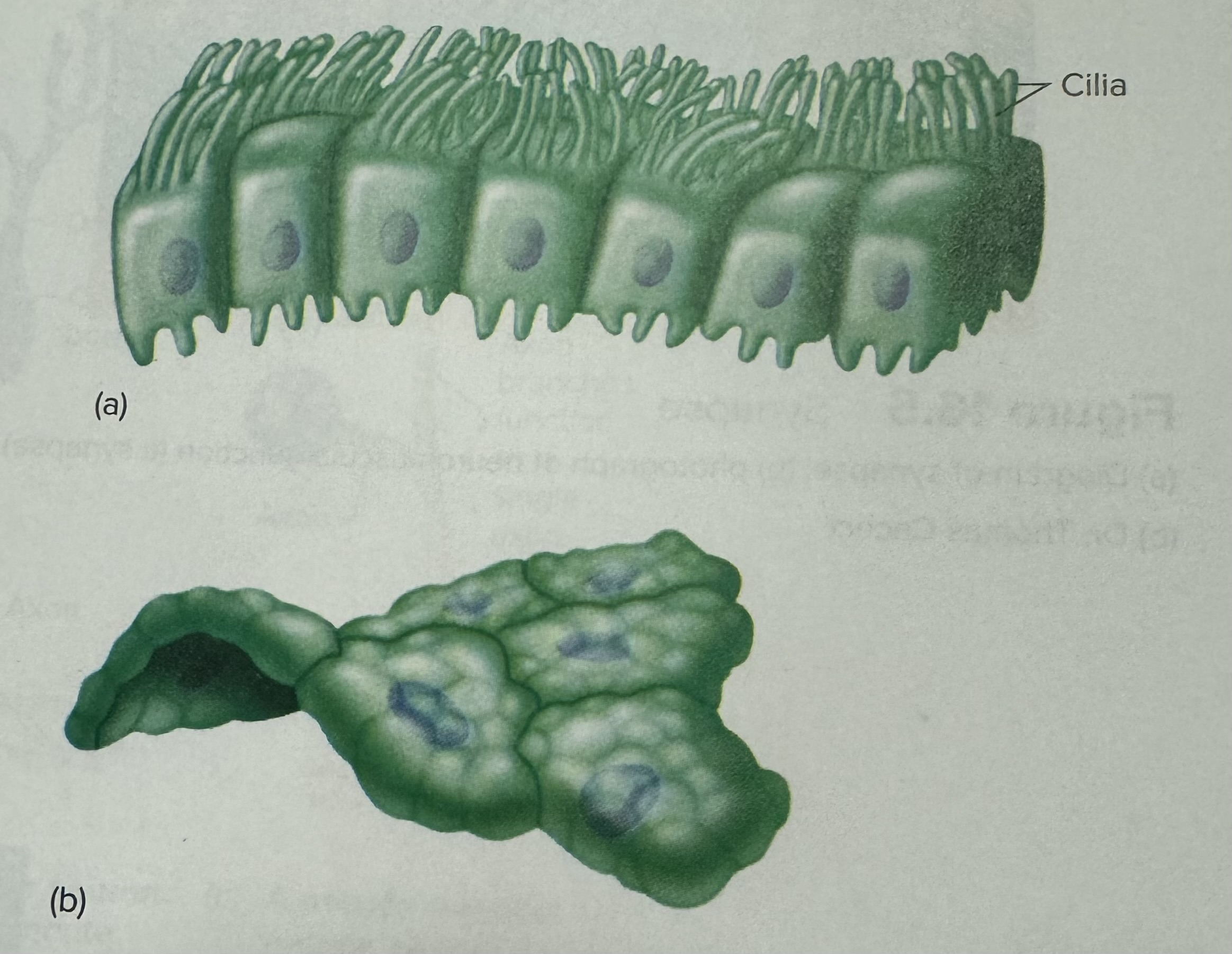
Describe and identify an ependymal cell (a type of neuroglia)
Produce cerebral spinal fluid
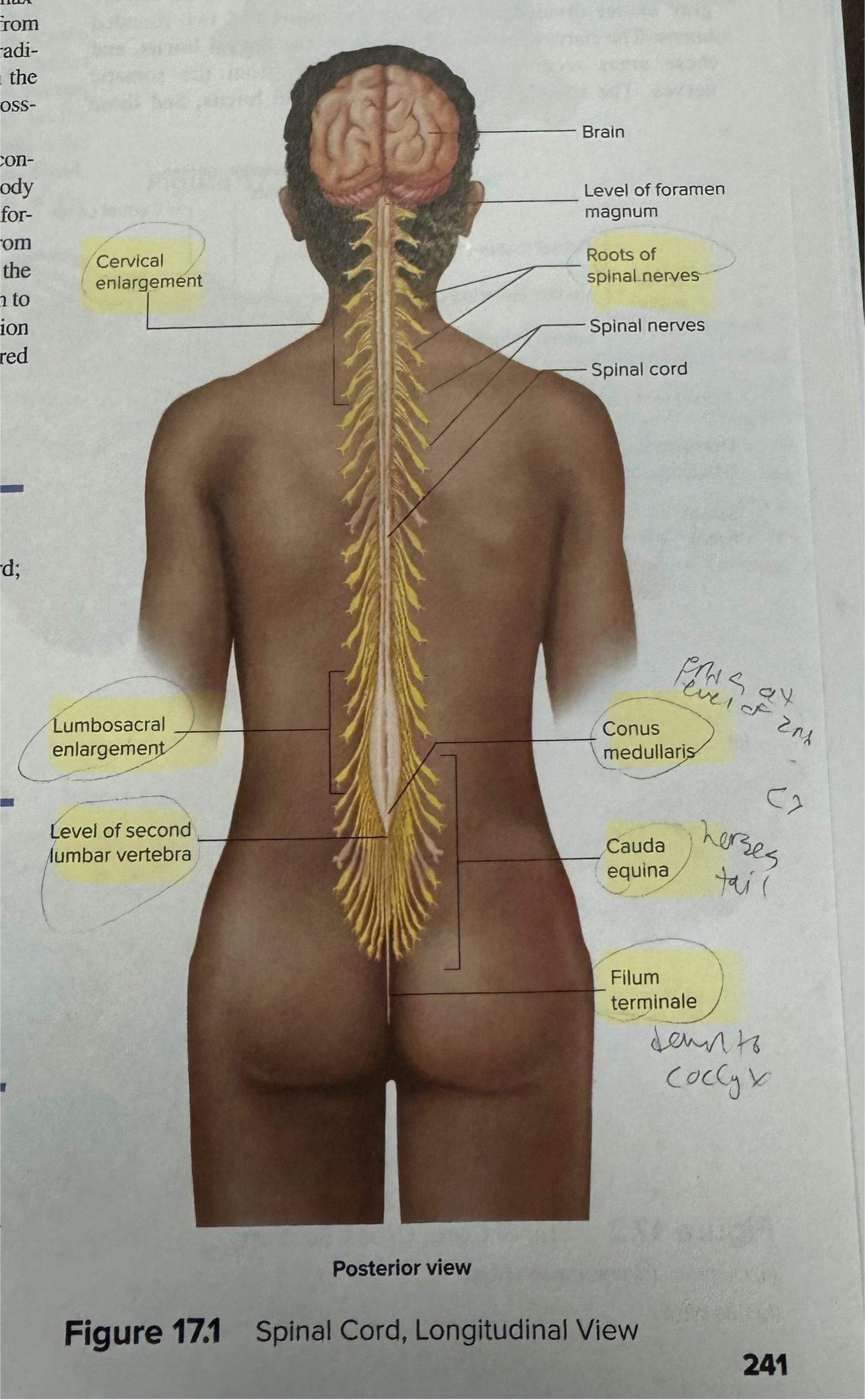
Identify enlargements of the spinal cord
Cervical and lumbar
Identify the roots of spinal nerves, spinal cord, conus medullaris, cauda equina, filum terminale
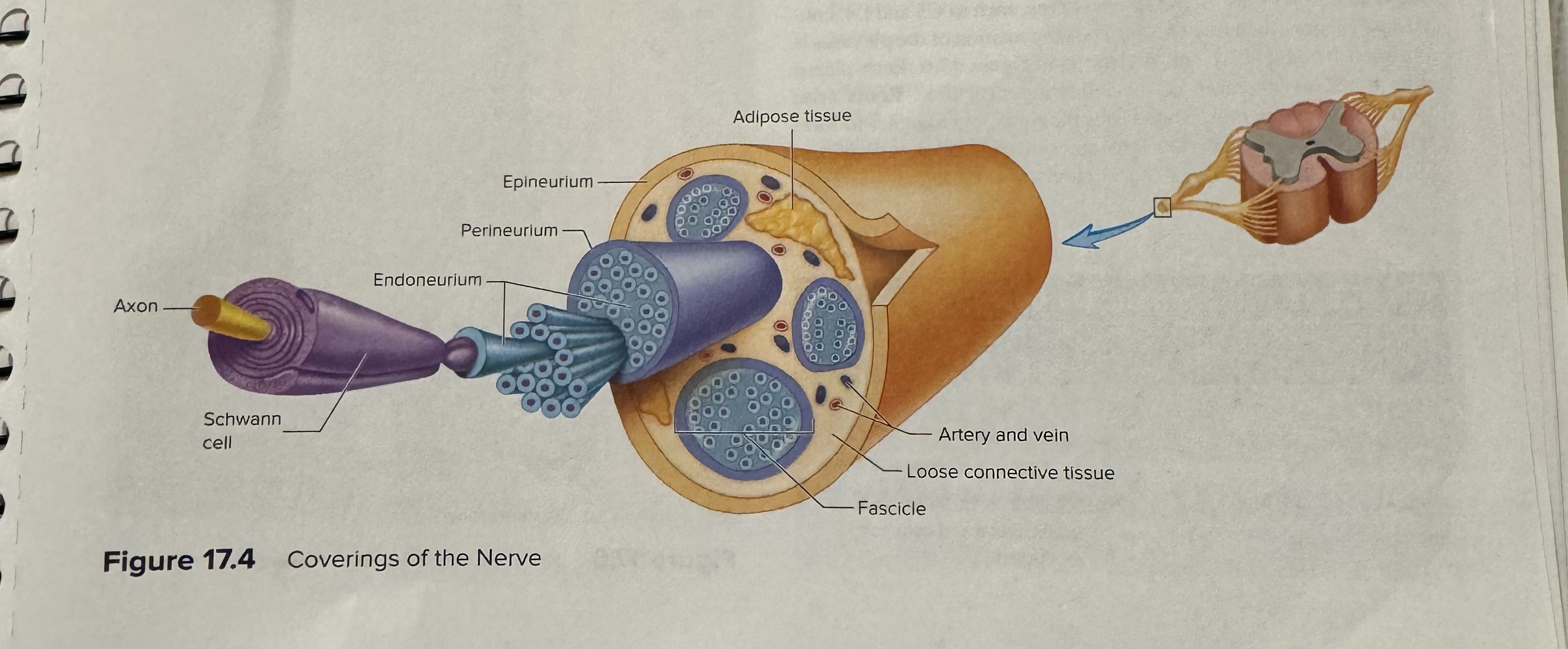
Identify and describe the structure of a nerve including the different coverings
Explain the clinical significance of cauda equina
A bundle of nerves and nerve roots at the lower end of the spinal cord, Cauda Equina Syndrome is when these nerves are compressed resulting in mainly pain in the lower back
Identify and label structures of a cross section of a spinal cord
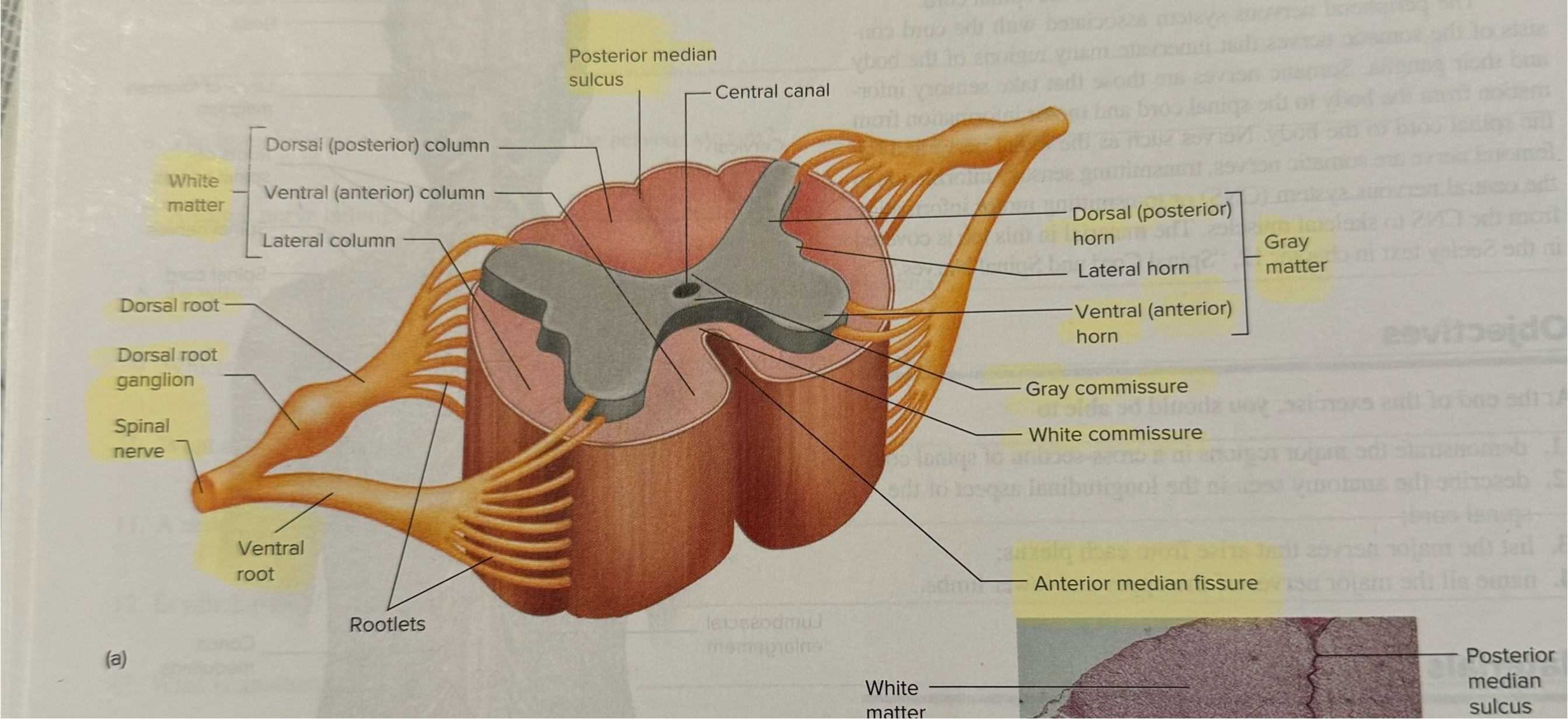
Identify the direction of action potentials through the various structures on the cross section of the spinal cord
pg 236
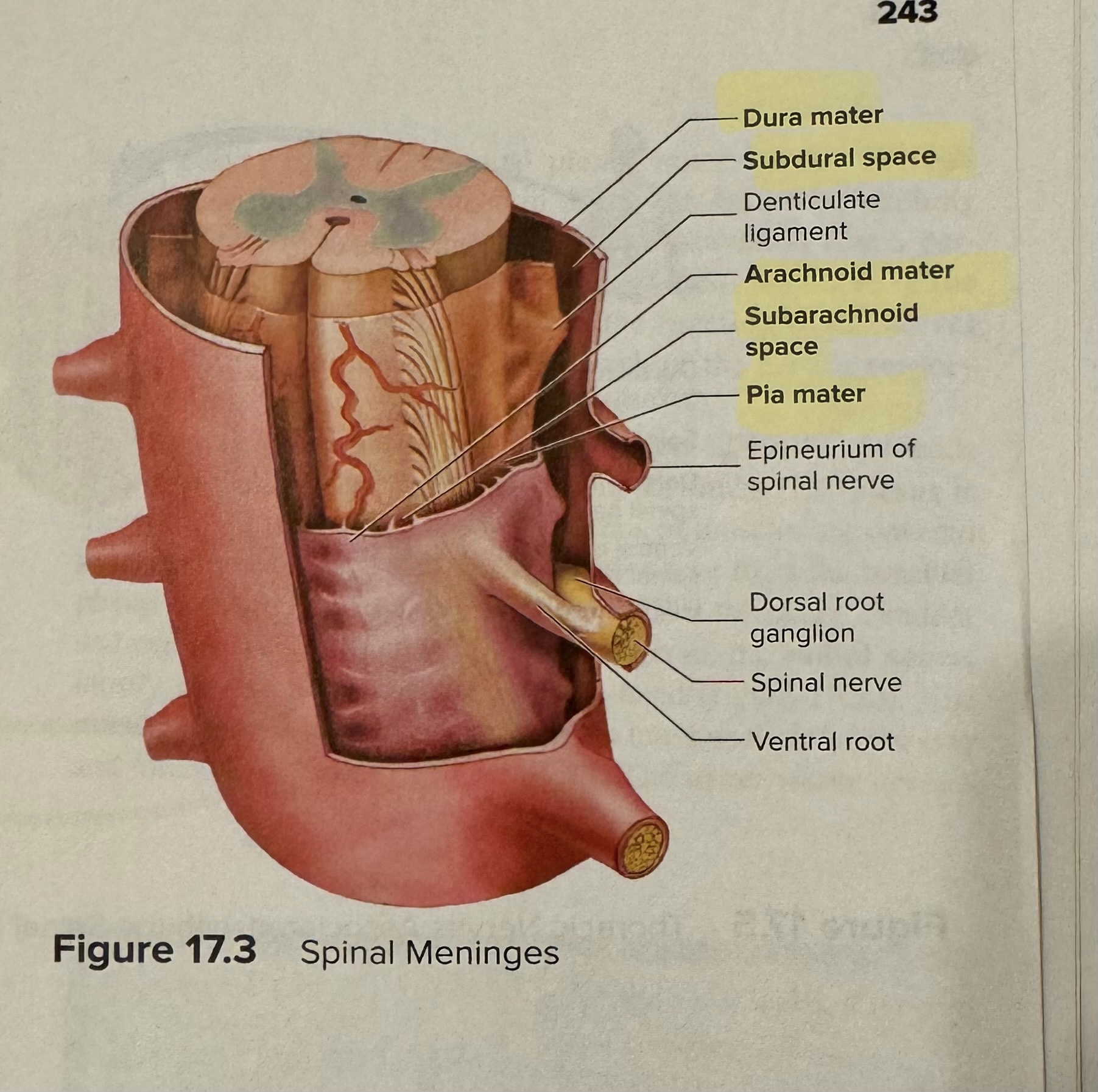
Identify the parts of the meninges of the spinal cord
bold
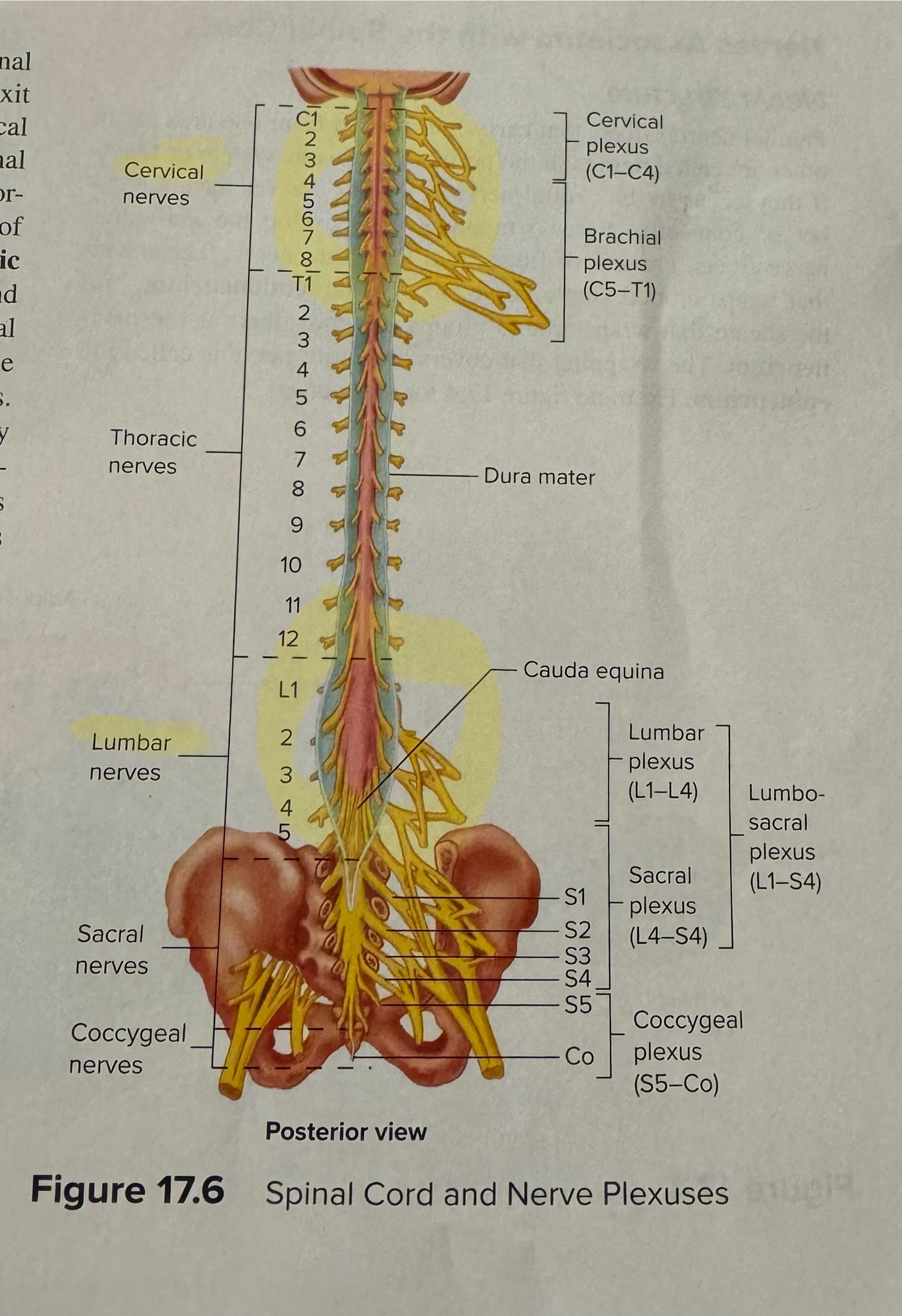
What is the number of each type of spinal nerve
Cervical - 8
Thoracic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Sacral - 5
Coccygeal - 1
Identify (or match) the four major plexuses of the body, the specific spinal nerves contributing to each plexus and the major nerves arising from each plexus
Cervical - C1-4 - Phrenic
Brachial - C5-T1 - Radial, median, ulnar, musculocutaneous, axillary
Lumbar - L1-4 - Femoral, obturator
Sacral - L4-S4 - Sciatic (tibial and common fibular)
Definition of plexus
Interwoven
Which extremity does the axillary nerve connect to
Shoulder
Which extremity does the radial nerve connect to
Arm, wrist and hand
Which extremity does the musculocutaneous nerve connect to
Arm
Which extremity does the ulnar nerve connect to
Forearm and hand
Which extremity does the median nerve connect to
Arm and hand
Which extremity does the obturator nerve connect to
Thigh
Which extremity does the femoral nerve connect to
Thigh
Which extremity does the tibial nerve connect to
Leg
Which extremity does the fibular nerve connect to
Leg and foot
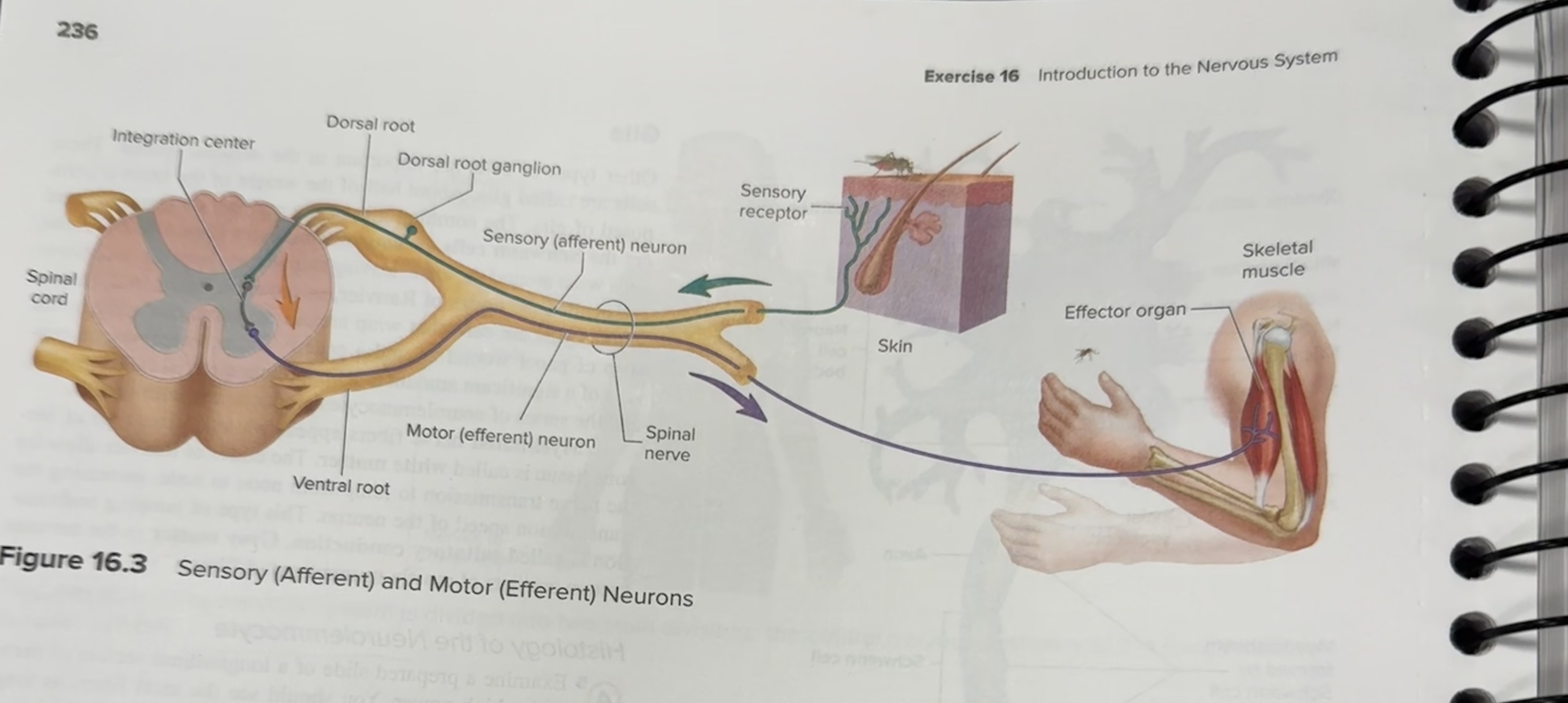
List the five structures involved in a reflex arc
Sensory receptor
Sensory neuron
Interneuron
Motor neuron
Effector organ
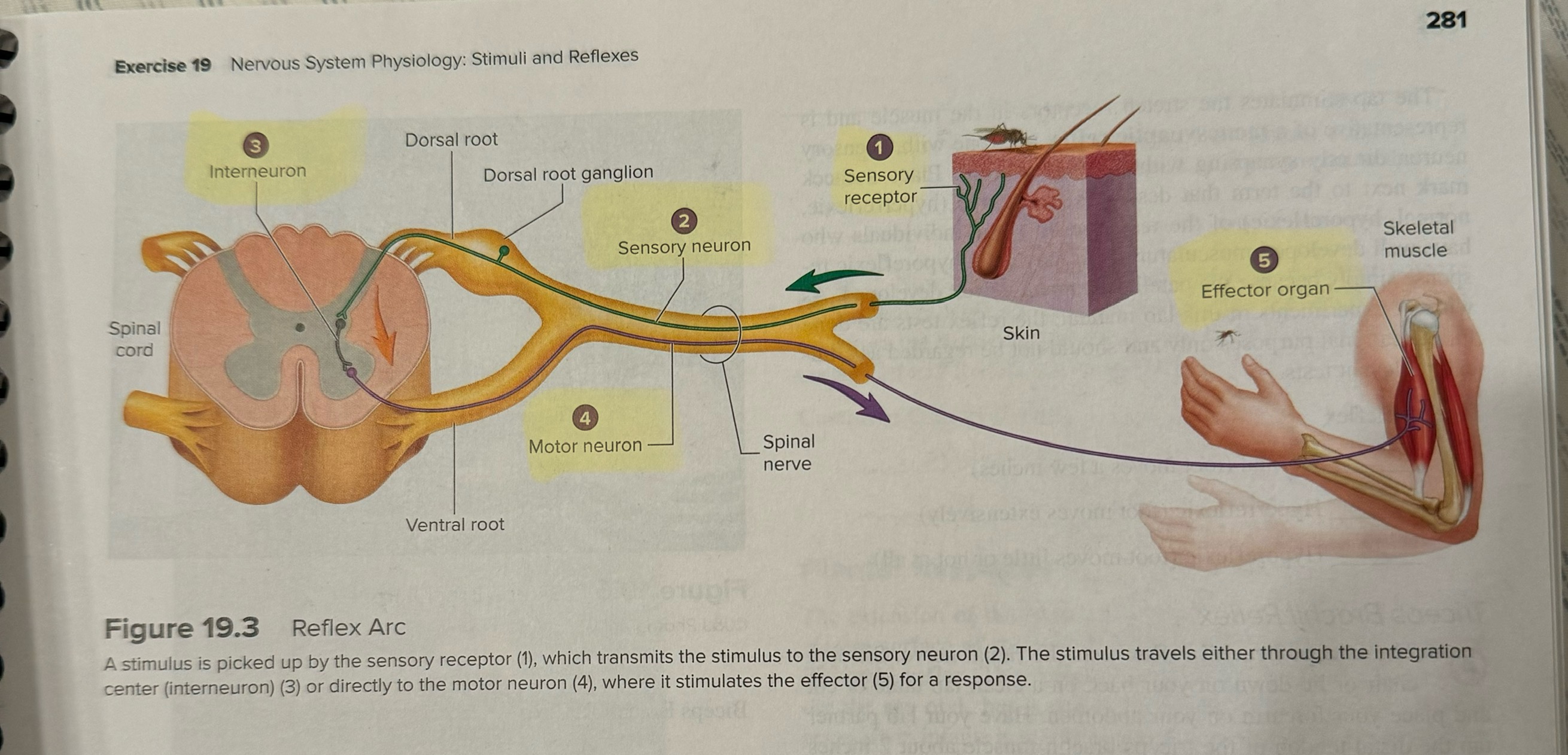
Difference between a stretch, golgi tendon, and withdrawal reflex
Stretch: muscle stretch
Golgi tendon: excessive tension
Withdrawal reflex: pain/damage threat
Match the patellar reflex with its description and know it’s corresponding nerve that is being tested
It occurs when the patellar tendon is tapped, stretching the quadriceps muscle
Femoral nerve
Triceps brachii
When tapped, it extends the elbow
Radial nerve
Biceps brachii
Tap on the biceps brachii causes the elbow to flex
Musculocutaneous nerve
Calcaneal tendon
When tapped, causes plantarflexion
Tibial nerve
Eye (blink and corneal)
When light is shined into one eye, the pupil constricts in both eyes
Optic nerve and oculomotor nerve
Normal
Movement of an inch or two
Hyporeflexic
Showing less than average response
Hyperreflexic
Showing an exaggerated response
What are the three different neuron shapes
Multipolar neuron: many dendrites and an axon
Bipolar neuron: has a dendrite and an axon
Pseudo-unipolar neuron: has an axon and no dendrites
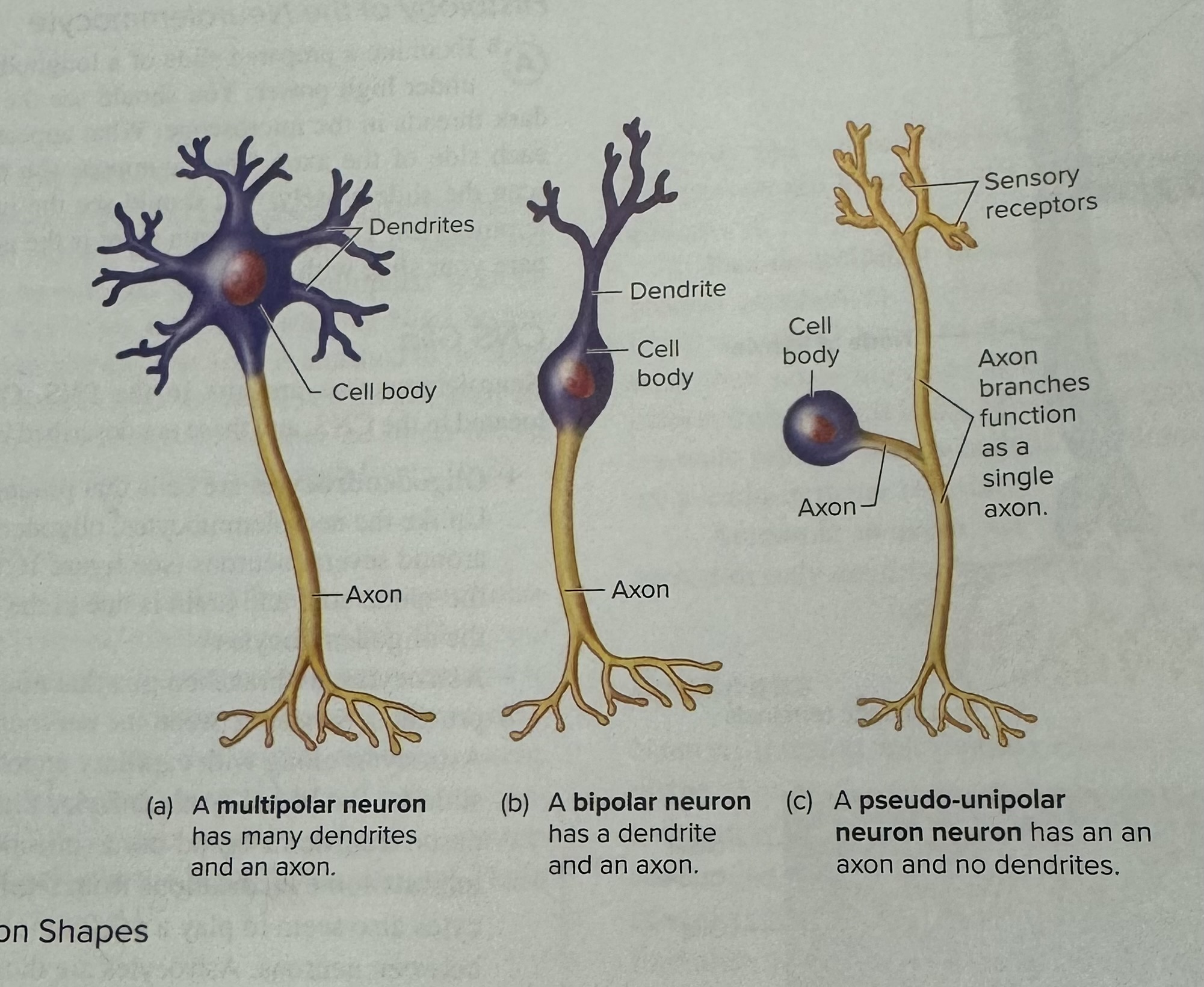
Which neuron shapes are motor and which are sensory?
Motor: multipolar neuron
Sensory: bipolar and pseudo-unipolar neuron
Which neuron shape is for special senses and which is for general senses
Special senses: bipolar neuron
General senses: pseudo-unipolar neuron
What are special senses
Smell, hear, taste and sight
What are general senses
Touch