The Colombian and Mexican Drug Cartels
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Definition of Cartel
criminal organizations specialized in the production and distribution of illegal narcotics
cartels finance and manage the central and most lucrative parts of cocaine (as well as other drugs) business through a 4-phase process: refining, smuggling, distributing, money laundering
DEA Definition of the Colombian Drug Cartels
the Colombian drug cartels are composed of independent trafficking organizations that pool their resources for efficiency
the Colombian cartels have quickly monopolized cocaine manufacturing and distribution throughout North America
Cartels Strategy
using compartments: one handles renting, another the drugs, and another the cash-flowing
each cell is self-contained to protect the whole operation
low-profile abroad (blending in with their neighbors, driving modest cars), high profile in their territories
omerta
Key Factors that Drive and Sustain the Drug Trade
geography: the world’s largest cocaine consumer - NA - lies to the north. and the biggest supplier - SA - lies to the south
climate: much of Latin America is well suited for growing cocoa and marijuana
widespread poverty and unemployment make society fragile (and voted easily purchasable): South America most successful businessmen are often the drug lords, who can act as benefactors within these communities
Weak Local Government, Widespread Corruption and the Expansion of Cartels
plata o plomo: strategy (P. Escobar) (silver or lead). Escobar ordered the killing of hundreds, if not thousands of politicians, judges, and policemen
buying votes: drug lords control local government, mayors, and town council, a formula already used by Al Capone in late 1920s Chigaco
drug lords are no longer interested in just selling drugs, now they want more power, political power, both at the local and national level
South American Mafias: Criminocracy
criminal groups and state institutions tend to coincide within a frame which is impossible to distinguish between legal and illegal power
the prevalent pattern has been one based on the usual interaction between crime, economy, political power, cultural code, and social consensus
Case Studies: Carlos Lehder Rivas and Pablo Escobar
Medellin cartel leader in Colombia eventually prosecuted by US authorities, Rivas bought and had an interest in local radio stations and newspapers, and even started a political party called the Latino nationalist party
in 1982, Escobar won the election as an alternative congressman - a sort of deputy representative to fill in during the absence of the main representative in the national congress
both behaved in perfect accordance with mafia ideology
The Influence of Increases Levels of Drug Addiction on the Workforce
health problems: diffusion of cheap drugs
drug addiction among the population has the important consequence of driving outside investors as they wouldn’t find enough people who can operate extensive high tech equipment safely and effectively
How Drug Money Causes Inflation
inflation is a decline in purchasing power
sometimes prices rise because of increased value
in the case of south America, inflation is usually due to drug money
The Colombian Cartels
estimated to control 70% of the cocaine processes in Columbia and 80% of that that was distributed in the US
The Medellin Carted (fell in 1993)
Pablo Escobar - born out of kidnapping
it came to supply 90% of the cocaine consumed in the US
Pablo Escobar, responsible for the murder of approximately 4000 people including more than 1200 policemen and 300 state officials
other cartels were: costa, valle del nord, pereira
The Cali Cartel (fell in 1995)
the biggest cartel controlling 90% of the world cocaine market
territorial control of their city, Santiago de Cali, is complete thanks to their infiltration of local political institutions
in the 1980s, cocaine production shifted to Colombia
in the 2000s, a new generation of Mafiosi known as the “invisibles” emerged that took over the production and distribution of cocaine made of white collars that use legitimate companies as a facade
How the US and Local Governments Have Tried to Cut Off the Drug Trade
in the 1990s, colombia’s main drug cartels were dismantled by the combined effort of US and Colombian authorities
but since the demand for drugs remained high, Mexico took over, taking advantage of the fact that they already controlled the drug distribution process
US federal government has called Mexican drug cartels the greatest threat facing the US government and is now using against then the same method that proved successful against the mafia in the 1980s-1990s
task forces led by prosecutors are the best was to fight drug cartels
US Federal Government Approach
the extensive use of coordinated intelligence
a strong focus on key cartel leaders — on investigating them, arresting them, and bringing them to the United States for trial
investigation and prosecution of gun, cash, and drug smuggling cases
prosecutions in federal court of those responsible for smuggling, kidnapping, and violence
Efforts to Seize Drug Cartels’ Assets
asset forfeiture is a powerful tool to strip criminals of illicit wealth, including homes and cars
part of every US government operation thought to involve drugs
The National Drug Intelligence Center estimates that Mexican cartel’s gross is between $17 billion and $38 billion annually just from drug sales
much of that ends up as “bulk currency” — suitcases or even truckloads of cash
The Mexican Cartels
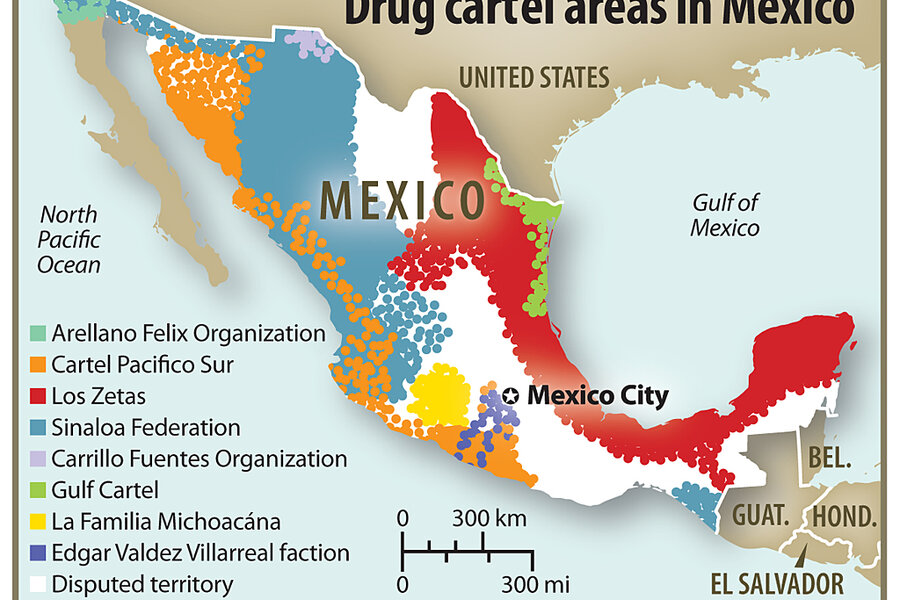
The Evolution of Cartels: New Pattern and Strategies
decentralized structure: previous cartels broke down into federations and alliances, with no more single leader or single group
new structures often coincide with cells or some franchises that operate most independently (ex. la Oficina de envigado, los rastrojos)
these new groups are less disciplined, more dispersed, less knowledgeable;e in terms of their activities and names, and much quicker to fill the gaps when one of their bosses is arrested
a generation of new bosses and drug traffickers that have diversified criminal activities including robbery, extortion, and kidnapping
closer relationship with politics and state bureaucracy both at the local and national level
more connections with Central America, especially Honduras, to trampoline drugs into Mexico and then into the US