
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
From DNA to Proteins
• DNA contains instructions to make proteins
• Genes are units of inheritance, each containing instructions to make a single protein
• The process involves transcription of
DNA into single-stranded mRNA,
which is then translated into a protein
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
DNA makes RNA makes Protein

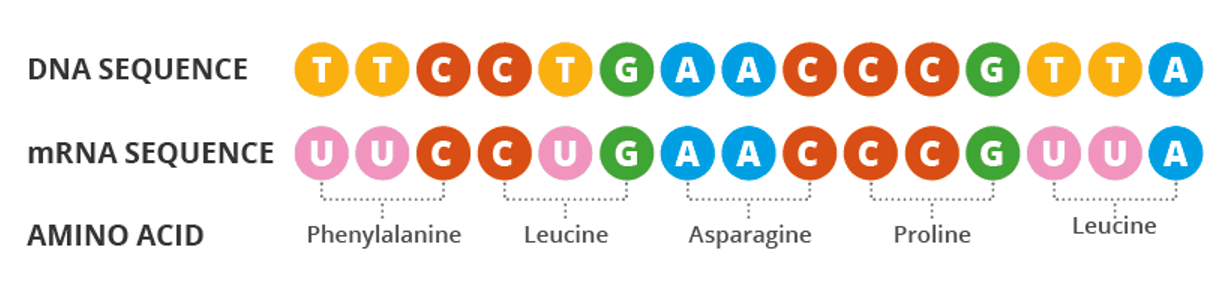
step 1 - Translation
Generation of mRNA from DNA by RNA polymerase
DNA strands separate and RNA polymerase makes a copy of one of the strands
notes from ppt:
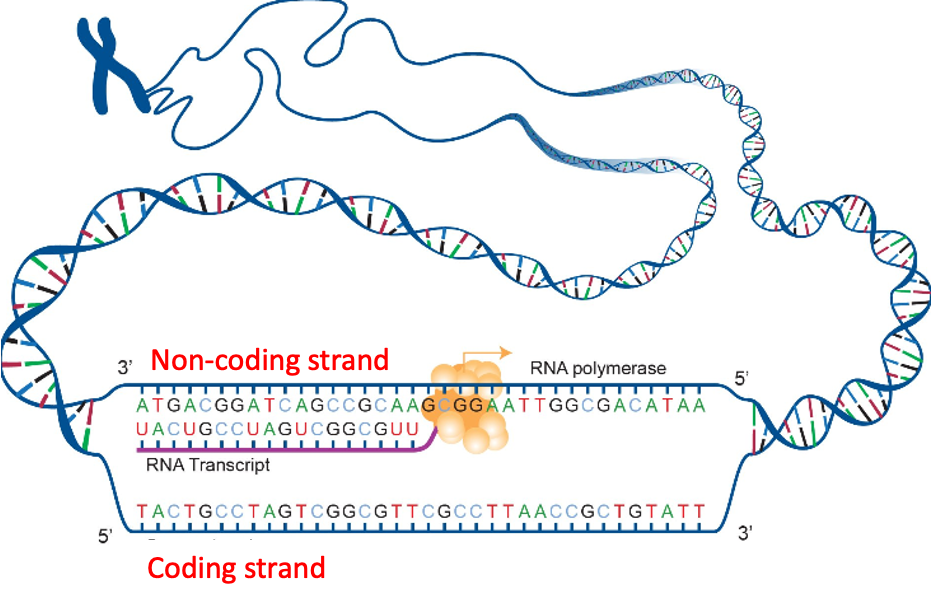
DNA holds the genetic information, but protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. Therefore, the cell needs to make a copy of the genetic information in the form of a mRNA, which exits the nucleus and move to the cytoplasm. If we compare DNA to a cookbook where each recipe contains the instructions to make a different protein, it is like going to the library (nucleus) and making a photocopy of the recipe (mRNA) to take home (cytoplasm) so that we can make the cake (protein).
Transcription
RNA is made using the anti-sense/non-coding strand as a template
The sequence of RNA is complementary to the antisense strand, and identical to the ‘sense’ or ‘coding strand’ (except for U instead of T)
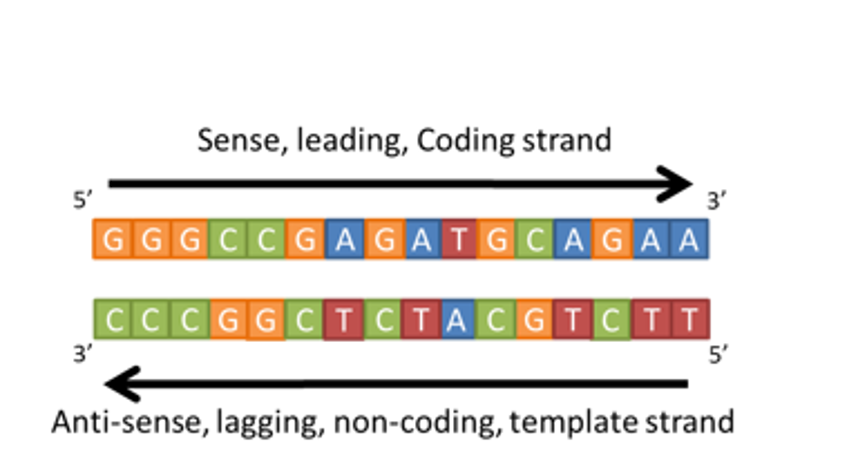
The copy needs to be identical to the coding strand, because only the coding strands has the correct sequence of nucleotides needed to make the right protein.
(example) A gene has the following sequence:
5’ ATGCCGTTAGCA 3’ coding strand/ sense strand
3’ TACGGCAATCGT 5’ non-coding/antisense strand
RNA polymerase transcribes the non-coding strand into a mRNA
5’ AUGCCGUUAGCA 3’ mRNA
3’ TACGGCAATCGT 5’ non-coding/antisense strand
The mRNA is identical to coding strand but with Us instead of T
practice
If the DNA sequence on the coding strand is 5’ GGGCCGAGAT 3’ what will be the sequence of the mRNA?
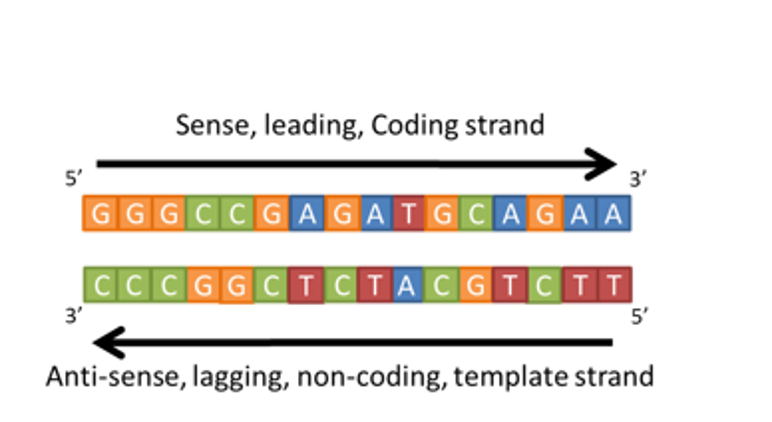
5’ ATGTCGGCCC 3’
5’ CCCGGCUCUA 3’
5’ GGGCCGAGAU 3’
5’ GGGCCGAGAT 3’
mRNA maturation
The transcribed RNA contains coding parts (exons) and non-coding parts (introns)
The mRNA undergoes ‘splicing’ which involves removing introns and ‘sticking’ the exons together
The mRNA is also given a ‘cap’ and a poly-A ‘tail’ that make it more stable and protect it from degradation
The mRNA is now ‘mature’ and ready for the next step
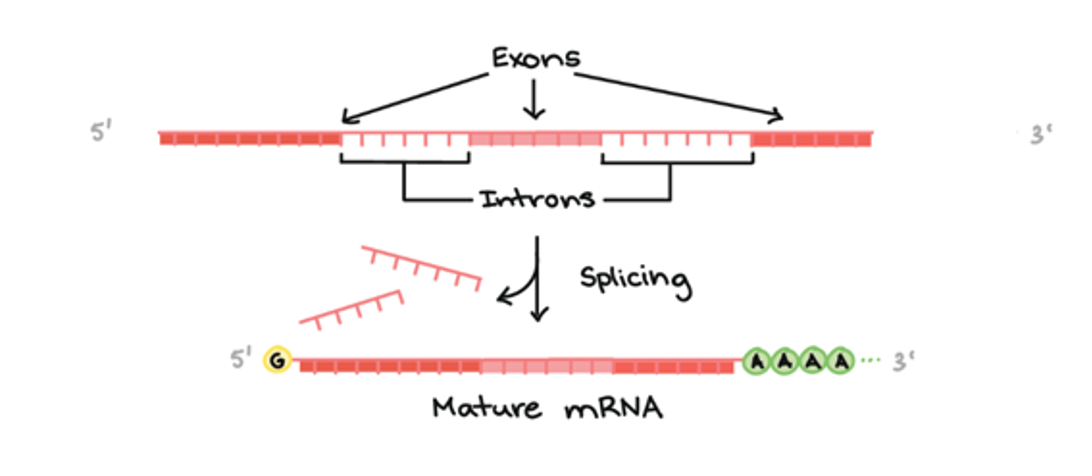
notes from ppt:
Going back to the analogy with the recipe book, splicing is like cutting out all the ‘useless’ information on the page (e.g. chef’s biography, advertising etc) and sticking together the bits of instructions that you actually need to make the dish.
step 2- Translation
conversion to mRNA to protein
It occurs outside the nucleus of the cell
It occurs via transport RNA (tRNAs) and the ribosome
The sequence of the bases determines the sequence of amino acids
Bases are read 3 at a time (codons)
the genetic code
Combination of 3 ‘letters’ = codon
Four bases: 43 codons = 64 possible combinations (codons)
61 codons encode amino acids
One of these, AUG (encoding for methionine) is found as first codon in all proteins (‘start codon’)
The remaining 3 codons function as ‘stop codons’; they signal the end of the protein chain
A ‘degenerate’ code
Note how some amino acids are coded by more than 1 codon.
This is because there are only 20 amino acids but 61 ‘coding’ codons
Degenerate/redundant code i.e. some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon
notes from ppt:
Note – methionine is only coded by one codon AUG
Ribosomes and Translation
Ribosomes are cell structures made of rRNA and proteins
mRNA passes through the ribosome like a tape and is translated in 5’ to 3’ direction
Each codon is ‘read’ and the correct amino acid is provided by a tRNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Type of RNA, with partially complementary sequence
‘Cloverleaf’ configuration
Includes a ‘stem’ and 3 loops
Amino acid carried at the amino acid attachment site
Each tRNA is adapted to carry one amino acid, determined by its anticodon
Anticodon is complementary to the mRNA codon
Start and End of Translation
Translation starts at the start codon (AUG).
Translation stops when a stop codon (UAA, UAG and UGA) is found.
Protein is released
MORE INFORMATION
practice 1
A codon found on a section of mRNA has the sequence of bases AUC. What are the bases found on the anti-codon of the corresponding tRNA:
1. AUC
2. ATC
3. TAG
4. UAG
practice 2
A protein is made of 250 amino acids. What is the length of the mRNA encoding for this protein *?
1. 250 nucleotides
2. 500 nucleotides
3. 750 nucleotides
4. 1000 nucleotides
* mRNA also have non-coding sequences but for this question we are only considering the coding part of the mRNA
practice 3
When DNA is copied, mistakes can occur (mutations). Which of these mutations will cause a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein?
1. GGC to GGA
2. CGT to CAT
3. ACT to ACG
4. TAA to TAG
Changes to the DNA code: mutation
A change to the sequence of DNA nucleotides is called mutation
It does not always alter the code for the sequence of amino acids in a protein
Even if the sequence of amino acid is changed, the protein may still be functional
notes from ppt:
Mutations and Polymorphisms are often confused by students. Both terms refer to a difference in the DNA sequence compared to the ‘standard’ or ‘most common’ sequence. However, polymorphisms refers to changes that are more common in the population (i.e. they are found in more than 1% of people) and that usually do not have a negative effect (i.e. do not cause disease).
Type of mutations and their effect
A fun way to understand the types of mutation!
THE MAN SAW THE BOY HIT THE CAN END (normal gene)
THE MAN SAW THE BOY HIT THE CAT END (missense mutation)
THE MAN SAW THE BOY END (nonsense)
THE MAN SAW THE BOY HIT THE CAN AND …. (readthrough)
THE MAN SAW THE BOA YHI TTH ECA NEN D (frameshift)
Example: Sickle cell anaemia
Haemoglobin is a protein made of 4 peptides
Two alpha-globin and two beta-globin chains
Each chain is linked to a haem group.
Oxygen binds to the haem group and is transported from the lungs to the tissues.
Sickle cell anaemia is a disease caused by a single base change
The mutation changes a Glutamic Acid into a Valine in the protein sequence of the beta chains
notes from ppt:
The haem group is a ring-like molecule containing an iron atom, which binds to oxygen
Haemoglobin amino acid sequence
val - leu ser pro ala asp lys thr asn val lys ala ala try gly lys val gly ala his ala gly glu tyr gly ala glu ala leu glu arg met phe leu ser phe pro thr thr lys thr tyr phe pro his phe - asp leu ser his gly ser ala - - - - - gln val lys gly his gly lys lys val ala asp ala leu thr asn ala val ala his val asp asp met pro asn ala leu ser ala leu ser asp leu his ala his lys leu arg val asp pro val asp phe lys leu leu ser his cys leu leu val thr leu ala ala his leu pro ala glu phe thr pro ala val his ala ser leu asp lys phe leu ala ser val ser thr val leu thr ser lys tyr arg =141 amino acids (x2)
val his leu thr pro glu glu lys ser ala val thr ala leu try gly lys val asn - - val asp glu val gly gly glu ala leu gly arg leu leu val val tyr pro try thr gln arg phe phe glu ser phe gly asp leu ser thr pro asp ala val met gly asn pro lys val lys ala his gly lys lys val leu gly ala phe ser asp gly leu ala his leu asp asn leu lys gly thr phe ala thr leu ser glu leu his cys asp lys leu his val asp pro glu asn phe arg leu leu gly asn val leu val cys val leu ala his his phe gly lys glu phe thr pro pro val gln ala ala tyr gln lys val val ala gly val ala asp ala leu ala his lys tyr his = (146 amino acids x2)
The single nucleotide change of the sickle cell anaemia mutation results in the replacement of the amino acid glutamic acid with the amino acid valine at the surface of the haemoglobin molecule. This small change is sufficient to change the protein and how it function. Why?
(TIP: go back to look at the different types of amino acid in Lecture 2)
Glutamic acid is charged, Valine is non-polar
The presence of a non-polar amino acid on the surface of the molecule makes the protein less soluble in water
Blood is made mostly of water, and so is the environment inside of red blood cells.
Consequences…
notes from ppt:
Red blood cells are usually round and flexible, so they move easily through blood vessels. The clumped haemoglobin associated with sickle cell anaemia causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and misshapen, which can slow or block blood flow.
More information on Sickle cell anaemia here: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sickle-cell-anemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355876
Summary
DNA makes RNA makes Protein
Gene expression requires processes of transcription of genes and translation into functional proteins
Gene expression profiles differentiate cells and tissues
Mutations can alter the function of a protein and cause disease