Lattice Enthalpy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the definition for the enthalpy of Formation?
The enthalpy change to form 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions. The compound will always be an ionic compound its its solid state
Na(s) + 1/2Cl2(g) →NaCl(s)
What is the enthalpy change of ionisation energy?
The enthalpy change to form 1 mole of 1+ ions by removing 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms (this definition needs to be amended for the 2nd and 3rd ionisation energies)
Na(g) →Na+(g) + e-
Why are ionisation energies always endothermic?
Because energy is required to overcome the attraction between the negative electron and positive nucleus.
What is the definition for the enthalpy change of electron affinity?
The standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions. (amend for 2nd and 3rd etc)
Cl(g) + e- →Cl-(g)
Is the first electron affinity exo or endothermic?
Is the second electron and 3rd affinity exo or endothermic?
and why
1st - exothermic
2nd, 3rd - endothermic
3rd would be more exothermic
2nd + 3rd are endothermic because it is a negative ion and a negative electron
Why is the first electron affinity exothermic?
Because the electron added is being attracted towards the nucleus
Why is the subsequent electron affinitites endothermic (after the first)?
Because a second electron is being gained by a negative ion which repels the electron so energy needs to be put in to force the negatively charged electron onto the negative ion.
What is the standard enthalpy of atomisation?
The enthalpy change that takes place for formation of 1 mole of atoms in the gas state from the element in its standard state under standard conditions.
½ Cl2(g) → Cl(g)
Na(s) → Na(g)
True or false enthalpy of atomisation is always an endothermic process?
True
Why is enthalpy of atomisation always an endothermic process?
Because bonds are broken to form gaseous atoms
When the element is a gas in its standard state what is the enthalpy of atomisation related to?
The bond enthalpy of the bonds broken

What occurs first atomisation or electron affinity?
atomisation
Is 1/2Cl2 the same as Cl?
NO
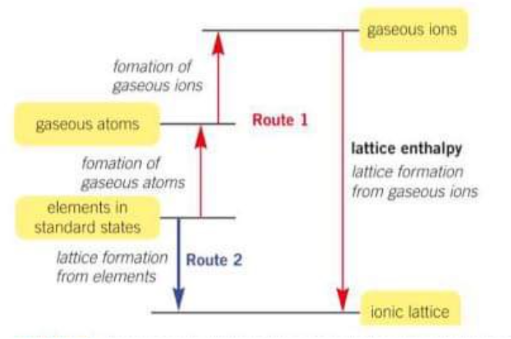
What is the enthalpy of lattice enthalpy?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its ions in the gas state under standard conditions.
True or false enthalpy change of formation is the direct rout and the other enthalpy changes are other routes
True
How can you calculate lattice enthalpy?
using Born-Haber cycles
What is Lattice enthalpy?
The enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
Where does the stability of solid ionic compounds come from?
The strength of ionic bonds and electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in the ionic lattice structure, giving rise to high mpt’s
What is lattice enthalpy a measure of?
The strength of ionic bonding in a giant ionic lattice
Is lattice enthalpy exo or endothermic?
Exothermic
True or false lattice enthalpy can be measured directly
False it must be calculated indirectly
What is the basis for born haber cycles (what is at each station)?
Complete the sentences…
Water molecules are able to break up the giant _______ ________ structure by overcoming the ______ electrostatic ____________ between oppositely charged _____.
Water molecules are able to break up the giant ionic lattice structure by overcoming the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
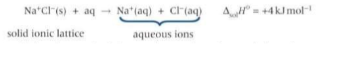
What is the standard enthalpy of solution?
The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a solute dissolves in a solvent.
If the solvent is water, the ions from the ionic lattice finish up surrounded with water molecules as aq ions.
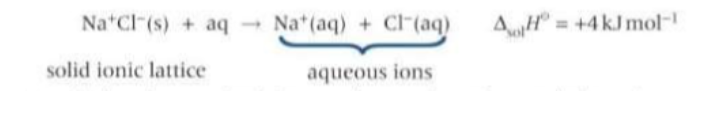
True or false enthalpy of solution is only endothermic?
False it is exo and endothermic
Describe NaCl(s) compared with NaCl(aq)
NaCl(s) Na+ and Cl- ions are attracted together in a giant ionic lattice
NaCl(aq) Na+ and Cl- ions are separate but now surrounded by water. In aq ions the delta+ and delta- partial charges in water molecules are attracted to the positive and negative ions.
Delta+ H attracted to Cl-
Delta- O attracted to Na+
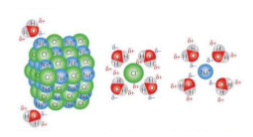
How does a solid ionic compound dissolve in water?
The ionic lattice breaks up and water molecules are attracted to and surround the ions.
What is enthalpy change of hydration?
The enthalpy change that accompanies the dissolving of aq ions in water to form 1 mole of aq ions.
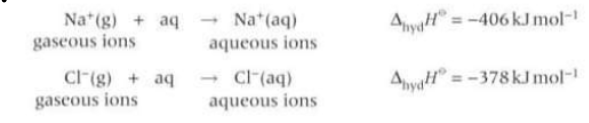
Is the enthalpy change of solution endo or exothermic?
Can be both depending on the size of the lattice enthalpy and enthalpy change of hydration.