Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Intermolecular Forces
interactions between molecules
van der Waal’s forces (every molecule has these)
dipole-dipole interactions
hydrogen bonding
van der Waal’s
induced dipole formed as e- clouds pass eachother
areas of partial negative and partial positive form as molecules are distorted
strength of van der Waal’s depends on polarizability (surface area), LARGER molecules=more surface area
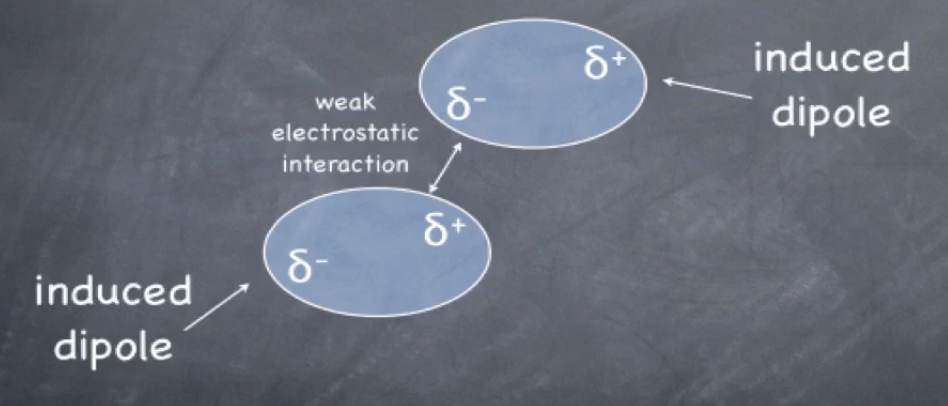
dipole-dipole interaction
electrostatic interaction between two molecules with PERMANENT dipoles
stronger than vdw (temporary dipoles)
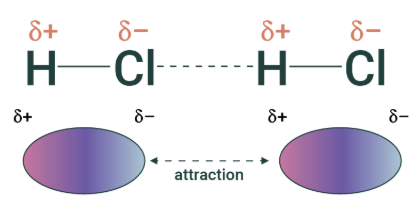
hydrogen bonding
NOT REAL BONDS
VERY strong dipole interaction
electrostatic attraction between H-atom bonded to O, N, F and lone pair on O, N, F in another molecule
IMFs and Physical Properties
IMFs control physical properties
greater/stronger IMFs = higher BP, MP
IMFs control solubility
Phase Transition: Boiling
BP= temp where liquid is converted to gas
stronger IMF = more energy required to break up interactions between molecules = higher BP
Phase Transition: Melting
MP = temp where solid → liquid
stronger IMF = more energy required to break up interactions between molecules = higher MP
Packing, only for MP
If all else is equal (IMF), consider which structure is more symmetrical
more symmetry = pack efficiently = more stable structure = more energy required to break up
Solubility
Like dissolves like
interactions between solute and solvent must make up for loss of interaction between solute molecules
Matching IMFs = dissolves