C6 Organic Chemistry
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
hydrocarbon
any compound formed from only carbon and hydrogen
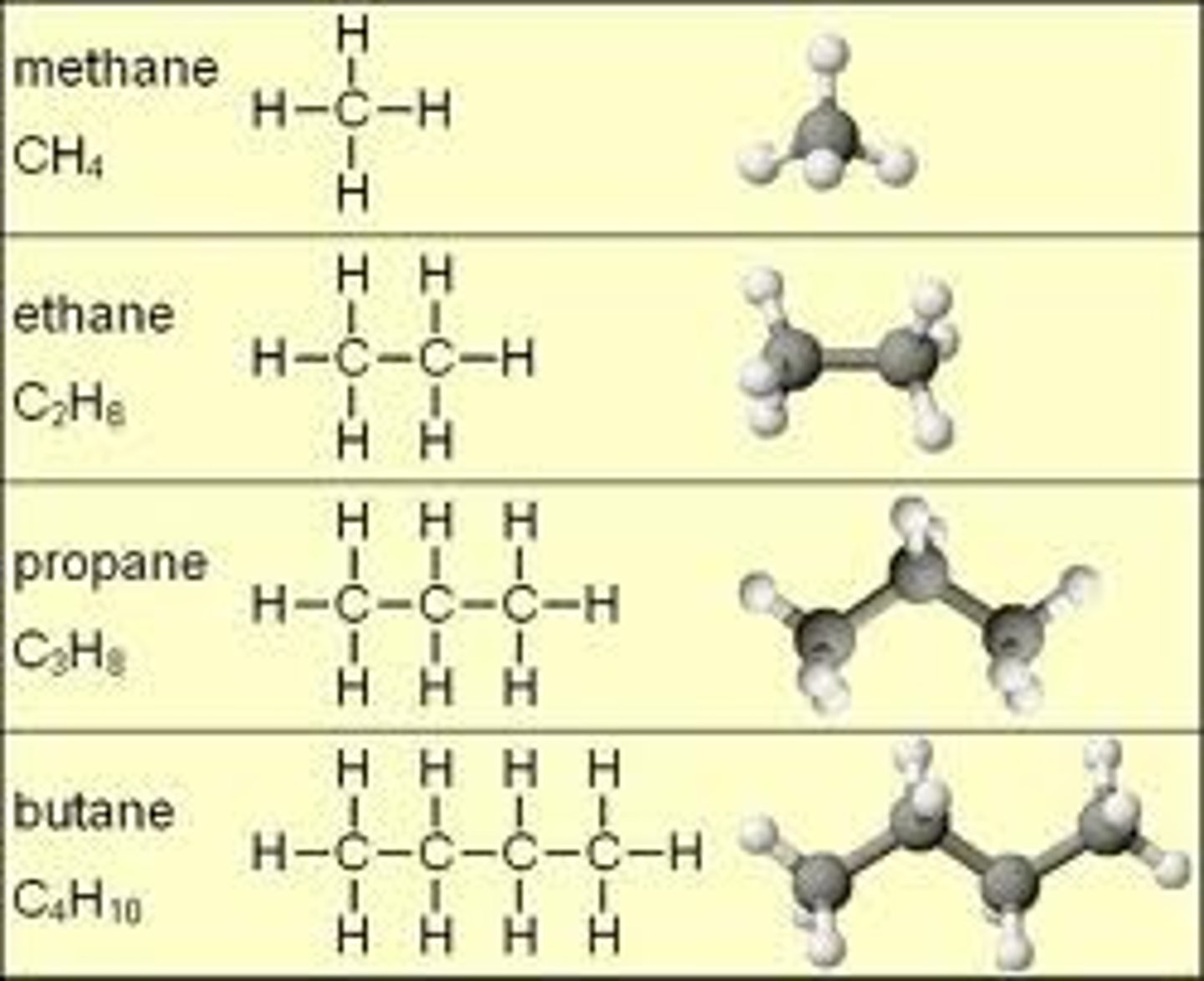
★Methane(CH^4)
★Ethane(C^2H^6)
★Propane(C^3H^8)
★Butane(C^4H^10)
alkanes
homologous series of molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms in single C-H & C-C bonds
Saturated compound
an organic compound in which all carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds; it contains as many hydrogen atoms as possible in their molecules
isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
★made of the same atoms, but the atoms are differently arranged
homologous series
group of organic compounds that have similar chemical properties, due to them having the same functional group e.g. alkanes
the shorter the chain length..
★less viscous
★more flammable(easier 2 ignite)
★more volatile(lower bps/easier evaporation)
alkenes features
★have a double bond C=C
★unsaturated
☆leads to them being more reactive than alkanes so they can react with bromine
★can be added together to form polymers because a double bond can break to form 2 or more bonds
test for alkenes
★bromine water mixed with alkenes- all of it reacts to lose its orange colour and turns colourless
How was crude oil formed? [4]
★formed from remains of dead plants & animals(plankton
★remains were covered by mud & sand and buried in the earth
★over millions of years they were compressed under lots of heat & pressure
★which chemically changed the organic remains into crude oil
Describe how crude oil is separated into fractions [4]
-crude oil/hydrocarbons is heated & evaporates
-temperature decreases from bottom to top
-vapours condense as they rise up the column
-at different points according to their boiling points
which three hydrocarbons are used as a fuel?
petrol, kerosene & diesel
feedstock
Raw materials used to provide reactants for an industrial reaction
★e.g. hydrocarbons in crude oil
petrochemical
a substance made from crude oil, via chemical reactions
★e.g. useful things made from hydrocarbons such as polymers
cracking(thermal decomposition reaction)
process in which large chain hydrocarbons are split into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons
catalytic cracking
1. vaporise hydrocarbon
2. pass over hot powdered aluminium oxide catalyst
3. long-chain molecules split apart into short-chain molecules and an alkene on the surface of the catalyst
How is steam cracking different to catalytic cracking?
Steam cracking is different because there is no catalyst involved.
Instead the vaporised long chain alkane is mixed with steam at very high temperatures.
Why will cracking produce at least one unsaturated alkene?
there are insufficient hydrogen atoms to form two alkanes
steam cracking
breaks large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller molecules by mixing w steam & heating to v high temperatures
complete combustion
both carbon & hydrogen from the hydrocarbon are oxidised
complete combustion equation
hydrocarbon + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
Why are hydrocarbons used as fuels?
★They release a lot of energy when they combust completely(exothermic reaction)
★they're also highly combustible
incomplete combustion
only hydrogen atoms are oxidised, combustion is incomplete due to a limited oxygen supply
Why is incomplete combustion dangerous?
★Carbon monoxide which is formed during incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons is odourless/colourless
★combines w/ blood, preventing it from carrying oxygen
uses of crude oil
★fuel - kerosene, diesel etc
makes new compounds like polymers and solvents
★petrochemical industry uses some hydrocarbons of crude oil as feedstock to make new compounds
polymers
long chain molecules formed by joining many smaller molecules(monomers) together
polymerisation
the process of joining lots of monomers together to form a polymer
monomer
small molecules that can be joined together with other small molecules to form a polymer
★have a double covalent bond
addition polymerisation
small molecules (monomers) add on to a growing polymer chain one at a time to form a very long saturated molecular chain (the addition polymer).
describe why sulfur should be removed from petrol
burning sulfur produced sulfur dioxide and cause acid rain
suggest two benefits of using cornstarch instead of poly(ethene) to make carrier bags
★polymers made from cornstarch are biodegradable
★so less space needed in landfill sites
★polymers from cornstarch come from a renewable source
what environmental problems are caused by poly(ethene) bags?
They are non-biodegradable. They can be eaten but not digested by animals. They block drains & cause flooding
how can ethanol be made from ethene?
by mixing ethEne with steam then passing it over a catalyst
cons of incomplete combustion
★releases less energy than complete combustion
★particulates(soot) make global warming
★carbon monoxide is produced
hydrogenation
hydrogen reacts w/ the double-bonded carbons to open up the double-bond & form the equivalent, saturated alkane
steam(to form alcohols)
water is added across the double bond & an alcohol is formed
★after the reaction takes place, the mixture is passed from the reactor into a condenser
★ethanol & water have higher bps than ethene so both condense whilst any unreacted ethene gas is recycled back into the reactor
★alcohol can be purified by frac. distillation
halogenation
form saturated molecules with the C=C carbons each becoming bonded to a halogen atom
unsaturated monomers
open up their double bonds & join together to form polymer chains
problems with polymers
★mostly non-biodegradable
★gases are produced during their disposal
★need to be sorted before melting/reforming into new products
what is the functional group of an alcohol?
-OH
what are properties of the alcohols?
-flammable, undergo complete combustion to produce H2O & CO2
-soluble in water & form neutral pH solution
-can be oxidised by adding an oxygen to form a carboxylic acid
-can react with sodium to produce hydrogen & salt
what are the conditions used for fermentation of sugar using yeast?
-warm temps(25-35)
-anaerobic
-presence of sugar dissolved
describe what happens when alcohols react with sodium
produces salt & hydrogen gas (effervesance)
describe what happens when alcohols react with water
alcohols dissolve readily in water to form a neutral solution
descibe what happens when alcohols react with oxidising agents
ethanol in wine is oxidised to ethanoic acid due to presence of oxygen
what happens when carboxylic acids dissolve in water?
-don't fully ionise- weak acids dont release all their hydrogen ions
*it is always the H+ attached to the OH group that ionises. Other hydrogen atoms strongly bond to carbon atoms
how are esters made?
when carboxylic acids react with alcohols
compare the polymerisation reaction used to produce poly(ethene) w the polymerisation reaction used to produce a polyester [4]
ADDITION:
-one monomer(alkene C=C)
-one product(polymer)
CONDENSATION:
-two different monomers(diols, diamines ,etc)
-two products(water & polymer)
describe what takes place during condensation polymerisation
-monomers containing different functional groups join together & bonds form between them, making polymer chains
-for each new bond that forms, a small molecule(water) is lost
-the simplest types of condensation polymers contain two different types of monomer, each w two of the same functional groups
describe the structure of DNA
-Two polymer chains made form four different monomers(nucleotides) in the form of a double helix
-large molecule(polymer)
explain why HDPE has a higger density than LDPE [2]
-in HDPE, polymer chains closer together
-as theres more atoms per unit volume