module 2: are carbs good for you?
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
how many carbons do hexose monosaccharides???
monosaccharides with 6 carbons
monosaccharides
6 carbons, 12 hydrogens and 6 oxygen atoms
Fructose is added to what??
candy, baked goods and sugar-sweetened beverages in the form of high fructose corn syrup (HFCS), which is 42-55% fructose
pentose monosaccharides
carbohydrates with 5 carbons
with heart failure patients
ribose supplementation improved heart and physical function by way of increasing ATP and preserving cellular function
Complex carbohydrates (oligosaccharides)
made up of 3-9 monosaccharides) and polysaccharides (>9 monosaccharides), such as starch and non-starch polysaccharides
simple carbohydrate
Simple carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides and sugar alcohols (polyols like sorbitol, xylitol and maltitol)
Monosaccharide (simple carbohydrate)
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Tagatose
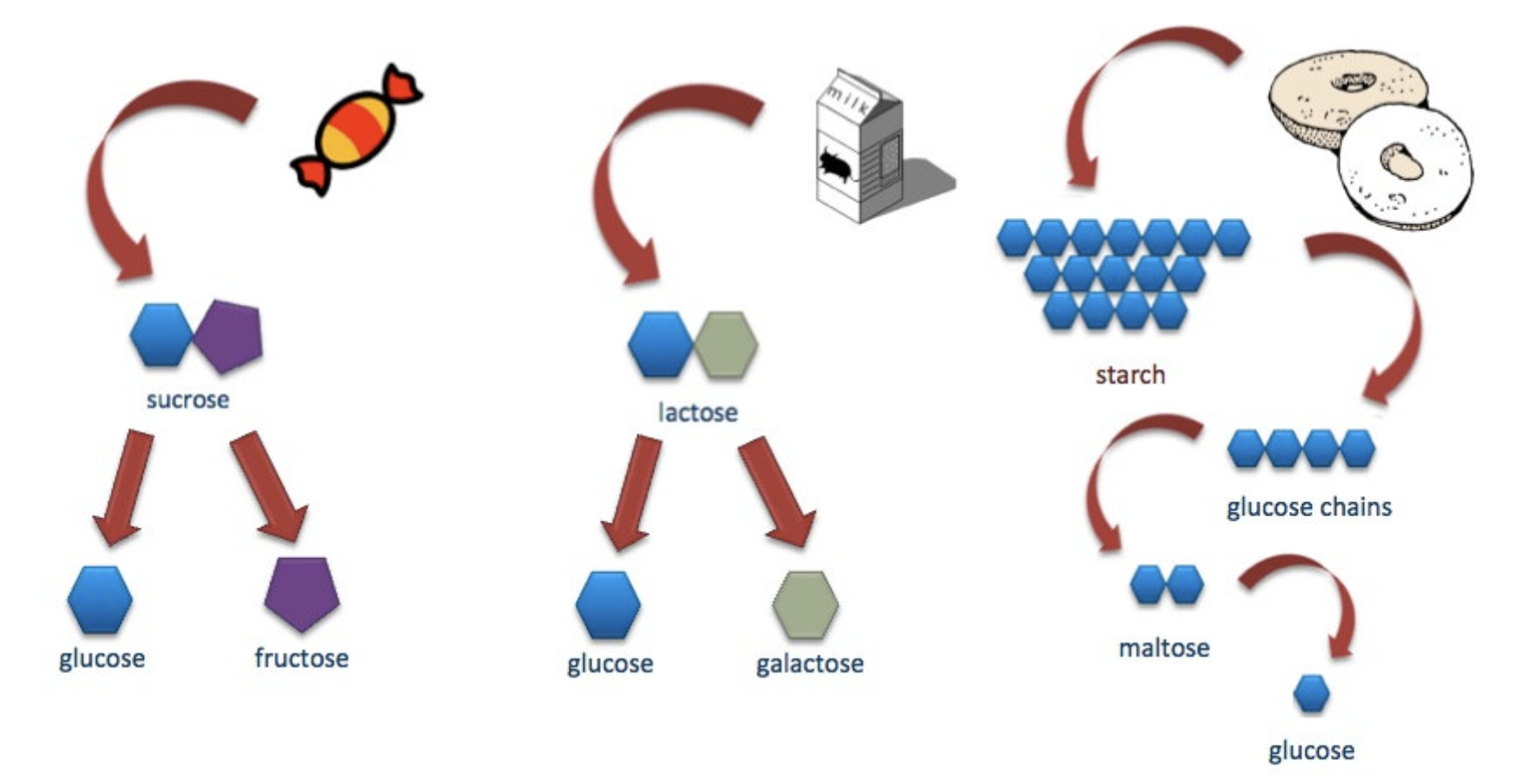
Disaccharide (simple carbohydrate)
Maltose (glucose + glucose)
Sucrose (fructose + glucose)
Lactose (glucose + galactose)
Polysaccharide (complex carbohydrate)
Glycogen
Starch
Fibre (non-starch polysaccharide)
how are carbs digested? eg. with granola bar
the teeth and tongue break apart the granola bar while the salivary glands secrete saliva which contains an enzyme called amylase which breaks down amylose starch molecules in the oats.
The food bolus arrives in the stomach where parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl). This HCl inactivates amylase and plays a bigger role in protein digestion (discussed in a later module). HCl is not involved in carbohydrate digestion. The cellulose fibre in the oats is not digested in the stomach, but will delay gastric emptying, which contributes to the feeling of satiety.
The small intestine is where the majority of carbohydrate digestion takes place. The small intestine is made up of 3 sections: duodenum, jejunum and ileum (Betts et al., 2017). This digestive organ is 10-20 feet long, is 1 inch in diameter and has a surface area of 200m2 ! This large surface area is attributed to circular folds, villi and microvilli in the small intestine (Figure 9). The villi are within the circular folds, and are made of absorptive epithelial cells. You will also notice that the villi have an artery, vein and lymphatic capillary, known as a lacteal. These structures are essential for the absorption of our macronutrients. The microvilli are smaller than the villi and are extensions of the plasma membrane of the absorptive epithelial cells. There are approximately 200 million microvilli per mm2 of small intestine! Collectively, the microvilli make up the brush border (Betts et al., 2017).
chemical digestion in the small intestine, there are 2 main players
amylase and brush border enzymes
brush border enzymes
Brush border enzymes are on the surface of the microvilli. These enzymes (maltase, sucrase and lactase) break down the disaccharides maltose, sucrose and lactose
brush border enzymes break down the disaccharides into monosaccharides
amylase
Pancreatic amylase is secreted into the small intestine from the pancreas and works to continue breaking down starch molecules into smaller polysaccharide molecules and maltose (glucose + glucose)
what kind of lactose intolerance are there??
primary or secondary lactose intolerance.
whats primary lactose intolerant
Primary causes are changes in expression of the LCT gene, leading to a reduction in lactase after the age of 2-3 years
whats secondary lactose intolerance
Secondary lactose intolerance can be due to damage to the intestine, such as untreated Celiac disease or intestinal inflammation Usually, when these conditions are treated, the issue of lactose intolerance is resolved.
lactase persistent
People who can consume large amounts of milk without complication
Homozygous persistent
These people can consume milk and do not experience symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Heterozygous
these people may produce less lactase, but there is still enough enzyme produced to break down lactose. But, if there is intestinal injury, lactose intolerance may develop.
Homozygous non-persistent
These people produce the least amount of lactase and are more likely to have lactose intolerance. They may be able to tolerate modest amounts of milk (like the amount added to coffee or tea).
how much of our foods should be carbs
45-65% of total calories consumed from carbohydrates
bliss point
the perfect amount of sweetness
One of the reasons that added sucrose is detrimental to our health is that the monosaccharide (fill in blank) is converted to (fill in blank) in the liver.
fructose, fat